Deck 5: Externalities, environmental Policy, and Public Goods
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/133
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Externalities, environmental Policy, and Public Goods
1
A positive externality results when
A)economists are sure that a good or service provides benefits to consumers.
B)someone pays for a good or service even though she is not directly affected by the production or consumption of it.
C)when people who live in one country benefit from the production of a good or service that occurs in another country.
D)people who are not directly involved in producing or paying for a good or service benefit from it.
A)economists are sure that a good or service provides benefits to consumers.
B)someone pays for a good or service even though she is not directly affected by the production or consumption of it.
C)when people who live in one country benefit from the production of a good or service that occurs in another country.
D)people who are not directly involved in producing or paying for a good or service benefit from it.
people who are not directly involved in producing or paying for a good or service benefit from it.
2
Which of the following could be evidence of a market failure?
A)Resources in an economy are not fully utilized.
B)The market price of a product is above the average cost of production.
C)There are only a handful of firms competing against each other in an industry.
D)Market prices do not reflect true production costs.
A)Resources in an economy are not fully utilized.
B)The market price of a product is above the average cost of production.
C)There are only a handful of firms competing against each other in an industry.
D)Market prices do not reflect true production costs.
Market prices do not reflect true production costs.
3
Which of the following describes how a negative externality affects a competitive market?
A)The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the social cost.
B)The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the private benefit from consumption.
C)The externality causes consumer surplus to exceed producer surplus.
D)The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the equilibrium price.
A)The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the social cost.
B)The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the private benefit from consumption.
C)The externality causes consumer surplus to exceed producer surplus.
D)The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the equilibrium price.
The externality causes a difference between the private cost of production and the social cost.
4
The cost borne by a producer in the production of a good or service is called
A)private cost.
B)public cost.
C)social cost.
D)internal cost.
A)private cost.
B)public cost.
C)social cost.
D)internal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
An external cost is created when you
A)graduate from college.
B)buy flowers for your mother on Mother's Day.
C)litter on the side of the road.
D)buy a sandwich for lunch.
A)graduate from college.
B)buy flowers for your mother on Mother's Day.
C)litter on the side of the road.
D)buy a sandwich for lunch.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Pollution is an example of a
A)public good.
B)positive externality.
C)private cost.
D)negative externality
A)public good.
B)positive externality.
C)private cost.
D)negative externality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
When there is a positive externality
A)the private benefit received by consumers is greater than the external benefit.
B)the social benefit received by consumers is greater than the private benefit.
C)the private benefit received by consumers is greater than the private cost.
D)the private benefit received by consumers is greater than the social benefit.
A)the private benefit received by consumers is greater than the external benefit.
B)the social benefit received by consumers is greater than the private benefit.
C)the private benefit received by consumers is greater than the private cost.
D)the private benefit received by consumers is greater than the social benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An externality
A)is a benefit or cost that affects someone who is not directly involved in the production or consumption of a good or service.
B)enhances market efficiency.
C)is a private cost or benefit that results from the production or consumption of a good or service that is external to a market.
D)refers to production or consumption that occurs outdoors.
A)is a benefit or cost that affects someone who is not directly involved in the production or consumption of a good or service.
B)enhances market efficiency.
C)is a private cost or benefit that results from the production or consumption of a good or service that is external to a market.
D)refers to production or consumption that occurs outdoors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Alternative approaches for reducing carbon dioxide emissions are
A)carbon taxes and carbon scrubbing.
B)carbon trading and carbon subsidies.
C)carbon taxes and carbon trading.
D)burning low carbon coal and deforestation.
A)carbon taxes and carbon scrubbing.
B)carbon trading and carbon subsidies.
C)carbon taxes and carbon trading.
D)burning low carbon coal and deforestation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When there is a negative externality,the private cost of production ________ the social cost of production.
A)is greater than
B)is equal to
C)eliminates
D)is less than
A)is greater than
B)is equal to
C)eliminates
D)is less than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the social benefit of consuming a good or a service exceeds the private benefit
A)a negative externality exists.
B)the market achieves economic efficiency.
C)a positive externality exists.
D)the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized.
A)a negative externality exists.
B)the market achieves economic efficiency.
C)a positive externality exists.
D)the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the past the federal government often employed what is called a "command and control" approach to the reduction of pollution emissions.Many economists are critical of this approach because
A)it does not lead to significant reductions in pollution.
B)they believe a market-based approach will reduce emissions more efficiently.
C)the "command and control" approach is designed to help firms at the expense of consumers.
D)the "command and control" approach leads to negative externalities.
A)it does not lead to significant reductions in pollution.
B)they believe a market-based approach will reduce emissions more efficiently.
C)the "command and control" approach is designed to help firms at the expense of consumers.
D)the "command and control" approach leads to negative externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A free market fails when
A)there is government intervention.
B)there is an external effect in either production,consumption,or both.
C)firms that produce goods which create positive externalities go bankrupt.
D)firms that produce goods which create negative externalities earn high profits.
A)there is government intervention.
B)there is an external effect in either production,consumption,or both.
C)firms that produce goods which create positive externalities go bankrupt.
D)firms that produce goods which create negative externalities earn high profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When there is an externality in a market
A)the externality will move the market to an economically efficient equilibrium.
B)the externality will cause the market price to be less than or greater than the equilibrium price.
C)the government should use price controls to enable the market to reach equilibrium.
D)government intervention may increase economic efficiency.
A)the externality will move the market to an economically efficient equilibrium.
B)the externality will cause the market price to be less than or greater than the equilibrium price.
C)the government should use price controls to enable the market to reach equilibrium.
D)government intervention may increase economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If there are no externalities a competitive market achieves economic efficiency.If there is a negative externality,economic efficiency will not be achieved because
A)too little of the good will be produced.
B)too much of the good will be produced.
C)a deadweight loss will occur that is equal to the area under the demand curve for the good.
D)economic surplus is maximized.
A)too little of the good will be produced.
B)too much of the good will be produced.
C)a deadweight loss will occur that is equal to the area under the demand curve for the good.
D)economic surplus is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If the social cost of producing a good or service exceeds the private cost,
A)a positive externality exists.
B)the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized.
C)the market achieves economic efficiency.
D)a negative externality exists.
A)a positive externality exists.
B)the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized.
C)the market achieves economic efficiency.
D)a negative externality exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following describes how a positive externality affects a competitive market?
A)The externality causes a difference between the private benefit from consumption and the social benefit.
B)The externality causes a difference between the private benefit from production and the social cost of production.
C)The externality causes quantity demanded to exceed quantity supplied.
D)The externality causes a difference between the social cost of production and the social cost of consumption.
A)The externality causes a difference between the private benefit from consumption and the social benefit.
B)The externality causes a difference between the private benefit from production and the social cost of production.
C)The externality causes quantity demanded to exceed quantity supplied.
D)The externality causes a difference between the social cost of production and the social cost of consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following would result in a positive externality?
A)A local government establishes a price ceiling on rental apartments.
B)An electric utility burns coal that causes acid rain.
C)Medical research results in a cure for malaria.
D)McDonald's adds new fat-free items to its menu.
A)A local government establishes a price ceiling on rental apartments.
B)An electric utility burns coal that causes acid rain.
C)Medical research results in a cure for malaria.
D)McDonald's adds new fat-free items to its menu.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
"A competitive market achieves economic efficiency by maximizing the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus." This statement
A)is true only if there are positive externalities in production in the market.
B)is true only if there are no negative externalities in the market.
C)is true only if there are no positive or negative externalities in the market.
D)is true in theory,but economic efficiency cannot be achieved in a real market.
A)is true only if there are positive externalities in production in the market.
B)is true only if there are no negative externalities in the market.
C)is true only if there are no positive or negative externalities in the market.
D)is true in theory,but economic efficiency cannot be achieved in a real market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When production generates a negative externality,the true cost of production is the
A)private cost of production.
B)public cost of production.
C)social cost of production.
D)average cost of production.
A)private cost of production.
B)public cost of production.
C)social cost of production.
D)average cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure 5-1 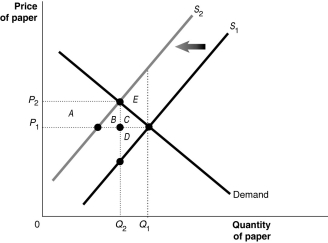 Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Figure 5-1.What does S1 represent?
A)the market supply curve that reflects social cost
B)the market supply curve that reflects only external cost
C)the market supply curve that reflects only private benefit
D)the market supply curve that reflects private cost
 Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).Refer to Figure 5-1.What does S1 represent?
A)the market supply curve that reflects social cost
B)the market supply curve that reflects only external cost
C)the market supply curve that reflects only private benefit
D)the market supply curve that reflects private cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Figure 5-1  Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Figure 5-1.What does S2 represent?
A)the market supply curve that reflects social cost
B)the market supply curve that reflect private cost
C)the market supply curve that reflects external cost
D)the market supply curve that reflects social benefit
 Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).Refer to Figure 5-1.What does S2 represent?
A)the market supply curve that reflects social cost
B)the market supply curve that reflect private cost
C)the market supply curve that reflects external cost
D)the market supply curve that reflects social benefit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 5-1  Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Figure 5-1.Why is there a deadweight loss?
A)because the marginal social cost of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the marginal benefit
B)because the marginal private cost of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the marginal benefit
C)because the marginal social benefit of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the private cost
D)because the marginal private benefit of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the social cost
 Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).Refer to Figure 5-1.Why is there a deadweight loss?
A)because the marginal social cost of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the marginal benefit
B)because the marginal private cost of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the marginal benefit
C)because the marginal social benefit of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the private cost
D)because the marginal private benefit of producing each additional unit in excess of Q2 exceeds the social cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Medical research that ends in a cure for a serious disease produces positive externalities.What is the impact of this positive externality on economic efficiency?
A)At equilibrium,less than the economically efficient quantity of medical research is produced.
B)A deadweight loss occurs because at equilibrium the marginal social cost of medical research is greater than the marginal social benefit.
C)At equilibrium,more than the economically efficient quantity of medical research is produced.
D)A deadweight loss occurs because at equilibrium the marginal social cost equals the marginal social benefit.
A)At equilibrium,less than the economically efficient quantity of medical research is produced.
B)A deadweight loss occurs because at equilibrium the marginal social cost of medical research is greater than the marginal social benefit.
C)At equilibrium,more than the economically efficient quantity of medical research is produced.
D)A deadweight loss occurs because at equilibrium the marginal social cost equals the marginal social benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When products that create positive externalities are produced,at the market equilibrium output,the social benefit generated by consuming the product exceeds the private benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Figure 5-3 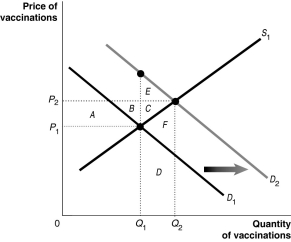 Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Refer to Figure 5-3.What does D2 represent?
A)the social welfare curve
B)the demand curve reflecting social benefit
C)the demand curve reflecting private benefit
D)the positive externalities curve
 Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.Refer to Figure 5-3.What does D2 represent?
A)the social welfare curve
B)the demand curve reflecting social benefit
C)the demand curve reflecting private benefit
D)the positive externalities curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 5-1  Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Figure 5-1.What is the economically efficient output level?
A)Q1
B)Q2 minus Q1
C)Q2
D)Q1 plus Q2
 Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).Refer to Figure 5-1.What is the economically efficient output level?
A)Q1
B)Q2 minus Q1
C)Q2
D)Q1 plus Q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The social cost of cutting trees for firewood in a government forest is
A)the increased likelihood of flooding as more trees are cut.
B)the increased likelihood of flooding as more trees are cut plus the private cost of cutting the trees.
C)opportunity cost to the individual of cutting the wood.
D)the marginal costs of cutting the last tree.
A)the increased likelihood of flooding as more trees are cut.
B)the increased likelihood of flooding as more trees are cut plus the private cost of cutting the trees.
C)opportunity cost to the individual of cutting the wood.
D)the marginal costs of cutting the last tree.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 5-3  Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Refer to Figure 5-3.What does D1 represent?
A)the demand curve reflecting social benefit
B)the positive externalities curve
C)the demand curve reflecting private benefit
D)the social welfare curve
 Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.Refer to Figure 5-3.What does D1 represent?
A)the demand curve reflecting social benefit
B)the positive externalities curve
C)the demand curve reflecting private benefit
D)the social welfare curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Figure 5-2 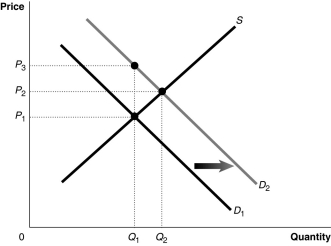 Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
Refer to Figure 5-2.If,because of an externality,the economically efficient output is Q2 and not the current equilibrium output of Q1,what does D2 represent?
A)the demand curve reflecting external benefits
B)the demand curve reflecting social benefits
C)the demand curve reflecting private benefits
D)the demand curve reflecting the sum of social and external benefits
 Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.Refer to Figure 5-2.If,because of an externality,the economically efficient output is Q2 and not the current equilibrium output of Q1,what does D2 represent?
A)the demand curve reflecting external benefits
B)the demand curve reflecting social benefits
C)the demand curve reflecting private benefits
D)the demand curve reflecting the sum of social and external benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Figure 5-1  Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Figure 5-1.What is the deadweight loss from producing at the market equilibrium?
A)area C
B)area E
C)area D
D)area F
 Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).
Suppose there are several paper mills producing paper for a market.These mills,located upstream from a fishing village,discharge a large amount of wastewater into the river.The waste material affects the number of fish in the river,and the use of the river for recreation and as a public water supply source.Figure 5-1 shows the paper market.Use this Figure to answer the following question(s).Refer to Figure 5-1.What is the deadweight loss from producing at the market equilibrium?
A)area C
B)area E
C)area D
D)area F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 5-3  Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Refer to Figure 5-3.Why is there a deadweight loss?
A)because the marginal private benefit for each additional unit between Q1 and Q2 exceeds the marginal cost
B)because the marginal private cost for each additional unit between Q1 and Q2 exceeds the marginal private benefit
C)because the marginal social cost for each additional unit between Q1 and Q2 exceeds the marginal social benefit
D)because the marginal social benefit for each additional unit between Q1 and Q2 exceeds the marginal cost
 Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.Refer to Figure 5-3.Why is there a deadweight loss?
A)because the marginal private benefit for each additional unit between Q1 and Q2 exceeds the marginal cost
B)because the marginal private cost for each additional unit between Q1 and Q2 exceeds the marginal private benefit
C)because the marginal social cost for each additional unit between Q1 and Q2 exceeds the marginal social benefit
D)because the marginal social benefit for each additional unit between Q1 and Q2 exceeds the marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The social cost of a good or service is the cost borne by the producer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Figure 5-3  Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Refer to Figure 5-3.What is the deadweight loss resulting from producing at the market equilibrium?
A)B + C
B)E + C
C)F
D)C
 Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.Refer to Figure 5-3.What is the deadweight loss resulting from producing at the market equilibrium?
A)B + C
B)E + C
C)F
D)C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Figure 5-3  Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Refer to Figure 5-3.What is the market equilibrium output level?
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q1 + Q2
D)Q2 - Q1
 Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.Refer to Figure 5-3.What is the market equilibrium output level?
A)Q1
B)Q2
C)Q1 + Q2
D)Q2 - Q1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An externality is an example of a market failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 5-2  Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
Refer to Figure 5-2.If,because of an externality,the economically efficient output is Q2 and not the current equilibrium output of Q1,what does D1 represent?
A)the demand curve reflecting external benefits
B)the demand curve reflecting social benefits
C)the demand curve reflecting private benefits
D)the demand curve reflecting the sum of private and social benefits
 Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.Refer to Figure 5-2.If,because of an externality,the economically efficient output is Q2 and not the current equilibrium output of Q1,what does D1 represent?
A)the demand curve reflecting external benefits
B)the demand curve reflecting social benefits
C)the demand curve reflecting private benefits
D)the demand curve reflecting the sum of private and social benefits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Figure 5-2  Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
Refer to Figure 5-2.Suppose the current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output because of an externality.The economically efficient output is Q2.In that case,diagram shows
A)the effect of a subsidy granted to producers of a good.
B)the effect of an excess demand in a market.
C)the effect of a positive externality in the consumption of a good.
D)the effect of a negative externality in the consumption of a good.
 Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.
Figure 5-2 shows a market with an externality.The current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output.The economically efficient output is Q2.Refer to Figure 5-2.Suppose the current market equilibrium output of Q1 is not the economically efficient output because of an externality.The economically efficient output is Q2.In that case,diagram shows
A)the effect of a subsidy granted to producers of a good.
B)the effect of an excess demand in a market.
C)the effect of a positive externality in the consumption of a good.
D)the effect of a negative externality in the consumption of a good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Assume that emissions from electric utilities contribute to pollution in the form of acid rain.Which of the following describes how this affects the market for electricity?
A)The equilibrium in the market is not efficient; the marginal benefit from electricity is greater than the marginal social cost.
B)A deadweight loss occurs; at equilibrium the additional social cost of production is greater than the additional benefit to consumers.
C)The equilibrium in the market is not efficient; because of the cost of the acid rain,economic efficiency would be greater if more electricity were produced.
D)The equilibrium in the market is not efficient; consumer surplus is equal to producer surplus.
A)The equilibrium in the market is not efficient; the marginal benefit from electricity is greater than the marginal social cost.
B)A deadweight loss occurs; at equilibrium the additional social cost of production is greater than the additional benefit to consumers.
C)The equilibrium in the market is not efficient; because of the cost of the acid rain,economic efficiency would be greater if more electricity were produced.
D)The equilibrium in the market is not efficient; consumer surplus is equal to producer surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Figure 5-3  Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Refer to Figure 5-3.What is the economically efficient output level?
A)Q1
B)Q1 + Q2
C)Q2 - Q1
D)Q2
 Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.
Figure 5-3 shows the market for measles vaccinations,a product whose use generates positive externalities.Refer to Figure 5-3.What is the economically efficient output level?
A)Q1
B)Q1 + Q2
C)Q2 - Q1
D)Q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
According to Steven Cheung: "Pollination contracts usually include stipulations regarding the number and strength of ...[bee] colonies,the rental fee per hive,the time of delivery...the protection of bees from pesticides,and the strategic placing of hives." Cheung cites this as evidence that
A)the high costs of writing and enforcing complicated written agreements between owners of beehives and apple orchards prevents economic efficiency from being achieved in these markets.
B)government intervention is not always necessary to bring about an economically efficient number of apple trees and beehives.
C)government regulation of contracts between owners of beehives and apple orchards is necessary to bring about an economically efficient number of apple trees and beehives.
D)the beekeeping and apple growing businesses have become more complicated and costly over time due to the legal costs involved.
A)the high costs of writing and enforcing complicated written agreements between owners of beehives and apple orchards prevents economic efficiency from being achieved in these markets.
B)government intervention is not always necessary to bring about an economically efficient number of apple trees and beehives.
C)government regulation of contracts between owners of beehives and apple orchards is necessary to bring about an economically efficient number of apple trees and beehives.
D)the beekeeping and apple growing businesses have become more complicated and costly over time due to the legal costs involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Assume that air pollution from a copper smelter imposes external costs on people who live near the smelter.If the victims of the pollution could not legally enforce the right of their property not to be damaged,the amount of pollution reduction
A)would be significantly less than if the owners of the smelter were legally liable for damages.
B)would be less than the amount at which the marginal benefit of pollution reduction equaled the marginal cost.
C)would be the same as if it would be if the owners of the smelter were legally liable.
D)would be too small; the government would have to intervene to bring about an efficient outcome.
A)would be significantly less than if the owners of the smelter were legally liable for damages.
B)would be less than the amount at which the marginal benefit of pollution reduction equaled the marginal cost.
C)would be the same as if it would be if the owners of the smelter were legally liable.
D)would be too small; the government would have to intervene to bring about an efficient outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When negative externalities exist,the competitive market supply curve does not include all of the costs borne by members of society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Compare two situations.(A)A firm is not legally responsible for damages that result from air pollution caused by its production of steel.(B)A firm is legally responsible for damages that result from its production of steel.Ronald Coase argued that
A)bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm will result in little reduction of pollution in either situation (A)or (B)because the firm has greater economic and political power than the victims.
B)bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm would lead to a greater reduction in pollution in situation (A)than situation (B).
C)bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm would lead to a smaller reduction in pollution in situation (A)than situation (B).
D)bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm would lead to an equal reduction in pollution in situation (A)and situation (B).
A)bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm will result in little reduction of pollution in either situation (A)or (B)because the firm has greater economic and political power than the victims.
B)bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm would lead to a greater reduction in pollution in situation (A)than situation (B).
C)bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm would lead to a smaller reduction in pollution in situation (A)than situation (B).
D)bargaining between the firm and the victims of the air pollution caused by the firm would lead to an equal reduction in pollution in situation (A)and situation (B).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A negative externality is an example of market failure.The root of the problem lies in the definition and enforcement of property rights.Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the marginal benefit of reducing emissions of some air pollutant is greater than the marginal cost,
A)further reductions will make society better off.
B)the marginal benefit will rise and the marginal cost will fall as further reductions are made.
C)economic efficiency will be achieved when emissions are reduced to zero.
D)private businesses,rather the consumers,should be made to pay for the cost of further reductions.
A)further reductions will make society better off.
B)the marginal benefit will rise and the marginal cost will fall as further reductions are made.
C)economic efficiency will be achieved when emissions are reduced to zero.
D)private businesses,rather the consumers,should be made to pay for the cost of further reductions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Private solutions to the problem of externalities are most likely when
A)government actively encourages these solutions.
B)transaction costs are low and the number of bargaining parties is small.
C)transaction costs are low and the number of bargaining parties is large.
D)transaction costs are low and the monetary damages to third parties is high.
A)government actively encourages these solutions.
B)transaction costs are low and the number of bargaining parties is small.
C)transaction costs are low and the number of bargaining parties is large.
D)transaction costs are low and the monetary damages to third parties is high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Congress passed the Clean Air Act in 1970.Since this act was passed,emissions of the six main air pollutants
A)have fallen by more than one-half.
B)have increased significantly due to the growth of the U.S.economy.
C)cannot be measured since Congress failed to appropriate money to monitor the level of emissions.
D)have remained essentially constant,even though significant economic growth has occurred in the United States since 1970.
A)have fallen by more than one-half.
B)have increased significantly due to the growth of the U.S.economy.
C)cannot be measured since Congress failed to appropriate money to monitor the level of emissions.
D)have remained essentially constant,even though significant economic growth has occurred in the United States since 1970.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is a private benefit from consumption? What is a social benefit from consumption? When is the private benefit from consumption equal to the social benefit from consumption?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Steven Cheung examined the relationship between beekeepers and apple growers.Cheung noted that: "Pollination contracts usually include stipulations regarding the number and strength of ...[bee] colonies,the rental fee per hive,the time of delivery...the protection of bees from pesticides,and the strategic placing of hives." Cheung's suggests that the relationship between beekeepers and apple growers is an example of
A)the Coase Theorem.
B)how excessive legal costs can prevent economic efficiency from being achieved.
C)negative externalities.
D)government intervention improving economic efficiency.
A)the Coase Theorem.
B)how excessive legal costs can prevent economic efficiency from being achieved.
C)negative externalities.
D)government intervention improving economic efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Kenneth Chay and Michael Greenstone examined the impact of reductions in air pollution since the passage of the Clean Air Act of 1970.Which of the following statements summarizes their findings?
A)The marginal benefit of reductions in air pollution was less than the marginal cost.
B)The marginal cost of reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide has increased over time as the marginal benefit of the reductions has increased.
C)The benefits of reducing the six main air pollutants in the two years following the Act greatly exceeded the costs.
D)In the two years following passage of the Act,fewer infants died than would have died if the Act had not been passed.
A)The marginal benefit of reductions in air pollution was less than the marginal cost.
B)The marginal cost of reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide has increased over time as the marginal benefit of the reductions has increased.
C)The benefits of reducing the six main air pollutants in the two years following the Act greatly exceeded the costs.
D)In the two years following passage of the Act,fewer infants died than would have died if the Act had not been passed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Figure 5-4 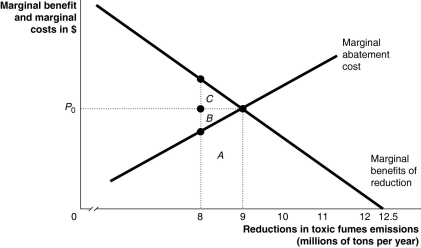 Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.
Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.
Refer to Figure 5-4.What is the economically efficient level of pollution reduction?
A)12.5 million tons
B)9 million tons
C)8 million tons
D)0 tons
 Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.
Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.Refer to Figure 5-4.What is the economically efficient level of pollution reduction?
A)12.5 million tons
B)9 million tons
C)8 million tons
D)0 tons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How does a positive externality in consumption reduce economic efficiency?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following statements about the economically efficient level of air pollution is correct?
A)The economically efficient level of pollution is zero.
B)The economically efficient level of pollution occurs where all social costs equal all social benefits.
C)The economically efficient level of pollution occurs where the marginal cost of pollution reduction equals the marginal social benefit of reduction.
D)The economically efficient level of pollution occurs where total benefits of pollution reduction are maximized.
A)The economically efficient level of pollution is zero.
B)The economically efficient level of pollution occurs where all social costs equal all social benefits.
C)The economically efficient level of pollution occurs where the marginal cost of pollution reduction equals the marginal social benefit of reduction.
D)The economically efficient level of pollution occurs where total benefits of pollution reduction are maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If electric utilities continually reduce their emissions of sulfur dioxide,
A)the utilities will eventually be forced to go out of business.
B)the marginal benefit of additional emissions will rise.
C)the marginal cost of further emissions will rise.
D)the total benefit of sulfur dioxide emissions will fall.
A)the utilities will eventually be forced to go out of business.
B)the marginal benefit of additional emissions will rise.
C)the marginal cost of further emissions will rise.
D)the total benefit of sulfur dioxide emissions will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An external benefit is created when you pursue a college education.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Ronald Coase was awarded the 1991 Nobel Prize in Economics primarily for addressing problems related to externalities.Which of the following describes Coase's work?
A)Coase argued that government intervention is necessary to achieve economic efficiency in markets that are affected by externalities.
B)Coase proved that economic efficiency cannot be achieved in a market that is affected by positive or negative externalities.
C)Coase argued that under some circumstances private solutions to the problems of externalities will occur.
D)Coase proved that a competitive market achieved a greater degree of economic efficiency than a non-competitive market when externalities occur.
A)Coase argued that government intervention is necessary to achieve economic efficiency in markets that are affected by externalities.
B)Coase proved that economic efficiency cannot be achieved in a market that is affected by positive or negative externalities.
C)Coase argued that under some circumstances private solutions to the problems of externalities will occur.
D)Coase proved that a competitive market achieved a greater degree of economic efficiency than a non-competitive market when externalities occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following statements describes the Coase Theorem?
A)It is not possible to completely eliminate an externality.
B)Under some circumstances private solutions to the problems that result from externalities can be found.
C)Completely eliminating an externality is not economically efficient.
D)A negative externality occurs when the marginal social cost of production exceeds the social benefit.
A)It is not possible to completely eliminate an externality.
B)Under some circumstances private solutions to the problems that result from externalities can be found.
C)Completely eliminating an externality is not economically efficient.
D)A negative externality occurs when the marginal social cost of production exceeds the social benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The costs in time and other resources that parties incur in the process of facilitating an exchange of goods and services are called
A)enforcement costs.
B)implicit costs.
C)explicit costs.
D)transaction costs.
A)enforcement costs.
B)implicit costs.
C)explicit costs.
D)transaction costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the marginal benefit of reducing emissions of some air pollutant is less than the marginal cost,
A)further reductions will make society better off.
B)further reduction will make society worse off.
C)pollution taxes should be imposed on producers to pay for further reductions.
D)economic efficiency will be increased if further reductions are made.
A)further reductions will make society better off.
B)further reduction will make society worse off.
C)pollution taxes should be imposed on producers to pay for further reductions.
D)economic efficiency will be increased if further reductions are made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What are transactions costs? Why do transactions costs create difficulties in finding a private solution to the problem of pollution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
State and local governments subsidize college students with grants and low-interest loans.The loans and subsidies are examples of
A)positive externalities.
B)Coase subsidies.
C)Pigovian subsidies.
D)emission allowances.
A)positive externalities.
B)Coase subsidies.
C)Pigovian subsidies.
D)emission allowances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure 5-4  Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.
Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.
Refer to Figure 5-4.Suppose the emissions reduction target is currently established at 8 million tons.What is the area that represents the cost of eliminating an additional 1 million tons?
A)A
B)B + C
C)A + B
D)A + B + C
 Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.
Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.Refer to Figure 5-4.Suppose the emissions reduction target is currently established at 8 million tons.What is the area that represents the cost of eliminating an additional 1 million tons?
A)A
B)B + C
C)A + B
D)A + B + C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The first economist to systematically analyze market failure was
A)Adam Smith.
B)Ronald Coase.
C)A.C.Pigou.
D)J.E.Meade.
A)Adam Smith.
B)Ronald Coase.
C)A.C.Pigou.
D)J.E.Meade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Congressman Murphy made the following proposal: "We should establish policies that completely eliminate air pollution.This is the only way to ensure that none of our citizens suffers the negative effects of air pollution." If Congressman Murphy's proposal was adopted and all forms of air pollution were eliminated,which of the following would be true?
A)The total cost of pollution reductions would equal the total benefit to society.
B)Economic efficiency would be maximized
C)The total benefit to society from reductions in air pollution would be maximized.
D)The marginal cost from pollution reductions would exceed the marginal benefit.
A)The total cost of pollution reductions would equal the total benefit to society.
B)Economic efficiency would be maximized
C)The total benefit to society from reductions in air pollution would be maximized.
D)The marginal cost from pollution reductions would exceed the marginal benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Figure 5-5 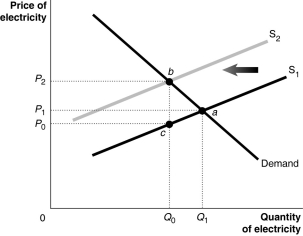 Coal burning utilities release sulfur dioxide and nitric acid which react with water to produce acid rain.Acid rain damages trees and crops and kills fish.Because the utilities do not bear the cost of the acid rain they overproduce the quantity of electricity.This is illustrated in Figure 5-5.
Coal burning utilities release sulfur dioxide and nitric acid which react with water to produce acid rain.Acid rain damages trees and crops and kills fish.Because the utilities do not bear the cost of the acid rain they overproduce the quantity of electricity.This is illustrated in Figure 5-5.
Refer to Figure 5-5.S1 represents the supply curve that reflects the private cost of production and S2 represents the supply curve that reflects the social cost of production.One way to internalize the external cost generated by utilities is to impose a Pigovian tax on the production of electricity.What is the size of the Pigovian tax that will internalize the cost of the externality?
A)P0
B)P2-P0
C)P1-P0
D)P2-P1
 Coal burning utilities release sulfur dioxide and nitric acid which react with water to produce acid rain.Acid rain damages trees and crops and kills fish.Because the utilities do not bear the cost of the acid rain they overproduce the quantity of electricity.This is illustrated in Figure 5-5.
Coal burning utilities release sulfur dioxide and nitric acid which react with water to produce acid rain.Acid rain damages trees and crops and kills fish.Because the utilities do not bear the cost of the acid rain they overproduce the quantity of electricity.This is illustrated in Figure 5-5.Refer to Figure 5-5.S1 represents the supply curve that reflects the private cost of production and S2 represents the supply curve that reflects the social cost of production.One way to internalize the external cost generated by utilities is to impose a Pigovian tax on the production of electricity.What is the size of the Pigovian tax that will internalize the cost of the externality?
A)P0
B)P2-P0
C)P1-P0
D)P2-P1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The efficient level of paper production will occur where the
A)marginal private benefit from consuming paper is equal to the marginal social cost of production.
B)marginal social benefit from consuming paper is equal to the marginal social cost of production.
C)the economically efficient level of the output of paper is equal to the economically efficient level of inputs.
D)production of paper no longer produces negative externalities.
A)marginal private benefit from consuming paper is equal to the marginal social cost of production.
B)marginal social benefit from consuming paper is equal to the marginal social cost of production.
C)the economically efficient level of the output of paper is equal to the economically efficient level of inputs.
D)production of paper no longer produces negative externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The Coase Theorem asserts that government intervention is a prerequisite for addressing externality problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If transactions costs are low,private bargaining will always result in an efficient solution to the problem of externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Figure 5-4  Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.
Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.
Refer to Figure 5-4.Suppose the emissions reduction target is currently established at 8 million tons.Should society undertake to reduce an additional 1 million tons so that the total reduction is 9 million tons?
A)No,because there is a net cost represented by the area B + C.
B)Yes,because the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal costs.
C)Yes,because toxic fumes are dangerous and must be eliminated at any cost.
D)No,because the firms will pass the additional cost on to consumers.
 Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.
Consider a chemical plant that discharges toxic fumes over a nearby community.To reduce the emissions of toxic fumes the firm can install pollution abatement devices.Figure 5-4 shows the marginal benefit and the marginal cost from reducing the toxic fumes emissions.Refer to Figure 5-4.Suppose the emissions reduction target is currently established at 8 million tons.Should society undertake to reduce an additional 1 million tons so that the total reduction is 9 million tons?
A)No,because there is a net cost represented by the area B + C.
B)Yes,because the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal costs.
C)Yes,because toxic fumes are dangerous and must be eliminated at any cost.
D)No,because the firms will pass the additional cost on to consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Assume that production from an electric utility caused acid rain.If the government imposed a tax on the utility equal to the cost of the acid rain,the government's action would
A)externalize the externality.
B)result in a marginal social benefit greater than the marginal cost of the electricity.
C)be an example of supply side economic policy.
D)internalize the externality.
A)externalize the externality.
B)result in a marginal social benefit greater than the marginal cost of the electricity.
C)be an example of supply side economic policy.
D)internalize the externality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Policies that mandate the installation of specific pollution control devices are called
A)command and control policies.
B)benefit policies.
C)welfare policies.
D)incentive policies.
A)command and control policies.
B)benefit policies.
C)welfare policies.
D)incentive policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Ronald Coase is famous for the Coase Theorem,which is based on the premise that there is an economically efficient level of pollution reduction.Many economists believe that the tradable emissions allowance program that has been used to deal with the problem of acid rain has been successful in reducing emissions of sulfur dioxide in an economically efficient manner.Why isn't this program an example of the Coase Theorem?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Economic incentives are designed to make individual self-interest coincide with social interest.According to economists,which of the following methods of pollution control best uses economic incentives to reduce pollution?
A)Rewarding environmental groups for monitoring the activities of private firms that produce products which generate pollution.
B)Imposing quantitative limits on the amount of pollution and imposing a penalty for non-compliance with these limits.
C)Requiring the installation of specific pollution control devices.
D)Instituting a system of tradable emissions allowances.
A)Rewarding environmental groups for monitoring the activities of private firms that produce products which generate pollution.
B)Imposing quantitative limits on the amount of pollution and imposing a penalty for non-compliance with these limits.
C)Requiring the installation of specific pollution control devices.
D)Instituting a system of tradable emissions allowances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following describes a positive externality?
A)John Henry paints the outside of his house in order to increase its market value just before he puts the house up for sale.
B)People who do not attend college still benefit from others who receive a college education.
C)The government imposes a tax on cigarettes in order to discourage smoking among teenagers.
D)Mary volunteers to drive her neighbor's children to soccer practice.
A)John Henry paints the outside of his house in order to increase its market value just before he puts the house up for sale.
B)People who do not attend college still benefit from others who receive a college education.
C)The government imposes a tax on cigarettes in order to discourage smoking among teenagers.
D)Mary volunteers to drive her neighbor's children to soccer practice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
State the Coase theorem.What are some of the limitations of the Coase theorem in practice?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose a negative externality exists in a market.If transactions costs are low and parties are willing to bargain then,according to the Coase theorem,
A)an efficient solution can be reached only if property rights are assigned to the victims of the pollution.
B)an efficient solution can be reached only if property rights are assigned to the polluters.
C)an efficient solution can be reached regardless of the initial assignment of property rights.
D)government intervention is critical to reach an efficient solution.
A)an efficient solution can be reached only if property rights are assigned to the victims of the pollution.
B)an efficient solution can be reached only if property rights are assigned to the polluters.
C)an efficient solution can be reached regardless of the initial assignment of property rights.
D)government intervention is critical to reach an efficient solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is an example of a Pigovian tax?
A)payments by utilities to obtain tradable emissions allowances
B)a payroll tax
C)payments for licenses to pollute
D)a tax imposed on a utility that internalizes the cost of externalities caused by the utility
A)payments by utilities to obtain tradable emissions allowances
B)a payroll tax
C)payments for licenses to pollute
D)a tax imposed on a utility that internalizes the cost of externalities caused by the utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 5-6 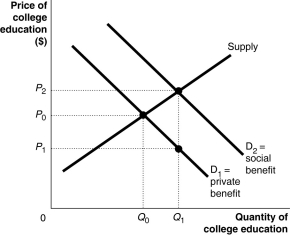 College education benefits society by producing a more employable workforce,reducing crime and creating a better informed citizenry.Thus,the social benefits of college education exceed the private benefits for any level of college education.This is illustrated in Figure 5-6.
College education benefits society by producing a more employable workforce,reducing crime and creating a better informed citizenry.Thus,the social benefits of college education exceed the private benefits for any level of college education.This is illustrated in Figure 5-6.
Refer to Figure 5-6.One way to obtain the economically efficient amount of college education is for governments to subsidize college education.What is the size of the per-student Pigovian subsidy that the government must provide to internalize the external benefits? (Note that the subsidy can be granted to the education institutions or to the students directly or indirectly; for example,through low-interest student loans.)
A)P2-P0
B)P2-P1
C)P0-P1
D)P1
 College education benefits society by producing a more employable workforce,reducing crime and creating a better informed citizenry.Thus,the social benefits of college education exceed the private benefits for any level of college education.This is illustrated in Figure 5-6.
College education benefits society by producing a more employable workforce,reducing crime and creating a better informed citizenry.Thus,the social benefits of college education exceed the private benefits for any level of college education.This is illustrated in Figure 5-6.Refer to Figure 5-6.One way to obtain the economically efficient amount of college education is for governments to subsidize college education.What is the size of the per-student Pigovian subsidy that the government must provide to internalize the external benefits? (Note that the subsidy can be granted to the education institutions or to the students directly or indirectly; for example,through low-interest student loans.)
A)P2-P0
B)P2-P1
C)P0-P1
D)P1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Assume that production from an electric utility caused acid rain and that the government imposed a tax on the utility equal to the cost of the acid rain.This is an example of
A)a transaction cost.
B)a Pigovian tax.
C)a Pigovian subsidy.
D)the Coase Theorem.
A)a transaction cost.
B)a Pigovian tax.
C)a Pigovian subsidy.
D)the Coase Theorem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 133 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



