Deck 15: Forward, Futures, and Swap Contracts
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/148
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Forward, Futures, and Swap Contracts
1
In the absence of arbitrage opportunities, the forward contract price should be equal to the current spot price plus interest.
False
2
According to the cost of carry model, the futures price is the present value of the spot price discounted at the risk-free rate.
False
3
The futures exchange requires each customer to post an initial margin account.
True
4
Forward rate agreements usually require substantial collateral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The cost-of-carry model is useful for pricing future contracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Like future contracts, all forward contracts are processed by the exchange clearinghouse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Some forward contracts, particularly in the foreign exchange market, are quite standard and liquid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Margin accounts are adjusted, or marked to market, at the end of each trading day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Interest rate parity is a key concept in managing risk in the commodities market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The number of future contracts needed to hedge a unit of the spot assets is solely a function of the variance of the spot prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The pure expectations hypothesis suggests futures prices serve as unbiased forecasts of future spot prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An investor in a hedge position is no longer exposed to the absolute price movement of the underlying asset, but the investor is still exposed to basis risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Because futures contracts are "marked-to-market" daily, the gains and losses are settled daily.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The settlement price is set by the futures exchange after trading ends to reflect the midpoint of the closing price range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The basis (Bt,T) at time t between the spot price (St) and a futures contract expiring at time T (Ft,T) is St - Ft,T.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Forward contracts are individually designed agreements and can be tailored to the specific needs of the ultimate end-user.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The goal of a hedge transaction is to increase expected returns of a fundamental holding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The basis is the spot price minus the future price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In the absence of arbitrage opportunities, the forward price should be equal to the spot price plus the cost of carry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In the cost of carry model, the inclusion of storage costs will increase the futures price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In a forward rate agreement (FRA), two parties agree today to a future exchange of cash flows based on two different interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Equity swaps are traded in the OTC markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In an interest rate swap, the fixed rate payer profits if interest rates fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The process by which invest on margin accounts are credited or debited to reflect daily trading gains or losses is referred to as the ____ process.
A) hedge rationing
B) daily settlement
C) marked-to-market
D) book-to-market
E) account realization
A) hedge rationing
B) daily settlement
C) marked-to-market
D) book-to-market
E) account realization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A riskless stock index arbitrage profit is possible if the following condition holds: F0,T = S0(1 + rf - d)T, where spot price now is S0, value now of a futures contract expiring at time T is (F0,T), rf is the risk free rate, and d is the dividend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If you were bearish on the near-term outlook for the stock market but did not want to sell your portfolio, you could hedge against the decline by selling stock index futures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The forward rate agreement is the most complicated of the OTC interest rate contracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
While LIBOR is usually used with forward rate agreements, it is rarely used with other interest rate agreements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The inclusion of dividends in the cost of carry model will increase the futures price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Like hedging, arbitrage results in increased returns with a disproportional increase in risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A plain vanilla swap agreement is used in similar situations as a forward rate agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The major difference between valuing futures versus forward contracts stems from the fact that future contracts are
A) traded on exchange.
B) backed by a clearinghouse.
C) marked-to-market daily.
D) less risky.
E) relatively inflexible.
A) traded on exchange.
B) backed by a clearinghouse.
C) marked-to-market daily.
D) less risky.
E) relatively inflexible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Stock index futures are useful in providing a hedge against movements in an underlying financial asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The Eurodollar futures contract is a popular hedging vehicle because it is based on the three-month LIBOR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If you have entered into a currency futures hedge for the Japanese yen in connection with buying Japanese equipment and if the yen goes from 110 yen/$1 to 100 yen/$1, you will lose in the spot market but have an offsetting gain in the futures market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An investor who wants a long position in a ____ must first place the order with a broker, who then passes it on to the trading pit or electronic network. Details of the order are then passed on to the exchange clearinghouse.
A) call option
B) put option
C) forward contract
D) futures contract
E) All of these are correct.
A) call option
B) put option
C) forward contract
D) futures contract
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Equity swaps are equivalent to portfolios of forward contracts calling for the exchange of cash flows based on two different investment rates: (1) a variable debt rate and (2) the return to an equity index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
As a contract approaches maturity, the spot price and forward price
A) increase.
B) diverge.
C) maintain a fixed price differential.
D) have a random relationship.
E) converge.
A) increase.
B) diverge.
C) maintain a fixed price differential.
D) have a random relationship.
E) converge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
On the settlement date for a forward rate agreement (FRA) contract, the difference between the two interest rates is multiplied by the FRA's par value and prorated by the length of the holding period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The Chicago Board of Trade (CBT) uses conversion factors to correct for differences in deliverable bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The cost of carry includes all of the following EXCEPT
A) storage costs.
B) insurance.
C) current price.
D) financing costs.
E) risk-free rate.
A) storage costs.
B) insurance.
C) current price.
D) financing costs.
E) risk-free rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
In late January 2004, The Union Cosmos Company is considering the sale of $100 million in 10-year bonds that will probably be rated AAA like the firm's other bond issues. The firm is anxious to proceed at today's rate of 10.5 percent. As treasurer, you know that it will take until sometime in April to get the issue registered and sold. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts each representing $100,000.
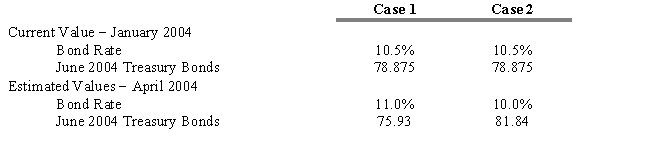
Refer to Exhibit 15.1. What is the dollar gain or loss assuming that future conditions described in Case 1 actually occur? (Ignore commissions and margin costs.)
A) $2,945,000.00 gain
B) $65,500.00 gain
C) $2,945,000.00 loss
D) $65,500.00 loss
E) $10,500.00 loss
In late January 2004, The Union Cosmos Company is considering the sale of $100 million in 10-year bonds that will probably be rated AAA like the firm's other bond issues. The firm is anxious to proceed at today's rate of 10.5 percent. As treasurer, you know that it will take until sometime in April to get the issue registered and sold. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts each representing $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.1. What is the dollar gain or loss assuming that future conditions described in Case 1 actually occur? (Ignore commissions and margin costs.)
A) $2,945,000.00 gain
B) $65,500.00 gain
C) $2,945,000.00 loss
D) $65,500.00 loss
E) $10,500.00 loss

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is true when F0,T < E(ST)?
A) occurs when long hedgers outnumber short hedgers
B) occurs when short hedgers outnumber long hedgers
C) The market is said to be in contango.
D) The market is said to be in normal contango.
E) The pure expectations hypothesis holds.
A) occurs when long hedgers outnumber short hedgers
B) occurs when short hedgers outnumber long hedgers
C) The market is said to be in contango.
D) The market is said to be in normal contango.
E) The pure expectations hypothesis holds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Assume you are the Treasurer for the Johnson Pharmaceutical Company and in late July 2004, the company is considering the sale of $500 million in 20-year bonds that will most likely be rated the same as the firm's other debt issues. The firm would like to proceed at the current rate of 8.5%, but you know that it will probably take until November to bring the issue to market. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts, which each represent $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.2. How you would go about hedging the bond issue?
A) buy 5,000 contracts
B) buy 50,000 contracts
C) sell 5,000,000 contracts
D) sell 5,000 contracts
E) sell 500 contracts
Assume you are the Treasurer for the Johnson Pharmaceutical Company and in late July 2004, the company is considering the sale of $500 million in 20-year bonds that will most likely be rated the same as the firm's other debt issues. The firm would like to proceed at the current rate of 8.5%, but you know that it will probably take until November to bring the issue to market. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts, which each represent $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.2. How you would go about hedging the bond issue?
A) buy 5,000 contracts
B) buy 50,000 contracts
C) sell 5,000,000 contracts
D) sell 5,000 contracts
E) sell 500 contracts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
According to the cost of carry model, the relationship between the spot (S0) and futures price (F0,T) is
A) S0 = F0,T/(1 + rf)T.
B) S0 = F0,T(1 + rf)T.
C) S0 + F0,T = (1 + rf)T.
D) S0 = F0,T + (1 + rf)T.
E) S0 - F0,T = (1 + rf)T.
A) S0 = F0,T/(1 + rf)T.
B) S0 = F0,T(1 + rf)T.
C) S0 + F0,T = (1 + rf)T.
D) S0 = F0,T + (1 + rf)T.
E) S0 - F0,T = (1 + rf)T.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is NOT considered a "cost of carry"?
A) commissions for physical storage
B) an opportunity cost for the net amount of invested capital
C) a premium for the convenience of consuming the asset now
D) a risk premium for uncertainty
E) the intrinsic price of the underlying
A) commissions for physical storage
B) an opportunity cost for the net amount of invested capital
C) a premium for the convenience of consuming the asset now
D) a risk premium for uncertainty
E) the intrinsic price of the underlying

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A backwardated futures market occurs when
A) F0,T < S0.
B) F0,T = S0.
C) F0,T > S0.
D) F0,T > E( ST).
E) F0,T > ST.
A) F0,T < S0.
B) F0,T = S0.
C) F0,T > S0.
D) F0,T > E( ST).
E) F0,T > ST.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
In late January 2004, The Union Cosmos Company is considering the sale of $100 million in 10-year bonds that will probably be rated AAA like the firm's other bond issues. The firm is anxious to proceed at today's rate of 10.5 percent. As treasurer, you know that it will take until sometime in April to get the issue registered and sold. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts each representing $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.1. What is the dollar gain or loss assuming that future conditions described in Case 2 actually occur? (Ignore commissions and margin costs).
A) $2,965,000.00 gain
B) $45,500.00 gain
C) $2,965,000.00 loss
D) $45,500.00 loss
E) $0
In late January 2004, The Union Cosmos Company is considering the sale of $100 million in 10-year bonds that will probably be rated AAA like the firm's other bond issues. The firm is anxious to proceed at today's rate of 10.5 percent. As treasurer, you know that it will take until sometime in April to get the issue registered and sold. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts each representing $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.1. What is the dollar gain or loss assuming that future conditions described in Case 2 actually occur? (Ignore commissions and margin costs).
A) $2,965,000.00 gain
B) $45,500.00 gain
C) $2,965,000.00 loss
D) $45,500.00 loss
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The basis (Bt,T) at time t between the spot price (St) and a futures contract expiring at time T (Ft,T) is
A) Bt,T = St + Ft,T.
B) Bt,T = St - Ft,T.
C) Bt,T = St * Ft,T.
D) Bt,T = St/Ft,T.
E) Bt,T = Ft,T/St.
A) Bt,T = St + Ft,T.
B) Bt,T = St - Ft,T.
C) Bt,T = St * Ft,T.
D) Bt,T = St/Ft,T.
E) Bt,T = Ft,T/St.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The inclusion of the following in the cost of carry model will increase the futures price.
A) dividends
B) storage costs
C) interest rate
D) taxes
E) transaction costs
A) dividends
B) storage costs
C) interest rate
D) taxes
E) transaction costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Financial futures include all of the following underlying securities EXCEPT
A) stock indexes.
B) treasury bonds.
C) bank deposits.
D) foreign currencies.
E) All of these are correct.
A) stock indexes.
B) treasury bonds.
C) bank deposits.
D) foreign currencies.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The most popular financial futures in terms of average daily volume are the
A) OEX contracts.
B) S&P 500 contracts.
C) LIBOR contracts.
D) t-bill contracts.
E) t-bond contracts.
A) OEX contracts.
B) S&P 500 contracts.
C) LIBOR contracts.
D) t-bill contracts.
E) t-bond contracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In your portfolio you have $1 million of 20-year, 8 5/8 percent bonds that are selling at 83.15 (or 83 15/32) against this position. Because you feel interest rates will rise, you sell 10 bond futures at 81.15 (or 81 15/32) against this position. Two months later, you decide to close your position. The bonds have fallen to 78, and the futures contracts are at 75.16 (75 16/32). Disregarding margin and transaction costs, what is your gain or loss?
A) $5,000 loss
B) $500 loss
C) breakeven
D) $500 gain
E) $5,000 gain
A) $5,000 loss
B) $500 loss
C) breakeven
D) $500 gain
E) $5,000 gain

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Assume you are the Treasurer for the Johnson Pharmaceutical Company and in late July 2004, the company is considering the sale of $500 million in 20-year bonds that will most likely be rated the same as the firm's other debt issues. The firm would like to proceed at the current rate of 8.5%, but you know that it will probably take until November to bring the issue to market. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts, which each represent $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.2. What is the dollar gain or loss assuming that future conditions described in Case 1 actually occur? (Ignore commissions and margin costs .)
A) $47,316,683.00 gain
B) $36,566,683.00 loss
C) $10,750,000.00 gain
D) $10,750,000.00 loss
E) $0
Assume you are the Treasurer for the Johnson Pharmaceutical Company and in late July 2004, the company is considering the sale of $500 million in 20-year bonds that will most likely be rated the same as the firm's other debt issues. The firm would like to proceed at the current rate of 8.5%, but you know that it will probably take until November to bring the issue to market. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts, which each represent $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.2. What is the dollar gain or loss assuming that future conditions described in Case 1 actually occur? (Ignore commissions and margin costs .)
A) $47,316,683.00 gain
B) $36,566,683.00 loss
C) $10,750,000.00 gain
D) $10,750,000.00 loss
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
In late January 2004, The Union Cosmos Company is considering the sale of $100 million in 10-year bonds that will probably be rated AAA like the firm's other bond issues. The firm is anxious to proceed at today's rate of 10.5 percent. As treasurer, you know that it will take until sometime in April to get the issue registered and sold. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts each representing $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.1. Explain how you would go about hedging the bond issue?
A) sell 1,000 contracts
B) buy 1,000 contracts
C) sell 100 contracts
D) sell 10,000 contracts
E) buy 10,000 contracts
In late January 2004, The Union Cosmos Company is considering the sale of $100 million in 10-year bonds that will probably be rated AAA like the firm's other bond issues. The firm is anxious to proceed at today's rate of 10.5 percent. As treasurer, you know that it will take until sometime in April to get the issue registered and sold. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts each representing $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.1. Explain how you would go about hedging the bond issue?
A) sell 1,000 contracts
B) buy 1,000 contracts
C) sell 100 contracts
D) sell 10,000 contracts
E) buy 10,000 contracts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When F0,T > E(ST), it is known as
A) backwardation.
B) normal backwardation.
C) normal contango.
D) inverted spread.
E) pure expectations equilibrium.
A) backwardation.
B) normal backwardation.
C) normal contango.
D) inverted spread.
E) pure expectations equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Assume you are the Treasurer for the Johnson Pharmaceutical Company and in late July 2004, the company is considering the sale of $500 million in 20-year bonds that will most likely be rated the same as the firm's other debt issues. The firm would like to proceed at the current rate of 8.5%, but you know that it will probably take until November to bring the issue to market. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts, which each represent $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.2. What is the dollar gain or loss assuming that future conditions described in Case 2 actually occur? (Ignore commissions and margin costs .)
A) $19,500,000.00 gain
B) $27,816,683.04 gain
C) $27,816,683.04 loss
D) $19,500,000.00 loss
E) $0
Assume you are the Treasurer for the Johnson Pharmaceutical Company and in late July 2004, the company is considering the sale of $500 million in 20-year bonds that will most likely be rated the same as the firm's other debt issues. The firm would like to proceed at the current rate of 8.5%, but you know that it will probably take until November to bring the issue to market. Therefore, you suggest that the firm hedge the pending issue using Treasury bond futures contracts, which each represent $100,000.

Refer to Exhibit 15.2. What is the dollar gain or loss assuming that future conditions described in Case 2 actually occur? (Ignore commissions and margin costs .)
A) $19,500,000.00 gain
B) $27,816,683.04 gain
C) $27,816,683.04 loss
D) $19,500,000.00 loss
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. If 90-day LIBOR rises to the levels "predicted" by the implied forward rates, what will the dollar level of the bank's interest receipt be at the end of the first quarter?
A) $35,250.00
B) $36,375.00
C) $38,250.00
D) $40,500.00
E) $0
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. If 90-day LIBOR rises to the levels "predicted" by the implied forward rates, what will the dollar level of the bank's interest receipt be at the end of the first quarter?
A) $35,250.00
B) $36,375.00
C) $38,250.00
D) $40,500.00
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Financial futures have become an increasingly attractive investment alternative because the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT) began trading them in 1977, and their hedging function partly accounts for the growth in trading. Which of the following statements concerning financial futures is true?
A) Financial futures protect the investment portfolio against inflation in the economy.
B) Investors seek protection against the increasing volatility of interest rates.
C) Unlike commodity futures, factors that influence price shifts are not supply and demand of the commodity but buyer psychology.
D) A reason for their popularity is that trading is restricted to government obligations, which reduces risks.
E) A reason for their popularity is that trading is tax-free.
A) Financial futures protect the investment portfolio against inflation in the economy.
B) Investors seek protection against the increasing volatility of interest rates.
C) Unlike commodity futures, factors that influence price shifts are not supply and demand of the commodity but buyer psychology.
D) A reason for their popularity is that trading is restricted to government obligations, which reduces risks.
E) A reason for their popularity is that trading is tax-free.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the absence of arbitrage opportunities, the forward contract price should be equal to the current price plus
A) contract price.
B) the cost of carry.
C) margin requirement.
D) the price discovery rate.
E) the convenience return.
A) contract price.
B) the cost of carry.
C) margin requirement.
D) the price discovery rate.
E) the convenience return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
A three-month T-bond futures contract (maturity 20 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $98,781.25 (implied yield 6.11 percent). A three-month T-note futures contract (maturity 10 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $101,468.80 (implied yield 5.80%). Assume semiannual compounding.
Refer to Exhibit 15.4. If you expected the yield curve to flatten, the appropriate note against bond futures spread strategy would be
A) go long the T-bond and short the T-note.
B) go short the T-bond and long the T-note.
C) go long the T-bond and long the T-note.
D) go short the T-bond and short the T-note.
E) None of these are correct.
A three-month T-bond futures contract (maturity 20 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $98,781.25 (implied yield 6.11 percent). A three-month T-note futures contract (maturity 10 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $101,468.80 (implied yield 5.80%). Assume semiannual compounding.
Refer to Exhibit 15.4. If you expected the yield curve to flatten, the appropriate note against bond futures spread strategy would be
A) go long the T-bond and short the T-note.
B) go short the T-bond and long the T-note.
C) go long the T-bond and long the T-note.
D) go short the T-bond and short the T-note.
E) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A bond portfolio manager expects a cash outflow of $35,000,000. The manager plans to hedge potential risk with a Treasury futures contract with a value of $105,215. The conversion factor between the CTD and the bond specified in the Treasury futures contract is 0.85. The duration of bond portfolio is eight years, and the duration of the CTD bond is 6.5 years. Indicate the number of contracts required and whether the position to be taken is short or long.
A) 333 contracts short
B) 333 contracts long
C) 348 contracts short
D) 348 contracts long
E) 300 contracts long
A) 333 contracts short
B) 333 contracts long
C) 348 contracts short
D) 348 contracts long
E) 300 contracts long

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets

Refer to Exhibit 15.5. If you expected the TED spread to widen over the next month, then an appropriate strategy would be to
A) go long T-Bill futures and long Eurodollar futures.
B) go short T-Bill futures and short Eurodollar futures.
C) go long T-Bill futures and short Eurodollar futures.
D) go short T-Bill futures and long Eurodollar futures.
E) None of these are correct.
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets

Refer to Exhibit 15.5. If you expected the TED spread to widen over the next month, then an appropriate strategy would be to
A) go long T-Bill futures and long Eurodollar futures.
B) go short T-Bill futures and short Eurodollar futures.
C) go long T-Bill futures and short Eurodollar futures.
D) go short T-Bill futures and long Eurodollar futures.
E) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. What is the implied 90-day forward rate at the beginning of the second quarter?
A) 4.70%
B) 4.85%
C) 4.60%
D) 4.94%
E) 0%
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. What is the implied 90-day forward rate at the beginning of the second quarter?
A) 4.70%
B) 4.85%
C) 4.60%
D) 4.94%
E) 0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets
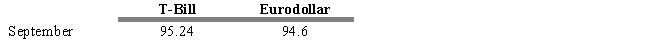
-Refer to Exhibit 15.6. Assume that a month later the price of the September T-Bill future is 96.25 and the price of the Eurodollar future is 95.9. Calculate the profit on the T-Bill futures position.
A) 101 basis points
B) 130 basis points
C) -101 basis points
D) -130 basis points
E) 29 basis points
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets
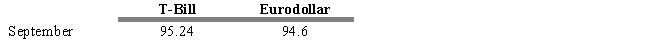
-Refer to Exhibit 15.6. Assume that a month later the price of the September T-Bill future is 96.25 and the price of the Eurodollar future is 95.9. Calculate the profit on the T-Bill futures position.
A) 101 basis points
B) 130 basis points
C) -101 basis points
D) -130 basis points
E) 29 basis points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. Assuming the yields inferred from the Eurodollar futures contract prices for the next three settlement periods are equal to the implied forward rates, calculate the dollar value of the annuity that would leave the bank indifferent between making the floating-rate loan and hedging it in the futures market and making a one-year fixed-rate loan.
A) $49,312.36
B) $35,120.62
C) $39,036.45
D) $44,452.36
E) $0
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. Assuming the yields inferred from the Eurodollar futures contract prices for the next three settlement periods are equal to the implied forward rates, calculate the dollar value of the annuity that would leave the bank indifferent between making the floating-rate loan and hedging it in the futures market and making a one-year fixed-rate loan.
A) $49,312.36
B) $35,120.62
C) $39,036.45
D) $44,452.36
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. If 90-day LIBOR rises to the levels "predicted" by the implied forward rates, what will the dollar level of the bank's interest receipt be at the end of the third quarter?
A) $35,250.00
B) $36,375.00
C) $38,250.00
D) $41,005.50
E) $0
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. If 90-day LIBOR rises to the levels "predicted" by the implied forward rates, what will the dollar level of the bank's interest receipt be at the end of the third quarter?
A) $35,250.00
B) $36,375.00
C) $38,250.00
D) $41,005.50
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A bond portfolio manager expects a cash inflow of $12,000,000. The manager plans to hedge potential risk with a Treasury futures contract with a value of $105,215. The conversion factor between the CTD and the bond specified in the Treasury futures contract is 0.85. The duration of bond portfolio is eight years, and the duration of the CTD bond is 6.5 years. Indicate the number of contracts required and whether the position to be taken is short or long.
A) 114 contracts short
B) 114 contracts long
C) 119 contracts short
D) 119 contracts long
E) 100 contracts long
A) 114 contracts short
B) 114 contracts long
C) 119 contracts short
D) 119 contracts long
E) 100 contracts long

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets
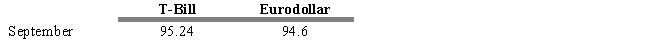
Refer to Exhibit 15.6. If you expected the spread to narrow over the next month, then an appropriate strategy would be to
A) go long T-Bill futures and long Eurodollar futures.
B) go short T-Bill futures and short Eurodollar futures.
C) go long T-Bill futures and short Eurodollar futures.
D) go short T-Bill futures and long Eurodollar futures.
E) None of these are correct.
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets
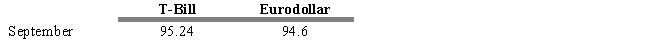
Refer to Exhibit 15.6. If you expected the spread to narrow over the next month, then an appropriate strategy would be to
A) go long T-Bill futures and long Eurodollar futures.
B) go short T-Bill futures and short Eurodollar futures.
C) go long T-Bill futures and short Eurodollar futures.
D) go short T-Bill futures and long Eurodollar futures.
E) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
A three-month T-bond futures contract (maturity 20 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $98,781.25 (implied yield 6.11 percent). A three-month T-note futures contract (maturity 10 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $101,468.80 (implied yield 5.80%). Assume semiannual compounding.
Refer to Exhibit 15.4. If you expected the yield curve to steepen, the appropriate NOTE AGAINST BOND futures spread strategy would be
A) go long the T-bond and short the T-note.
B) go short the T-bond and long the T-note.
C) go long the T-bond and long the T-note.
D) go short the T-bond and short the T-note.
E) None of these are correct.
A three-month T-bond futures contract (maturity 20 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $98,781.25 (implied yield 6.11 percent). A three-month T-note futures contract (maturity 10 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $101,468.80 (implied yield 5.80%). Assume semiannual compounding.
Refer to Exhibit 15.4. If you expected the yield curve to steepen, the appropriate NOTE AGAINST BOND futures spread strategy would be
A) go long the T-bond and short the T-note.
B) go short the T-bond and long the T-note.
C) go long the T-bond and long the T-note.
D) go short the T-bond and short the T-note.
E) None of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. If the bank wanted to hedge its exposure to falling LIBOR on this loan commitment, describe the sequence of transactions in the futures markets it could undertake.
A) buy three Eurodollar futures contracts that expire at the end of the first quarter
B) buy three Eurodollar futures contracts that expire at the end of the first quarter, three that expire at the end of the second quarter, and three that expire at the end of the third quarter.
C) sell three Eurodollar futures contracts that expire at the end of the year.
D) sell one Eurodollar futures contract that expires at the end of the first quarter, one that expires at the end of the second quarter, and one that expires at the end of the third quarter.
E) buy three Eurodollar futures contracts that expire at the end of the year.
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. If the bank wanted to hedge its exposure to falling LIBOR on this loan commitment, describe the sequence of transactions in the futures markets it could undertake.
A) buy three Eurodollar futures contracts that expire at the end of the first quarter
B) buy three Eurodollar futures contracts that expire at the end of the first quarter, three that expire at the end of the second quarter, and three that expire at the end of the third quarter.
C) sell three Eurodollar futures contracts that expire at the end of the year.
D) sell one Eurodollar futures contract that expires at the end of the first quarter, one that expires at the end of the second quarter, and one that expires at the end of the third quarter.
E) buy three Eurodollar futures contracts that expire at the end of the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. If 90-day LIBOR rises to the levels "predicted" by the implied forward rates, what will the dollar level of the bank's interest receipt be at the end of the second quarter?
A) $40,500.00
B) $38,250.00
C) $35,250.00
D) $37,064.25
E) $34,500.00
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. If 90-day LIBOR rises to the levels "predicted" by the implied forward rates, what will the dollar level of the bank's interest receipt be at the end of the second quarter?
A) $40,500.00
B) $38,250.00
C) $35,250.00
D) $37,064.25
E) $34,500.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets

-Refer to Exhibit 15.5. Assume that a month later the price of the September T-Bill future is 93 and the price of the Eurodollar future is 90.25. Calculate the profit on the T-Bill futures position.
A) 25 basis points
B) 110 basis points
C) -25 basis points
D) -110 basis points
E) 50 basis points
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets

-Refer to Exhibit 15.5. Assume that a month later the price of the September T-Bill future is 93 and the price of the Eurodollar future is 90.25. Calculate the profit on the T-Bill futures position.
A) 25 basis points
B) 110 basis points
C) -25 basis points
D) -110 basis points
E) 50 basis points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. What is the implied 90-day forward rate at the beginning of the third quarter?
A) 5.10%
B) 5.47%
C) 4.70%
D) 4.85%
E) 0%
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. What is the implied 90-day forward rate at the beginning of the third quarter?
A) 5.10%
B) 5.47%
C) 4.70%
D) 4.85%
E) 0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. If 90-day LIBOR rises to the levels "predicted" by the implied forward rates, what will the dollar level of the bank's interest receipt be at the end of the fourth quarter?
A) $36,223.50
B) $40,500.00
C) $38,250.00
D) $36,375.00
E) $0
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. If 90-day LIBOR rises to the levels "predicted" by the implied forward rates, what will the dollar level of the bank's interest receipt be at the end of the fourth quarter?
A) $36,223.50
B) $40,500.00
C) $38,250.00
D) $36,375.00
E) $0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
A three-month T-bond futures contract (maturity 20 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $98,781.25 (implied yield 6.11 percent). A three-month T-note futures contract (maturity 10 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $101,468.80 (implied yield 5.80%). Assume semiannual compounding.
-Refer to Exhibit 15.4. Suppose the yield curve changed so the that the new yield on the T-bond contract rose to 6.5 percent, and the new yield on the T-note contract fell to 5.5 percent. Calculate the profit on the note against bond futures spread. (Assume coupons are paid semiannually)
A) -$5850.92
B) -$6,671.42
C) $6,671.42
D) $5850.92
E) $4550.42
A three-month T-bond futures contract (maturity 20 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $98,781.25 (implied yield 6.11 percent). A three-month T-note futures contract (maturity 10 years, coupon 6 percent, face $100,000) currently trades at $101,468.80 (implied yield 5.80%). Assume semiannual compounding.
-Refer to Exhibit 15.4. Suppose the yield curve changed so the that the new yield on the T-bond contract rose to 6.5 percent, and the new yield on the T-note contract fell to 5.5 percent. Calculate the profit on the note against bond futures spread. (Assume coupons are paid semiannually)
A) -$5850.92
B) -$6,671.42
C) $6,671.42
D) $5850.92
E) $4550.42

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets
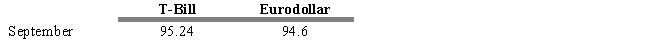
-Refer to Exhibit 15.6. Assume that a month later the price of the September T-Bill future is 96.25 and the price of the Eurodollar future is 95.9. Calculate the profit on the Eurodollar futures position.
A) 101 basis points
B) 130 basis points
C) -101 basis points
D) -130 basis point.
E) 29 basis points
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets
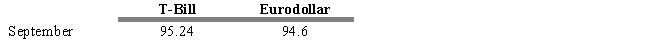
-Refer to Exhibit 15.6. Assume that a month later the price of the September T-Bill future is 96.25 and the price of the Eurodollar future is 95.9. Calculate the profit on the Eurodollar futures position.
A) 101 basis points
B) 130 basis points
C) -101 basis points
D) -130 basis point.
E) 29 basis points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. Assuming the yields inferred from the Eurodollar futures contract prices for the next three settlement periods are equal to the implied forward rates, calculate, in annual (360-day) percentage terms, the annuity that would leave the bank indifferent between making the floating-rate loan and hedging it in the futures market and making a one-year fixed-rate loan.
A) 20.86%
B) 5.10%
C) 4.91%
D) 5.20%
E) 0%
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. Assuming the yields inferred from the Eurodollar futures contract prices for the next three settlement periods are equal to the implied forward rates, calculate, in annual (360-day) percentage terms, the annuity that would leave the bank indifferent between making the floating-rate loan and hedging it in the futures market and making a one-year fixed-rate loan.
A) 20.86%
B) 5.10%
C) 4.91%
D) 5.20%
E) 0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. What is the implied 90-day forward rate at the beginning of the fourth quarter?
A) 6.19%
B) 5.10%
C) 6.07%
D) 5.68%
E) 0%
As a relationship officer for a money-center commercial bank, one of your corporate accounts has just approached you about a one-year loan for $3,000,000. The customer would pay a quarterly interest expense based on the prevailing level of LIBOR at the beginning of each quarter. As is the bank's convention on all such loans, the amount of the interest payment would then be paid at the end of the quarterly cycle when the new rate for the next cycle is determined. You observe the following LIBOR yield curve in the cash market:

Refer to Exhibit 15.3. What is the implied 90-day forward rate at the beginning of the fourth quarter?
A) 6.19%
B) 5.10%
C) 6.07%
D) 5.68%
E) 0%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
USE THE INFORMATION BELOW FOR THE FOLLOWING PROBLEM(S)
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets

-Refer to Exhibit 15.5. Assume that a month later the price of the September T-Bill future is 93 and the price of the Eurodollar future is 90.25. Calculate the profit on the Eurodollar futures position.
A) 190 basis points
B) 210 basis points
C) -190 basis points
D) -210 basis points
E) 100 basis points
Assume that you observe the following prices in the T-Bill and Eurodollar futures markets

-Refer to Exhibit 15.5. Assume that a month later the price of the September T-Bill future is 93 and the price of the Eurodollar future is 90.25. Calculate the profit on the Eurodollar futures position.
A) 190 basis points
B) 210 basis points
C) -190 basis points
D) -210 basis points
E) 100 basis points

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 148 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



