Deck 4: Arterial Blood Gas Assessments
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/10
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Arterial Blood Gas Assessments
1
All of the following will be seen in the arterial blood gas values of a patient with acute ventilatory failure EXCEPT:
A) an acidic pH.
B)a near-normal bicarbonate level.
C)an alkaline pH.
D)a high carbon dioxide level.
A) an acidic pH.
B)a near-normal bicarbonate level.
C)an alkaline pH.
D)a high carbon dioxide level.
an alkaline pH.
2
An anion gap of 15 would indicate:
A) metabolic acidosis.
B)respiratory alkalosis.
C)respiratory acidosis.
D)metabolic alkalosis.
A) metabolic acidosis.
B)respiratory alkalosis.
C)respiratory acidosis.
D)metabolic alkalosis.
metabolic acidosis.
3
Common causes of metabolic alkalosis include:
1) diuretic therapy.
2) vomiting.
3) excessive sodium bicarbonate administration.
4) gastric suctioning.
A)1, 3
B)2, 4
C)2, 3, 4
D)1, 2, 3, 4
1) diuretic therapy.
2) vomiting.
3) excessive sodium bicarbonate administration.
4) gastric suctioning.
A)1, 3
B)2, 4
C)2, 3, 4
D)1, 2, 3, 4
1, 2, 3, 4
4
Your patient has had chronic ventilatory failure for several years. What is the primary factor that determines her breathing pattern?
A) Muscle efficiency
B)Ventilatory efficiency
C)Heart function
D)Work efficiency
A) Muscle efficiency
B)Ventilatory efficiency
C)Heart function
D)Work efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following would be a normal person's arterial carbon dioxide pressure (PaCO2)?
A) 25 to 35 mm Hg
B)35 to 45 mm Hg
C)45 to 60 mm Hg
D)60 to 80 mm Hg
A) 25 to 35 mm Hg
B)35 to 45 mm Hg
C)45 to 60 mm Hg
D)60 to 80 mm Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following would be a normal person's venous oxygen pressure (PaO2)?
A) 35 to 45 mm Hg
B)45 to 80 mm Hg
C)80 to 100 mm Hg
D)100 to 120 mm Hg
A) 35 to 45 mm Hg
B)45 to 80 mm Hg
C)80 to 100 mm Hg
D)100 to 120 mm Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What causes stimulation of the peripheral chemoreceptors to increase the ventilator rate?
A) Pain or anxiety
B)PaCO2 of about 40 mm Hg
C)PaO2 of about 60 mm Hg
D)Venous pH of 7.30 to 7.40
A) Pain or anxiety
B)PaCO2 of about 40 mm Hg
C)PaO2 of about 60 mm Hg
D)Venous pH of 7.30 to 7.40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following would be found in a stable patient with longstanding obstructive lung disease?
A) Low bicarbonate level and low carbon dioxide level
B)Low bicarbonate level and high carbon dioxide level
C)High bicarbonate level and low carbon dioxide level
D)High bicarbonate level and high carbon dioxide level
A) Low bicarbonate level and low carbon dioxide level
B)Low bicarbonate level and high carbon dioxide level
C)High bicarbonate level and low carbon dioxide level
D)High bicarbonate level and high carbon dioxide level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Common causes of metabolic acidosis include all of the following EXCEPT:
A) diabetic ketoacidosis.
B)shallow breathing from a sedative overdose.
C)lactic acidosis.
D)renal (kidney) failure.
A) diabetic ketoacidosis.
B)shallow breathing from a sedative overdose.
C)lactic acidosis.
D)renal (kidney) failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Your patient with chronic ventilatory failure and hypoxemia has been given supplemental oxygen. Within an hour, he is found to be breathing shallowly and very lethargic. The physician suspects that he was given too much oxygen. What physiologic effects could have led to this?
1) Oxygen-induced redistribution of the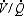 ratio
ratio
2) Oxygen-induced peripheral chemoreceptor depression
3) Respiratory acidosis
4) Increased shunt percentage
A)1, 2
B)2, 3
C)3, 4
D)1, 2, 3
1) Oxygen-induced redistribution of the
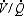 ratio
ratio2) Oxygen-induced peripheral chemoreceptor depression
3) Respiratory acidosis
4) Increased shunt percentage
A)1, 2
B)2, 3
C)3, 4
D)1, 2, 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 10 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



