Deck 4: Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/240
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions
1
According to the following reaction,what amount of Al2S3 remains when 20.00 g of Al2S3 and 2.00 g of H2O are reacted? A few of the molar masses are as follows: Al2S3 = 150.17 g/mol,H2O = 18.02 g/mol. Al2S3(s)+ 6 H2O(l)→ 2 Al(OH)3(s)+ 3 H2S(g)
A) 28.33 g
B) 14.00 g
C) 8.33 g
D) 19.78 g
E) 17.22 g
A) 28.33 g
B) 14.00 g
C) 8.33 g
D) 19.78 g
E) 17.22 g
17.22 g
2
Two samples of potassium iodide are decomposed into their constituent elements.The first sample produced 13.0 g of potassium and 42.3 g of iodine.If the second sample produced 24.4 kg of potassium,how many kg of iodine were produced?
A) 13.3 kg
B) 22.5 kg
C) 79.4 kg
D) 44.4 kg
E) 92.4 kg
A) 13.3 kg
B) 22.5 kg
C) 79.4 kg
D) 44.4 kg
E) 92.4 kg
79.4 kg
3
Determine the molarity of a solution formed by dissolving 4.00 moles of KBr in enough water to yield 3.00 L of solution.
A) 1.33 M
B) 2.00 M
C) 0.750 M
D) 3.00 M
E) 12.00 M
A) 1.33 M
B) 2.00 M
C) 0.750 M
D) 3.00 M
E) 12.00 M
1.33 M
4
Determine the molarity of a solution formed by dissolving 468 mg of MgI2 in enough water to yield 50.0 mL of solution.
A) 0.0297 M
B) 0.0337 M
C) 0.0936 M
D) 0.0107 M
E) 0.0651 M
A) 0.0297 M
B) 0.0337 M
C) 0.0936 M
D) 0.0107 M
E) 0.0651 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Determine the molarity of a solution formed by dissolving 97.7 g LiBr in enough water to yield 750.0 mL of solution.
A) 1.50 M
B) 1.18 M
C) 0.130 M
D) 0.768 M
E) 2.30 M
A) 1.50 M
B) 1.18 M
C) 0.130 M
D) 0.768 M
E) 2.30 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Determine the theoretical yield of HCl if 60.0 g of BCl3 and 37.5 g of H2O are reacted according to the following balanced reaction.A possibly useful molar mass is BCl3 = 117.16 g/mol. BCl3(g)+ 3 H2O(l)→ H3BO3(s)+ 3 HCl(g)
A) 75.9 g HCl
B) 132 g HCl
C) 187 g HCl
D) 56.0 g HCl
E) 25.3 g HCl
A) 75.9 g HCl
B) 132 g HCl
C) 187 g HCl
D) 56.0 g HCl
E) 25.3 g HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How many moles of nitrogen are formed when 58.6 g of KNO3 decomposes according to the following reaction? The molar mass of KNO3 is 101.11 g/mol. 4 KNO3(s)→ 2 K2O(s)+ 2 N2(g)+ 5 O2(g)
A) 0.290 mol N2
B) 0.580 mol N2
C) 18.5 mol N2
D) 0.724 mol N2
E) 1.73 mol N2
A) 0.290 mol N2
B) 0.580 mol N2
C) 18.5 mol N2
D) 0.724 mol N2
E) 1.73 mol N2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A 12.39 g sample of phosphorus reacts with 42.54 g of chlorine to form only phosphorus trichloride (PCl3).If it is the only product,what mass of PCl3 is formed?
A) 30.15 g
B) 54.93 g
C) 140.01 g
D) 79.71 g
E) 91.86 g
A) 30.15 g
B) 54.93 g
C) 140.01 g
D) 79.71 g
E) 91.86 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Determine the limiting reactant (LR)and the mass (in g)of nitrogen that can be formed from 50.0 g N2O4 and 45.0 g N2H4.Some possibly useful molar masses are as follows: N2O4 = 92.02 g/mol,N2H4 = 32.05 g/mol. N2O4(l)+ 2 N2H4(l)→ 3 N2(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
A) LR = N2H4, 59.0 g N2 formed
B) LR = N2O4, 105 g N2 formed
C) LR = N2O4, 45.7 g N2 formed
D) LR = N2H4, 13.3 g N2 formed
E) No LR, 45.0 g N2 formed
A) LR = N2H4, 59.0 g N2 formed
B) LR = N2O4, 105 g N2 formed
C) LR = N2O4, 45.7 g N2 formed
D) LR = N2H4, 13.3 g N2 formed
E) No LR, 45.0 g N2 formed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
How many grams of Li3N can be formed from 1.75 moles of Li? Assume an excess of nitrogen. 6 Li(s)+ N2(g)→ 2 Li3N(s)
A) 18.3 g Li3N
B) 20.3 g Li3N
C) 58.3 g Li3N
D) 61.0 g Li3N
E) 15.1 g Li3N
A) 18.3 g Li3N
B) 20.3 g Li3N
C) 58.3 g Li3N
D) 61.0 g Li3N
E) 15.1 g Li3N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to the following reaction,how many grams of sulfur are formed when 37.4 g of water are formed? 2 H2S(g)+ SO2(g)→ 3 S(s)+ 2 H2O(l)
A) 99.8 g S
B) 66.6 g S
C) 56.1 g S
D) 44.4 g S
E) 14.0 g S
A) 99.8 g S
B) 66.6 g S
C) 56.1 g S
D) 44.4 g S
E) 14.0 g S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Determine the molarity of a solution formed by dissolving 3.00 moles of NaCl in enough water to yield 4.00 L of solution.
A) 1.33 M
B) 2.00 M
C) 0.750 M
D) 3.00 M
E) 12.00 M
A) 1.33 M
B) 2.00 M
C) 0.750 M
D) 3.00 M
E) 12.00 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
How many moles of oxygen are formed when 58.6 g of KNO3 decomposes according to the following reaction? The molar mass of KNO3 is 101.11 g/mol. 4 KNO3(s)→ 2 K2O(s)+ 2 N2(g)+ 5 O2(g)
A) 0.290 mol O2
B) 0.580 mol O2
C) 18.5 mol O2
D) 0.724 mol O2
E) 1.73 mol O2
A) 0.290 mol O2
B) 0.580 mol O2
C) 18.5 mol O2
D) 0.724 mol O2
E) 1.73 mol O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How many molecules of H2S are required to form 79.0 g of sulfur according to the following reaction? Assume excess SO2. 2 H2S(g)+ SO2(g)→ 3 S(s)+ 2 H2O(l)
A) 1.48 × 1024 molecules H2S
B) 9.89 × 1023 molecules H2S
C) 5.06 × 1025 molecules H2S
D) 3.17 × 1025 molecules H2S
E) 2.44 × 1023 molecules H2S
A) 1.48 × 1024 molecules H2S
B) 9.89 × 1023 molecules H2S
C) 5.06 × 1025 molecules H2S
D) 3.17 × 1025 molecules H2S
E) 2.44 × 1023 molecules H2S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A 14.01 g sample of N2 reacts with 3.02 g of H2 to form ammonia (NH3).If ammonia is the only product,what mass of ammonia is formed?
A) 17.01 g
B) 1.10 g
C) 14.01 g
D) 3.02 g
E) 23.07 g
A) 17.01 g
B) 1.10 g
C) 14.01 g
D) 3.02 g
E) 23.07 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Determine the percent yield of a reaction that produces 28.65 g of Fe when 50.00 g of Fe2O3 react with excess Al according to the following reaction. Fe2O3(s)+ 2 Al(s)→ Al2O3(s)+ 2 Fe(s)
A) 61.03%
B) 28.65%
C) 57.30%
D) 20.02%
E) 81.93%
A) 61.03%
B) 28.65%
C) 57.30%
D) 20.02%
E) 81.93%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Consider the following balanced reaction.How many grams of water are required to form 75.9 g of HNO3? Assume that there is excess NO2 present.The molar masses are as follows: H2O = 18.02 g/mol,HNO3 = 63.02 g/mol. 3 NO2(g)+ H2O(l)→ 2 HNO3(aq)+ NO(g)
A) 38.0 g H2O
B) 21.7 g H2O
C) 43.4 g H2O
D) 10.9 g H2O
E) 26.5 g H2O
A) 38.0 g H2O
B) 21.7 g H2O
C) 43.4 g H2O
D) 10.9 g H2O
E) 26.5 g H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Define a greenhouse gas.
A) Greenhouse gases prevent visible light from passing through and warming the Earth's surface, and prevent heat energy from radiating back out into space.
B) Greenhouse gases allow visible light to pass through and warm the Earth's surface, and also allow heat energy to radiate back out into space.
C) Greenhouse gases allow visible light to pass through and cool the Earth's surface, and prevent heat energy from radiating back out into space.
D) Greenhouse gases allow visible light to pass through and warm the Earth's surface, and prevent heat energy from radiating back out into space.
E) Greenhouse gases prevent visible light from passing through and cooling the Earth's surface, and prevent heat energy from radiating back out into space.
A) Greenhouse gases prevent visible light from passing through and warming the Earth's surface, and prevent heat energy from radiating back out into space.
B) Greenhouse gases allow visible light to pass through and warm the Earth's surface, and also allow heat energy to radiate back out into space.
C) Greenhouse gases allow visible light to pass through and cool the Earth's surface, and prevent heat energy from radiating back out into space.
D) Greenhouse gases allow visible light to pass through and warm the Earth's surface, and prevent heat energy from radiating back out into space.
E) Greenhouse gases prevent visible light from passing through and cooling the Earth's surface, and prevent heat energy from radiating back out into space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Consider the following balanced reaction.What mass (in g)of CO2 can be formed from 288 mg of O2? Assume that there is excess C3H7SH present. C3H7SH(l)+ 6 O2(g)→ 3 CO2(g)+ SO2(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
A) 0.396 g CO2
B) 0.209 g CO2
C) 0.792 g CO2
D) 0.126 g CO2
E) 0.198 g CO2
A) 0.396 g CO2
B) 0.209 g CO2
C) 0.792 g CO2
D) 0.126 g CO2
E) 0.198 g CO2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Two samples of calcium fluoride are decomposed into their constituent elements.The first sample produced 0.154 g of calcium and 0.146 g of fluorine.If the second sample produced 294 mg of fluorine,how many g of calcium were formed?
A) 0.280 g
B) 3.09 × 102 g
C) 3.13 g
D) 0.309 g
E) 2.80 × 102 g
A) 0.280 g
B) 3.09 × 102 g
C) 3.13 g
D) 0.309 g
E) 2.80 × 102 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Give the spectator ions for the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of H2SO4 and KOH are mixed.
A) H+ and OH-
B) K+ and SO42-
C) H+ and SO42-
D) OH- and K+
E) No spectator ions are present.
A) H+ and OH-
B) K+ and SO42-
C) H+ and SO42-
D) OH- and K+
E) No spectator ions are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Identify the spectator ions for the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of lithium sulfide and copper(II)nitrate are mixed.
A) Cu2+ and NO3-
B) Li+ and Cu2+
C) Li+ and NO3-
D) S2- and Cu2+
E) No spectator ions are present.
A) Cu2+ and NO3-
B) Li+ and Cu2+
C) Li+ and NO3-
D) S2- and Cu2+
E) No spectator ions are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Determine the number of grams H2 formed when 250.0 mL of 0.743 M HCl solution reacts with 3.41 × 1023 atoms of Fe according to the following reaction. 2 HCl(aq)+ Fe(s)→ H2(g)+ FeCl2(aq)
A) 0.374 g
B) 1.33 g
C) 1.14 g
D) 0.187 g
E) 1.51 g
A) 0.374 g
B) 1.33 g
C) 1.14 g
D) 0.187 g
E) 1.51 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Give the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of K2S and Fe(NO3)2 are mixed.
A) K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → KNO3(s)
B) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → FeS(s) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)
C) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 KNO3(s)
D) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) → FeS(s)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → KNO3(s)
B) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → FeS(s) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)
C) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 KNO3(s)
D) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) → FeS(s)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Identify ammonia.
A) strong electrolyte, strong base
B) strong electrolyte, weak base
C) weak electrolyte, strong base
D) weak electrolyte, weak base
E) nonelectrolyte
A) strong electrolyte, strong base
B) strong electrolyte, weak base
C) weak electrolyte, strong base
D) weak electrolyte, weak base
E) nonelectrolyte

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How many molecules of sucrose (C12H22O11,molar mass = 342.30 g/mol)are contained in 14.3 mL of 0.140 M sucrose solution?
A) 8.29 × 1022 molecules C12H22O11
B) 1.21 × 1021 molecules C12H22O11
C) 6.15 × 1022 molecules C12H22O11
D) 1.63 × 1023 molecules C12H22O11
E) 5.90 × 1024 molecules C12H22O11
A) 8.29 × 1022 molecules C12H22O11
B) 1.21 × 1021 molecules C12H22O11
C) 6.15 × 1022 molecules C12H22O11
D) 1.63 × 1023 molecules C12H22O11
E) 5.90 × 1024 molecules C12H22O11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
According to the following reaction,what mass of PbCl2 can form from 235 mL of 0.110 M KCl solution? Assume that there is excess Pb(NO3)2. 2 KCl(aq)+ Pb(NO3)2(aq)→ PbCl2(s)+ 2 KNO3(aq)
A) 7.19 g
B) 3.59 g
C) 1.80 g
D) 5.94 g
E) 1.30 g
A) 7.19 g
B) 3.59 g
C) 1.80 g
D) 5.94 g
E) 1.30 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Give the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of H2SO4 and KOH are mixed.
A) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
B) 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → K2SO4(s)
C) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H2O(l) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
D) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + K2SO4(s)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
B) 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → K2SO4(s)
C) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H2O(l) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
D) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + K2SO4(s)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Give the spectator ions for the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of K2S and Fe(NO3)2 are mixed.
A) K+ and NO3-
B) Fe2+ and K+
C) S2- and NO3-
D) Fe2+ and S2-
E) No spectator ions are present.
A) K+ and NO3-
B) Fe2+ and K+
C) S2- and NO3-
D) Fe2+ and S2-
E) No spectator ions are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
According to the following reaction,what volume of 0.244 M KCl solution is required to react exactly with 50.0 mL of 0.210 M Pb(NO3)2 solution? 2 KCl(aq)+ Pb(NO3)2(aq)→ PbCl2(s)+ 2 KNO3(aq)
A) 97.4 mL
B) 116 mL
C) 43.0 mL
D) 86.1 mL
E) 58.1 mL
A) 97.4 mL
B) 116 mL
C) 43.0 mL
D) 86.1 mL
E) 58.1 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Give the complete ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of K2S and Fe(NO3)2 are mixed.
A) K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → KNO3(s)
B) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → FeS(s) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)
C) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 KNO3(s)
D) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) → FeS(s)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) K+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → KNO3(s)
B) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → FeS(s) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)
C) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 KNO3(s)
D) Fe2+(aq) + S2-(aq) → FeS(s)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Give the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of Na2CO3 and HCl are mixed.
A) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
B) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2 NaCl(s)
C) 2 H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g)
D) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
B) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2 NaCl(s)
C) 2 H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g)
D) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What mass (in g)of AgCl is formed from the reaction of 75.0 mL of a 0.078 M AgC2H3O2 solution with 55.0 mL of 0.109 M MgCl2 solution? 2 AgC2H3O2(aq)+ MgCl2(aq)→ 2 AgCl(s)+ Mg(C2H3O2)2(aq)
A) 0.838 g
B) 1.72 g
C) 0.859 g
D) 2.56 g
E) 1.70 g
A) 0.838 g
B) 1.72 g
C) 0.859 g
D) 2.56 g
E) 1.70 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What volume of 0.305 M AgNO3 is required to react exactly with 155.0 mL of 0.274 M Na2SO4 solution? Hint: You will want to write a balanced reaction.
A) 581 mL
B) 173 mL
C) 345 mL
D) 139 mL
E) 278 mL
A) 581 mL
B) 173 mL
C) 345 mL
D) 139 mL
E) 278 mL

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Give the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of lithium sulfide and copper(II)nitrate are mixed.
A) Li+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → LiNO3(s)
B) S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) → CuS(s)
C) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 LiNO3(s)
D) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) Li+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → LiNO3(s)
B) S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) → CuS(s)
C) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 LiNO3(s)
D) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Choose the statement below that is TRUE.
A) A weak acid solution consists of mostly nonionized acid molecules.
B) The term "strong electrolyte" means that the substance is extremely reactive.
C) A strong acid solution consists of only partially ionized acid molecules.
D) The term "weak electrolyte" means that the substance is inert.
E) A molecular compound that does not ionize in solution is considered a strong electrolyte.
A) A weak acid solution consists of mostly nonionized acid molecules.
B) The term "strong electrolyte" means that the substance is extremely reactive.
C) A strong acid solution consists of only partially ionized acid molecules.
D) The term "weak electrolyte" means that the substance is inert.
E) A molecular compound that does not ionize in solution is considered a strong electrolyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
According to the following reaction,how many moles of Fe(OH)2 can form from 175.0 mL of 0.227 M LiOH solution? Assume that there is excess FeCl2. FeCl2(aq)+ 2 LiOH(aq)→ Fe(OH)2(s)+ 2 LiCl(aq)
A) 3.97 × 10-2 moles
B) 2.52 × 10-2 moles
C) 1.99 × 10-2 moles
D) 5.03 × 10-2 moles
E) 6.49 × 10-2 moles
A) 3.97 × 10-2 moles
B) 2.52 × 10-2 moles
C) 1.99 × 10-2 moles
D) 5.03 × 10-2 moles
E) 6.49 × 10-2 moles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Give the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of Al(C2H3O2)3 and LiNO3 are mixed.
A) Al3+(aq) + 3 NO3-(aq) → Al(NO3)3(s)
B) Li+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) → LiC2H3O2(s)
C) Al3+(aq) + 3 NO3-(aq) + Li+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) → Al(NO3)3(aq) + LiC2H3O2(s)
D) 3 Li+(aq) + (C2H3O2)33-(aq) → Li3(C2H3O2)3(s)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) Al3+(aq) + 3 NO3-(aq) → Al(NO3)3(s)
B) Li+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) → LiC2H3O2(s)
C) Al3+(aq) + 3 NO3-(aq) + Li+(aq) + C2H3O2-(aq) → Al(NO3)3(aq) + LiC2H3O2(s)
D) 3 Li+(aq) + (C2H3O2)33-(aq) → Li3(C2H3O2)3(s)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Give the complete ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of lithium sulfide and copper(II)nitrate are mixed.
A) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)
B) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 LiNO3(s)
C) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 LiNO3(s)
D) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)
B) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 LiNO3(s)
C) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 LiNO3(s)
D) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Give the complete ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of H2SO4 and KOH are mixed.
A) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
B) 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → K2SO4(s)
C) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H2O(l) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
D) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + K2SO4(s)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) → H2O(l)
B) 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → K2SO4(s)
C) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H2O(l) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq)
D) H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + 2 K+(aq) + SO42-(aq) → H+(aq) + OH-(aq) + K2SO4(s)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Give the spectator ions for the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of MgSO3 and HI are mixed.
A) H+ and SO32-
B) Mg2+ and I-
C) H+ and I-
D) SO32- and Mg2+
E) No spectator ions are present.
A) H+ and SO32-
B) Mg2+ and I-
C) H+ and I-
D) SO32- and Mg2+
E) No spectator ions are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Determine the oxidation state of P in PO33-.
A) +3
B) +6
C) +2
D) 0
E) -3
A) +3
B) +6
C) +2
D) 0
E) -3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Choose the reaction that represents the combustion of C6H12O2.
A) C6H12O2(l) + 8 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g)
B) Mg(s) + C6H12O2(l) → MgC6H12O2(aq)
C) 6 C(s) + 6 H2(g) + O2(g) → C6H12O2(l)
D) C6H12O2(l) → 6 C(s) + 6 H2(g) + O2(g)
E) None of the above represents the combustion of C6H12O2.
A) C6H12O2(l) + 8 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(g)
B) Mg(s) + C6H12O2(l) → MgC6H12O2(aq)
C) 6 C(s) + 6 H2(g) + O2(g) → C6H12O2(l)
D) C6H12O2(l) → 6 C(s) + 6 H2(g) + O2(g)
E) None of the above represents the combustion of C6H12O2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Identify the combustion reaction.
A) 2 C3H7OH(l) + 9 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 8 H2O(g)
B) 2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(g)
C) C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O
D) C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
E) All of the reactions are examples of combustion reactions.
A) 2 C3H7OH(l) + 9 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 8 H2O(g)
B) 2 H2(g) + O2(g) → 2 H2O(g)
C) C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) → 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O
D) C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
E) All of the reactions are examples of combustion reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Identify the oxidizing agent. 2 Al3+(aq)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 2 Al(s)+ 3 Fe2+(aq)
A) Al3+
B) Fe
C) Al
D) Fe2+
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) Al3+
B) Fe
C) Al
D) Fe2+
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What element is undergoing oxidation (if any)in the following reaction? CH4(g)+ 2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)+ 2 H2O(g)
A) O
B) H
C) C
D) both C and H
E) None of the elements is undergoing oxidation.
A) O
B) H
C) C
D) both C and H
E) None of the elements is undergoing oxidation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Determine the oxidizing agent in the following reaction. Ni(s)+ 2 AgClO4(aq)→ Ni(ClO4)2(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)
A) Ag
B) Ni
C) Cl
D) O
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) Ag
B) Ni
C) Cl
D) O
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Define an Arrhenius base.
A) an electron pair donor
B) an electron pair receiver
C) produces H+ ions in aqueous solution
D) accepts H+ ions
E) produces OH- ions in aqueous solution
A) an electron pair donor
B) an electron pair receiver
C) produces H+ ions in aqueous solution
D) accepts H+ ions
E) produces OH- ions in aqueous solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Give the complete ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of MgSO3 and HI are mixed.
A) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g)
B) Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → MgI2(s)
C) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → H2SO3(s) + MgI2(aq)
D) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g)
B) Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → MgI2(s)
C) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → H2SO3(s) + MgI2(aq)
D) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Define an Arrhenius acid.
A) an electron pair donor
B) an electron pair receiver
C) produces H+ ions in aqueous solution
D) accepts H+ ions
E) produces OH- ions in aqueous solution
A) an electron pair donor
B) an electron pair receiver
C) produces H+ ions in aqueous solution
D) accepts H+ ions
E) produces OH- ions in aqueous solution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Identify the reducing agent. 2 Al3+(aq)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 2 Al(s)+ 3 Fe2+(aq)
A) Al3+
B) Fe
C) Al
D) Fe2+
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) Al3+
B) Fe
C) Al
D) Fe2+
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The titration of 80.0 mL of an unknown concentration H3PO4 solution requires 126 mL of 0.218 M KOH solution.What is the concentration of the H3PO4 solution (in M)?
A) 1.03 M
B) 0.343 M
C) 0.114 M
D) 0.138 M
E) 0.0461 M
A) 1.03 M
B) 0.343 M
C) 0.114 M
D) 0.138 M
E) 0.0461 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What element is undergoing oxidation (if any)in the following reaction? Zn(s)+ 2 AgNO3(aq)→ Zn(NO3)2(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)
A) Zn
B) N
C) O
D) Ag
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) Zn
B) N
C) O
D) Ag
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The titration of 25.0 mL of an unknown concentration H2SO4 solution requires 83.6 mL of 0.12 M LiOH solution.What is the concentration of the H2SO4 solution (in M)?
A) 0.20 M
B) 0.40 M
C) 0.10 M
D) 0.36 M
E) 0.25 M
A) 0.20 M
B) 0.40 M
C) 0.10 M
D) 0.36 M
E) 0.25 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Give the complete ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of Na2CO3 and HCl are mixed.
A) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
B) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2 NaCl(s)
C) 2 H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g)
D) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
B) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2 NaCl(s)
C) 2 H+(aq) + CO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + CO2(g)
D) 2 Na+(aq) + CO32-(aq) + 2 H+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) → H2CO3(s) + 2 Na+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Give the net ionic equation for the reaction (if any)that occurs when aqueous solutions of MgSO3 and HI are mixed.
A) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g)
B) Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → MgI2(s)
C) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → H2SO3(s) + MgI2(aq)
D) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.
A) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g)
B) Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → MgI2(s)
C) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → H2SO3(s) + MgI2(aq)
D) 2 H+(aq) + SO32-(aq) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq) → H2O(l) + SO2(g) + Mg2+(aq) + 2 I-(aq)
E) No reaction occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Identify the species reduced. 2 Al3+(aq)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 2 Al(s)+ 3 Fe2+(aq)
A) Al3+
B) Fe
C) Al
D) Fe2+
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) Al3+
B) Fe
C) Al
D) Fe2+
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What element is undergoing reduction (if any)in the following reaction? Zn(s)+ 2 AgNO3(aq)→ Zn(NO3)2(aq)+ 2 Ag(s)
A) Zn
B) N
C) O
D) Ag
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) Zn
B) N
C) O
D) Ag
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Give the spectator ions for the reaction that occurs when aqueous solutions of Na2CO3 and HCl are mixed.
A) H+ and CO32-
B) Na+ and CO32-
C) H+ and Cl-
D) Na+ and Cl-
E) No spectator ions are present.
A) H+ and CO32-
B) Na+ and CO32-
C) H+ and Cl-
D) Na+ and Cl-
E) No spectator ions are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Determine the reducing agent in the following reaction. 2 Li(s)+ Fe(C2H3O2)2(aq)→ 2 LiC2H3O2(aq)+ Fe(s)
A) O
B) H
C) C
D) Fe
E) Li
A) O
B) H
C) C
D) Fe
E) Li

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Lithium and nitrogen react to produce lithium nitride: 6 Li(s)+ 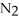 (g)→ 2 Li3N(s)
(g)→ 2 Li3N(s)
How many moles of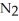 are needed to react with 0.550 mol of lithium?
are needed to react with 0.550 mol of lithium?
A) 3.30
B) 0.550
C) 0.183
D) 1.65
E) 0.0917
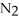 (g)→ 2 Li3N(s)
(g)→ 2 Li3N(s)How many moles of
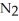 are needed to react with 0.550 mol of lithium?
are needed to react with 0.550 mol of lithium?A) 3.30
B) 0.550
C) 0.183
D) 1.65
E) 0.0917

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
How many grams of water react to form 6.21 moles of Ca(OH)2? CaO(s)+ H2O(l)→ Ca(OH)2(s)
A) 6.21 g of H2O
B) 24.8 g of H2O
C) 49.7 g of H2O
D) 112 g of H2O
E) 99.4 g of H2O
A) 6.21 g of H2O
B) 24.8 g of H2O
C) 49.7 g of H2O
D) 112 g of H2O
E) 99.4 g of H2O

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Automotive air bags inflate when sodium azide decomposes explosively to its constituent elements: 2 NaN3(s)→ 2 Na(s)+ 3 N2(g)
How many moles of N2 are produced by the decomposition of 1.75 mol of sodium azide?
A) 1.17
B) 5.25
C) 2.63
D) 0.583
E) 0.875
How many moles of N2 are produced by the decomposition of 1.75 mol of sodium azide?
A) 1.17
B) 5.25
C) 2.63
D) 0.583
E) 0.875

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How many molecules of HCl are formed when 70.0 g of water reacts according to the following balanced reaction? Assume excess ICl3. 2 ICl3 + 3 H2O → ICl + HIO3 + 5 HCl
A) 3.90 × 1024 molecules HCl
B) 2.34 × 1024 molecules HCl
C) 7.02 × 1024 molecules HCl
D) 4.68 × 1024 molecules HCl
E) 3.90 × 1025 molecules HCl
A) 3.90 × 1024 molecules HCl
B) 2.34 × 1024 molecules HCl
C) 7.02 × 1024 molecules HCl
D) 4.68 × 1024 molecules HCl
E) 3.90 × 1025 molecules HCl

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
According to the following balanced reaction,how many moles of Ca(OH)2 will be formed from 3.22 moles of H2O? CaO(s)+ H2O(l)→ Ca(OH)2(s)
A) 3.22 moles of Ca(OH)2
B) 6.44 moles of Ca(OH)2
C) 12.9 moles of Ca(OH)2
D) 1.61 moles of Ca(OH)2
E) 0.53 moles of Ca(OH)2
A) 3.22 moles of Ca(OH)2
B) 6.44 moles of Ca(OH)2
C) 12.9 moles of Ca(OH)2
D) 1.61 moles of Ca(OH)2
E) 0.53 moles of Ca(OH)2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How many grams of calcium chloride are needed to produce 5.00 g of potassium chloride? CaCl2(aq)+ K2CO3(aq)→ 2 KCl(aq)+ CaCO3(aq)
A) 0.269 g
B) 3.72 g
C) 7.44 g
D) 14.9 g
A) 0.269 g
B) 3.72 g
C) 7.44 g
D) 14.9 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Balance the chemical equation given below,and determine the number of moles of iodine that react with 40.0 g of aluminum. _____ Al(s)+ _____ I2(s)→ _____ Al2I6(s)
A) 0.988 mol
B) 2.22 mol
C) 2.97 mol
D) 4.45 mol
A) 0.988 mol
B) 2.22 mol
C) 2.97 mol
D) 4.45 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Magnesium burns in air with a dazzling brilliance to produce magnesium oxide: 2 Mg(s)+ O2(g)→ 2 MgO(s)
How many moles of O2 are consumed when 2.10 mol of magnesium burns?
A) 0.0864
B) 0.952
C) 2.10
D) 4.20
E) 1.05
How many moles of O2 are consumed when 2.10 mol of magnesium burns?
A) 0.0864
B) 0.952
C) 2.10
D) 4.20
E) 1.05

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Automotive air bags inflate when sodium azide decomposes explosively to its constituent elements: 2 NaN3(s)→ 2 Na(s)+ 3 N2(g)
How many grams of sodium azide are required to produce 25.0 g of nitrogen?
A) 1.34
B) 0.595
C) 58.0
D) 38.7
E) 87.0
How many grams of sodium azide are required to produce 25.0 g of nitrogen?
A) 1.34
B) 0.595
C) 58.0
D) 38.7
E) 87.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Identify the species oxidized. 2 Al3+(aq)+ 2 Fe(s)→ 2 Al(s)+ 3 Fe2+(aq)
A) Al3+
B) Fe
C) Al
D) Fe2+
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.
A) Al3+
B) Fe
C) Al
D) Fe2+
E) This is not an oxidation-reduction reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Lithium and nitrogen react to produce lithium nitride: 6 Li(s)+  (g)→ 2 Li3N(s)
(g)→ 2 Li3N(s)
How many moles of lithium nitride are produced when 0.750 mol of lithium react in this fashion?
A) 0.250
B) 1.50
C) 0.125
D) 2.25
E) 0.375
 (g)→ 2 Li3N(s)
(g)→ 2 Li3N(s)How many moles of lithium nitride are produced when 0.750 mol of lithium react in this fashion?
A) 0.250
B) 1.50
C) 0.125
D) 2.25
E) 0.375

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
According to the following balanced reaction,how many moles of HNO3 are formed from 2.50 moles of NO2 if there is plenty of water present? 3 NO2(g)+ H2O(l)→ 2 HNO3(aq)+ NO(g)
A) 7.50 moles NO
B) 3.75 moles NO
C) 2.50 moles NO
D) 1.67 moles NO
E) 0.834 moles NO
A) 7.50 moles NO
B) 3.75 moles NO
C) 2.50 moles NO
D) 1.67 moles NO
E) 0.834 moles NO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Lithium and nitrogen react in a combination reaction to produce lithium nitride: 6 Li(s)+ 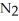 (g)→ 2 Li3N(s)
(g)→ 2 Li3N(s)
How many moles of lithium are needed to produce 0.31 mol of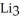 N when the reaction is carried out in the presence of excess nitrogen?
N when the reaction is carried out in the presence of excess nitrogen?
A) 0.16
B) 0.93
C) 0.10
D) 0.21
E) 1.9
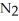 (g)→ 2 Li3N(s)
(g)→ 2 Li3N(s)How many moles of lithium are needed to produce 0.31 mol of
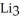 N when the reaction is carried out in the presence of excess nitrogen?
N when the reaction is carried out in the presence of excess nitrogen?A) 0.16
B) 0.93
C) 0.10
D) 0.21
E) 1.9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
How many moles of CuO can be produced from 0.450 mol of Cu2O in the following reaction? 2 Cu2O(s)+ O2(g)→ 4 CuO(s)
A) 0.225 mol
B) 0.450 mol
C) 0.900 mol
D) 1.80 mol
E) 63.2 mol
A) 0.225 mol
B) 0.450 mol
C) 0.900 mol
D) 1.80 mol
E) 63.2 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
According to the following balanced reaction,how many moles of NO are formed from 12.66 moles of NO2 if there is plenty of water present? 3 NO2(g)+ H2O(l)→ 2 HNO3(aq)+ NO(g)
A) 37.98 moles NO
B) 18.99 moles NO
C) 12.66 moles NO
D) 8.44 moles NO
E) 4.22 moles NO
A) 37.98 moles NO
B) 18.99 moles NO
C) 12.66 moles NO
D) 8.44 moles NO
E) 4.22 moles NO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Carbonic acid can form water and carbon dioxide upon heating.How much carbon dioxide is formed from 1.55 g of carbonic acid? H2CO3 → H2O + CO2
A) 1.10 g
B) 2.18 g
C) 1.55 g
D) 0.450 g
E) 5.33 g
A) 1.10 g
B) 2.18 g
C) 1.55 g
D) 0.450 g
E) 5.33 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Global warming is thought to be caused by the increase of one particular gas.Name the gas.
A) hydrogen
B) chlorine
C) carbon dioxide
D) nitrogen
E) helium
A) hydrogen
B) chlorine
C) carbon dioxide
D) nitrogen
E) helium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
According to the following balanced reaction,how many moles of CaO are required to exactly react with 3.22 moles of H2O? CaO(s)+ H2O(l)→ Ca(OH)2(s)
A) 3.22 moles of CaO
B) 6.44 moles of CaO
C) 12.9 moles of CaO
D) 1.61 moles of CaO
E) 0.70 moles of CaO
A) 3.22 moles of CaO
B) 6.44 moles of CaO
C) 12.9 moles of CaO
D) 1.61 moles of CaO
E) 0.70 moles of CaO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the following reaction.How many moles of oxygen are required to produce 4.00 moles of water? Assume that there is excess C3H7SH present. C3H7SH(l)+ 6 O2(g)→ 3 CO2(g)+ SO2(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
A) 2.67 moles O2
B) 6.00 moles O2
C) 4.00 moles O2
D) 16.0 moles O2
E) 1.00 moles O2
A) 2.67 moles O2
B) 6.00 moles O2
C) 4.00 moles O2
D) 16.0 moles O2
E) 1.00 moles O2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
How many moles of BCl3 are needed to produce 25.0 g of HCl(aq)in the following reaction? BCl3(g)+ 3 H2O(l)→ 3 HCl(aq)+ B(OH)3(aq)
A) 0.229 mol
B) 0.686 mol
C) 2.06 mol
D) 4.38 mol
A) 0.229 mol
B) 0.686 mol
C) 2.06 mol
D) 4.38 mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 240 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



