Deck 13: Markets and Government
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/113
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Markets and Government
1
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

When all the costs and benefits of a transaction are borne by the participants of that transaction, _____.
A)the market outcome will be inefficient
B)the private costs and social costs are identical
C)negative externalities exist
D)positive externalities exist
E)the free rider problem arises

When all the costs and benefits of a transaction are borne by the participants of that transaction, _____.
A)the market outcome will be inefficient
B)the private costs and social costs are identical
C)negative externalities exist
D)positive externalities exist
E)the free rider problem arises
the private costs and social costs are identical
2
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

When the benefits of an activity are received by those who are not directly involved in it, _____.
A)a negative externality exists
B)the government is producing a free good
C)resources are being used in their highest-valued activity
D)the government has to compensate for the loss in social welfare
E)a positive externality exists

When the benefits of an activity are received by those who are not directly involved in it, _____.
A)a negative externality exists
B)the government is producing a free good
C)resources are being used in their highest-valued activity
D)the government has to compensate for the loss in social welfare
E)a positive externality exists
a positive externality exists
3
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

In the case of public goods, _____.
A)the free rider problem does not arise
B)one person's consumption of the good reduces the consumption of the good by others
C)individuals can be easily excluded from consuming the good once it is provided
D)the quantity produced by a private market would be too large from society's viewpoint
E)the principle of mutual excludability and principle of rivalry do not apply

In the case of public goods, _____.
A)the free rider problem does not arise
B)one person's consumption of the good reduces the consumption of the good by others
C)individuals can be easily excluded from consuming the good once it is provided
D)the quantity produced by a private market would be too large from society's viewpoint
E)the principle of mutual excludability and principle of rivalry do not apply
the principle of mutual excludability and principle of rivalry do not apply
4
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

Why do externalities arise?
A)The costs of production are not borne by the producer.
B)An economic activity imposes a burden on those who are not directly involved in it.
C)The consumption of a public good is nonexcludable.
D)The government produces goods and services which are consumed by only a particular group of people.
E)Goods of mass consumption are not produced as they do not yield profit for the producers.

Why do externalities arise?
A)The costs of production are not borne by the producer.
B)An economic activity imposes a burden on those who are not directly involved in it.
C)The consumption of a public good is nonexcludable.
D)The government produces goods and services which are consumed by only a particular group of people.
E)Goods of mass consumption are not produced as they do not yield profit for the producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

Why do market failures arise in case of public goods?
A)The quantity produced is much more than is actually required by the people.
B)The quality of these goods is not good enough.
C)The quantity produced is too less from the society's point of view.
D)The government wastes a lot of resources for producing a public good.
E)The users of such goods are required to pay a high price for these goods.

Why do market failures arise in case of public goods?
A)The quantity produced is much more than is actually required by the people.
B)The quality of these goods is not good enough.
C)The quantity produced is too less from the society's point of view.
D)The government wastes a lot of resources for producing a public good.
E)The users of such goods are required to pay a high price for these goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

When a negative externality exists in the case of a particular good, and if that is not reflected in the price, _____.
A)too little of that good is produced and consumed
B)too much of that good is produced and consumed
C)all resources are taken away from the production of that good
D)the government completely prohibits the consumption of that good
E)all resources are allocated to the production of that good

When a negative externality exists in the case of a particular good, and if that is not reflected in the price, _____.
A)too little of that good is produced and consumed
B)too much of that good is produced and consumed
C)all resources are taken away from the production of that good
D)the government completely prohibits the consumption of that good
E)all resources are allocated to the production of that good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

The owner of a good has the right to decide how that good is used and to restrict others from using that good. This idea is known as:
A)the principle of mutual excludability.
B)the principle of comparative advantage.
C)the principle of public ownership.
D)the principle of negative externalities.
E)the law of demand.

The owner of a good has the right to decide how that good is used and to restrict others from using that good. This idea is known as:
A)the principle of mutual excludability.
B)the principle of comparative advantage.
C)the principle of public ownership.
D)the principle of negative externalities.
E)the law of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

The consumption of a club good like cable television:
A)is nonexcludable and nonrivalrous.
B)is excludable and rivalrous.
C)is excludable and nonrivalrous.
D)is nonexcludable and rivalrous.
E)gives rise to the free rider problem.

The consumption of a club good like cable television:
A)is nonexcludable and nonrivalrous.
B)is excludable and rivalrous.
C)is excludable and nonrivalrous.
D)is nonexcludable and rivalrous.
E)gives rise to the free rider problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

The social cost of a transaction is _____.
A)the sum of fixed and variable costs
B)the difference between the total cost and opportunity cost
C)the sum of private and external costs
D)the difference between the private and external costs
E)the sum of fixed costs and opportunity costs

The social cost of a transaction is _____.
A)the sum of fixed and variable costs
B)the difference between the total cost and opportunity cost
C)the sum of private and external costs
D)the difference between the private and external costs
E)the sum of fixed costs and opportunity costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

A market failure occurs when:
A)the market outcome is viewed as unfair by a majority of consumers.
B)a market fails to provide the good at a zero price.
C)quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied.
D)the market outcome is not the socially efficient outcome.
E)prices are determined by the interaction of the forces of demand and supply and not through central planning.

A market failure occurs when:
A)the market outcome is viewed as unfair by a majority of consumers.
B)a market fails to provide the good at a zero price.
C)quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied.
D)the market outcome is not the socially efficient outcome.
E)prices are determined by the interaction of the forces of demand and supply and not through central planning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

Which of the following is an example of a positive externality?
A)Smoking a cigarette
B)Driving a less fuel efficient vehicle
C)Setting up a chemicals factory in a residential area
D)Overuse of chemical fertilizers
E)Beekeepers keeping bees for honey

Which of the following is an example of a positive externality?
A)Smoking a cigarette
B)Driving a less fuel efficient vehicle
C)Setting up a chemicals factory in a residential area
D)Overuse of chemical fertilizers
E)Beekeepers keeping bees for honey

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

For which of the following goods will the free rider problem arise?
A)Private golf course
B)Cable television
C)Privately owned apartment
D)National defense
E)Movie theatres

For which of the following goods will the free rider problem arise?
A)Private golf course
B)Cable television
C)Privately owned apartment
D)National defense
E)Movie theatres

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

A good that is both excludable and rivalrous is a(n):
A)public good.
B)club good.
C)private good.
D)inferior good.
E)necessary good.

A good that is both excludable and rivalrous is a(n):
A)public good.
B)club good.
C)private good.
D)inferior good.
E)necessary good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

Which of the following statements is true?
A)In the case of positive externalities, a private market will produce too little of a good compared to the socially efficient level of output.
B)In the case of positive externalities, a private market will produce too much of a good compared to the socially efficient level of output.
C)Negative externalities occur when benefits accrue to individuals not directly involved in a transaction.
D)Positive externalities occur when costs are imposed on individuals not directly involved in a transaction.
E)In the case of negative externalities, a private market will produce too little of a good compared to the socially efficient level of output.

Which of the following statements is true?
A)In the case of positive externalities, a private market will produce too little of a good compared to the socially efficient level of output.
B)In the case of positive externalities, a private market will produce too much of a good compared to the socially efficient level of output.
C)Negative externalities occur when benefits accrue to individuals not directly involved in a transaction.
D)Positive externalities occur when costs are imposed on individuals not directly involved in a transaction.
E)In the case of negative externalities, a private market will produce too little of a good compared to the socially efficient level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

The good for which neither the principle of mutual excludability nor the principle of rivalry applies is referred to as a:
A)public good.
B)commons good.
C)club good.
D)normal good.
E)private good.

The good for which neither the principle of mutual excludability nor the principle of rivalry applies is referred to as a:
A)public good.
B)commons good.
C)club good.
D)normal good.
E)private good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

The free rider problem arises when a good is:
A)rivalrous.
B)excludable.
C)nonexcludable.
D)nonrivalrous.
E)an absolute necessity.

The free rider problem arises when a good is:
A)rivalrous.
B)excludable.
C)nonexcludable.
D)nonrivalrous.
E)an absolute necessity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

The free rider problem occurs because:
A)it is easy to exclude others from consuming a good.
B)consumption is rivalrous, so the consumption of a product by one individual diminishes the amount available for others.
C)exclusion is costly or impossible, so a consumer or producer can use a good without having to pay for it.
D)external costs are imposed on others not directly involved in the transaction.
E)individuals are not required to pay for those goods which do not yield any utility to them.

The free rider problem occurs because:
A)it is easy to exclude others from consuming a good.
B)consumption is rivalrous, so the consumption of a product by one individual diminishes the amount available for others.
C)exclusion is costly or impossible, so a consumer or producer can use a good without having to pay for it.
D)external costs are imposed on others not directly involved in the transaction.
E)individuals are not required to pay for those goods which do not yield any utility to them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

Higher the economic freedom in a country, _____.
A)lower is the standard of living of the people
B)higher is the life expectancy of the people
C)greater is the bureaucratic freedom and red-tapism
D)lower is the level of access to education due to lack of government schools
E)lower is the literacy rate

Higher the economic freedom in a country, _____.
A)lower is the standard of living of the people
B)higher is the life expectancy of the people
C)greater is the bureaucratic freedom and red-tapism
D)lower is the level of access to education due to lack of government schools
E)lower is the literacy rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

Which of the following activities will generate a negative externality?
A)A beekeeper keeping bees for honey
B)Inoculations for communicable diseases
C)Research and development activities of a firm
D)A chemical factory set up in a residential area
E)Improvement in education facilities

Which of the following activities will generate a negative externality?
A)A beekeeper keeping bees for honey
B)Inoculations for communicable diseases
C)Research and development activities of a firm
D)A chemical factory set up in a residential area
E)Improvement in education facilities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

When a private transaction imposes costs on others not directly involved in the transaction, _____.
A)a negative externality exists
B)a positive externality exists
C)the good involved in the transaction is a club good
D)the tragedy of commons problem arises
E)a free rider problem arises

When a private transaction imposes costs on others not directly involved in the transaction, _____.
A)a negative externality exists
B)a positive externality exists
C)the good involved in the transaction is a club good
D)the tragedy of commons problem arises
E)a free rider problem arises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Overfishing along the coastline of Helsking village led the government to impose a fee on the boats used for fishing. The fishermen were charged $50 on each boat they sent out for fishing. The following table shows the total pounds of fish caught per hour and the number of boats used for fishing.Table 13.2

One of the reasons that communism failed in the Soviet Union is that, under communism:
A)no one had property rights, so there was little incentive to use resources efficiently.
B)there were high rates of unemployment and homelessness accompanied by a high rate of inflation.
C)planners did not have all the information necessary to make efficient decisions.
D)there was a high degree of political freedom.
E)there was a high degree of economic freedom.

One of the reasons that communism failed in the Soviet Union is that, under communism:
A)no one had property rights, so there was little incentive to use resources efficiently.
B)there were high rates of unemployment and homelessness accompanied by a high rate of inflation.
C)planners did not have all the information necessary to make efficient decisions.
D)there was a high degree of political freedom.
E)there was a high degree of economic freedom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Overfishing along the coastline of Helsking village led the government to impose a fee on the boats used for fishing. The fishermen were charged $50 on each boat they sent out for fishing. The following table shows the total pounds of fish caught per hour and the number of boats used for fishing.Table 13.2

Refer to Table 13.2. Suppose fish sells for $1 per pound. If each fisherman decides whether or not to fish based on the average catch, what is the profit that each fisherman earns?
A)$500
B)$1,000
C)$3,000
D)$5,000
E)0

Refer to Table 13.2. Suppose fish sells for $1 per pound. If each fisherman decides whether or not to fish based on the average catch, what is the profit that each fisherman earns?
A)$500
B)$1,000
C)$3,000
D)$5,000
E)0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The following table shows the costs and benefit of producing a commodity.Table 13.1
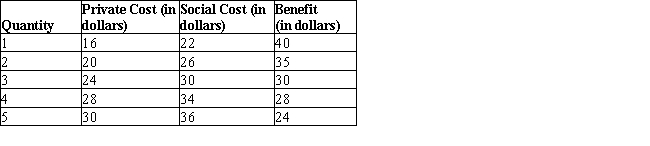
According to Table 13.1, at the social equilibrium:
A)4 units of output is produced.
B)5 units of output is produced.
C)2 units of output is produced.
D)3 units of output is produced.
E)1 unit of output is produced.

According to Table 13.1, at the social equilibrium:
A)4 units of output is produced.
B)5 units of output is produced.
C)2 units of output is produced.
D)3 units of output is produced.
E)1 unit of output is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The following table shows the costs and benefit of producing a commodity.Table 13.1

When the commons are converted into privately owned resources, _____.
A)utilization is increased, and benefits to the society decline
B)utilization is increased, and the benefits to the society also increase
C)utilization is decreased, and the benefits to the society also decrease
D)utilization remains unchanged, and the benefits to the society increase
E)utilization is decreased, and the benefits to the society increase

When the commons are converted into privately owned resources, _____.
A)utilization is increased, and benefits to the society decline
B)utilization is increased, and the benefits to the society also increase
C)utilization is decreased, and the benefits to the society also decrease
D)utilization remains unchanged, and the benefits to the society increase
E)utilization is decreased, and the benefits to the society increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

When there is a divergence between social costs and private costs in a market, _____.
A)the market will always provide an efficient allocation of resources
B)there will be too much or too little production and consumption in the market
C)there will be an acute shortage of goods and services in the market
D)there will be an excess supply of goods and services in the market
E)all resources are being used in their highest-valued activity

When there is a divergence between social costs and private costs in a market, _____.
A)the market will always provide an efficient allocation of resources
B)there will be too much or too little production and consumption in the market
C)there will be an acute shortage of goods and services in the market
D)there will be an excess supply of goods and services in the market
E)all resources are being used in their highest-valued activity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

Which of the following is true of an externality?
A)An externality enhances the efficiency of the market system.
B)An externality is not an economic problem because it is external to the market.
C)An externality is a cost borne by the people who are directly or indirectly involved in the production of a good or service.
D)An externality accrues to someone who had nothing to do with the production or consumption of a good or service.
E)An externality refers to some unexpected change in the equilibrium price or quantity of a product.

Which of the following is true of an externality?
A)An externality enhances the efficiency of the market system.
B)An externality is not an economic problem because it is external to the market.
C)An externality is a cost borne by the people who are directly or indirectly involved in the production of a good or service.
D)An externality accrues to someone who had nothing to do with the production or consumption of a good or service.
E)An externality refers to some unexpected change in the equilibrium price or quantity of a product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The following table shows the costs and benefit of producing a commodity.Table 13.1

According to Table 13.1, at the free market equilibrium:
A)1 unit of output is produced.
B)2 units of output is produced.
C)5 units of output is produced.
D)4 units of output is produced.
E)3 units of output is produced.

According to Table 13.1, at the free market equilibrium:
A)1 unit of output is produced.
B)2 units of output is produced.
C)5 units of output is produced.
D)4 units of output is produced.
E)3 units of output is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Overfishing along the coastline of Helsking village led the government to impose a fee on the boats used for fishing. The fishermen were charged $50 on each boat they sent out for fishing. The following table shows the total pounds of fish caught per hour and the number of boats used for fishing.Table 13.2

Refer to Table 13.2. Suppose fish sells for $1 per pound. What is the socially optimal number of boats that will maximize the profit earned by the fishermen?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Refer to Table 13.2. Suppose fish sells for $1 per pound. What is the socially optimal number of boats that will maximize the profit earned by the fishermen?
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

The existence of positive externalities in the consumption of a good implies that:
A)the social supply curve of the good lies to the right of the private supply curve.
B)the government will need to provide subsidies to ensure a socially efficient level of consumption.
C)the socially efficient quantity of the good will be less than the market equilibrium quantity.
D)the good generates an external cost.
E)the market equilibrium price of the good will be greater than the social equilibrium price.

The existence of positive externalities in the consumption of a good implies that:
A)the social supply curve of the good lies to the right of the private supply curve.
B)the government will need to provide subsidies to ensure a socially efficient level of consumption.
C)the socially efficient quantity of the good will be less than the market equilibrium quantity.
D)the good generates an external cost.
E)the market equilibrium price of the good will be greater than the social equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

When the social costs of producing or consuming a good exceed the private costs, _____.
A)a positive externality exists
B)an inefficiently high quantity of the good will be produced and consumed, from the society's point of view
C)the direct consumers of the good will bear the external costs
D)the individuals involved in the production of the good do not bear the private costs
E)the quantity of the good produced will be less than the socially efficient level

When the social costs of producing or consuming a good exceed the private costs, _____.
A)a positive externality exists
B)an inefficiently high quantity of the good will be produced and consumed, from the society's point of view
C)the direct consumers of the good will bear the external costs
D)the individuals involved in the production of the good do not bear the private costs
E)the quantity of the good produced will be less than the socially efficient level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The following table shows the costs and benefit of producing a commodity.Table 13.1

Why are cows and chickens less prone to becoming extinct?
A)They are usually consumed in huge numbers
B)They are mainly privately owned
C)They are a part of common resources
D)Poaching these animals for their meat is banned by the government
E)They are not used for commercial purposes

Why are cows and chickens less prone to becoming extinct?
A)They are usually consumed in huge numbers
B)They are mainly privately owned
C)They are a part of common resources
D)Poaching these animals for their meat is banned by the government
E)They are not used for commercial purposes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The following table shows the costs and benefit of producing a commodity.Table 13.1

According to Table 13.1, the external cost of producing 5 units of output is:
A)$5.
B)$6.
C)$10.
D)$8.
E)$4.

According to Table 13.1, the external cost of producing 5 units of output is:
A)$5.
B)$6.
C)$10.
D)$8.
E)$4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The following table shows the costs and benefit of producing a commodity.Table 13.1

One reason that some whales were hunted close to extinction is that no one can claim ownership of a whale until it is killed. If property rights to the whale population were established:
A)then whales would surely be hunted to extinction.
B)the owners would have the incentive to ensure a sustainable yield of whales, so the whale population could recover.
C)no one would hunt whales.
D)the price of whales would be kept artificially low so that trade in whales would become unprofitable.
E)the whales would be hunted to extinction only when the price is high and it is profitable to trade in whales.

One reason that some whales were hunted close to extinction is that no one can claim ownership of a whale until it is killed. If property rights to the whale population were established:
A)then whales would surely be hunted to extinction.
B)the owners would have the incentive to ensure a sustainable yield of whales, so the whale population could recover.
C)no one would hunt whales.
D)the price of whales would be kept artificially low so that trade in whales would become unprofitable.
E)the whales would be hunted to extinction only when the price is high and it is profitable to trade in whales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The following table shows the costs and benefit of producing a commodity.Table 13.1

According to Table 13.1, what level of tax per unit would be appropriate to internalize the externality?
A)$4
B)$6
C)$1
D)$8
E)$2

According to Table 13.1, what level of tax per unit would be appropriate to internalize the externality?
A)$4
B)$6
C)$1
D)$8
E)$2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Overfishing along the coastline of Helsking village led the government to impose a fee on the boats used for fishing. The fishermen were charged $50 on each boat they sent out for fishing. The following table shows the total pounds of fish caught per hour and the number of boats used for fishing.Table 13.2

Refer to Table 13.2. Suppose fish sells for $1 per pound. What is the amount of total profit earned when the fishermen use the socially optimal number of boats?
A)$50
B)$80
C)$45
D)$90
E)$0

Refer to Table 13.2. Suppose fish sells for $1 per pound. What is the amount of total profit earned when the fishermen use the socially optimal number of boats?
A)$50
B)$80
C)$45
D)$90
E)$0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Overfishing along the coastline of Helsking village led the government to impose a fee on the boats used for fishing. The fishermen were charged $50 on each boat they sent out for fishing. The following table shows the total pounds of fish caught per hour and the number of boats used for fishing.Table 13.2

Refer to Table 13.2. Suppose fish sells for $1 per pound. If each fisherman decides whether or not to fish based on the average catch, how many boats per hour will go out to fish?
A)6
B)5
C)4
D)3
E)2

Refer to Table 13.2. Suppose fish sells for $1 per pound. If each fisherman decides whether or not to fish based on the average catch, how many boats per hour will go out to fish?
A)6
B)5
C)4
D)3
E)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The following table shows the costs and benefit of producing a commodity.Table 13.1

Which of the following is not a problem with a public good?
A)An incentive to free-ride
B)A public good is often underconsumed
C)An absence of private property rights
D)An inability to limit consumption to those who purchase the good
E)A public good is usually underproduced

Which of the following is not a problem with a public good?
A)An incentive to free-ride
B)A public good is often underconsumed
C)An absence of private property rights
D)An inability to limit consumption to those who purchase the good
E)A public good is usually underproduced

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The following table shows the costs and benefit of producing a commodity.Table 13.1

In China prior to 1990, most residential buildings were dilapidated because:
A)people were not aware of maintenance and beautification techniques.
B)the government did not encourage wastage of resources for such purposes.
C)no one had a property right to a home.
D)all the properties were inherited.
E)the people had private property rights so they did not have an incentive to repair the houses.

In China prior to 1990, most residential buildings were dilapidated because:
A)people were not aware of maintenance and beautification techniques.
B)the government did not encourage wastage of resources for such purposes.
C)no one had a property right to a home.
D)all the properties were inherited.
E)the people had private property rights so they did not have an incentive to repair the houses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

The existence of externalities in a market implies that:
A)resources are being used efficiently.
B)there is no other allocation of resources that would make society as a whole better off.
C)consumers cannot be excluded from consuming the good once it is provided.
D)resources are not being used in their highest valued activity.
E)the social welfare is maximized.

The existence of externalities in a market implies that:
A)resources are being used efficiently.
B)there is no other allocation of resources that would make society as a whole better off.
C)consumers cannot be excluded from consuming the good once it is provided.
D)resources are not being used in their highest valued activity.
E)the social welfare is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The table below shows the payoff (profit) matrix of Firm A and Firm B indicating the profit outcome that corresponds to each firm's pricing strategy (where $500 and $200 are the pricing strategies of two firms).Table 12.2

When negative externalities exist in production, _____.
A)the social supply curve lies to the left of the private supply curve
B)the social supply curve lies to the right of the private supply curve
C)the social supply curve is identical to the private supply curve
D)the private demand curve lies to the right of the social demand curve
E)the private demand curve lies to the left of the social demand curve

When negative externalities exist in production, _____.
A)the social supply curve lies to the left of the private supply curve
B)the social supply curve lies to the right of the private supply curve
C)the social supply curve is identical to the private supply curve
D)the private demand curve lies to the right of the social demand curve
E)the private demand curve lies to the left of the social demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
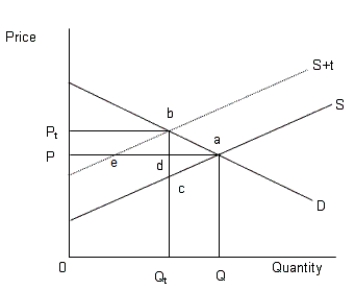
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of automobiles.Figure 13.3
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax
Suppose that the current price of a marketable permit to emit one ton of gunk is $60. For firm A, the marginal cost of reducing one ton of gunk is $50. For firm B, the marginal cost of reducing one ton of gunk is $70. Under a marketable permit system, _____.
A)both firms will buy a permit and emit one more ton of gunk
B)firm A will buy a permit and emit one more ton of gunk, whereas firm B will reduce its emissions of gunk by one ton
C)firm B will buy a permit and emit one more ton of gunk, whereas firm A will reduce its emissions of gunk by one ton
D)both firms will reduce their emissions of gunk by one ton
E)both firms will go out of business
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

Suppose that the current price of a marketable permit to emit one ton of gunk is $60. For firm A, the marginal cost of reducing one ton of gunk is $50. For firm B, the marginal cost of reducing one ton of gunk is $70. Under a marketable permit system, _____.
A)both firms will buy a permit and emit one more ton of gunk
B)firm A will buy a permit and emit one more ton of gunk, whereas firm B will reduce its emissions of gunk by one ton
C)firm B will buy a permit and emit one more ton of gunk, whereas firm A will reduce its emissions of gunk by one ton
D)both firms will reduce their emissions of gunk by one ton
E)both firms will go out of business

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Overfishing along the coastline of Helsking village led the government to impose a fee on the boats used for fishing. The fishermen were charged $50 on each boat they sent out for fishing. The following table shows the total pounds of fish caught per hour and the number of boats used for fishing.Table 13.2

If education has positive externalities, _____.
A)the resources will be efficiently allocated in providing education
B)the private costs of production will be lower than the social costs
C)the government can help to bring about a more efficient allocation through subsidies
D)the benefits of consumption accrue only to the consumers
E)the government can help to bring about a more efficient allocation by levying education cess

If education has positive externalities, _____.
A)the resources will be efficiently allocated in providing education
B)the private costs of production will be lower than the social costs
C)the government can help to bring about a more efficient allocation through subsidies
D)the benefits of consumption accrue only to the consumers
E)the government can help to bring about a more efficient allocation by levying education cess

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43

Refer to Figure 13.4. Suppose the government wishes to reduce pollution to a quantity of Qb. If it sells marketable pollution permits for a pollution quantity of Qb, then:
A)firms will bid the price of the permits up to a price of Pa, and Qa amount of pollution will result.
B)firms will bid the price of the permits up to a price of Pb, and Qb amount of pollution will result.
C)firms will bid the price of the permits up to a price of Pc, and Qc amount of pollution will result.
D)firms will bid the price of the permits up to a price of Pc, and Qb amount of pollution will result.
E)firms will not be willing to pay any price for the permits, so there will be no reduction in pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Overfishing along the coastline of Helsking village led the government to impose a fee on the boats used for fishing. The fishermen were charged $50 on each boat they sent out for fishing. The following table shows the total pounds of fish caught per hour and the number of boats used for fishing.Table 13.2

If the government is successful in internalizing the external costs of production in a market, then:
A)social costs will equal private costs.
B)an inefficient level of output will be produced.
C)social costs will exceed private costs.
D)social costs will be less than private costs.
E)social costs will fall to zero.

If the government is successful in internalizing the external costs of production in a market, then:
A)social costs will equal private costs.
B)an inefficient level of output will be produced.
C)social costs will exceed private costs.
D)social costs will be less than private costs.
E)social costs will fall to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of automobiles.Figure 13.3
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

The Clean Air Act of 1972 required some companies to install the "best available" pollution control technologies. This is an example of:
A)the government using a subsidy to encourage a negative externality.
B)the government using the command approach to discourage a negative externality.
C)the government using the command approach to encourage a positive externality.
D)a marketable pollution permit.
E)a pollution tax.
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

The Clean Air Act of 1972 required some companies to install the "best available" pollution control technologies. This is an example of:
A)the government using a subsidy to encourage a negative externality.
B)the government using the command approach to discourage a negative externality.
C)the government using the command approach to encourage a positive externality.
D)a marketable pollution permit.
E)a pollution tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of automobiles.Figure 13.3
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

Which of the following is an example of the command approach to regulation?
A)The sale of tradable permits to emit sulfur dioxide in the Chicago Mercantile Exchange
B)Enforcing private property rights and private ownership of elephants in Africa
C)Zoning in many areas that restricts the types of buildings that can be built
D)The government providing subsidies for public education
E)A Pigouvian tax
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

Which of the following is an example of the command approach to regulation?
A)The sale of tradable permits to emit sulfur dioxide in the Chicago Mercantile Exchange
B)Enforcing private property rights and private ownership of elephants in Africa
C)Zoning in many areas that restricts the types of buildings that can be built
D)The government providing subsidies for public education
E)A Pigouvian tax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of automobiles.Figure 13.3
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

When the government tries to control pollution through cap and trade, it _____.
A)issues permits that enables the owners of the permit to pollute
B)allows polluting firms to produce public goods that reduce pollution
C)levies tax on the polluting firm
D)gives subsidies to the firms who adopt clean production technologies
E)takes legal actions against the firms who pollute beyond the specified level
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

When the government tries to control pollution through cap and trade, it _____.
A)issues permits that enables the owners of the permit to pollute
B)allows polluting firms to produce public goods that reduce pollution
C)levies tax on the polluting firm
D)gives subsidies to the firms who adopt clean production technologies
E)takes legal actions against the firms who pollute beyond the specified level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Overfishing along the coastline of Helsking village led the government to impose a fee on the boats used for fishing. The fishermen were charged $50 on each boat they sent out for fishing. The following table shows the total pounds of fish caught per hour and the number of boats used for fishing.Table 13.2

The commons problem refers to:
A)a problem that arises when everything is privately owned.
B)a situation when the resources are owned by the government and the common people have limited access to them.
C)a problem that arises when government takes incorrect measures which adversely affect common people.
D)a problem that arises when everyone has access to a particular resource.
E)the adverse situation that arises when the government fails to take adequate measures to solve common problems.

The commons problem refers to:
A)a problem that arises when everything is privately owned.
B)a situation when the resources are owned by the government and the common people have limited access to them.
C)a problem that arises when government takes incorrect measures which adversely affect common people.
D)a problem that arises when everyone has access to a particular resource.
E)the adverse situation that arises when the government fails to take adequate measures to solve common problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The figure below shows the demand and supply curves in the market for elementary education.Figure 13.1
In the figure,
D: Private demand curve for elementary education
D + s: Demand curve which includes public benefits
S: Supply curve of education
Price and Quantity have been taken on vertical and horizontal axes respectively.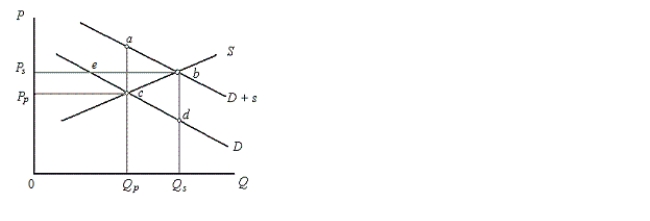
According to Figure 13.1, the outcome of an unregulated, unsubsidized market would be:
A) point a.
B) point b.
C) point c.
D) point d.
E) point e.
In the figure,
D: Private demand curve for elementary education
D + s: Demand curve which includes public benefits
S: Supply curve of education
Price and Quantity have been taken on vertical and horizontal axes respectively.
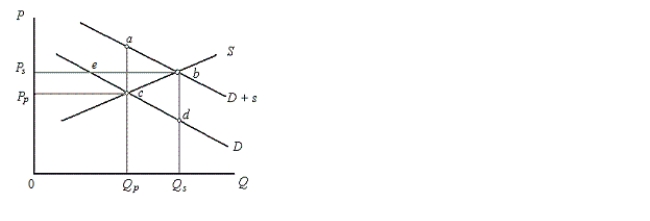
According to Figure 13.1, the outcome of an unregulated, unsubsidized market would be:
A) point a.
B) point b.
C) point c.
D) point d.
E) point e.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of steel. Sp is the private supply curve, and Ss is the social supply curve that includes both private costs and external costs.Figure 13.2
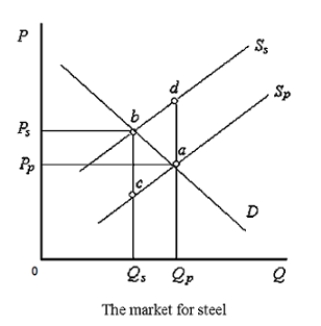
In Figure 13.2, external costs are equal to _____.
A)Ps − Pp
B)da
C)Qp − Qs
D)ab
E)bc

In Figure 13.2, external costs are equal to _____.
A)Ps − Pp
B)da
C)Qp − Qs
D)ab
E)bc

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Overfishing along the coastline of Helsking village led the government to impose a fee on the boats used for fishing. The fishermen were charged $50 on each boat they sent out for fishing. The following table shows the total pounds of fish caught per hour and the number of boats used for fishing.Table 13.2

When the government imposes a tax on the production of a commodity:
A)production will invariably increase.
B)the cost of production increases, so the supply curve shifts to the left.
C)the benefits of consumption increases, so the demand curve shifts to the right.
D)there is no change in demand or supply of the commodity.
E)both the demand and supply curves shift to the right.

When the government imposes a tax on the production of a commodity:
A)production will invariably increase.
B)the cost of production increases, so the supply curve shifts to the left.
C)the benefits of consumption increases, so the demand curve shifts to the right.
D)there is no change in demand or supply of the commodity.
E)both the demand and supply curves shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of automobiles.Figure 13.3
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

Figure 13.3 represents a situation of:
A)positive externality.
B)Pareto efficiency.
C)negative externality.
D)the commons problem.
E)the free rider problem.
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

Figure 13.3 represents a situation of:
A)positive externality.
B)Pareto efficiency.
C)negative externality.
D)the commons problem.
E)the free rider problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of steel. Sp is the private supply curve, and Ss is the social supply curve that includes both private costs and external costs.Figure 13.2

According to Figure 13.2:
A)both points a and b are socially efficient.
B)both points a and b are inefficient, from the society's point of view.
C)point a represents the social equilibrium, whereas point b represents the private equilibrium.
D)point a represents the private equilibrium, whereas point b represents the social equilibrium.
E)when external costs are zero, the socially efficient output level is equal to 0Qs units.

According to Figure 13.2:
A)both points a and b are socially efficient.
B)both points a and b are inefficient, from the society's point of view.
C)point a represents the social equilibrium, whereas point b represents the private equilibrium.
D)point a represents the private equilibrium, whereas point b represents the social equilibrium.
E)when external costs are zero, the socially efficient output level is equal to 0Qs units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of automobiles.Figure 13.3
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

The European Union Emission Trading Scheme is an example of:
A)a pollution tax.
B)a pollution subsidy.
C)a command approach.
D)cap and trade.
E)enforcing private property rights.
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

The European Union Emission Trading Scheme is an example of:
A)a pollution tax.
B)a pollution subsidy.
C)a command approach.
D)cap and trade.
E)enforcing private property rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The figure below shows the demand and supply curves in the market for elementary education.Figure 13.1
In the figure,
D: Private demand curve for elementary education
D + s: Demand curve which includes public benefits
S: Supply curve of education
Price and Quantity have been taken on vertical and horizontal axes respectively.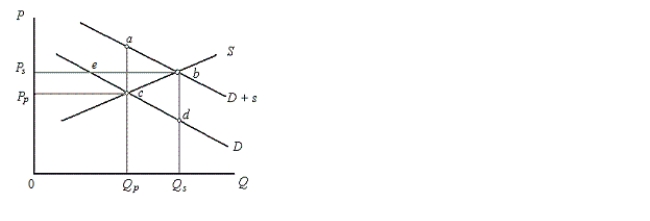
According to figure 13.1, the optimal subsidy is equal to:
A)0Qs -0Qp.
B)0Ps - 0Pp.
C)Qpa - Qpc.
D)Qsb - Qsd.
E)the distance bc.
In the figure,
D: Private demand curve for elementary education
D + s: Demand curve which includes public benefits
S: Supply curve of education
Price and Quantity have been taken on vertical and horizontal axes respectively.
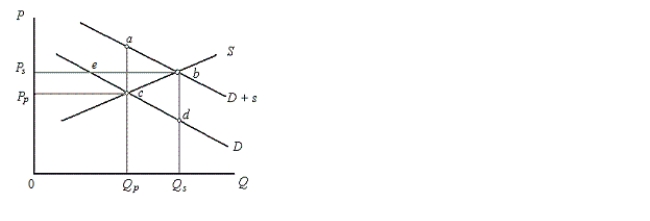
According to figure 13.1, the optimal subsidy is equal to:
A)0Qs -0Qp.
B)0Ps - 0Pp.
C)Qpa - Qpc.
D)Qsb - Qsd.
E)the distance bc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The figure below shows the demand and supply curves in the market for elementary education.Figure 13.1
In the figure,
D: Private demand curve for elementary education
D + s: Demand curve which includes public benefits
S: Supply curve of education
Price and Quantity have been taken on vertical and horizontal axes respectively.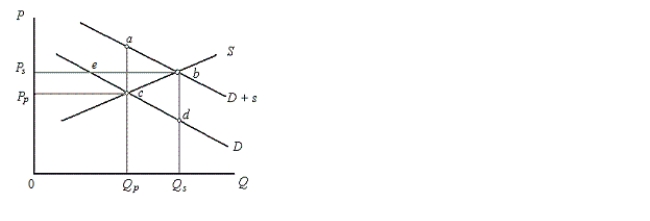
Figure 13.1 represents a situation of:
A)positive externalities.
B)negative externalities.
C)excess capacity.
D)optimal provision of a public good.
E)comparative advantage.
In the figure,
D: Private demand curve for elementary education
D + s: Demand curve which includes public benefits
S: Supply curve of education
Price and Quantity have been taken on vertical and horizontal axes respectively.
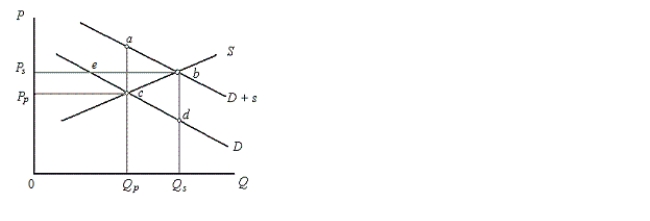
Figure 13.1 represents a situation of:
A)positive externalities.
B)negative externalities.
C)excess capacity.
D)optimal provision of a public good.
E)comparative advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57

In Figure 13.4, if the government sells Qb permits to pollute at a price of Pb each, then:
A)only one firm will buy all the permits.
B)firms in the market will be forced to shut down due to excessive government regulation.
C)the allocation of pollution reduction is efficient, because only those firms with a marginal cost of pollution reduction greater than Pb will buy the permits.
D)the allocation of pollution reduction is efficient, because only those firms with a marginal cost of pollution reduction less than Pb will buy the permits.
E)the allocation of pollution reduction is inefficient, because only those firms with the lowest costs of pollution reduction will purchase the permits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of automobiles.Figure 13.3
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

Suppose the current price of a marketable permit to emit one ton of sulfur dioxide is $100. If the marginal cost for a firm to reduce one ton of sulfur dioxide is $80, then:
A)the firm will buy the permit and emit one more ton of sulfur dioxide.
B)the firm will reduce its emissions of sulfur dioxide by one ton.
C)the firm will buy the permit and increase its emissions by 20 tons.
D)the firm will shut down.
E)the firm will be willing to pay up to $200 for a permit.
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

Suppose the current price of a marketable permit to emit one ton of sulfur dioxide is $100. If the marginal cost for a firm to reduce one ton of sulfur dioxide is $80, then:
A)the firm will buy the permit and emit one more ton of sulfur dioxide.
B)the firm will reduce its emissions of sulfur dioxide by one ton.
C)the firm will buy the permit and increase its emissions by 20 tons.
D)the firm will shut down.
E)the firm will be willing to pay up to $200 for a permit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of automobiles.Figure 13.3
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

In Figure 13.3, the amount of tax levied by the government is equal to:
A)0Pt
B)0P.
C)Qtd - Qtc.
D)0Q - 0Qt.
E)Qtb - Qtd.
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

In Figure 13.3, the amount of tax levied by the government is equal to:
A)0Pt
B)0P.
C)Qtd - Qtc.
D)0Q - 0Qt.
E)Qtb - Qtd.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The figure given below shows the demand and supply curves of automobiles.Figure 13.3
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

According to Figure 13.3, the market attains equilibrium before the tax is imposed at:
A) point d.
B) point a.
C) point b.
D) point c.
E) point e.
In the figure,
D: Demand curve of automobiles
S: Supply of automobiles prior to the tax
S+t: Supply of automobiles after the tax

According to Figure 13.3, the market attains equilibrium before the tax is imposed at:
A) point d.
B) point a.
C) point b.
D) point c.
E) point e.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61

Which of the following is a measure taken by the government to internalize externalities?
A)Value Added Tax
B)Income Tax
C)Cap and trade
D)Tariffs
E)Deficit financing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62

The "Public Choice" school of economists argue that:
A)the invisible hand of the market is inefficient in allocating resources to their best uses.
B)the government often does not take correct economic decisions as it is run by self-interested politicians.
C)the government takes correct decisions as it is run by conscious and educated individuals.
D)the market fails to maximize social efficiency.
E)the government is a non-profit making organization which works to maximize social efficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63

The QWERTY story illustrates:
A)the commons problem.
B)a negative network externality.
C)the path dependence to technology.
D)the problem of adverse selection.
E)a situation of moral hazard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64

Moral hazard is the term used to describe the situation in which:
A)a consumer may buy a low-quality product.
B)consumers receive a lower price because of a mistake on the part of the clerk.
C)a consumer is being compensated for a defective product.
D)people may change their behavior after they have signed a contract or agreed to a specified behavior.
E)people want to change their behavior after they have signed a contract or agreed to a specified behavior but are unable to do so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65

Why does an existing less efficient technology drive out a new, more efficient technology?
A)The existing technology is a network that has become locked in.
B)People are receptive to the new technology.
C)The new technology is costlier to hire.
D)The existing technology is a network that has become locked out.
E)The government imposes taxes on the new technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66

Suppose that if there are n users of a network, the value of the membership is proportional to n(n − 1). If the value of a network to a single user is $1 for each other user on the network, then a network of size 100 has a value of:
A)$9,500.
B)$9,900.
C)$9,000.
D)$10,000.
E)$10,100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67

Why does a network externality arise?
A)Each additional unit of a good sold reduces the value of the previously sold units.
B)As more and more units of a good are produced, the average cost declines.
C)Consumption of a good by one user does not affect the consumption of subsequent users.
D)The firms enjoy economies of scale in the long run.
E)Each additional unit of a good sold increases the value of the previously sold units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68

Mary is a low-risk applicant for a loan at a bank, while John is a high-risk applicant. If the bank increases the interest rates it charges on loans, _____.
A)John is likely to leave the market for loans
B)the problem of moral hazard will prevent John from getting a loan
C)the commons problem will prevent Mary from getting a loan
D)Mary is likely to leave the market for loans
E)both Mary and John will leave the market for loans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69

_____ occurs when unobservable qualities are valued incorrectly because of a lack of information.
A)Moral hazard
B)Adverse selection
C)Conspicuous consumption
D)Marginal selection
E)Statistical discrimination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

The Austrian school of economists stressed on the efficiency of the markets on the pretext that:
A)resources could be efficiently allocated through price system and free markets.
B)governmental intervention was necessary for the efficient allocation of resources.
C)the price charged under the free market system was always lower than under central planning.
D)the market had never failed earlier.
E)the market did not suffer from imperfect information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71

One cause of market failure may be the absence of clearly defined property rights.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72

Which of the following may be explained by adverse selection?
A)When banks raise the interest rate on loans, high-risk applicants leave the market.
B)When health insurance companies decrease insurance charges but increase deductibles, less healthy people are more willing to purchase insurance.
C)As the cost of insurance rises, low-risk applicants reduce their coverage.
D)Products are sold at prices that reflect their true value.
E)Loan companies do not require down payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73

When a good commodity is driven out of the market by a bad commodity, the result is called:
A)moral hazard.
B)adverse selection.
C)positive externality.
D)negative externality.
E)the commons problem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74

A market failure occurs when the market outcome is not the socially efficient outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75

If the price of marketable permits is kept very high, _____.
A)the quantity of pollution in the economy will increase
B)a network externality will arise
C)firms will adopt more efficient pollution abatement equipment
D)environmental groups will start selling additional permits in the market
E)firms will have a greater incentive to pollute

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76

James insured his car with a renowned insurance company that checked his driving skills and verified his accident records before insuring his car. After paying two premiums for this insurance, James took to drinking and driving. This action of James is likely to create:
A)an economic loss.
B)a positive externality.
C)an economic bad.
D)a moral hazard.
E)diseconomies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77

The existence of network externalities implies that:
A)the value of a network falls as the number of members rises.
B)the opportunity cost of switching networks is higher for larger networks.
C)smaller networks are more successful than larger ones.
D)newer networks are more likely to become locked in.
E)only the most efficient and superior technology prevails in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78

Both the principles of rivalry and mutual excludability apply for club goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79

Asymmetric information arises when:
A)both the parties to an exchange have perfect information about the good.
B)none of the parties to exchange have any information about the good.
C)one party to an exchange knows more than the other party.
D)a good is provided by the government.
E)the market is perfectly competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80

In which of the following markets adverse selection may not occur?
A)The market for pre-owned residential apartments
B)The lemons market
C)The market for new sports utility vehicles
D)The capital market
E)The market for health insurance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 113 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



