Deck 2: International Monetary Arrangements
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: International Monetary Arrangements
1
Special Drawing Rights are issued by
A) The International Monetary Fund
B) The United Nations
C) The World Bank
D) The Central banks of England, Japan, and the United States
A) The International Monetary Fund
B) The United Nations
C) The World Bank
D) The Central banks of England, Japan, and the United States
The International Monetary Fund
2
Which of the following exchange rate systems is the least flexible?
A) Free floating
B) Managed floating.
C) Currency board
D) Fixed peg arrangement
A) Free floating
B) Managed floating.
C) Currency board
D) Fixed peg arrangement
Currency board
3
Use the graph below to answer questions 9-11.
Figure 2.3: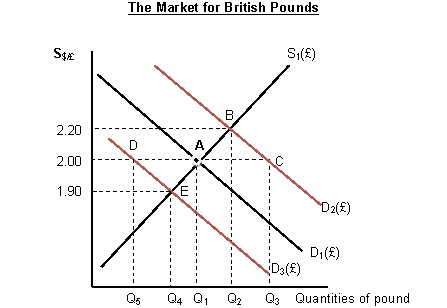
Refer to Figure 2.3.Suppose that the spot exchange rate of British pound is $2.00 per pound.Suppose that the U.S.decreases its imports from the U.K.Under flexible exchange rate system,the Bank of England will:
A) let the British pound appreciates
B) let the British pound depreciates
C) sell pounds and buy dollars in foreign exchange market.
D) sell dollars and buy pounds in foreign exchange market.
Figure 2.3:

Refer to Figure 2.3.Suppose that the spot exchange rate of British pound is $2.00 per pound.Suppose that the U.S.decreases its imports from the U.K.Under flexible exchange rate system,the Bank of England will:
A) let the British pound appreciates
B) let the British pound depreciates
C) sell pounds and buy dollars in foreign exchange market.
D) sell dollars and buy pounds in foreign exchange market.
let the British pound depreciates
4
The gold standard was an example of:
A) An optimum currency area
B) A commodity money standard
C) A standard currency board
D) All of the above
A) An optimum currency area
B) A commodity money standard
C) A standard currency board
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When the United States suspended the convertibility of dollars into gold in 1971,this lead to:
A) The collapse of the Bretton Woods system
B) Creation of the regional currency boards
C) Creation of the International Monetary Fund
D) All of the above
A) The collapse of the Bretton Woods system
B) Creation of the regional currency boards
C) Creation of the International Monetary Fund
D) All of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Small nations whose trade and financial relationships are mainly with a single partner tend to utilize:
A) pegged exchange rates
B) free floating exchange rates
C) managed floating exchange rates
D) target bands - pegged exchange rates
A) pegged exchange rates
B) free floating exchange rates
C) managed floating exchange rates
D) target bands - pegged exchange rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements is correct about the SDR?
A) The SDR is a fixed exchange rate system created by the IMF.
B) The SDR was designed to replace the U.S. dollar.
C) The SDR is the most popular trading currency among traders.
D) The SDR is used as international reserve assets between central banks.
A) The SDR is a fixed exchange rate system created by the IMF.
B) The SDR was designed to replace the U.S. dollar.
C) The SDR is the most popular trading currency among traders.
D) The SDR is used as international reserve assets between central banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
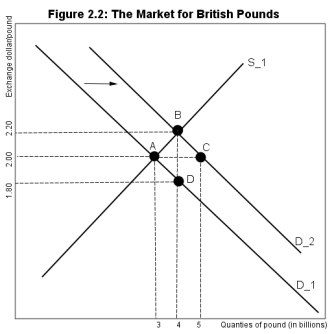
Referring to Figure 2.2,an increase in the demand for British goods by the U.S.importers has led to pressure on the pound to appreciate against the dollar.If the Bank of England wants to maintain a peg of $2.0/pound,what currency should it sell and how much?
A) Pounds, 1 billion
B) Pounds, 2 billion
C) Dollars, 1 billion
D) Dollars, 2 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following could be considered a cause of the collapse of the Bretton Woods system?
A) The existence of Japanese budget deficits offset currency reserves as the yen become increasingly overvalued.
B) The United States gold stock became increasingly too small to meet foreign dollar liabilities.
C) Countries in Europe devalued currencies to increase export competitiveness.
D) In order to meet reserve requirements imposed by the IMF, France and Germany mandated private holders of gold to purchase U.S. dollars destabilizing the U.S. dollar to gold peg.
A) The existence of Japanese budget deficits offset currency reserves as the yen become increasingly overvalued.
B) The United States gold stock became increasingly too small to meet foreign dollar liabilities.
C) Countries in Europe devalued currencies to increase export competitiveness.
D) In order to meet reserve requirements imposed by the IMF, France and Germany mandated private holders of gold to purchase U.S. dollars destabilizing the U.S. dollar to gold peg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
__________ occurs when a country abolishes its own currency and adopts the currency of some other country.
A) Demonetization
B) Dollarization
C) A currency swap
D) A currency board
A) Demonetization
B) Dollarization
C) A currency swap
D) A currency board

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose that under a gold standard,that the price of gold in the United States is $450 per ounce and the price of gold in the United Kingdom is 200£ per ounce.The exchange rate is thus:
A) 2.25£ per dollar
B) $0.45 per pound.
C) $2.25 per pound.
D) 1£ per dollar.
A) 2.25£ per dollar
B) $0.45 per pound.
C) $2.25 per pound.
D) 1£ per dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider the market for Chinese currency yuan.Suppose that the initial equilibrium exchange rate was $0.125 per one yuan.Then assume that American consumers like Chinese products more than before.If China's central bank wants to peg the exchange rate at its initial level $0.125 per yuan,the central bank will have to
A) buy yuan and sell dollar.
B) sell yuan and buy dollar.
C) buy yuan and buy dollar.
D) sell yuan and sell dollar.
A) buy yuan and sell dollar.
B) sell yuan and buy dollar.
C) buy yuan and buy dollar.
D) sell yuan and sell dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the graph below to answer questions 9-11.
Figure 2.3:
Refer to Figure 2.3.Suppose that the U.K agreed to peg its currency against the U.S.dollar at $2.00 per pound during the Bretton Woods system.Assume that the U.S.decreases its imports from the U.K.As a result,the Bank of England would have to:
A) let the British pound appreciates
B) let the British pound depreciates
C) sell pounds and buy dollars in foreign exchange market.
D) sell dollars and buy pounds in foreign exchange market.
Figure 2.3:

Refer to Figure 2.3.Suppose that the U.K agreed to peg its currency against the U.S.dollar at $2.00 per pound during the Bretton Woods system.Assume that the U.S.decreases its imports from the U.K.As a result,the Bank of England would have to:
A) let the British pound appreciates
B) let the British pound depreciates
C) sell pounds and buy dollars in foreign exchange market.
D) sell dollars and buy pounds in foreign exchange market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following economies has adopted a "currency board" exchange rate system?
A) Malaysia
B) South Korea
C) China
D) Hong Kong
A) Malaysia
B) South Korea
C) China
D) Hong Kong

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15

Referring to Figure 2.2,an increase in the demand for British goods by the U.S.importers has led to pressure on the pound to appreciate against the dollar.If the Bank of England wishes to intervene to maintain a peg of $2.0/pound,what distance represents that intervention?
A) A to B
B) B to A
C) A to C
D) B to C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Use the graph below to answer questions 9-11.
Figure 2.3:
Refer to Figure 2.3.Suppose that the U.K agreed to peg its currency against the U.S.dollar at $2.00 per pound during the Bretton Woods system.Assume that the U.S.increases its imports from the U.K.As a result,the Bank of England would have to:
A) let the British pound appreciates
B) let the British pound depreciates
C) sell pounds and buy dollars in foreign exchange market.
D) sell dollars and buy pounds in foreign exchange market.
Figure 2.3:

Refer to Figure 2.3.Suppose that the U.K agreed to peg its currency against the U.S.dollar at $2.00 per pound during the Bretton Woods system.Assume that the U.S.increases its imports from the U.K.As a result,the Bank of England would have to:
A) let the British pound appreciates
B) let the British pound depreciates
C) sell pounds and buy dollars in foreign exchange market.
D) sell dollars and buy pounds in foreign exchange market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statement is correct?
A) Since 1974, the major industrial countries have operated under a system of fixed exchange rates based on the gold standard.
B) Many developing nations with low inflation rates have pegged their currencies to the U.S. dollar as a way of allowing modest increases in domestic inflation rates.
C) Large industrial nations with diversified economies and small trade sectors have generally pegged their currencies to one of the world's key currencies.
D) Today, fixed exchange rates are used primarily by small, developing countries that tie their currencies to a key currency such as the U.S. dollar.
A) Since 1974, the major industrial countries have operated under a system of fixed exchange rates based on the gold standard.
B) Many developing nations with low inflation rates have pegged their currencies to the U.S. dollar as a way of allowing modest increases in domestic inflation rates.
C) Large industrial nations with diversified economies and small trade sectors have generally pegged their currencies to one of the world's key currencies.
D) Today, fixed exchange rates are used primarily by small, developing countries that tie their currencies to a key currency such as the U.S. dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The Bretton Woods agreement required that each country,other than the U.S.,fix the value of its currency in terms of an:
A) Ounce of gold
B) Common currency
C) Commodity basket
D) Anchor currency
A) Ounce of gold
B) Common currency
C) Commodity basket
D) Anchor currency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If Mexico fully dollarizes its economy,it agrees to:
A) print pesos only to finance deficits of its national government.
B) use the U.S. dollar alongside its peso to finance transactions.
C) have the U.S. Treasury be in charge of its tax collections.
D) replace pesos with U.S. dollars in its economy.
A) print pesos only to finance deficits of its national government.
B) use the U.S. dollar alongside its peso to finance transactions.
C) have the U.S. Treasury be in charge of its tax collections.
D) replace pesos with U.S. dollars in its economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The Bretton Woods Agreement of 1944 established a monetary system based on:
A) Special Drawing Rights and managed floating exchange rates
B) Special Drawing Rights and adjustable pegged exchange rates
C) gold and managed floating exchange rates
D) gold and adjustable pegged exchange rates
A) Special Drawing Rights and managed floating exchange rates
B) Special Drawing Rights and adjustable pegged exchange rates
C) gold and managed floating exchange rates
D) gold and adjustable pegged exchange rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The U.S.dollar is called a ________ because it is often used as a medium of exchange in international markets.
A) Transit currency
B) Main currency
C) Reserve currency
D) Target currency
A) Transit currency
B) Main currency
C) Reserve currency
D) Target currency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Countries use reserve currencies as an international unit of account,a medium of exchange,and a store of value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The gold standard eliminates the possibility of a balance of payments disequilibrium by:
A) Changing the peg value of the currency to an ounce of gold.
B) Inflating prices in countries with net inflows of gold and deflating prices in countries with net outflows.
C) Shifting trade to the British pound.
D) Encouraging the discovery of gold deposits.
A) Changing the peg value of the currency to an ounce of gold.
B) Inflating prices in countries with net inflows of gold and deflating prices in countries with net outflows.
C) Shifting trade to the British pound.
D) Encouraging the discovery of gold deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The geographic area that would maximize economic benefits by keeping the exchange rate fixed within the area is a an:
A) Trade union
B) Currency board
C) Trade bloc
D) Optimal currency area
A) Trade union
B) Currency board
C) Trade bloc
D) Optimal currency area

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following exchange rate systems is best suited for a country with trade concentrated with one major country?
A) Fixed peg
B) Currency standard
C) Free floating
D) Managed floating
A) Fixed peg
B) Currency standard
C) Free floating
D) Managed floating

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Countries with floating exchange rates tend to have large,closed economies and trade largely with a single foreign country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Countries with a floating exchange rate tend have what features?
I.Trade concentrated with a single country
II.Similar inflation rates with trading partners
III.Large,closed economies
IV.Trade diversified across many countries
A) I only
B) I and II
C) III and IV
D) II, III, and IV
I.Trade concentrated with a single country
II.Similar inflation rates with trading partners
III.Large,closed economies
IV.Trade diversified across many countries
A) I only
B) I and II
C) III and IV
D) II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Perfect mobility of factors of production is a requirement for
A) Spatially concentrated trade zones
B) Optimal currency areas
C) Commodity money standards
D) Free floating exchange rates
A) Spatially concentrated trade zones
B) Optimal currency areas
C) Commodity money standards
D) Free floating exchange rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
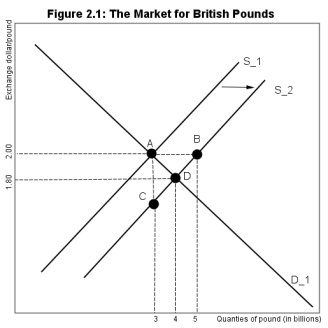
Referring to Figure 2.1,the pound per dollar exchange rate starts at 2.00.Assume that an increase in the taste for U.S.imports by U.K.residents leads to a shift in the supply of pounds.If the Bank of England wishes to intervene by buying pounds to restore the peg of $2.0/pound,what distance represents that intervention?
A) A to B
B) B to A
C) A to D
D) D to B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Following the breakdown of the Bretton Woods system,the major currency countries:
A) Moved to the gold standard
B) Temporarily pegged currencies to the Swiss Franc
C) Moved to a free market floating arrangement
D) Introduced silver as an alternative backing to the dollar
A) Moved to the gold standard
B) Temporarily pegged currencies to the Swiss Franc
C) Moved to a free market floating arrangement
D) Introduced silver as an alternative backing to the dollar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What exchange rate is maintained with a central rate that is frequently adjusted?
A) Fixed Peg
B) Currency board
C) Managed floating
D) Crawling bands
A) Fixed Peg
B) Currency board
C) Managed floating
D) Crawling bands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The European Monetary System was established in 1979 to form a common currency for all member countries to be managed by a European Central Bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Arrange the following currency exchange systems from the one with least independent monetary policy to the most independent monetary policy.
I.Horizontal bands
II.Currency board
III.Fixed peg
IV.Free floating
A) Free floating, horizontal bands, fixed peg, currency board
B) Currency board, horizontal bands, free floating, fixed peg
C) Currency board, fixed peg, horizontal bands, free floating
D) Horizontal bands, currency board, free floating, fixed peg
I.Horizontal bands
II.Currency board
III.Fixed peg
IV.Free floating
A) Free floating, horizontal bands, fixed peg, currency board
B) Currency board, horizontal bands, free floating, fixed peg
C) Currency board, fixed peg, horizontal bands, free floating
D) Horizontal bands, currency board, free floating, fixed peg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The International Monetary Fund was created at the beginning of the:
A) Bretton Woods system
B) Gold standard
C) Interwar period
D) Smithsonian agreement
A) Bretton Woods system
B) Gold standard
C) Interwar period
D) Smithsonian agreement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
During the gold standard,national money supplies were constrained by:
A) International treaties
B) The growth of trade
C) Commodity indexes
D) The growth of the stock of gold
A) International treaties
B) The growth of trade
C) Commodity indexes
D) The growth of the stock of gold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

Referring to Figure 2.1,the pound per dollar exchange rate starts at 2.00.Assume that an increase in the taste for U.S.imports by U.K.residents leads to a shift in the supply of pounds.How many pounds will the Bank of England need to purchase to restore the exchange of 2.00?
A) 0.2 billion
B) 1 billion
C) 2 billion
D) 4 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Seigniorage is the system where the dominant money producer limits the supply of money to leverage foreign currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following currencies do not exist in physical form?
A) U.S. Dollar
B) Swiss Franc
C) Euro
D) Special Drawing Rights
A) U.S. Dollar
B) Swiss Franc
C) Euro
D) Special Drawing Rights

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Destabilizing speculation is the process where
A) In a free floating exchange system, speculators cause wide fluctuations to the exchange rate.
B) In a fixed peg exchange system, speculators hold foreign reserves too long and destabilize the peg.
C) In a free floating exchange system, the International Monetary Fund is forced to issue Special Drawing Rights.
D) In a fixed peg exchange system, speculators sell all holdings of Special Drawing Rights.
A) In a free floating exchange system, speculators cause wide fluctuations to the exchange rate.
B) In a fixed peg exchange system, speculators hold foreign reserves too long and destabilize the peg.
C) In a free floating exchange system, the International Monetary Fund is forced to issue Special Drawing Rights.
D) In a fixed peg exchange system, speculators sell all holdings of Special Drawing Rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The International Monetary Fund was created to assist countries with balance of payment difficulties and monitor an adjustable peg system with the U.S.dollar as the anchor currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is seignorage?
A) The reward for holding foreign currency reserves.
B) The difference between printing money and the return to the assets it acquires.
C) The special interest rates associated with Special Drawing Rights.
D) The process of adopting a currency peg.
A) The reward for holding foreign currency reserves.
B) The difference between printing money and the return to the assets it acquires.
C) The special interest rates associated with Special Drawing Rights.
D) The process of adopting a currency peg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An example of a fixed exchange rate was the gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Consider the following scenario.The Swiss franc is operating under a managed float exchange system.Under this system,what actions can the Swiss central bank take to influence the current exchange?
A) Purchase or sell foreign currencies to bring the currency in line with its desired value
B) Announce a new target exchange rates
C) Commit to a new fixed rate against the current basket of foreign currencies
D) Set guidelines for when inflationary pressures will force action on money supply changes
A) Purchase or sell foreign currencies to bring the currency in line with its desired value
B) Announce a new target exchange rates
C) Commit to a new fixed rate against the current basket of foreign currencies
D) Set guidelines for when inflationary pressures will force action on money supply changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The introduction of the Bretton Woods system meant that the Federal Reserve had to take an active role in managing currency exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Why was the European Monetary System established?
A) To establish a common currency the euro.
B) To peg all member currencies to the Swiss Franc.
C) To maintain small exchange rate fluctuation among member countries.
D) To unite the coal and steel workers in France and Germany
A) To establish a common currency the euro.
B) To peg all member currencies to the Swiss Franc.
C) To maintain small exchange rate fluctuation among member countries.
D) To unite the coal and steel workers in France and Germany

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A managed floating exchange rate is a market determined exchange system as long as rates stay between target zones as mandated by legislative commitments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A pegged exchange rate is:
I.Fixed to a currency or basket of currencies
II.Responds to indicators such as inflation differentials
III.May require intervention to maintain the target pegged rate
A) I only
B) III only
C) I and III
D) I, II, and III
I.Fixed to a currency or basket of currencies
II.Responds to indicators such as inflation differentials
III.May require intervention to maintain the target pegged rate
A) I only
B) III only
C) I and III
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An example of an optimal currency area would be
A) United States
B) Southeast Asia
C) Latin America
D) Both A and C
A) United States
B) Southeast Asia
C) Latin America
D) Both A and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In general,the smaller the country is,the more likely it is to peg its exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Consider the following scenario.The Swiss franc is fixed to the U.S.dollar.Market pressures lead to a move away from the peg.Which of the following can be used to restore the previous peg?
A) The Swiss central bank can use a commodity such as gold to back the previous peg.
B) The Swiss government can lower domestic prices to offset import pressures.
C) Allow the exchange by the market and in the long run the peg will be restored.
D) The Swiss central bank can purchase or sell U.S. dollars.
A) The Swiss central bank can use a commodity such as gold to back the previous peg.
B) The Swiss government can lower domestic prices to offset import pressures.
C) Allow the exchange by the market and in the long run the peg will be restored.
D) The Swiss central bank can purchase or sell U.S. dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What exchange rate system allows for periodic intervention without fixing to any other foreign currency?
A) Free floating
B) Horizontal band
C) Crawling peg
D) Dollarization
A) Free floating
B) Horizontal band
C) Crawling peg
D) Dollarization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
"Dollarization" and currency boards are examples of exchange rate systems that provide relatively large independent monetary policy as compared to floating exchange rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 52 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



