Deck 11: Fiscal Policy and the Federal Budget
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/162
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Fiscal Policy and the Federal Budget
1
A permanent marginal tax rate cut would be expected to shift both the short-run and the long-run aggregate supply curves to the right.
True
2
A value-added tax (VAT)is a less visible form of a sales tax.
True
3
According to Keynesian theory,a recessionary gap can be closed using expansionary fiscal policy.
True
4
To finance a budget deficit the federal government borrows funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A "flat tax" is another term for a regressive tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The transmission lag is the period that elapses between the time fiscal policy is enacted and the time it is put into effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
To identify whether fiscal policy is expansionary or contractionary,one should focus on the cyclical deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When the government decides to increase income taxes,this is an example of contractionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Crowding out results when an increase in government spending leads to declines in consumption,investment,and/or net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A tax rate increase necessarily leads to an increase in tax revenue for the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The United States currently has a progressive income tax structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The AD curve shifts to the right with an increase in taxes or a decrease in government purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
With a progressive income tax,as taxable income rises (up to a certain point),one's tax rate rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The distinctive feature of a progressive tax is that the dollar value of taxes paid rises as income rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The marginal tax rate is found by dividing a person's tax payment by the person's taxable income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to the textbook,in 2011 the top 1 percent of income earners in the U.S.earned more than $388,905.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A structural deficit refers to that part of the deficit that exists as a result of a downturn in economic activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A federal budget surplus occurs when government expenditures exceed tax revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Laffer curve shows the exclusively direct relationship that exists between tax rates and tax revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Complete crowding out occurs when an increase in government spending is completely offset by an equal increase in tax revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Suppose Congress decreases income taxes.This is an example of
A)expansionary fiscal policy.
B)expansionary monetary policy.
C)contractionary fiscal policy.
D)contractionary monetary policy.
A)expansionary fiscal policy.
B)expansionary monetary policy.
C)contractionary fiscal policy.
D)contractionary monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When the economy is in a recessionary gap,Keynesian economists will often advocate expansionary policy measures.Why?
A)Keynesians believe the economy sometimes gets stuck in a recessionary gap and can't get itself out without government intervention.
B)Keynesians believe the economy itself sometimes takes too long to eliminate the recessionary gap and return to full-employment output.
C)Keynesians are generally in favor of increasing taxes.
D)a and b
E)a and c
A)Keynesians believe the economy sometimes gets stuck in a recessionary gap and can't get itself out without government intervention.
B)Keynesians believe the economy itself sometimes takes too long to eliminate the recessionary gap and return to full-employment output.
C)Keynesians are generally in favor of increasing taxes.
D)a and b
E)a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A subsidy is the same thing as a tax deduction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A balanced budget occurs when
A)the national debt is reduced to zero dollars.
B)a budget deficit during one year is matched by a budget surplus in the next year.
C)transfer payments equal tax revenues.
D)government expenditures equal tax revenues.
E)the deficit-GDP ratio equals one.
A)the national debt is reduced to zero dollars.
B)a budget deficit during one year is matched by a budget surplus in the next year.
C)transfer payments equal tax revenues.
D)government expenditures equal tax revenues.
E)the deficit-GDP ratio equals one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose the economy is at a position below its institutional production possibilities frontier.To improve this situation,Keynesian economists might propose that government __________ taxes,which will cause the aggregate demand curve to shift to the __________ and Real GDP will __________.
A)increase;right;increase
B)increase;left;decrease
C)decrease;left;decrease
D)decrease;right;decrease
E)decrease;right;increase
A)increase;right;increase
B)increase;left;decrease
C)decrease;left;decrease
D)decrease;right;decrease
E)decrease;right;increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose aggregate demand is too low to bring about the Natural Real GDP level.A Keynesian policy prescription would call for a(n)_____________________ to close this recessionary gap.
A)increase in government spending
B)decrease in government spending
C)increase in taxes
D)decrease in taxes
E)a or d
A)increase in government spending
B)decrease in government spending
C)increase in taxes
D)decrease in taxes
E)a or d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Buchanan and Wagner assert that there is a political bias toward contractionary fiscal policy and not expansionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose the economy is at a point below its institutional production possibilities frontier.To improve this situation,Keynesian economists might propose that the government should __________ expenditures,which will cause the aggregate demand curve to shift to the __________ in an attempt to close this __________ gap.
A)decrease;left;inflationary
B)increase;right;inflationary
C)decrease;right;inflationary
D)increase;right;recessionary
E)decrease;left;recessionary
A)decrease;left;inflationary
B)increase;right;inflationary
C)decrease;right;inflationary
D)increase;right;recessionary
E)decrease;left;recessionary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Suppose the economy is at a point below its physical production possibilities frontier but above its institutional production possibilities frontier.In response to this situation,Keynesian economists may propose that government enact __________ fiscal policy to correct this __________ gap by __________ government expenditures.
A)expansionary;inflationary;increasing
B)contractionary;inflationary;decreasing
C)expansionary;recessionary;increasing
D)contractionary;recessionary;decreasing
E)contractionary;inflationary;increasing
A)expansionary;inflationary;increasing
B)contractionary;inflationary;decreasing
C)expansionary;recessionary;increasing
D)contractionary;recessionary;decreasing
E)contractionary;inflationary;increasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Expansionary fiscal policy actions include __________ government spending and/or __________ taxes,while contractionary fiscal policy actions include __________ government spending and/or __________ taxes.
A)increasing;increasing;decreasing;decreasing
B)decreasing;decreasing;increasing;increasing
C)increasing;decreasing;increasing;decreasing
D)decreasing;increasing;increasing;decreasing
E)increasing;decreasing;decreasing;increasing
A)increasing;increasing;decreasing;decreasing
B)decreasing;decreasing;increasing;increasing
C)increasing;decreasing;increasing;decreasing
D)decreasing;increasing;increasing;decreasing
E)increasing;decreasing;decreasing;increasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose Congress increases income taxes.This is an example of
A)expansionary fiscal policy.
B)expansionary monetary policy.
C)contractionary fiscal policy.
D)contractionary monetary policy.
A)expansionary fiscal policy.
B)expansionary monetary policy.
C)contractionary fiscal policy.
D)contractionary monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An expansionary fiscal policy will
A)always result in a budget deficit.
B)always result in a budget surplus.
C)sometimes result in a budget deficit.
D)never result in a budget surplus.
E)More information is necessary to answer this question.
A)always result in a budget deficit.
B)always result in a budget surplus.
C)sometimes result in a budget deficit.
D)never result in a budget surplus.
E)More information is necessary to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Fiscal policy refers to
A)efforts to balance a government's budget.
B)changes in the money supply to achieve particular economic goals.
C)changes in government expenditures and taxation to achieve particular economic goals.
D)the change in private expenditures that occurs as a consequence of changes in government spending.
A)efforts to balance a government's budget.
B)changes in the money supply to achieve particular economic goals.
C)changes in government expenditures and taxation to achieve particular economic goals.
D)the change in private expenditures that occurs as a consequence of changes in government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
According to the textbook,if the government had taxed everyone who earned more than $1 million an income tax rate of 100 percent in 2012,the budget deficit for that year would have been completely eliminated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An example of automatic fiscal policy is
A)the unemployed automatically become eligible for unemployment benefits when they lose their jobs in a recession.
B)when interest rates automatically fall in a recession.
C)Congress passes a law during a recession that automatically extends unemployment benefits for those whose benefits will soon expire.
D)a and b
E)a,b and c
A)the unemployed automatically become eligible for unemployment benefits when they lose their jobs in a recession.
B)when interest rates automatically fall in a recession.
C)Congress passes a law during a recession that automatically extends unemployment benefits for those whose benefits will soon expire.
D)a and b
E)a,b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Crowding out results in a decrease in
A)transfer payments.
B)defense spending.
C)private spending.
D)government spending.
A)transfer payments.
B)defense spending.
C)private spending.
D)government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Reductions in private spending as a result of increased government spending or the need to finance a budget deficit is called
A)pushing in.
B)rushing forth.
C)crowding in.
D)crowding out.
A)pushing in.
B)rushing forth.
C)crowding in.
D)crowding out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A budget deficit
A)occurs when government expenditures exceed tax revenues.
B)occurs when tax revenues exceed government expenditures.
C)occurs when transfer payments exceed tax revenues.
D)will always result when Congress and the president cannot agree on expenditures.
E)occurs when monetary policy works in the opposite direction of fiscal policy.
A)occurs when government expenditures exceed tax revenues.
B)occurs when tax revenues exceed government expenditures.
C)occurs when transfer payments exceed tax revenues.
D)will always result when Congress and the president cannot agree on expenditures.
E)occurs when monetary policy works in the opposite direction of fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A budget surplus
A)occurs when government expenditures exceed tax revenues.
B)occurs when tax revenues exceed government expenditures.
C)occurs when tax revenues exceed transfer payments.
D)occurs when monetary policy works in the opposite direction of fiscal policy.
E)is an impossibility.
A)occurs when government expenditures exceed tax revenues.
B)occurs when tax revenues exceed government expenditures.
C)occurs when tax revenues exceed transfer payments.
D)occurs when monetary policy works in the opposite direction of fiscal policy.
E)is an impossibility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
__________ flows from government to households.
A)A transfer payment
B)A tax payment
C)The Laffer Curve
D)Crowding out
A)A transfer payment
B)A tax payment
C)The Laffer Curve
D)Crowding out

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose the government increases spending on public education by $700 million and individual spending on private education drops by $700 million.This is an example of
A)incomplete crowding out.
B)complete crowding out.
C)zero crowding out.
D)a and c
E)none of the above
A)incomplete crowding out.
B)complete crowding out.
C)zero crowding out.
D)a and c
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Some economists argue that a rise in the interest rate,brought about by a rise in government borrowing in the loanable funds market to finance a budget deficit,brings in foreign funds in search of the higher interest rate return.This,in turn,dampens the rise in the interest rate.If this is true as far as it goes,there will be __________ crowding out than there would be if foreign funds did not flow into the country.
A)more
B)less
C)the same amount of
D)none of the above
A)more
B)less
C)the same amount of
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Fiscal policy may not work as policymakers intend it to work because of
A)crowding out.
B)lags.
C)the position of the physical production possibilities frontier.
D)a and b
E)a,b,and c
A)crowding out.
B)lags.
C)the position of the physical production possibilities frontier.
D)a and b
E)a,b,and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The AD curve shifts to the right with a __________ in government purchases (G)or a __________ in taxes.
A)rise;rise
B)rise;fall
C)fall;rise
D)fall;fall
A)rise;rise
B)rise;fall
C)fall;rise
D)fall;fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Exhibit 11-1 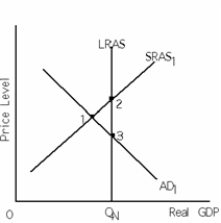
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The economy is currently at point 1.Suppose the federal government increases purchases and there is complete crowding out.As a result,the aggregate demand (AD)curve in the exhibit
A)will maintain its present position at AD1.
B)will shift rightward,ideally so that it goes through point 2.
C)will shift rightward,ideally so that it goes beyond point 2.
D)will shift leftward.
E)does not shift,but the SRAS curve will shift rightward so that it goes through point 3.

Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The economy is currently at point 1.Suppose the federal government increases purchases and there is complete crowding out.As a result,the aggregate demand (AD)curve in the exhibit
A)will maintain its present position at AD1.
B)will shift rightward,ideally so that it goes through point 2.
C)will shift rightward,ideally so that it goes beyond point 2.
D)will shift leftward.
E)does not shift,but the SRAS curve will shift rightward so that it goes through point 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Exhibit 11-1 
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The economy is currently at point 1.In this situation,supply-side economists would most likely propose _______________ to make the price level ______________ and Real GDP ___________.
A)cutting marginal tax rates;fall;rise
B)raising marginal tax rates;fall;rise
C)raising government spending;fall;rise
D)cutting government spending;rise;fall
E)cutting marginal tax rates;rise;fall

Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The economy is currently at point 1.In this situation,supply-side economists would most likely propose _______________ to make the price level ______________ and Real GDP ___________.
A)cutting marginal tax rates;fall;rise
B)raising marginal tax rates;fall;rise
C)raising government spending;fall;rise
D)cutting government spending;rise;fall
E)cutting marginal tax rates;rise;fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The AD curve shifts to the left with a __________ in government purchases (G)or a __________ in taxes.
A)rise;rise
B)rise;fall
C)fall;rise
D)fall;fall
A)rise;rise
B)rise;fall
C)fall;rise
D)fall;fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
With complete crowding out,an increase in government spending
A)is completely offset by a reduction in private spending.
B)is matched by an increase in private spending.
C)results in an increase in aggregate supply.
D)results in an increase in aggregate demand.
A)is completely offset by a reduction in private spending.
B)is matched by an increase in private spending.
C)results in an increase in aggregate supply.
D)results in an increase in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The period that elapses between the passage of legislation reducing taxes and the time the tax cut is put into effect is called the __________ lag.
A)data
B)wait-and-see
C)legislative
D)transmission
A)data
B)wait-and-see
C)legislative
D)transmission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If an individual pays an additional $0.30 in taxes as a result of a $1.00 increase in income,then that individual must have a(n)__________ tax rate of 30 percent.
A)average
B)fixed
C)total
D)marginal
A)average
B)fixed
C)total
D)marginal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is an example of crowding out?
A)A decrease in the rate of growth of the money supply which causes a decrease in Real GDP.
B)A budget deficit causes an increase in interest rates,which causes a decrease in investment spending.
C)An increase in tariffs which causes a decrease in imports.
D)A decrease in government housing subsidies which causes an increase in private spending on housing.
A)A decrease in the rate of growth of the money supply which causes a decrease in Real GDP.
B)A budget deficit causes an increase in interest rates,which causes a decrease in investment spending.
C)An increase in tariffs which causes a decrease in imports.
D)A decrease in government housing subsidies which causes an increase in private spending on housing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If there is complete crowding out as a result of an increase in government spending there will be
A)a decrease in aggregate demand.
B)no change in aggregate demand.
C)an increase in aggregate demand.
D)a downward movement along the aggregate demand curve.
A)a decrease in aggregate demand.
B)no change in aggregate demand.
C)an increase in aggregate demand.
D)a downward movement along the aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Exhibit 11-1 
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The economy is currently at point 1.Suppose the federal government increases purchases and there is no crowding out.As a result,the aggregate demand (AD)curve in the exhibit
A)maintains its present position at AD1.
B)shifts rightward,ideally so that it goes through point 2.
C)shifts rightward,ideally so that it goes beyond point 2.
D)shifts leftward.
E)does not shift,but the SRAS curve will shift rightward so that it goes through point 3.

Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The economy is currently at point 1.Suppose the federal government increases purchases and there is no crowding out.As a result,the aggregate demand (AD)curve in the exhibit
A)maintains its present position at AD1.
B)shifts rightward,ideally so that it goes through point 2.
C)shifts rightward,ideally so that it goes beyond point 2.
D)shifts leftward.
E)does not shift,but the SRAS curve will shift rightward so that it goes through point 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose the government attempts to stimulate the economy by increasing spending without increasing taxes.Which of the following statements is most likely to be accepted by someone who believes in crowding out?
A)The government's actions will have their intended effect.
B)The government's actions will cause businesses to become more optimistic about the economy,and they will increase their output even more than the government had intended.
C)The government's actions will raise interest rates,causing decreased investment and consumption,and the economy will not expand as much as the government had intended.
D)This is a trick question,because the federal government is required by law to increase taxes by the same amount as it increases expenditures.
A)The government's actions will have their intended effect.
B)The government's actions will cause businesses to become more optimistic about the economy,and they will increase their output even more than the government had intended.
C)The government's actions will raise interest rates,causing decreased investment and consumption,and the economy will not expand as much as the government had intended.
D)This is a trick question,because the federal government is required by law to increase taxes by the same amount as it increases expenditures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose the government increases spending on public education by $700 million and individual spending on private education drops by $500 million.This is an example of
A)incomplete crowding out.
B)complete crowding out.
C)zero crowding out.
D)a and c
E)none of the above
A)incomplete crowding out.
B)complete crowding out.
C)zero crowding out.
D)a and c
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Exhibit 11-1 
Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The economy is currently at point 1.In this situation,Keynesian economists would most likely propose
A)an increase in government purchases.
B)a decrease in government purchases.
C)an increase in taxes.
D)a and c
E)b and c

Refer to Exhibit 11-1.The economy is currently at point 1.In this situation,Keynesian economists would most likely propose
A)an increase in government purchases.
B)a decrease in government purchases.
C)an increase in taxes.
D)a and c
E)b and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following illustrates the effectiveness lag?
A)Policymakers believe an economic downturn has occurred,but they decide not to take action until they are sure.
B)Policymakers are in the process of proposing policy measures to deal with the current economic slowdown.
C)Policymakers first learn of the recession when it is five months old.
D)Policymakers implement policy X,but it will be a few months before it starts working.
E)Policymakers agree to policy X,but it will be at least two months before the policy is implemented.
A)Policymakers believe an economic downturn has occurred,but they decide not to take action until they are sure.
B)Policymakers are in the process of proposing policy measures to deal with the current economic slowdown.
C)Policymakers first learn of the recession when it is five months old.
D)Policymakers implement policy X,but it will be a few months before it starts working.
E)Policymakers agree to policy X,but it will be at least two months before the policy is implemented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following illustrates the wait-and-see lag?
A)Policymakers believe an economic downturn has occurred,but they decide not to take action until they are sure.
B)Policymakers are in the process of proposing policy measures to deal with the current economic slowdown.
C)Policymakers first learn of the recession when it is five months old.
D)Policymakers implement policy X,but it will be a few months before it starts working.
E)Policymakers agree to policy X,but it will be at least two months before the policy is implemented.
A)Policymakers believe an economic downturn has occurred,but they decide not to take action until they are sure.
B)Policymakers are in the process of proposing policy measures to deal with the current economic slowdown.
C)Policymakers first learn of the recession when it is five months old.
D)Policymakers implement policy X,but it will be a few months before it starts working.
E)Policymakers agree to policy X,but it will be at least two months before the policy is implemented.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The lag between an increase in government spending and the impact of this increased spending on the economy is called the __________ lag.
A)effectiveness
B)transmission
C)legislative
D)data
A)effectiveness
B)transmission
C)legislative
D)data

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following illustrates the data lag?
A)The economy turns down on January 8,2006,but policymakers do not figure this out until April 19,2006.
B)Policymakers wait and see what is really going on with the economy.
C)
C)Policymakers implement policy X on September 12,2006,but the effects are not felt until six months later.
D)The data lag is illustrated equally well by a,b,and
A)The economy turns down on January 8,2006,but policymakers do not figure this out until April 19,2006.
B)Policymakers wait and see what is really going on with the economy.
C)
C)Policymakers implement policy X on September 12,2006,but the effects are not felt until six months later.
D)The data lag is illustrated equally well by a,b,and

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An example of contractionary fiscal policy is
A)an increase in government expenditures,or an increase in taxes,or both.
B)a decrease in government expenditures,or a decrease in taxes,or both.
C)an increase in government expenditures,or a decrease in taxes,or both.
D)a decrease in government expenditures,or an increase in taxes,or both.
E)increasing government expenditures while holding taxes constant.
A)an increase in government expenditures,or an increase in taxes,or both.
B)a decrease in government expenditures,or a decrease in taxes,or both.
C)an increase in government expenditures,or a decrease in taxes,or both.
D)a decrease in government expenditures,or an increase in taxes,or both.
E)increasing government expenditures while holding taxes constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Crowding out suggests that
A)high taxes reduce both consumption and saving.
B)increases in consumption are always at the expense of saving.
C)increases in government spending may raise the interest rate,thereby reducing investment.
D)increases in government spending will close a recessionary gap.
A)high taxes reduce both consumption and saving.
B)increases in consumption are always at the expense of saving.
C)increases in government spending may raise the interest rate,thereby reducing investment.
D)increases in government spending will close a recessionary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An example of expansionary fiscal policy is
A)an increase in government spending,or an increase in taxes,or both.
B)a decrease in government spending,or a decrease in taxes,or both.
C)an increase in government spending,or a decrease in taxes,or both.
D)a decrease in government spending,or an increase in taxes,or both.
E)holding government spending constant while increasing taxes.
A)an increase in government spending,or an increase in taxes,or both.
B)a decrease in government spending,or a decrease in taxes,or both.
C)an increase in government spending,or a decrease in taxes,or both.
D)a decrease in government spending,or an increase in taxes,or both.
E)holding government spending constant while increasing taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Exhibit 11-2 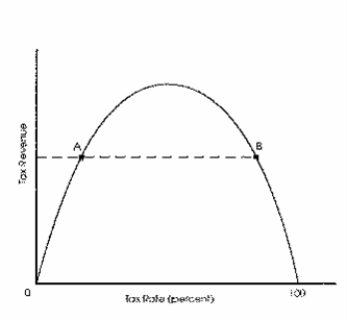
Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Compare points A and
B)Which of the following is true?
A)At A and B,the tax rates are the same,but tax revenues are different.
B)At A tax rates are higher than at B,but tax revenues are the same at both points.
C)At B tax rates are higher than at A,but tax revenues are the same at both points.
D)none of the above

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.Compare points A and
B)Which of the following is true?
A)At A and B,the tax rates are the same,but tax revenues are different.
B)At A tax rates are higher than at B,but tax revenues are the same at both points.
C)At B tax rates are higher than at A,but tax revenues are the same at both points.
D)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Exhibit 11-6 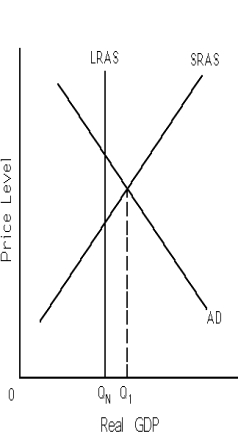
Elaine's taxable income increases by $1 and her tax payment increases by $0.28.Her marginal tax rate is
A)72 percent.
B)28 percent.
C)56 percent.
D)There is not enough information to answer the question.

Elaine's taxable income increases by $1 and her tax payment increases by $0.28.Her marginal tax rate is
A)72 percent.
B)28 percent.
C)56 percent.
D)There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose the economy's current AD and SRAS curves intersect to the right of Natural Real GDP.Keynesians might advise a policy of tax __________ to shift __________.
A)increases;SRAS to the left
B)increases;AD to the left
C)cuts;SRAS to the right
D)cuts;AD to the right
A)increases;SRAS to the left
B)increases;AD to the left
C)cuts;SRAS to the right
D)cuts;AD to the right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Exhibit 11-2 
Refer to Exhibit 11-2.At point B,if we cut tax rates slightly,tax revenues will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)will not change.
D)immediately drop to zero.

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.At point B,if we cut tax rates slightly,tax revenues will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)will not change.
D)immediately drop to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Fiscal policy is implemented primarily by
A)local governments alone.
B)the defense department.
C)state governments alone.
D)the federal government.
E)state and local governments.
A)local governments alone.
B)the defense department.
C)state governments alone.
D)the federal government.
E)state and local governments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Exhibit 11-6 
Refer to Exhibit 11-6.The economy is currently in short-run equilibrium producing Q1.In this situation,Keynesian economists would most likely propose
A)an increase in government purchases.
B)a decrease in government purchases.
C)an increase in taxes.
D)a or c
E)b or c

Refer to Exhibit 11-6.The economy is currently in short-run equilibrium producing Q1.In this situation,Keynesian economists would most likely propose
A)an increase in government purchases.
B)a decrease in government purchases.
C)an increase in taxes.
D)a or c
E)b or c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Between the data lag and the legislative lag falls the __________ lag.
A)effectiveness
B)wait-and-see
C)expansionary
D)legislative
A)effectiveness
B)wait-and-see
C)expansionary
D)legislative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Exhibit 11-6 
A curve showing the relationship between tax rates and tax revenues is called a __________ curve.
A)Phillips
B)Keynesian
C)Gaussian
D)Laffer

A curve showing the relationship between tax rates and tax revenues is called a __________ curve.
A)Phillips
B)Keynesian
C)Gaussian
D)Laffer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When we speak of expansionary fiscal policy,we are talking about policymakers __________ government spending,or __________ taxes,or both.
A)decreasing;decreasing
B)increasing;increasing
C)increasing;decreasing
D)decreasing;increasing
A)decreasing;decreasing
B)increasing;increasing
C)increasing;decreasing
D)decreasing;increasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
All other things held constant,lower marginal (income)tax rates
A)necessarily increase tax revenues.
B)necessarily decrease tax revenues.
C)decrease the attractiveness of productive activities relative to leisure and tax- avoidance activities,and shift the SRAS curve rightward.
D)do not affect the attractiveness of productive activities relative to leisure and tax- avoidance activities and therefore the SRAS does not shift rightward or leftward.
E)increase the attractiveness of productive activities relative to leisure and tax- avoidance activities and shift the SRAS curve rightward.
A)necessarily increase tax revenues.
B)necessarily decrease tax revenues.
C)decrease the attractiveness of productive activities relative to leisure and tax- avoidance activities,and shift the SRAS curve rightward.
D)do not affect the attractiveness of productive activities relative to leisure and tax- avoidance activities and therefore the SRAS does not shift rightward or leftward.
E)increase the attractiveness of productive activities relative to leisure and tax- avoidance activities and shift the SRAS curve rightward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An example of expansionary fiscal policy is
A)increasing government expenditures.
B)increasing taxes.
C)decreasing government expenditures.
D)decreasing taxes.
E)a and d
A)increasing government expenditures.
B)increasing taxes.
C)decreasing government expenditures.
D)decreasing taxes.
E)a and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Exhibit 11-2 
Refer to Exhibit 11-2.At point A,if we cut tax rates slightly,tax revenues will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)will not change.
D)drop to zero.

Refer to Exhibit 11-2.At point A,if we cut tax rates slightly,tax revenues will
A)increase.
B)decrease.
C)will not change.
D)drop to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Supply-side economists believe reductions in tax rates can
A)shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B)shift the short run aggregate supply curve to the left.
C)increase output and lower prices.
D)decrease output and lower prices.
A)shift the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B)shift the short run aggregate supply curve to the left.
C)increase output and lower prices.
D)decrease output and lower prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Fiscal policy refers to
A)changes in the amount of government expenditures and taxes to achieve particular economic objectives.
B)changes in the composition of a given amount of government expenditures to achieve particular economic objectives.
C)changes in interest rates initiated by government action.
D)any change in government spending or taxes that has the intended effect of destabilizing the economy.
A)changes in the amount of government expenditures and taxes to achieve particular economic objectives.
B)changes in the composition of a given amount of government expenditures to achieve particular economic objectives.
C)changes in interest rates initiated by government action.
D)any change in government spending or taxes that has the intended effect of destabilizing the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Fiscal policy is
A)the money supply policy that the Fed pursues to achieve particular economic goals.
B)the spending and tax policy that the government pursues to achieve particular macroeconomic goals.
C)the investment policy that businesses pursue to achieve particular macroeconomic goals.
D)the spending and saving policy that consumers pursue to achieve particular macroeconomic goals.
E)none of the above
A)the money supply policy that the Fed pursues to achieve particular economic goals.
B)the spending and tax policy that the government pursues to achieve particular macroeconomic goals.
C)the investment policy that businesses pursue to achieve particular macroeconomic goals.
D)the spending and saving policy that consumers pursue to achieve particular macroeconomic goals.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Increased government spending and tax cuts characterize
A)contractionary fiscal policy.
B)expansionary fiscal policy.
C)expansionary monetary policy.
D)deflationary policy.
E)none of the above
A)contractionary fiscal policy.
B)expansionary fiscal policy.
C)expansionary monetary policy.
D)deflationary policy.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Some of the crowding out of private expenditures may come in the form of
A)an increase in consumption.
B)an increase in net exports.
C)a decrease in taxes.
D)a decrease in net exports.
A)an increase in consumption.
B)an increase in net exports.
C)a decrease in taxes.
D)a decrease in net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 162 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



