Deck 20: Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/136
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry
1
Write the nuclear equation for the alpha decay of  Ra.
Ra.
A) Ra +
Ra +
 He →
He →
 Th
Th
B) Ra →
Ra →
 n +
n +
 Ra
Ra
C) Ra →
Ra →
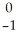 e +
e +
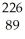 Ac
Ac
D)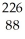 Ra +
Ra +
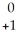 e →
e →
 Ac
Ac
E) Ra →
Ra →
 He +
He +
 Rn
Rn
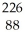 Ra.
Ra.A)
 Ra +
Ra + He →
He →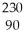 Th
ThB)
 Ra →
Ra → n +
n + Ra
RaC)
 Ra →
Ra →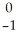 e +
e + Ac
AcD)
 Ra +
Ra +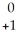 e →
e → Ac
AcE)
 Ra →
Ra → He +
He + Rn
Rn Ra →
Ra → He +
He + Rn
Rn 2
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of  O.
O.
A)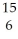 C
C
B)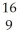 F
F
C)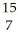 N
N
D)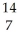 N
N
E) C
C
 O.
O.A)
 C
CB)
 F
FC)
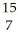 N
ND)
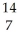 N
NE)
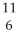 C
C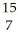 N
N 3
Which of the following nuclides are most likely to decay via positron emission?
A) Na-26
B) I-121
C) Ca-42
D) S-30
E) Sb-122
A) Na-26
B) I-121
C) Ca-42
D) S-30
E) Sb-122
S-30
4
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by 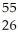 Fe.
Fe.
A)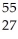 Co
Co
B)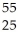 Mn
Mn
C)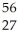 Co
Co
D) Mn
Mn
E) Cr
Cr
 Fe.
Fe.A)
 Co
CoB)
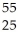 Mn
MnC)
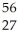 Co
CoD)
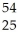 Mn
MnE)
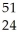 Cr
Cr
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Identify a nuclide.
A) a particular radical
B) a particular cation
C) a particular atom
D) a particular isotope
E) a particular anion
A) a particular radical
B) a particular cation
C) a particular atom
D) a particular isotope
E) a particular anion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Identify the radioactive element that is so radioactive that it glows visibly and emits heat.
A) radium
B) xenon
C) curium
D) radon
E) cesium
A) radium
B) xenon
C) curium
D) radon
E) cesium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Write the nuclear equation for the alpha decay of 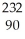 Th.
Th.
A)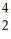 He +
He +
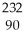 Th →
Th →
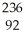 U
U
B)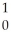 n +
n +
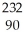 Th →
Th →
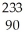 Th
Th
C)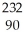 Th →
Th →
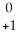 e +
e +
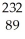 Ac
Ac
D)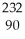 Th →
Th →
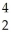 He +
He +
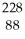 Ra
Ra
E)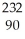 Th →
Th →
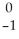 e +
e +
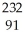 Pa
Pa
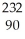 Th.
Th.A)
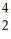 He +
He +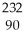 Th →
Th →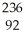 U
UB)
 n +
n +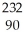 Th →
Th →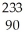 Th
ThC)
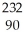 Th →
Th →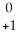 e +
e +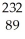 Ac
AcD)
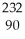 Th →
Th →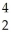 He +
He +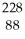 Ra
RaE)
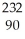 Th →
Th →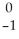 e +
e +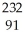 Pa
Pa
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Write a nuclear equation for the alpha decay of 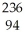 Pu.
Pu.
A)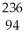 Pu →
Pu →
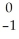 e +
e +
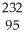 Am
Am
B) Pu →
Pu →
 He +
He +
 U
U
C) Pu →
Pu →
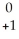 e +
e +
 Np
Np
D) Pu →
Pu →
 n +
n +
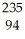 Pu
Pu
E)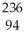 Pu →
Pu →
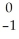 e +
e +
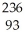 Np
Np
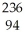 Pu.
Pu.A)
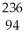 Pu →
Pu → e +
e +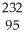 Am
AmB)
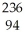 Pu →
Pu → He +
He +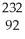 U
UC)
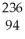 Pu →
Pu → e +
e + Np
NpD)
 Pu →
Pu → n +
n +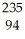 Pu
PuE)
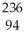 Pu →
Pu →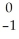 e +
e +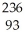 Np
Np
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) If N/Z ratio is too high, there are too many protons and the nuclide will undergo positron emission or electron capture.
B) If N/Z ratio lies somewhere below 1, the nuclide is stable.
C) If N/Z ratio is too low, there are too many neutrons and the nuclide will undergo beta decay.
D) The valley of stability is the geographic location where many of the known nuclides were first discovered.
E) None of the above is true.
A) If N/Z ratio is too high, there are too many protons and the nuclide will undergo positron emission or electron capture.
B) If N/Z ratio lies somewhere below 1, the nuclide is stable.
C) If N/Z ratio is too low, there are too many neutrons and the nuclide will undergo beta decay.
D) The valley of stability is the geographic location where many of the known nuclides were first discovered.
E) None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Identify the scientist(s)that were awarded the Nobel Prize in physics for the discovery of radioactivity in 1903.
A) Johannes Geiger, Marie Curie
B) Albert Einstein
C) Antoine-Henri Becquerel, Marie Curie, Pierre Curie
D) Ernest Rutherford, Johannes Geiger
E) Galileo Galilei
A) Johannes Geiger, Marie Curie
B) Albert Einstein
C) Antoine-Henri Becquerel, Marie Curie, Pierre Curie
D) Ernest Rutherford, Johannes Geiger
E) Galileo Galilei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following nuclides are most likely to decay via beta decay?
A) I-126
B) Al-24
C) N-13
D) Cs-137
E) Na-20
A) I-126
B) Al-24
C) N-13
D) Cs-137
E) Na-20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following nuclides are most likely to decay via beta decay?
A) I-131
B) Ar-40
C) F-18
D) Zr-90
E) Pb-206
A) I-131
B) Ar-40
C) F-18
D) Zr-90
E) Pb-206

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by  Rb.
Rb.
A) Kr
Kr
B) Sr
Sr
C) Br
Br
D) Y
Y
E) Kr
Kr
 Rb.
Rb.A)
 Kr
KrB)
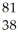 Sr
SrC)
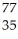 Br
BrD)
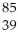 Y
YE)
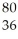 Kr
Kr
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Write a nuclear equation for the alpha decay of 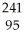 Am.
Am.
A)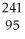 Am →
Am →
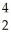 He +
He +
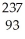 Np
Np
B)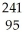 Am →
Am →
 He +
He +
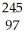 Bk
Bk
C)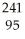 Am →
Am →
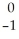 e +
e +
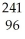 Cm
Cm
D)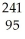 Am →
Am →
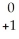 e +
e +
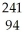 Pu
Pu
E)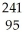 Am →
Am →
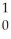 n +
n +
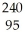 Am
Am
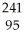 Am.
Am.A)
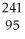 Am →
Am → He +
He +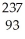 Np
NpB)
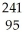 Am →
Am →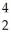 He +
He +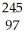 Bk
BkC)
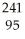 Am →
Am →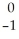 e +
e +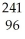 Cm
CmD)
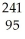 Am →
Am →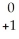 e +
e +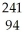 Pu
PuE)
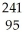 Am →
Am →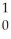 n +
n +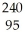 Am
Am
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Write a nuclear equation for the alpha decay of 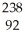 U.
U.
A)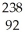 U →
U →
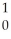 n +
n +
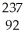 U
U
B)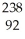 U →
U →
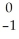 e +
e +
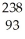 Np
Np
C)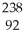 U →
U →
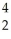 He +
He +
 Th
Th
D) U →
U →
 e +
e +
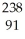 Pa
Pa
E)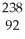 U →
U →
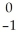 e +
e +
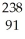 Pa
Pa
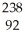 U.
U.A)
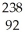 U →
U → n +
n +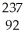 U
UB)
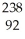 U →
U →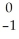 e +
e +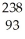 Np
NpC)
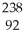 U →
U →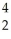 He +
He +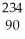 Th
ThD)
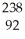 U →
U →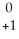 e +
e +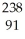 Pa
PaE)
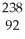 U →
U →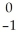 e +
e +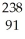 Pa
Pa
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Identify the elements discovered by Marie Curie.
A) polonium and radium
B) radium and cesium
C) argon and xenon
D) radon and xenon
E) selenium and tungsten
A) polonium and radium
B) radium and cesium
C) argon and xenon
D) radon and xenon
E) selenium and tungsten

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Positrons are similar in ionizing power and penetrating power to beta particles.
B) A positron is the antiparticle of the electron.
C) Beta decay occurs when a neutron changes into a proton while emitting an electron.
D) An alpha particle is a helium 2+ ion.
E) All of the above are true.
A) Positrons are similar in ionizing power and penetrating power to beta particles.
B) A positron is the antiparticle of the electron.
C) Beta decay occurs when a neutron changes into a proton while emitting an electron.
D) An alpha particle is a helium 2+ ion.
E) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of 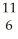 C.
C.
A)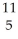 B
B
B)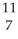 N
N
C)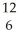 C
C
D) B
B
E) N
N
 C.
C.A)
 B
BB)
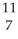 N
NC)
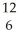 C
CD)
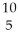 B
BE)
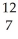 N
N
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following nuclides are most likely to decay via positron emission?
A) Cs-137
B) I-131
C) Al-24
D) K-42
E) N-14
A) Cs-137
B) I-131
C) Al-24
D) K-42
E) N-14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of 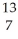 N.
N.
A)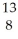 O
O
B)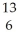 C
C
C)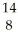 O
O
D)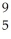 B
B
E)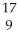 F
F
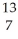 N.
N.A)
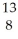 O
OB)
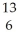 C
CC)
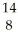 O
OD)
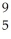 B
BE)
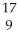 F
F
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The age of an ancient tree trunk is estimated using radiocarbon dating.If the trunk has a C-14 decay rate that is 34% of what it is in living plants,how old is the trunk? The half-life of C-14 is 5730 years.
A) 2.92 × 104 years
B) 1.94 × 104 years
C) 8.92 × 103 years
D) 5.31 × 103 years
E) 1.74 × 102 years
A) 2.92 × 104 years
B) 1.94 × 104 years
C) 8.92 × 103 years
D) 5.31 × 103 years
E) 1.74 × 102 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An archaeologist graduate student found a leg bone of a large animal during the building of a new science building.The bone had a carbon-14 decay rate of 14.8 disintegrations per minute per gram of carbon.Living organisms have a decay rate of 15.3 disintegrations per minute.How old is the bone?
A) 53.3 years
B) 275 years
C) 111 years
D) 25 years
E) 83 years
A) 53.3 years
B) 275 years
C) 111 years
D) 25 years
E) 83 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Write a nuclear equation to describe the neutron induced fission of U-235 to form Xe-134 and Sr-100.Determine how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.
A) 4
B) 3
C) 1
D) 0
E) 2
A) 4
B) 3
C) 1
D) 0
E) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
the atomic bomb has the power of ________ tons of dynamite.
A) 18.,000
B) 22,000
C) 50,000
D) 10,000
E) 15,000
A) 18.,000
B) 22,000
C) 50,000
D) 10,000
E) 15,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Identify the instrument(s)used to detect radiation.
A) film-badge dosimeter
B) Geiger-Muller counter
C) scintillation counter
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) film-badge dosimeter
B) Geiger-Muller counter
C) scintillation counter
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Identify the elements used in radiometric dating.
A) carbon-14 to nitrogen-14
B) uranium-238 to lead-206
C) potassium-40 to argon-40
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) carbon-14 to nitrogen-14
B) uranium-238 to lead-206
C) potassium-40 to argon-40
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The nuclide As-76 has a half-life of 26.0 hours.If a sample of As-76 weighs 344 g,what mass of As-76 remains after 538 minutes?
A) 67.8 g
B) 271 g
C) 144 g
D) 437 g
E) 251 g
A) 67.8 g
B) 271 g
C) 144 g
D) 437 g
E) 251 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Calculate the mass defect in Fe-56 if the mass of an Fe-56 nucleus is 55.921 amu.The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and the mass of a neutron is 1.008665 amu.
A) 0.528 amu
B) 3.507 amu
C) 0.564 amu
D) 1.056 amu
E) 0.079 amu
A) 0.528 amu
B) 3.507 amu
C) 0.564 amu
D) 1.056 amu
E) 0.079 amu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Identify the technique used to predict the age of the Shroud of Turin.
A) uranium-238 to lead-206
B) potassium-40 to argon-40
C) carbon-14 to nitrogen-14
D) none of the above
E) all of the above
A) uranium-238 to lead-206
B) potassium-40 to argon-40
C) carbon-14 to nitrogen-14
D) none of the above
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Define mass defect.
A) the difference in mass between an atom and the sum of its separate components
B) an atom with too many neutrons
C) the difference in mass between a radioactive atom and a nonradioactive atom
D) energy released in a radioactive reaction
E) energy absorbed in a radioactive reaction
A) the difference in mass between an atom and the sum of its separate components
B) an atom with too many neutrons
C) the difference in mass between a radioactive atom and a nonradioactive atom
D) energy released in a radioactive reaction
E) energy absorbed in a radioactive reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The splitting of the uranium atom is an example of
A) radioactive cleavage.
B) nuclear fission.
C) nuclear fusion.
D) radioactive merge.
E) half-life.
A) radioactive cleavage.
B) nuclear fission.
C) nuclear fusion.
D) radioactive merge.
E) half-life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Write a nuclear equation to describe the neutron induced fission of 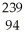 Pu to form
Pu to form 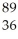 Kr and
Kr and 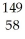 Ce.Determine how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.
Ce.Determine how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.
A) 2
B) 0
C) 3
D) 1
E) 4
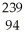 Pu to form
Pu to form 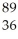 Kr and
Kr and 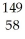 Ce.Determine how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.
Ce.Determine how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.A) 2
B) 0
C) 3
D) 1
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Write a nuclear equation to describe the spontaneous fission of 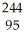 Am to form I-134 and Mo-107.Determine how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.
Am to form I-134 and Mo-107.Determine how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
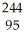 Am to form I-134 and Mo-107.Determine how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.
Am to form I-134 and Mo-107.Determine how many neutrons are produced in the reaction.A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A geological sample is found to have a Pb-206/U-238 mass ratio of 0.337/1.00.Assuming there was no Pb-206 present when the sample was formed,how old is it? The half-life of U-238 is 4.5 × 109 years.
A) 7.3 × 1011 years
B) 1.4 × 1010 years
C) 2.4 × 1010 years
D) 2.1 × 109 years
E) 7.1 × 109 years
A) 7.3 × 1011 years
B) 1.4 × 1010 years
C) 2.4 × 1010 years
D) 2.1 × 109 years
E) 7.1 × 109 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Fluorine-18 undergoes positron emission with a half-life of 1.10 × 102 minutes.If a patient is given a 248 mg dose for a PET scan,how long will it take for the amount of fluorine-18 to drop to 83 mg? (Assume that none of the fluorine is excreted from the body.)
A) 99 minutes
B) 1.74 × 102 minutes
C) 1.32 × 102 minutes
D) 3.00 × 102 minutes
E) 2.11 × 102 minutes
A) 99 minutes
B) 1.74 × 102 minutes
C) 1.32 × 102 minutes
D) 3.00 × 102 minutes
E) 2.11 × 102 minutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The splitting of a heavy nucleus to form two or more lighter ones is called
A) radioactive cleavage.
B) nuclear fission.
C) nuclear fusion.
D) radioactive merge.
E) half-life.
A) radioactive cleavage.
B) nuclear fission.
C) nuclear fusion.
D) radioactive merge.
E) half-life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Calculate the mass defect in Mo-96 if the mass of a Mo-96 nucleus is 95.962 amu.The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and the mass of a neutron is 1.008665 amu.
A) 0.197 amu
B) 0.795 amu
C) 0.212 amu
D) 0.812 amu
E) 0.188 amu
A) 0.197 amu
B) 0.795 amu
C) 0.212 amu
D) 0.812 amu
E) 0.188 amu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Identify the nuclide that has the shortest half-life.
A)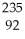 U
U
B)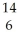 C
C
C)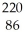 Rn
Rn
D)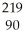 Th
Th
E)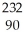 Th
Th
A)
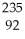 U
UB)
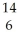 C
CC)
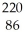 Rn
RnD)
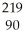 Th
ThE)
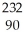 Th
Th
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Give the goal of the Manhattan project.
A) to build an hydrogen bomb
B) to build the first particle accelerator at Cornell
C) to build an atomic bomb
D) to build the first nuclear reactor to generate electricity for Manhattan
E) to set up the electrification of Manhattan using DC current
A) to build an hydrogen bomb
B) to build the first particle accelerator at Cornell
C) to build an atomic bomb
D) to build the first nuclear reactor to generate electricity for Manhattan
E) to set up the electrification of Manhattan using DC current

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Identify the nuclide that has the longest half-life.
A)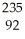 U
U
B)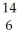 C
C
C)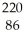 Rn
Rn
D)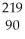 Th
Th
E)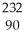 Th
Th
A)
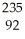 U
UB)
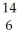 C
CC)
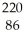 Rn
RnD)
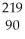 Th
ThE)
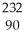 Th
Th
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Identify the radioactive green light that glows in the dark.
A) phenol red
B) radioactivity
C) phosphorescence
D) desensitivity
E) argon
A) phenol red
B) radioactivity
C) phosphorescence
D) desensitivity
E) argon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Determine the binding energy of an O-16 nucleus.The O-16 nucleus has a mass of 15.9905 amu.A proton has a mass of 1.00728 amu,a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 amu,and 1 amu is equivalent to 931 MeV of energy.
A) 8.84 MeV
B) 128 MeV
C) 138 MeV
D) 78.1 MeV
E) 38.2 MeV
A) 8.84 MeV
B) 128 MeV
C) 138 MeV
D) 78.1 MeV
E) 38.2 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Identify the radiotracer used to study the thyroid.
A) iron-59
B) phosphorus-32
C) thallium-201
D) iodine-131
E) fluorine-18
A) iron-59
B) phosphorus-32
C) thallium-201
D) iodine-131
E) fluorine-18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In a linear accelerator,
A) an uncharged particle is accelerated in an evacuated tube.
B) a similarly alternating voltage is used to accelerate a charged particle.
C) a charged particle is accelerated in an evacuated tube.
D) a single phase voltage is used to accelerate a charged particle.
E) a similarly alternating voltage is used to accelerate an uncharged particle.
A) an uncharged particle is accelerated in an evacuated tube.
B) a similarly alternating voltage is used to accelerate a charged particle.
C) a charged particle is accelerated in an evacuated tube.
D) a single phase voltage is used to accelerate a charged particle.
E) a similarly alternating voltage is used to accelerate an uncharged particle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Determine the binding energy per nucleon of an Mg-24 nucleus.The Mg-24 nucleus has a mass of 23.985045.A proton has a mass of 1.00728 amu,a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 amu,and 1 amu is equivalent to 931.5 MeV of energy.
A) 0.3050 MeV
B) 8.83 MeV
C) 0.113 MeV
D) 192 MeV
E) 4.41 MeV
A) 0.3050 MeV
B) 8.83 MeV
C) 0.113 MeV
D) 192 MeV
E) 4.41 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In a cyclotron,
A) an uncharged particle is accelerated in an evacuated tube.
B) a similarly alternating voltage is used to accelerate a charged particle.
C) a charged particle is accelerated in an evacuated tube.
D) a single phase voltage is used to accelerate a charged particle.
E) a similarly alternating voltage is used to accelerate an uncharged particle.
A) an uncharged particle is accelerated in an evacuated tube.
B) a similarly alternating voltage is used to accelerate a charged particle.
C) a charged particle is accelerated in an evacuated tube.
D) a single phase voltage is used to accelerate a charged particle.
E) a similarly alternating voltage is used to accelerate an uncharged particle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Identify the part of the body that can be studied with radiotracers.
A) spleen
B) brain
C) heart
D) tumors
E) all of the above
A) spleen
B) brain
C) heart
D) tumors
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Identify the radiotracer used to study problems with blood.
A) iron-59
B) phosphorus-32
C) thallium-201
D) iodine-131
E) fluorine-18
A) iron-59
B) phosphorus-32
C) thallium-201
D) iodine-131
E) fluorine-18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Identify an alpha particle.
A)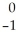 n
n
B)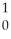 n
n
C)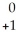 e
e
D)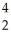 He
He
E)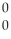 γ
γ
A)
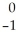 n
nB)
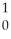 n
nC)
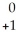 e
eD)
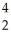 He
HeE)
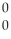 γ
γ
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Define transmutation.
A) the transformation of one element into another
B) the loss of neutrons from an atom
C) the loss of electrons from an atom
D) the loss of protons from an atom
E) the gain of neutrons to an atom
A) the transformation of one element into another
B) the loss of neutrons from an atom
C) the loss of electrons from an atom
D) the loss of protons from an atom
E) the gain of neutrons to an atom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Calculate the mass defect in Ni-59 if the mass of a Ni-59 nucleus is 58.69344 amu.The mass of a proton is 1.00728 amu and the mass of a neutron is 1.008665 amu.
A) 0.232 amu
B) 0.779 amu
C) 0.230 amu
D) 0.775 amu
E) 0.221 amu
A) 0.232 amu
B) 0.779 amu
C) 0.230 amu
D) 0.775 amu
E) 0.221 amu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Identify the lowest natural radiation.
A) cosmic radiation from outer space
B) terrestrial radiation
C) natural radionuclides in the body
D) a five-hour jet airplane ride
E) radon gas
A) cosmic radiation from outer space
B) terrestrial radiation
C) natural radionuclides in the body
D) a five-hour jet airplane ride
E) radon gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The combination of two light nuclei to form a heavier nucleus is called
A) radioactive cleavage.
B) nuclear fission.
C) nuclear fusion.
D) radioactive merge.
E) half-life.
A) radioactive cleavage.
B) nuclear fission.
C) nuclear fusion.
D) radioactive merge.
E) half-life.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which particle changes the mass of the isotope the most?
A) alpha particle
B) neutron particle
C) gamma capture
D) positron emission
E) electron capture
A) alpha particle
B) neutron particle
C) gamma capture
D) positron emission
E) electron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A hydrogen bomb has up to ________ times the explosive force of the first atomic bomb.
A) 2000
B) 1000
C) 500
D) 200
E) 100
A) 2000
B) 1000
C) 500
D) 200
E) 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Identify the highest natural radiation.
A) cosmic radiation from outer space
B) terrestrial radiation
C) natural radionuclides in the body
D) a five-hour jet airplane ride
E) radon gas
A) cosmic radiation from outer space
B) terrestrial radiation
C) natural radionuclides in the body
D) a five-hour jet airplane ride
E) radon gas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Determine the binding energy of an F-19 nucleus.The F-19 nucleus has a mass of 18.99840325 amu.A proton has a mass of 1.00728 amu,a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 amu,and 1 amu is equivalent to 931 MeV of energy.
A) 142 MeV
B) 796 MeV
C) 1080 MeV
D) 143 MeV
E) 145 MeV
A) 142 MeV
B) 796 MeV
C) 1080 MeV
D) 143 MeV
E) 145 MeV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Give the conditions for nuclear fusion.
A) 1 atmosphere
B) catalyst
C) low temperature
D) low pressure
E) high temperature
A) 1 atmosphere
B) catalyst
C) low temperature
D) low pressure
E) high temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Identify the radiotracer used to for PET studies of the heart.
A) iron-59
B) phosphorus-32
C) thallium-201
D) iodine-131
E) fluorine-18
A) iron-59
B) phosphorus-32
C) thallium-201
D) iodine-131
E) fluorine-18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which particle changes the mass of the isotope the least?
A) alpha emission
B) proton capture
C) gamma particle
D) positron capture
E) electron capture
A) alpha emission
B) proton capture
C) gamma particle
D) positron capture
E) electron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe what changes occur during beta decay.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number increases and the atomic number is unchanged.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number increases and the atomic number is unchanged.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Describe what changes occur during alpha decay.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number increases and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number increases and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number increases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of 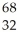 Ge.
Ge.
A)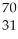 Ga
Ga
B)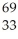 As
As
C)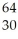 Zn
Zn
D)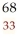 As
As
E)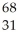 Ga
Ga
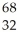 Ge.
Ge.A)
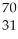 Ga
GaB)
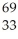 As
AsC)
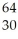 Zn
ZnD)
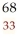 As
AsE)
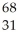 Ga
Ga
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Identify a gamma particle.
A)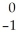 n
n
B)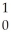 n
n
C)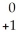 e
e
D)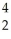 He
He
E)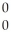 γ
γ
A)
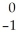 n
nB)
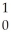 n
nC)
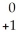 e
eD)
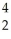 He
HeE)
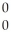 γ
γ
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The following reaction represents what nuclear process? 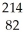 Pb →
Pb → 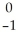 e +
e + 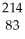 Bi
Bi
A) alpha emission
B) gamma capture
C) electron capture
D) proton capture
E) beta emission
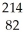 Pb →
Pb → 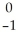 e +
e +  Bi
BiA) alpha emission
B) gamma capture
C) electron capture
D) proton capture
E) beta emission

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Describe what changes occur during gamma ray emission.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number increases and the atomic number decreases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number increases and the atomic number decreases.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Describe what changes occur during positron emission.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number decreases and the atomic number is unchanged.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number decreases and the atomic number is unchanged.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the beta decay of 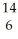 C.
C.
A)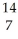 N
N
B)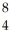 Be
Be
C)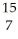 N
N
D)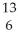 C
C
E)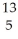 B
B
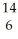 C.
C.A)
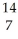 N
NB)
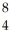 Be
BeC)
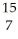 N
ND)
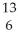 C
CE)
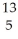 B
B
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the beta decay of 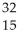 P.
P.
A)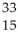 P
P
B)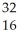 S
S
C)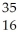 S
S
D)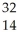 Si
Si
E)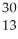 Al
Al
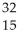 P.
P.A)
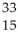 P
PB)
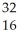 S
SC)
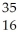 S
SD)
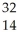 Si
SiE)
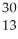 Al
Al
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the alpha decay of 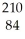 Po.
Po.
A)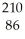 Rn
Rn
B)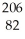 Pb
Pb
C)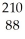 Ra
Ra
D)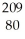 Hg
Hg
E)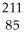 At
At
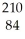 Po.
Po.A)
 Rn
RnB)
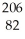 Pb
PbC)
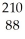 Ra
RaD)
 Hg
HgE)
 At
At
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by  Be.
Be.
A) C
C
B)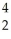 He
He
C)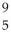 B
B
D)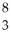 Li
Li
E)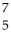 B
B
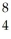 Be.
Be.A)
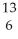 C
CB)
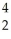 He
HeC)
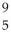 B
BD)
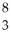 Li
LiE)
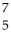 B
B
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Alpha particles have the lowest penetrating power of any radioactivity.
B) Beta radiation has the lowest ionizing power of any radioactivity.
C) Beta emitters will do more damage than alpha emitters within the body.
D) Beta radiation has the highest ionizing power of any radioactivity.
E) None of the above is true.
A) Alpha particles have the lowest penetrating power of any radioactivity.
B) Beta radiation has the lowest ionizing power of any radioactivity.
C) Beta emitters will do more damage than alpha emitters within the body.
D) Beta radiation has the highest ionizing power of any radioactivity.
E) None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Identify a positron.
A)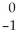 n
n
B)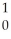 n
n
C)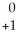 e
e
D)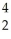 e
e
E)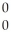 γ
γ
A)
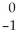 n
nB)
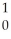 n
nC)
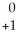 e
eD)
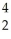 e
eE)
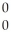 γ
γ
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the positron emission of  F.
F.
A) Na
Na
B) F
F
C) N
N
D)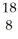 O
O
E)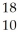 Ne
Ne
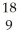 F.
F.A)
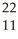 Na
NaB)
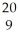 F
FC)
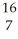 N
ND)
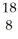 O
OE)
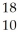 Ne
Ne
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the alpha decay of 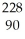 Th.
Th.
A)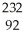 U
U
B)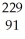 Pa
Pa
C)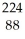 Ra
Ra
D)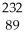 Ac
Ac
E)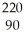 Th
Th
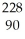 Th.
Th.A)
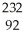 U
UB)
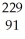 Pa
PaC)
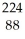 Ra
RaD)
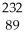 Ac
AcE)
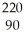 Th
Th
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Determine the identity of the daughter nuclide from the electron capture by 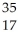 Cl.
Cl.
A)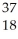 Ar
Ar
B)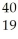 K
K
C)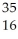 S
S
D)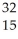 P
P
E)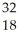 Ar
Ar
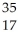 Cl.
Cl.A)
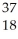 Ar
ArB)
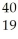 K
KC)
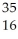 S
SD)
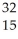 P
PE)
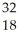 Ar
Ar
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The following reaction represents what nuclear process? 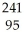 Am →
Am → 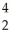 He +
He + 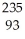 Np
Np
A) beta emission
B) alpha capture
C) alpha emission
D) electron capture
E) positron capture
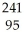 Am →
Am → 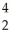 He +
He + 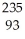 Np
NpA) beta emission
B) alpha capture
C) alpha emission
D) electron capture
E) positron capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Describe what changes occur during electron capture.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number decreases and the atomic number is unchanged.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.
A) The mass number and atomic number decrease.
B) The mass number and atomic number increase.
C) The mass number is unchanged and the atomic number decreases.
D) The mass number decreases and the atomic number is unchanged.
E) The mass number and atomic number do not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The following reaction represents what nuclear process? 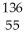 Cs +
Cs + 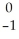 e →
e → 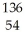 Xe
Xe
A) beta capture
B) positron emission
C) gamma emission
D) electron capture
E) alpha capture
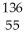 Cs +
Cs + 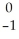 e →
e → 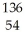 Xe
XeA) beta capture
B) positron emission
C) gamma emission
D) electron capture
E) alpha capture

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Identify a beta particle.
A)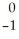 e
e
B)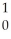 n
n
C)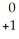 e
e
D)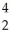 n
n
E)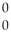 γ
γ
A)
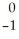 e
eB)
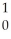 n
nC)
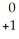 e
eD)
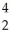 n
nE)
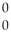 γ
γ
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 136 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



