Deck 11: Chemical Equilibria
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/94
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Chemical Equilibria
1
If G = 27.1 kJ at 25 C for the reaction CH3COOH(aq)+ H2O(l) → CH3COO-(aq)+ H3O+(aq)
What is Ka for this reaction at 298 K?
A)1.15 *10-11
B)5.63 * 104
C)1.78 * 10-5
D)1.01
E)9.89 * 10-1
What is Ka for this reaction at 298 K?
A)1.15 *10-11
B)5.63 * 104
C)1.78 * 10-5
D)1.01
E)9.89 * 10-1
1.78 * 10-5
2
The equilibrium constant for the reaction
HNO2(aq)+ H2O(l) →NO2 (aq)+ H3O+(aq)
is 4.3 * 10-4 at 25 C.Will nitrous acid spontaneously dissociate when
[HNO2(aq)] = 1.0 M and [NO2-(aq)] = [H3O+(aq)] = 1.0 * 10-5 M?
Show your calculations.
HNO2(aq)+ H2O(l) →NO2 (aq)+ H3O+(aq)
is 4.3 * 10-4 at 25 C.Will nitrous acid spontaneously dissociate when
[HNO2(aq)] = 1.0 M and [NO2-(aq)] = [H3O+(aq)] = 1.0 * 10-5 M?
Show your calculations.
Yes
3
Consider the reaction 2Fe2O3(s)+ 3C(s) 4Fe(s)+ 3CO2(g), H = 462 kJ, S = 558 J.K-1
Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction at 525 C.
A)3.04 * 10-3
B)8.07 * 10-2
C)5.20 * 10-7
D)1.9 * 106
E)2.18 * 10-2
Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction at 525 C.
A)3.04 * 10-3
B)8.07 * 10-2
C)5.20 * 10-7
D)1.9 * 106
E)2.18 * 10-2
8.07 * 10-2
4
The equilibrium constant expression for the reaction
CuSO4(s) → CuO(s)+ SO3(g)
is K = [CuO(s)][SO3(g)]/[CuSO4(s)].
CuSO4(s) → CuO(s)+ SO3(g)
is K = [CuO(s)][SO3(g)]/[CuSO4(s)].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a 1-L flask containing D2(g),N2(g),and ND3(g)at equilibrium at 300 K and a 1-L flask of H2(g),N2(g),and NH3(g)at equilibrium at 300 K are mixed,analysis of the reaction mixture shows that HD(g),NHD2(g),and NH2D(g)are also present.What conclusion(s)can be drawn?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The equilibrium constant for the reaction
HNO2(aq)+ H2O(l) →NO2 (aq)+ H3O+(aq)
is 4.3 * 10-4 at 25 C.Will nitrous acid spontaneously dissociate when
[HNO2(aq)] = [NO2-(aq)] = [H3O+(aq)] = 1.0 M? Show your calculations.
HNO2(aq)+ H2O(l) →NO2 (aq)+ H3O+(aq)
is 4.3 * 10-4 at 25 C.Will nitrous acid spontaneously dissociate when
[HNO2(aq)] = [NO2-(aq)] = [H3O+(aq)] = 1.0 M? Show your calculations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consider the reaction
CuSO4(s) CuO(s)+ SO3(g)
If G = -14.6 kJ at 950 C for this reaction,what is G for an SO3(g)pressure of 50 bar at this temperature?
A)2.68 kJ
B)25.2 kJ
C)54.4 kJ
D)16.3 kJ
E)-54.4 kJ
CuSO4(s) CuO(s)+ SO3(g)
If G = -14.6 kJ at 950 C for this reaction,what is G for an SO3(g)pressure of 50 bar at this temperature?
A)2.68 kJ
B)25.2 kJ
C)54.4 kJ
D)16.3 kJ
E)-54.4 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Consider the reaction NO(g)+ 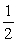 O2(g) NO2(g)
O2(g) NO2(g)
If H = -56.52 kJ and S = -72.60 J.K-1 at 298 K,what is the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 298 K?
A)1.31 * 106
B)7.63 * 10-7
C)660
D)1.22 * 1014
E)8.08 * 109
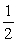 O2(g) NO2(g)
O2(g) NO2(g)If H = -56.52 kJ and S = -72.60 J.K-1 at 298 K,what is the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 298 K?
A)1.31 * 106
B)7.63 * 10-7
C)660
D)1.22 * 1014
E)8.08 * 109

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Consider the following reaction at a certain temperature:
Ni(s)+ 4CO(g) →Ni(CO)4(g)
Calculate K for this reaction if,at equilibrium,the partial pressures of CO(g)and Ni(CO)4(g)are 1.25 and 6.65 atm over 1.00 kg of nickel.
Ni(s)+ 4CO(g) →Ni(CO)4(g)
Calculate K for this reaction if,at equilibrium,the partial pressures of CO(g)and Ni(CO)4(g)are 1.25 and 6.65 atm over 1.00 kg of nickel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Consider the reaction
CuSO4(s) CuO(s)+ SO3(g)
If G = -14.6 kJ at 950 C for this reaction,what is G for an SO3(g)pressure of 20 bar at this temperature.
A)15.9 kJ
B)45.1 kJ
C)-14.6 kJ
D)30.5 kJ
E)-45.1 kJ
CuSO4(s) CuO(s)+ SO3(g)
If G = -14.6 kJ at 950 C for this reaction,what is G for an SO3(g)pressure of 20 bar at this temperature.
A)15.9 kJ
B)45.1 kJ
C)-14.6 kJ
D)30.5 kJ
E)-45.1 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Consider the reaction
2CuBr2(s) 2CuBr(s)+ Br2(g)
If the equilibrium vapor pressure of Br2(g)is 1.43 * 10-5 Torr at 298 K,what is G at this temperature when Br2(g)is produced at a pressure of 7.50 * 10-8 Torr.
A)-5.65 kJ
B)13.0 kJ
C)5.65 kJ
D)-3.42 kJ
E)-13.0 kJ
2CuBr2(s) 2CuBr(s)+ Br2(g)
If the equilibrium vapor pressure of Br2(g)is 1.43 * 10-5 Torr at 298 K,what is G at this temperature when Br2(g)is produced at a pressure of 7.50 * 10-8 Torr.
A)-5.65 kJ
B)13.0 kJ
C)5.65 kJ
D)-3.42 kJ
E)-13.0 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
For the equilibrium N2O4(g) →2NO2(g),plot,on the same graph,the forward and reverse reaction rates as a function of time.If possible,mark on the graph where equilibrium is reached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Calculate G at 298 K for the reaction C2H5OH(l) C2H5OH(g,0.0263 bar)
Given G = 6.2 kJ at 298 K.
A)6.2 kJ
B)15 kJ
C)2.8 kJ
D)-2.8 kJ
E)-15 kJ
Given G = 6.2 kJ at 298 K.
A)6.2 kJ
B)15 kJ
C)2.8 kJ
D)-2.8 kJ
E)-15 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For the equilibrium CaCO3(s) → CaO(s)+ CO2(g),(a)represents the composition at equilibrium at a certain temperature.In (b),a small amount of Ca*CO3(s)has been added (Ca*CO3(s)represents Ca14CO3(s)or labeled calcium carbonate).Draw the composition in (c)at equilibrium and explain your drawing. 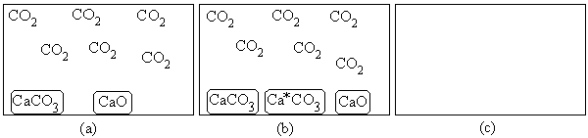


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Calculate the value of K at 700 K for the reaction H2(g)+ I2(g) → 2HI(g)
Given that Kc = 54 at the same temperature.
A)3100
B)2.2
C)54
D)9.3
E)1300
Given that Kc = 54 at the same temperature.
A)3100
B)2.2
C)54
D)9.3
E)1300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 25 C 2TiCl3(s)+ 2HCl(g) → 2TiCl4(g)+ H2(g)
Given G = +46.6 kJ.
A)3.8 * 10-98
B)1.5* 10-19
C)6.7 * 10-9
D)6.6 * 1018
E)1.5 * 108
Given G = +46.6 kJ.
A)3.8 * 10-98
B)1.5* 10-19
C)6.7 * 10-9
D)6.6 * 1018
E)1.5 * 108

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Calculate G at 298 K for the reaction C2H5OH(l) C2H5OH(g,0.0400 bar)
Given G = 6.2 kJ at 298 K.
A)14 kJ
B)2.7 kJ
C)-14 kJ
D)-1.8 kJ
E)1.8 kJ
Given G = 6.2 kJ at 298 K.
A)14 kJ
B)2.7 kJ
C)-14 kJ
D)-1.8 kJ
E)1.8 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consider the reaction
2CuBr2(s) 2CuBr(s)+ Br2(g)
If the equilibrium vapor pressure of Br2(g)is 1.43 * 10-5 Torr at 298 K,what is G at this temperature when Br2(g)is produced at a pressure of 7.50 * 10-7 Torr?
A)-7.31 kJ
B)7.31 kJ
C)39.9 kJ
D)-3.17 kJ
E)-4.15 kJ
2CuBr2(s) 2CuBr(s)+ Br2(g)
If the equilibrium vapor pressure of Br2(g)is 1.43 * 10-5 Torr at 298 K,what is G at this temperature when Br2(g)is produced at a pressure of 7.50 * 10-7 Torr?
A)-7.31 kJ
B)7.31 kJ
C)39.9 kJ
D)-3.17 kJ
E)-4.15 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the relation between K and Kc for the reaction H2(g)+ I2(g) →2HI(g)
A)K = Kc
B)K = RTKc
C)Kc = (RT)2K
D)K = (RT)2Kc
E)Kc = RTK
A)K = Kc
B)K = RTKc
C)Kc = (RT)2K
D)K = (RT)2Kc
E)Kc = RTK

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If Gro = 27.1 kJ∙mol-1 at 25 C for the dissociation of acetic acid in aqueous solution,what is K for the reaction
CH3COO-(aq)+ H3O+(aq) → CH3COOH(aq)+ H2O(l)
CH3COO-(aq)+ H3O+(aq) → CH3COOH(aq)+ H2O(l)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Given: 4NH3(g)+ 5O2(g) → 4NO(g)+ 6H2O(g)
K
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
2NH3(g)+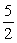 O2(g) →2NO(g)+ 3H2O(g)
O2(g) →2NO(g)+ 3H2O(g)
A)K
B)K-1
C)2K
D)0.5K
E)K1/2
K
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
2NH3(g)+
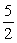 O2(g) →2NO(g)+ 3H2O(g)
O2(g) →2NO(g)+ 3H2O(g)A)K
B)K-1
C)2K
D)0.5K
E)K1/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Given: 2SO2(g)+ O2(g) →2SO3(g) At equilibrium at a certain temperature,the concentrations of SO3(g),SO2(g),and O2(g)are 0.12 M,0.86 M,and 0.33 M,respectively.Calculate the value of Kc for this reaction.
A)1.31
B)0.42
C)0.014
D)0.059
E)0.87
A)1.31
B)0.42
C)0.014
D)0.059
E)0.87

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Given: C(s)+ CO2(g) → 2CO(g) At equilibrium at a certain temperature,the partial pressures of CO(g)and CO2(g)are 1.22 atm and 0.780 atm,respectively.Calculate the value of K for this reaction.
A)3.13
B)2.00
C)1.91
D)1.56
E)0.640
A)3.13
B)2.00
C)1.91
D)1.56
E)0.640

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At 600 C,the equilibrium constant for the reaction 2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l)+ O2(g)
Is 2.8.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction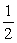 1/2O2(g)+ Hg(l) → HgO(s)
1/2O2(g)+ Hg(l) → HgO(s)
A)-1.7
B)1.1
C)0.60
D)0.36
E)1.7
Is 2.8.Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction
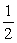 1/2O2(g)+ Hg(l) → HgO(s)
1/2O2(g)+ Hg(l) → HgO(s)A)-1.7
B)1.1
C)0.60
D)0.36
E)1.7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Given: 4NH3(g)+ 5O2(g) → 4NO(g)+ 6H2O(g)
K
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
2NO(g)+ 3H2O(g) →2NH3(g)+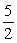 O2(g)
O2(g)
A)-0.5K
B)-2K
C)K-1/2
D)-K
E)K-1
K
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
2NO(g)+ 3H2O(g) →2NH3(g)+
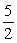 O2(g)
O2(g)A)-0.5K
B)-2K
C)K-1/2
D)-K
E)K-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
At 25 C,Kc = 4.1 * 108 for the reaction N2(g)+ 3H2(g) →2NH3(g)
Calculate K at 25 C for this reaction.
A)9.7 * 107
B)6.9 * 105
C)4.1 * 108
D)1.7 * 109
E)2.5 * 1011
Calculate K at 25 C for this reaction.
A)9.7 * 107
B)6.9 * 105
C)4.1 * 108
D)1.7 * 109
E)2.5 * 1011

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
At 25 C,K = 6.9 * 105 for the reaction N2(g)+ 3H2(g) →2NH3(g)
Calculate Kc at 25 C for this reaction.
A)2.8 * 104
B)6.8 * 105
C)1.1 * 103
D)1.7 * 107
E)4.1 * 108
Calculate Kc at 25 C for this reaction.
A)2.8 * 104
B)6.8 * 105
C)1.1 * 103
D)1.7 * 107
E)4.1 * 108

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
At 25 C,Kc = 1.58 * 10-8 for the reaction NH4(NH2CO2)(s)b 2NH3(g)+ CO2(g)
Calculate K at 25 C for this reaction.
A)3.87 * 10-7
B)2.31 * 10-4
C)9.45 * 10-5
D)5.69 * 10-3
E)1.36 * 10-7
Calculate K at 25 C for this reaction.
A)3.87 * 10-7
B)2.31 * 10-4
C)9.45 * 10-5
D)5.69 * 10-3
E)1.36 * 10-7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Given: 2SO2(g)+ O2(g) →2SO3(g) At equilibrium at a certain temperature,the concentrations of SO3(g),SO2(g),and O2(g)are 0.24 M,0.82 M,and 0.33 M,respectively.Calculate the value of Kc for this reaction.
A)0.89
B)0.21
C)0.79
D)0.26
E)1.04
A)0.89
B)0.21
C)0.79
D)0.26
E)1.04

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Given: P4(s)+ 6Cl2(g)b 4PCl3(l)
K
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
2PCl3(l) →3Cl2(g)+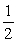 P4(s)
P4(s)
A)-K1/2
B)1/K1/2
C)1/K2
D)1/K
E)K1/2
K
Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction.
2PCl3(l) →3Cl2(g)+
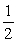 P4(s)
P4(s)A)-K1/2
B)1/K1/2
C)1/K2
D)1/K
E)K1/2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The reaction free energy Gr = G°r - RTln(K).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the relationship between K and Kc for the reaction below? NH4(NH2CO2)(s) →2NH3(g)+ CO2(g)
A)Kc = (RT)2K
B)K = RTKc
C)K = (RT)2Kc
D)K = (RT)3Kc
E)Kc = (RT)3K
A)Kc = (RT)2K
B)K = RTKc
C)K = (RT)2Kc
D)K = (RT)3Kc
E)Kc = (RT)3K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The value of K for a given reaction is a constant and does not have units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
At 700 K,K = 54 for the reaction H2(g)+ I2(g) →2HI(g)
Calculate Kc at 700 K for this reaction.
A)3.2 * 10-4
B)0.94
C)7.7 * 10-4
D)0.45
E)54
Calculate Kc at 700 K for this reaction.
A)3.2 * 10-4
B)0.94
C)7.7 * 10-4
D)0.45
E)54

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The equilibrium constant,K,for the reaction 2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l)+ O2(g)
Is 1.2 * 10-30.Calculate K for the reaction
1/2O2(g)+ Hg(l) → HgO(s).
A)-1.1 * 10-15
B)8.3 * 1029
C)4.2 * 1029
D)9.1 * 1014
E)1.1 * 10-15
Is 1.2 * 10-30.Calculate K for the reaction
1/2O2(g)+ Hg(l) → HgO(s).
A)-1.1 * 10-15
B)8.3 * 1029
C)4.2 * 1029
D)9.1 * 1014
E)1.1 * 10-15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Given: SO2(g) →O2(g)+ S(s)
Kc = 2.5 * 10-53
SO3(g) →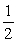 O2(g)+ SO2(g)
O2(g)+ SO2(g)
Kc = 4.0 * 10-13
Calculate Kc for the reaction
2S(s)+ 3O2(g) →2SO3(g)
A)1.6 * 10103
B)1.6 * 1080
C)1.0 *10130
D)1.6 * 1040
E)1.0 * 1065
Kc = 2.5 * 10-53
SO3(g) →
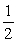 O2(g)+ SO2(g)
O2(g)+ SO2(g)Kc = 4.0 * 10-13
Calculate Kc for the reaction
2S(s)+ 3O2(g) →2SO3(g)
A)1.6 * 10103
B)1.6 * 1080
C)1.0 *10130
D)1.6 * 1040
E)1.0 * 1065

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the relationship between K and Kc for the reaction below?
N2(g)+ 3H2(g) →2NH3(g)
A)K = (RT)6Kc
B)Kc = (RT)-2K
C)Kc = (RT)2K
D)K = (RT)-2Kc
E)K = (RT)2Kc
N2(g)+ 3H2(g) →2NH3(g)
A)K = (RT)6Kc
B)Kc = (RT)-2K
C)Kc = (RT)2K
D)K = (RT)-2Kc
E)K = (RT)2Kc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the relationship between K and Kc for the reaction below?
2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l)+ O2(g)
A)Kc = (RT)2K
B)K = Kc
C)Kc = RTK
D)K = RTKc
E)K = (RT)2Kc
2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l)+ O2(g)
A)Kc = (RT)2K
B)K = Kc
C)Kc = RTK
D)K = RTKc
E)K = (RT)2Kc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Given: C(s)+ CO2(g) → 2CO(g) At equilibrium at a certain temperature,the partial pressures of CO(g)and CO2(g)are 1.44 atm and 0.820 atm,respectively.Calculate the value of K for this reaction.
A)2.53
B)10.1
C)1.76
D)3.08
E)3.51
A)2.53
B)10.1
C)1.76
D)3.08
E)3.51

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
At 600 C,Kc = 2.8 for the reaction 2HgO(s) → 2Hg(l)+ O2(g)
Calculate K at 600 C for this reaction.
A)6800
B)200
C)1.4 * 104
D)2.8
E)138
Calculate K at 600 C for this reaction.
A)6800
B)200
C)1.4 * 104
D)2.8
E)138

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
At equilibrium,Q = K and G°r = 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider the following reaction at a certain temperature:
PCl5(g) →PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
Kc = 0.100
At equilibrium,[PCl5] = 2.00 M and [PCl3] = [Cl2] = 1.00 M.If suddenly 1.00 M PCl5(g),PCl3(g),and Cl2(g)is added,what is the equilibrium concentration of PCl5(g)?
A)0.65 M
B)4.35 M
C)1.35 M
D)essentially zero
E)2.35 M
PCl5(g) →PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
Kc = 0.100
At equilibrium,[PCl5] = 2.00 M and [PCl3] = [Cl2] = 1.00 M.If suddenly 1.00 M PCl5(g),PCl3(g),and Cl2(g)is added,what is the equilibrium concentration of PCl5(g)?
A)0.65 M
B)4.35 M
C)1.35 M
D)essentially zero
E)2.35 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The equilibrium constant,Kc,for the reaction 2NOCl(g) →2NO(g)+ Cl2(g)
Is 0.51 at a certain temperature.A mixture of NOCl,NO,and Cl2 with concentrations 1.3,1.2,and 0.60 M,respectively,was introduced into a container at this temperature.Which of the following is true?
A)Cl2(g)is produced until equilibrium is reached.
B)[NOCl] = [NO] = [Cl2] at equilibrium.
C)NOCl(g)is produced until equilibrium is reached.
D)[Cl2] = 0.30 M at equilibrium.
E)No apparent reaction takes place.
Is 0.51 at a certain temperature.A mixture of NOCl,NO,and Cl2 with concentrations 1.3,1.2,and 0.60 M,respectively,was introduced into a container at this temperature.Which of the following is true?
A)Cl2(g)is produced until equilibrium is reached.
B)[NOCl] = [NO] = [Cl2] at equilibrium.
C)NOCl(g)is produced until equilibrium is reached.
D)[Cl2] = 0.30 M at equilibrium.
E)No apparent reaction takes place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider the following reaction at a certain temperature:
PCl5(g) →PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
Kc = 0.100
At equilibrium,[PCl5] = 2.00 M and [PCl3] = [Cl2] = 1.00 M.If suddenly 1.00 M PCl3(g)and Cl2(g)is added,what is the equilibrium concentration of PCl5(g)?
A)essentially 4.00 M
B)0.58 M
C)2.58 M
D)3.42 M
E)1.42 M
PCl5(g) →PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
Kc = 0.100
At equilibrium,[PCl5] = 2.00 M and [PCl3] = [Cl2] = 1.00 M.If suddenly 1.00 M PCl3(g)and Cl2(g)is added,what is the equilibrium concentration of PCl5(g)?
A)essentially 4.00 M
B)0.58 M
C)2.58 M
D)3.42 M
E)1.42 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The equilibrium constant,Kc,for the reaction 2SO2(g)+ O2(g) →2SO3(g)
Is 11.7 at 1100 K.A mixture of SO2,O2,and SO3,each with a concentration of 0.015 M,was introduced into a container at 1100 K.Which of the following is true?
A)SO2(g)and O2(g)will be formed until equilibrium is reached.
B)[SO3] = 0.045 M at equilibrium.
C)[SO3] = 0.015 M at equilibrium.
D)SO3(g)will be formed until equilibrium is reached.
E)[SO3] = [SO2] = [O2] at equilibrium.
Is 11.7 at 1100 K.A mixture of SO2,O2,and SO3,each with a concentration of 0.015 M,was introduced into a container at 1100 K.Which of the following is true?
A)SO2(g)and O2(g)will be formed until equilibrium is reached.
B)[SO3] = 0.045 M at equilibrium.
C)[SO3] = 0.015 M at equilibrium.
D)SO3(g)will be formed until equilibrium is reached.
E)[SO3] = [SO2] = [O2] at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following statements is true?
A)When the value of Q is large,the equilibrium lies on the product side of the equilibrium reaction.
B)When the value of K is large,the equilibrium lies on the reactant side of the equilibrium reaction.
C)A small value of K means that the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants are small compared to the equilibrium concentrations of the products.
D)A large value of K means that the equilibrium concentrations of products are large compared to the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants.
E)When the value of K is small,the equilibrium lies on the product side of the equilibrium reaction.
A)When the value of Q is large,the equilibrium lies on the product side of the equilibrium reaction.
B)When the value of K is large,the equilibrium lies on the reactant side of the equilibrium reaction.
C)A small value of K means that the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants are small compared to the equilibrium concentrations of the products.
D)A large value of K means that the equilibrium concentrations of products are large compared to the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants.
E)When the value of K is small,the equilibrium lies on the product side of the equilibrium reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A mixture consisting of 0.250 M N2(g)and 0.500 M H2(g)reaches equilibrium according to the equation below: N2(g)3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
At equilibrium,the concentration of ammonia is 0.150 M.Calculate the concentration of N2(g)at equilibrium.
A)0.150 M
B)0.100 M
C)0.0750 M
D)0.0500 M
E)0.175 M
At equilibrium,the concentration of ammonia is 0.150 M.Calculate the concentration of N2(g)at equilibrium.
A)0.150 M
B)0.100 M
C)0.0750 M
D)0.0500 M
E)0.175 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The effect of a volume decrease on the reaction C(s)+ H2O(g) → CO(g)+ H2(g)
Is
A)that K decreases.
B)more CO(g)and H2(g)are produced.
C)no change.
D)more H2O(g)is produced.
E)that K increases.
Is
A)that K decreases.
B)more CO(g)and H2(g)are produced.
C)no change.
D)more H2O(g)is produced.
E)that K increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Consider the reaction
Na+(g)+ Cl-(g) → NaCl(s)
If the temperature is lowered,the products/reactants are favored.
Na+(g)+ Cl-(g) → NaCl(s)
If the temperature is lowered,the products/reactants are favored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the reaction
N2(g)3H2(g) →2NH3(g)
If the initial concentrations of nitrogen and hydrogen are each 1.0 M,and X is the equilibrium concentration of ammonia,what is the correct equilibrium expression?
N2(g)3H2(g) →2NH3(g)
If the initial concentrations of nitrogen and hydrogen are each 1.0 M,and X is the equilibrium concentration of ammonia,what is the correct equilibrium expression?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A mixture consisting of 0.250 M N2(g)and 0.500 M H2(g)reaches equilibrium according to the equation below: N2(g)3H2(g) →2NH3(g)
At equilibrium,the concentration of ammonia is 0.150 M.Calculate the concentration of H2(g)at equilibrium.
A)0.0750 M
B)0.350 M
C)0.425 M
D)0.275 M
E)0.150 M
At equilibrium,the concentration of ammonia is 0.150 M.Calculate the concentration of H2(g)at equilibrium.
A)0.0750 M
B)0.350 M
C)0.425 M
D)0.275 M
E)0.150 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider the reaction PCl5(g) →PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
At a certain temperature,if the initial concentration of PCl5(g)is 3.0 M,at equilibrium the concentration of Cl2(g)is 0.80 M.Calculate the value of Kc at this temperature.
A)0.21
B)0.29
C)0.64
D)3.4
E)0.46
At a certain temperature,if the initial concentration of PCl5(g)is 3.0 M,at equilibrium the concentration of Cl2(g)is 0.80 M.Calculate the value of Kc at this temperature.
A)0.21
B)0.29
C)0.64
D)3.4
E)0.46

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
For the reaction NH3(g)+ H2S(g) →NH4HS(s)
Kc = 9.7 at 900 K.If the initial concentrations of NH3(g)and H2S(g)are 2.0 M,what is the equilibrium concentration of NH3(g)?
A)1.9 M
B)1.7 M
C)0.20 M
D)0.10 M
E)0.32 M
Kc = 9.7 at 900 K.If the initial concentrations of NH3(g)and H2S(g)are 2.0 M,what is the equilibrium concentration of NH3(g)?
A)1.9 M
B)1.7 M
C)0.20 M
D)0.10 M
E)0.32 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Consider the reaction PCl5(g) →PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
At a certain temperature,if the initial concentration of PCl5(g)is 2.0 M,at equilibrium the concentration of Cl2(g)is 0.30 M.Calculate the value of Kc at this temperature.
A)0.064
B)0.053
C)0.090
D)19
E)0.045
At a certain temperature,if the initial concentration of PCl5(g)is 2.0 M,at equilibrium the concentration of Cl2(g)is 0.30 M.Calculate the value of Kc at this temperature.
A)0.064
B)0.053
C)0.090
D)19
E)0.045

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
For the reaction 2CaSO4(s) → 2CaO(s)+ 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)
K = 0.032 at 700 K.What is the total pressure starting from pure CaSO4(s)?
A)0.22 bar
B)0.011 bar
C)0.60 bar
D)0.20 bar
E)0.40 bar
K = 0.032 at 700 K.What is the total pressure starting from pure CaSO4(s)?
A)0.22 bar
B)0.011 bar
C)0.60 bar
D)0.20 bar
E)0.40 bar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Consider the following reaction: Ni(CO)4(g) → Ni(s)+ 4CO(g)
If the initial concentration of Ni(CO)4(g)is 1.0 M,and x is the equilibrium concentration of CO(g),what is the correct equilibrium relation?
A)Kc = X4/(1.0 - 4X)
B)Kc = X/(1.0 - X/4)
C)Kc = X4/(1.0 - X/4)
D)Kc = X5/(1.0 - X/4)
E)Kc = 4X/(1.0 -4X)
If the initial concentration of Ni(CO)4(g)is 1.0 M,and x is the equilibrium concentration of CO(g),what is the correct equilibrium relation?
A)Kc = X4/(1.0 - 4X)
B)Kc = X/(1.0 - X/4)
C)Kc = X4/(1.0 - X/4)
D)Kc = X5/(1.0 - X/4)
E)Kc = 4X/(1.0 -4X)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Consider the following reaction at a certain temperature:
PCl5(g) →PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
Kc = 0.100
At equilibrium,[PCl5] = 2.00 M and [PCl3] = [Cl2] = 1.00 M.If suddenly 1.00 M PCl5(g),PCl3(g),and Cl2(g)is added,what is the equilibrium concentration of Cl2(g)?
A)3.0 M
B)essentially zero
C)0.65 M
D)2.75 M
E)3.35 M
PCl5(g) →PCl3(g)+ Cl2(g)
Kc = 0.100
At equilibrium,[PCl5] = 2.00 M and [PCl3] = [Cl2] = 1.00 M.If suddenly 1.00 M PCl5(g),PCl3(g),and Cl2(g)is added,what is the equilibrium concentration of Cl2(g)?
A)3.0 M
B)essentially zero
C)0.65 M
D)2.75 M
E)3.35 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Write the equilibrium constant for 2NaBr(aq)+ Pb(ClO4)2(aq) →PbBr2(s)+ 2NaClO4(aq).
A)K = [Pb2+][Br-2
B)K = 1/([Pb2+][Br-2)
C)K = [NaClO4]2/([NaBr]2[Pb(ClO4)2]
D)K = [PbBr2]/([Pb2+][Br-]2)
E)K = 1/([Pb(ClO4)2][NaBr]2)
A)K = [Pb2+][Br-2
B)K = 1/([Pb2+][Br-2)
C)K = [NaClO4]2/([NaBr]2[Pb(ClO4)2]
D)K = [PbBr2]/([Pb2+][Br-]2)
E)K = 1/([Pb(ClO4)2][NaBr]2)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
For the reaction NH3(g)+ H2S(g) →NH4HS(s)
Kc = 9.7 at 900 K.If the initial concentrations of NH3(g)and H2S(g)are 2.0 M,what is the equilibrium concentration of H2S(g)?
A)1.9 M
B)0.20 M
C)1.7 M
D)0.10 M
E)0.32 M
Kc = 9.7 at 900 K.If the initial concentrations of NH3(g)and H2S(g)are 2.0 M,what is the equilibrium concentration of H2S(g)?
A)1.9 M
B)0.20 M
C)1.7 M
D)0.10 M
E)0.32 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider the reaction 3Fe(s)+ 4H2O(g) → 4H2(g)+ Fe3O4(s)
If the volume of the container is reduced,
A)the equilibrium constant increases.
B)more H2(g)is produced.
C)no change occurs.
D)more H2O(g)is produced.
E)more Fe(s)is produced.
If the volume of the container is reduced,
A)the equilibrium constant increases.
B)more H2(g)is produced.
C)no change occurs.
D)more H2O(g)is produced.
E)more Fe(s)is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Consider the reaction CO(g)+ 2H2(g) →CH3OH(g)
At room temperature,K is approximately 2 * 104,but at a higher temperature K is substantially smaller.Which of the following is true?
A)The reaction is endothermic.
B)The value of Kc for this reaction is smaller at all temperatures.
C)At the higher temperature,more CH3OH(g)is produced.
D)The reaction is exothermic.
E)The reaction becomes spontaneous at higher temperatures.
At room temperature,K is approximately 2 * 104,but at a higher temperature K is substantially smaller.Which of the following is true?
A)The reaction is endothermic.
B)The value of Kc for this reaction is smaller at all temperatures.
C)At the higher temperature,more CH3OH(g)is produced.
D)The reaction is exothermic.
E)The reaction becomes spontaneous at higher temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
For the decomposition of ammonia to nitrogen and hydrogen,the equilibrium constant is 1.47 * 10-6 at 298 K.Calculate the temperature at which K = 1.00.For this reaction, H = 92.38 kJ.mol-1.
A)193 K
B)353 K
C)466 K
D)492 K
E)219 K
A)193 K
B)353 K
C)466 K
D)492 K
E)219 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
For the reaction 2NOCl(g) → 2NO(g)+ Cl2(g),if,initially,[NOCl(g)] = 2.8 M,at equilibrium [NO(g)] = 1.2 M.Calculate the equilibrium concentration of NOCl(g).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Consider the reaction 4NH3(g)+ 3O2(g) →2N2(g)+ 6H2O(g),K = 1080 at a certain temperature.
Initially,all reactants and products have concentrations equal to 12 M.At equilibrium,the approximate concentration of ammonia is
A)6 M.
B)3 M.
C)12 M.
D)18 M.
E)0 M.
Initially,all reactants and products have concentrations equal to 12 M.At equilibrium,the approximate concentration of ammonia is
A)6 M.
B)3 M.
C)12 M.
D)18 M.
E)0 M.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
For the reaction 2NOCl(g) → 2NO(g)+ Cl2(g),K = 98 at a certain temperature.If the equilibrium concentrations in a 1 L container are [NOCl(g)] = 1.0 M,[NO(g)] = 3.5 M and [Cl2(g)] = 8.0 M,and 2.0 mol of each gas is added,in which direction does the reaction shift?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Consider the reaction
4NH3(g)+ 7O2(g) →2N2O4(g)+ 6H2O(g)
If,initially,[NH3(g)] = [O2(g)] = 3.60 M,at equilibrium,[N2O4(g)] = 0.60 M.Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of all other species.
4NH3(g)+ 7O2(g) →2N2O4(g)+ 6H2O(g)
If,initially,[NH3(g)] = [O2(g)] = 3.60 M,at equilibrium,[N2O4(g)] = 0.60 M.Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of all other species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The equilibrium constant K for the dissociation of N2O4(g)to NO2(g)is 1700 at 500 K.Predict its value at 300 K.For this reaction, H is 56.8 kJ.mol-1.
A)1.32 * 10-6
B)1.11 * 10-4
C)15.5
D)0.188
E)1.54 * 107
A)1.32 * 10-6
B)1.11 * 10-4
C)15.5
D)0.188
E)1.54 * 107

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Consider the reaction 4NH3(g)+ 3O2(g) →2N2(g)+ 6H2O(g),K = 1080 at a certain temperature.
Initially,all reactants and products have concentrations equal to 12 M.At equilibrium,the approximate concentration of oxygen is
A)6 M.
B)0 M.
C)3 M.
D)12 M.
E)18 M.
Initially,all reactants and products have concentrations equal to 12 M.At equilibrium,the approximate concentration of oxygen is
A)6 M.
B)0 M.
C)3 M.
D)12 M.
E)18 M.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the equilibrium constant for the reaction Ni(s)+ 4CO(g) →Ni(CO)4(g)is 2.72 at a certain temperature,what is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at the same temperature?
Ni(CO)4(g) → Ni(s)+ 4CO(g)
Ni(CO)4(g) → Ni(s)+ 4CO(g)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Consider the reaction below:
F2(g) → 2F(g)
(a)Compressing the reaction mixture results in a change in Q.True or false?
(b)Heating the reaction mixture causes the reaction to shift to the left.True or false?
(c)At 1000 K,the equilibrium constant for the reaction is about 10-4.If the reaction is perturbed such that Q = 1,the reaction must shift to the left.
F2(g) → 2F(g)
(a)Compressing the reaction mixture results in a change in Q.True or false?
(b)Heating the reaction mixture causes the reaction to shift to the left.True or false?
(c)At 1000 K,the equilibrium constant for the reaction is about 10-4.If the reaction is perturbed such that Q = 1,the reaction must shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
For the reaction N2O4(g) →2NO2(g)
Which of the following disturbances will cause an increase in NO2(g)concentration?
A)a decrease in temperature
B)need to know H for the reaction to predict
C)removal of some N2O4(g)
D)an increase in pressure
E)an increase in temperature
Which of the following disturbances will cause an increase in NO2(g)concentration?
A)a decrease in temperature
B)need to know H for the reaction to predict
C)removal of some N2O4(g)
D)an increase in pressure
E)an increase in temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The vapor pressure of acetic acid at 25 C is 16 Torr. Gr for the reaction CH3COOH(l) →CH3COOH(g)
At 25 C is
A)0
B)+9.57 kJ·mol-1
C)-9.57 kJ·mol-1
D)+1.85 kJ·mol-1
At 25 C is
A)0
B)+9.57 kJ·mol-1
C)-9.57 kJ·mol-1
D)+1.85 kJ·mol-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
For any reaction at equilibrium, G < 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Consider the reaction 2HI(g) →H2(g)+ I2(g)
At 298 K,Kc = 1.3 *10-3,whereas at 783 K,Kc = 2.2 * 10-2.Which of the following is true?
A)The reaction is exothermic.
B)The reaction is endothermic.
C)At 298 K,K = 3.2 * 10-2.
D)At 298 K,the reaction is likely to be spontaneous.
E)At 783 K,more HI(g)is produced.
At 298 K,Kc = 1.3 *10-3,whereas at 783 K,Kc = 2.2 * 10-2.Which of the following is true?
A)The reaction is exothermic.
B)The reaction is endothermic.
C)At 298 K,K = 3.2 * 10-2.
D)At 298 K,the reaction is likely to be spontaneous.
E)At 783 K,more HI(g)is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
For a pure solid or liquid,the molar free energy always has its standard value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
From a plot of Gibbs free energy versus progress of reaction,the sign of Gr at any point along the curve is given by the slope of the curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If a reaction mixture that is not at equilibrium contains more products than reactants, G > 0 for the forward reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
For the decomposition of ammonia to nitrogen and hydrogen,the equilibrium constant is 1.47 * 10-6 at 298 K.Calculate the temperature at which K = 0.0100.For this reaction, H = 92.38 kJ.mol-1.
A)241 K
B)332 K
C)59 K
D)390 K
E)117 K
A)241 K
B)332 K
C)59 K
D)390 K
E)117 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the following
N2O4(g) →2NO2(g)
The equilibrium constant for this reaction will decrease with an increase in temperature.
N2O4(g) →2NO2(g)
The equilibrium constant for this reaction will decrease with an increase in temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Consider the reaction Ni(s)+ 4CO(g) →Ni(CO)4(g)
At 30 C and PCO = 1 atm,Ni reacts with CO(g)to form Ni(CO)4(g).At 200 C,Ni(CO)4(g)decomposes to Ni(s)and CO(g).This means
A)adding an inert gas like argon favors the forward reaction.
B)the activation energy for the forward reaction is greater than for the reverse reaction.
C)the forward reaction is endothermic.
D)K at 30 C is greater than K at 200 C.
E)a decrease in pressure favors the forward reaction.
At 30 C and PCO = 1 atm,Ni reacts with CO(g)to form Ni(CO)4(g).At 200 C,Ni(CO)4(g)decomposes to Ni(s)and CO(g).This means
A)adding an inert gas like argon favors the forward reaction.
B)the activation energy for the forward reaction is greater than for the reverse reaction.
C)the forward reaction is endothermic.
D)K at 30 C is greater than K at 200 C.
E)a decrease in pressure favors the forward reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



