Deck 15: Chemical Kinetics: the Rates of Chemical Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Chemical Kinetics: the Rates of Chemical Reactions
1
Given the initial rate data for the decomposition reaction,
A B + C
Determine the rate expression for the reaction.
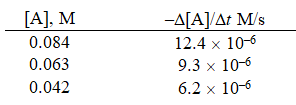
A)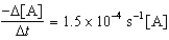
B)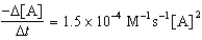
C)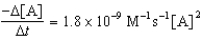
D)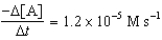
E)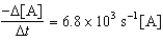
A B + C
Determine the rate expression for the reaction.

A)
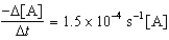
B)
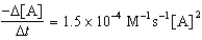
C)
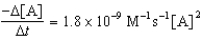
D)
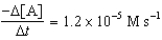
E)
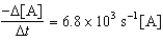
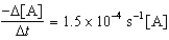
2
Which of the following is/are expected to affect the rate of a chemical reaction?
1)Addition of a catalyst.
2)Increasing the reaction temperature.
3)Doubling the volume of the reaction container.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1,2,and 3
1)Addition of a catalyst.
2)Increasing the reaction temperature.
3)Doubling the volume of the reaction container.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1,2,and 3
1 and 2
3
Nitrosyl chloride is produced from the reaction of nitrogen monoxide and chlorine:
2NO(g)+ Cl2(g) 2NOCl(g)
The following initial rates at a given temperature were obtained for the concentrations listed below.
![<strong>Nitrosyl chloride is produced from the reaction of nitrogen monoxide and chlorine: 2NO(g)+ Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) \to 2NOCl(g) The following initial rates at a given temperature were obtained for the concentrations listed below. What is the experimental rate law?</strong> A) Rate = k[Cl<sub>2</sub>] B) Rate = k[NO] C) Rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> D) Rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>] E) Rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1/2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ec6bcc_8b94_aeb0_ac74_577f687432cd_TB4499_11.jpg)
What is the experimental rate law?
A) Rate = k[Cl2]
B) Rate = k[NO]
C) Rate = k[NO][Cl2]2
D) Rate = k[NO]2[Cl2]
E) Rate = k[NO][Cl2]1/2
2NO(g)+ Cl2(g) 2NOCl(g)
The following initial rates at a given temperature were obtained for the concentrations listed below.
![<strong>Nitrosyl chloride is produced from the reaction of nitrogen monoxide and chlorine: 2NO(g)+ Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) \to 2NOCl(g) The following initial rates at a given temperature were obtained for the concentrations listed below. What is the experimental rate law?</strong> A) Rate = k[Cl<sub>2</sub>] B) Rate = k[NO] C) Rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> D) Rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>[Cl<sub>2</sub>] E) Rate = k[NO][Cl<sub>2</sub>]<sup>1/2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ec6bcc_8b94_aeb0_ac74_577f687432cd_TB4499_11.jpg)
What is the experimental rate law?
A) Rate = k[Cl2]
B) Rate = k[NO]
C) Rate = k[NO][Cl2]2
D) Rate = k[NO]2[Cl2]
E) Rate = k[NO][Cl2]1/2
Rate = k[NO]2[Cl2]
4
What is the name given to a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction but is not itself consumed?
A) catalyst
B) reactant
C) intermediate
D) enthalpy
E) rate constant
A) catalyst
B) reactant
C) intermediate
D) enthalpy
E) rate constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement concerning relative rates of reaction is correct for the chemical equation given below?
2 CH3OH(g)+ 3 O2(g) 2 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
A) The rate of disappearance of CH3OH is equal to the rate of disappearance of O2.
B) The rate of disappearance of CH3OH is two times the rate of appearance of H2O.
C) The rate of disappearance of CH3OH is half the rate of appearance of CO2.
D) The rate of appearance of H2O is two times the rate of appearance of CO2.
E) The rate of appearance of H2O is four times the rate of disappearance of CH3OH.
2 CH3OH(g)+ 3 O2(g) 2 CO2(g)+ 4 H2O(g)
A) The rate of disappearance of CH3OH is equal to the rate of disappearance of O2.
B) The rate of disappearance of CH3OH is two times the rate of appearance of H2O.
C) The rate of disappearance of CH3OH is half the rate of appearance of CO2.
D) The rate of appearance of H2O is two times the rate of appearance of CO2.
E) The rate of appearance of H2O is four times the rate of disappearance of CH3OH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following conclusions concerning the concentration-time plot provided below is/are correct?
1)The concentration of substance D is decreasing over time.
2)The instantaneous reaction rate at point A is less than the instantaneous reaction rate at point B.
3)Substance D is a product of the reaction.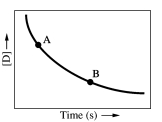
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3
1)The concentration of substance D is decreasing over time.
2)The instantaneous reaction rate at point A is less than the instantaneous reaction rate at point B.
3)Substance D is a product of the reaction.

A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
For the reaction provided,the rate of disappearance of IO3-(aq)at a particular time and concentration is 2.3 10-3 mol/L·s.
IO3-(aq)+ 5I-(aq) + 6H+(aq) 3I2(aq)+ 3H2O(l)
What is the relative rate of appearance of I2(aq)?
A) 7.7 10-3 mol/L·s
B) 2.3 10-3 mol/L·s
C) -6.9 10-3 mol/L·s
D) 6.9 10-3 mol/L·s
E) 1.3 10-3 mol/L·s
IO3-(aq)+ 5I-(aq) + 6H+(aq) 3I2(aq)+ 3H2O(l)
What is the relative rate of appearance of I2(aq)?
A) 7.7 10-3 mol/L·s
B) 2.3 10-3 mol/L·s
C) -6.9 10-3 mol/L·s
D) 6.9 10-3 mol/L·s
E) 1.3 10-3 mol/L·s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Given the initial rate data for the reaction A + B C,determine the rate expression for the reaction.
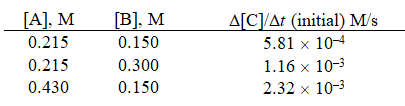
A)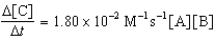
B)
C)
D)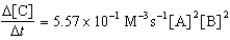
E)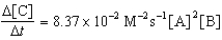

A)
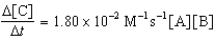
B)

C)

D)
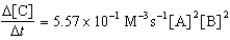
E)
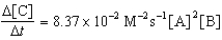

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Assume the reaction below
2 NO(g)+ O2(g) 2 NO2(g)
Proceeds via the following rate expression: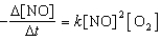
Which of the following statements concerning the above chemical reaction and rate equation is/are CORRECT?
1)The reaction is second-order with respect to NO.
2)The rate of disappearance of O2 is two times the rate of appearance of NO2.
3)According to the balanced chemical equation,the reaction is fifth-order overall.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3
2 NO(g)+ O2(g) 2 NO2(g)
Proceeds via the following rate expression:
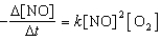
Which of the following statements concerning the above chemical reaction and rate equation is/are CORRECT?
1)The reaction is second-order with respect to NO.
2)The rate of disappearance of O2 is two times the rate of appearance of NO2.
3)According to the balanced chemical equation,the reaction is fifth-order overall.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The following data were obtained in a kinetics study of the hypothetical reaction A + B + C products.
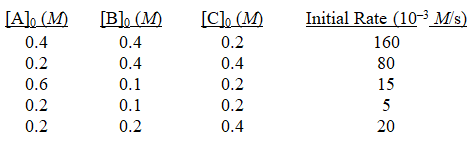
Using the initial-rate method,what is the order of the reaction with respect to B?
A) zero-order
B) first-order
C) second-order
D) third-order
E) impossible to tell from the data given

Using the initial-rate method,what is the order of the reaction with respect to B?
A) zero-order
B) first-order
C) second-order
D) third-order
E) impossible to tell from the data given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Given the initial rate data for the reaction A + B C,determine the rate expression for the reaction.
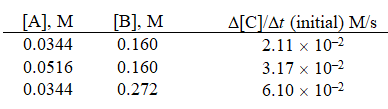
A)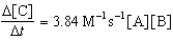
B)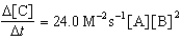
C)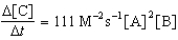
D)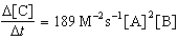
E)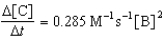

A)
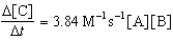
B)
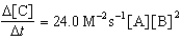
C)
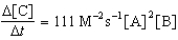
D)
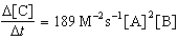
E)
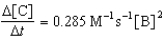

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the overall order of the reaction below
NO(g)+ O3(g) NO2(g)+ O2(g)
If it proceeds via the following rate expression?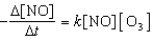
A) zero-order
B) first-order
C) second-order
D) third-order
E) fourth-order
NO(g)+ O3(g) NO2(g)+ O2(g)
If it proceeds via the following rate expression?
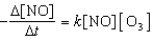
A) zero-order
B) first-order
C) second-order
D) third-order
E) fourth-order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following expressions does not represent a proper expression for the rate of this reaction?
2A + 3B F + 2G
A)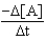
B)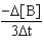
C)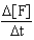
D)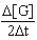
E)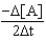
2A + 3B F + 2G
A)
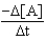
B)
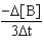
C)
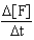
D)
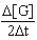
E)
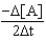

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
For a certain overall third-order reaction with the general form aA products,the initial rate of reaction is 0.42 M·s-1 when the initial concentration of the reactant is 0.25 M.What is the rate constant for this reaction?
A) 0.0093 M-2.s-1
B) 27 M-2.s-1
C) 0.42 M-2.s-1
D) 0.15 M-2.s-1
E) 110 M-2.s-1
A) 0.0093 M-2.s-1
B) 27 M-2.s-1
C) 0.42 M-2.s-1
D) 0.15 M-2.s-1
E) 110 M-2.s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider the exothermic combustion of coal.Which of the following could increase the rate of reaction?
A) using smaller pieces of coal
B) increasing the concentration of oxygen
C) lowering the temperature
D) both (a)and (b)are correct
E) choices (a),(b)and (c)are all correct
A) using smaller pieces of coal
B) increasing the concentration of oxygen
C) lowering the temperature
D) both (a)and (b)are correct
E) choices (a),(b)and (c)are all correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The rate law for a reaction is rate = k[A]2[B].Which of the following mixtures of reactants will give the
A) 1.0 M A,1.0 M B
B) 2.0 M A,0.50 M B
C) 0.50 M A,0.50 M B
D) 0.125 M A,3.0 M B
E) 1.5 M A,0.50 M B
A) 1.0 M A,1.0 M B
B) 2.0 M A,0.50 M B
C) 0.50 M A,0.50 M B
D) 0.125 M A,3.0 M B
E) 1.5 M A,0.50 M B

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which relationship correctly compares the rates of the following reactants and products?
2 NOCl(g) 2 NO(g)+ Cl2(g)
A)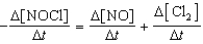
B)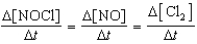
C)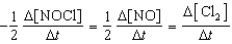
D)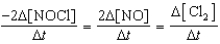
E)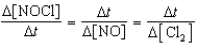
2 NOCl(g) 2 NO(g)+ Cl2(g)
A)
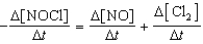
B)
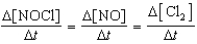
C)
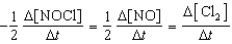
D)
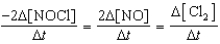
E)
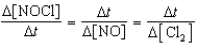

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The average rate of disappearance of ozone in the following reaction is found to be 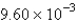 atm/s.
atm/s. 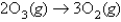
What is the rate of appearance of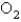
During this interval?
A)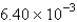 atm/s
atm/s
B)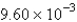 atm/s
atm/s
C)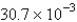 atm/s
atm/s
D)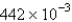 atm/s
atm/s
E)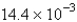 atm/s
atm/s
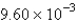 atm/s.
atm/s. 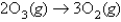
What is the rate of appearance of
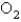
During this interval?
A)
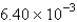 atm/s
atm/sB)
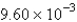 atm/s
atm/sC)
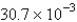 atm/s
atm/sD)
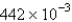 atm/s
atm/sE)
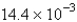 atm/s
atm/s
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The reactants A and B are mixed,and the reaction is timed until a color change occurs.The data are as follows:
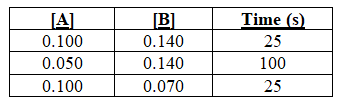
The order of the reaction with respect to reactant A is
A) 2.
B)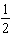 .
.
C) 1.
D)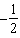 .
.
E) 0.

The order of the reaction with respect to reactant A is
A) 2.
B)
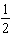 .
.C) 1.
D)
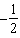 .
.E) 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a reaction is third-order with respect to a particular reactant,when the concentration of that reactant is decreased by a factor of 2,the reaction rate will _____.
A) decrease by a factor of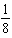 .
.
B) remain constant.
C) increase by a factor of 8.
D) decrease by a factor of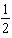 .
.
E) increase by a factor of 4.
A) decrease by a factor of
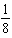 .
.B) remain constant.
C) increase by a factor of 8.
D) decrease by a factor of
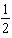 .
.E) increase by a factor of 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How are the exponents in a rate law determined?
A) They are equal to the inverse of the coefficients in the overall balanced chemical equation.
B) They are determined by experimentation.
C) They are equal to the coefficients in the overall balanced chemical equation.
D) They are equal to the reactant concentrations.
E) They are equal to the ln(2)divided by the rate constant.
A) They are equal to the inverse of the coefficients in the overall balanced chemical equation.
B) They are determined by experimentation.
C) They are equal to the coefficients in the overall balanced chemical equation.
D) They are equal to the reactant concentrations.
E) They are equal to the ln(2)divided by the rate constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
For the first-order decomposition of N2O5 at a high temperature,determine the rate constant if the N2O5 concentration decreases from 1.04 M to 0.62 M in 375 seconds.
A) 5.99 10-4 s-1
B) 1.59 10-3 s-1
C) 1.74 10-3 s-1
D) 1.38 10-3 s-1
E) 1.94 102 s-1
A) 5.99 10-4 s-1
B) 1.59 10-3 s-1
C) 1.74 10-3 s-1
D) 1.38 10-3 s-1
E) 1.94 102 s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Given the initial rate data for the reaction A + B C,determine the rate expression for the reaction.

A)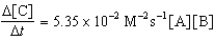
B)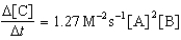
C)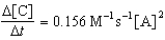
D)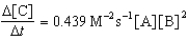
E)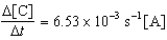

A)
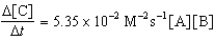
B)
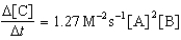
C)
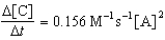
D)
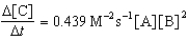
E)
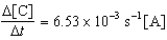

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In a first-order reaction,the half-life is 137 minutes.What is the rate constant?
A) 1.22 10-4 s-1
B) 5790 s-1
C) 0.304 s-1
D) 5.06 10-3 s-1
E) 8.43 10-5 s-1
A) 1.22 10-4 s-1
B) 5790 s-1
C) 0.304 s-1
D) 5.06 10-3 s-1
E) 8.43 10-5 s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following units are consistent with the units of the reaction rate in a first order reaction?
A)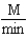
B)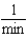
C)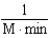
D)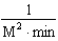
E)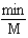
A)
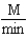
B)
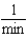
C)
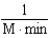
D)
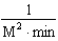
E)
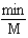

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
For a reaction,A B + C,which of the following equations corresponds to the integrated expression for a second-order decomposition reaction?
A)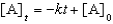
B)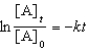
C)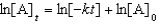
D)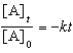
E)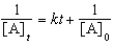
A)
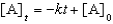
B)
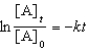
C)
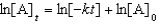
D)
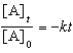
E)
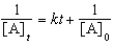

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is a correct representation of the integrated rate expression for a decomposition first-order reaction?
A)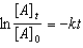
B)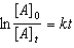
C)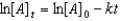
D)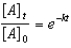
E)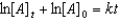
A)
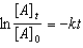
B)
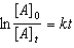
C)
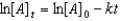
D)
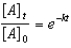
E)
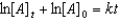

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
For a certain reaction of the general form aA products,the experimental data plotted as [A] versus time is linear.The slope of this plot must equal
A) -1.
B) the negative of the rate constant.
C) one over the rate constant.
D) the rate constant.
E) 1.
A) -1.
B) the negative of the rate constant.
C) one over the rate constant.
D) the rate constant.
E) 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The reaction of NO and O2 produces NO2.
2 NO(g)+ O2(g) 2 NO2(g)
The reaction is second-order with respect to NO(g)and first-order with respect to O2(g).At a given temperature,the rate constant,k,equals 4.7 102 M-2s-1.What is the rate of reaction when the initial concentrations of NO and O2 are 0.025 M and 0.015 M,respectively?
A) 2.6 10-3 M/s
B) 4.4 10-3 M/s
C) 0.18 M/s
D) 2.0 10-8 M/s
E) 3.8 102 M/s
2 NO(g)+ O2(g) 2 NO2(g)
The reaction is second-order with respect to NO(g)and first-order with respect to O2(g).At a given temperature,the rate constant,k,equals 4.7 102 M-2s-1.What is the rate of reaction when the initial concentrations of NO and O2 are 0.025 M and 0.015 M,respectively?
A) 2.6 10-3 M/s
B) 4.4 10-3 M/s
C) 0.18 M/s
D) 2.0 10-8 M/s
E) 3.8 102 M/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
For the reaction 2A + B C,the rate law is
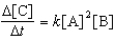 .
.
Which of the factor(s)will affect the value of the for this reaction?
1)decreasing the temperature
2)adding a catalyst
3)decreasing the concentration of reactant A
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 2 and 3
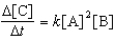 .
.Which of the factor(s)will affect the value of the for this reaction?
1)decreasing the temperature
2)adding a catalyst
3)decreasing the concentration of reactant A
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 2 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
At a given temperature,a first-order reaction has a rate constant of 3.5 10-3 s-1.How long will it take for the reaction to be 24% complete?
A) 410 s
B) 1200 s
C) 910 s
D) 34 s
E) 78 s
A) 410 s
B) 1200 s
C) 910 s
D) 34 s
E) 78 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A student analyzed a first-order reaction and obtained the graph below.Unfortunately,the student forgot to label the axes.What are the correct labels for the x and y axes? ![<strong>A student analyzed a first-order reaction and obtained the graph below.Unfortunately,the student forgot to label the axes.What are the correct labels for the x and y axes? </strong> A) x axis = time,y axis = ln[A] B) x axis = ln[time] ,y axis = [A] C) x axis = ln[time],y axis = [A] D) x axis = time,y axis = 1/[A] E) x axis = 1/time,y axis = 1/[A]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7b_437e_a16d_4715c254541c_TB4499_00.jpg)
A) x axis = time,y axis = ln[A]
B) x axis = ln[time] ,y axis = [A]
C) x axis = ln[time],y axis = [A]
D) x axis = time,y axis = 1/[A]
E) x axis = 1/time,y axis = 1/[A]
![<strong>A student analyzed a first-order reaction and obtained the graph below.Unfortunately,the student forgot to label the axes.What are the correct labels for the x and y axes? </strong> A) x axis = time,y axis = ln[A] B) x axis = ln[time] ,y axis = [A] C) x axis = ln[time],y axis = [A] D) x axis = time,y axis = 1/[A] E) x axis = 1/time,y axis = 1/[A]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7b_437e_a16d_4715c254541c_TB4499_00.jpg)
A) x axis = time,y axis = ln[A]
B) x axis = ln[time] ,y axis = [A]
C) x axis = ln[time],y axis = [A]
D) x axis = time,y axis = 1/[A]
E) x axis = 1/time,y axis = 1/[A]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The rate constant for a particular reaction is 0.0040 M.s-1.What is the overall order of this reaction?
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4
A) 0
B) 1
C) 2
D) 3
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The reaction A B follows first-order kinetics with a half-life of 21.7 hours.If the concentration of A is 0.023 M after 48.0 hours,what is the initial concentration of A?
A) 0.0050 M
B) 0.051 M
C) 0.51 M
D) 0.11 M
E) 2.0 102 M
A) 0.0050 M
B) 0.051 M
C) 0.51 M
D) 0.11 M
E) 2.0 102 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements is correct for the first-order reaction: A 2B?
A) The concentration of A decreases linearly with respect to time.
B) The concentration of A is constant with respect to time.
C) The natural logarithm of the concentration of A decreases linearly with respect to time.
D) The rate of reaction is constant with respect to time.
E) The rate constant,k,of the reaction decreases linearly with respect to time.
A) The concentration of A decreases linearly with respect to time.
B) The concentration of A is constant with respect to time.
C) The natural logarithm of the concentration of A decreases linearly with respect to time.
D) The rate of reaction is constant with respect to time.
E) The rate constant,k,of the reaction decreases linearly with respect to time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A first-order chemical reaction is observed to have a rate constant of 34 min-1.What is the corresponding half-life for the reaction?
A) 1.2 s
B) 1.2 min
C) 49 min
D) 1.8 s
E) 48.6 s
A) 1.2 s
B) 1.2 min
C) 49 min
D) 1.8 s
E) 48.6 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
For which of the following hypothetical rate laws would the units of the rate constant have the general form M-2.h-1?
A) rate = k[A]3
B) rate = k[A]2
C) rate = k[A]
D) rate = k
E) rate = k[A]4
A) rate = k[A]3
B) rate = k[A]2
C) rate = k[A]
D) rate = k
E) rate = k[A]4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The rate constant of a first-order decomposition reaction is 0.0147 s-1.If the initial concentration of reactant is 0.178 M,what is the concentration of reactant after 30.0 seconds?
A) 8.72 105 M
B) 0.0645 M
C) 0.115 M
D) 0.0785 M
E) 0.643 M
A) 8.72 105 M
B) 0.0645 M
C) 0.115 M
D) 0.0785 M
E) 0.643 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
For the reaction A + 2B C,the rate law is
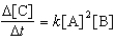 .
.
What are the units of the rate constant where time is measured in seconds?
A)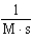
B)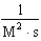
C)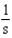
D)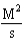
E)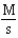
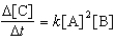 .
.What are the units of the rate constant where time is measured in seconds?
A)
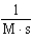
B)
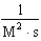
C)
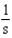
D)
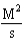
E)
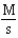

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
For a certain reaction of the general form aA products,a plot of the experimental data as 1/[A] versus time is linear.What is the reaction order with respect to reactant A?
A) zero
B) first
C) second
D) third
E) fourth
A) zero
B) first
C) second
D) third
E) fourth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The rate constant at 366 K for a first-order reaction is 7.7 10-3 s-1 and the activation energy is 15.9 kJ/mol.What is the value of the frequency factor,A,in the Arrhenius equation? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 0.0047 s-1
B) 0.70 s-1
C) 0.93 s-1
D) 1.1 s-1
E) 1.4 s-1
A) 0.0047 s-1
B) 0.70 s-1
C) 0.93 s-1
D) 1.1 s-1
E) 1.4 s-1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Arrhenius equation, 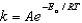 expresses the dependence of the rate constant on the reaction temperature.The slope of a plot of ln(k)versus 1/T is equal to
expresses the dependence of the rate constant on the reaction temperature.The slope of a plot of ln(k)versus 1/T is equal to
A)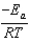
B)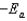
C)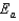
D)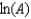
E)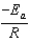
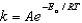 expresses the dependence of the rate constant on the reaction temperature.The slope of a plot of ln(k)versus 1/T is equal to
expresses the dependence of the rate constant on the reaction temperature.The slope of a plot of ln(k)versus 1/T is equal toA)
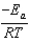
B)
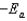
C)
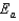
D)
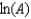
E)
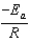

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
For the hypothetical reaction aA products,the experimental data showed the following behavior (below).What is the reaction order with respect to reactant A? 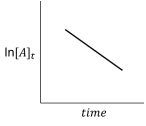
A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

A) zero order
B) first order
C) second order
D) third order
E) fourth order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For a chemical reaction,the activation energy for the forward reaction is +181 kJ and the activation energy for the backward reaction is +62 kJ.What is the overall energy change for the forward reaction?
A) -119 kJ
B) -62 kJ
C) +119 kJ
D) +181 kJ
E) +243 kJ
A) -119 kJ
B) -62 kJ
C) +119 kJ
D) +181 kJ
E) +243 kJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The decomposition of formic acid follows first-order kinetics.
HCO2H(g) CO2(g)+ H2(g)
The half-life for the reaction at 550 C is 24 seconds.How many seconds does it take for the formic acid concentration to decrease by 87.5%?
A) 24 s
B) 36 s
C) 48 s
D) 72 s
E) 96 s
HCO2H(g) CO2(g)+ H2(g)
The half-life for the reaction at 550 C is 24 seconds.How many seconds does it take for the formic acid concentration to decrease by 87.5%?
A) 24 s
B) 36 s
C) 48 s
D) 72 s
E) 96 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Molecules must overcome a barrier called the activation energy if they are to react.The highest energy point reached during the progress of a reaction is called the ____.
A) rate determining step
B) transition state
C) half-life
D) elementary step
E) intermediate state
A) rate determining step
B) transition state
C) half-life
D) elementary step
E) intermediate state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For the formation of 1 mol of nitrosyl chloride at a given temperature, rH = -36 kJ/mol.
NO(g)+ ½ Cl2(g) NOCl(g)
The activation energy for this reaction is 67 kJ/mol.What is the activation energy for the reverse reaction?
A) 67 kJ/mol
B) 31 kJ/mol
C) 103 kJ/mol
D) -36 kJ/mol
E) -103 kJ/mol
NO(g)+ ½ Cl2(g) NOCl(g)
The activation energy for this reaction is 67 kJ/mol.What is the activation energy for the reverse reaction?
A) 67 kJ/mol
B) 31 kJ/mol
C) 103 kJ/mol
D) -36 kJ/mol
E) -103 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The decomposition of phosphine,PH3,follows first-order kinetics.
4 PH3(g) P4(g)+ 6 H2(g)
The half-life for the reaction at 550 C is 81.3 seconds.What percentage of phosphine remains after 195 seconds?
A) 2.2%
B) 9.8%
C) 19%
D) 42%
E) 58%
4 PH3(g) P4(g)+ 6 H2(g)
The half-life for the reaction at 550 C is 81.3 seconds.What percentage of phosphine remains after 195 seconds?
A) 2.2%
B) 9.8%
C) 19%
D) 42%
E) 58%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A second-order reaction starts with an initial concentration of 0.100 mol/L of the reactant.If the rate constant is 1.4 10-2 L/mol·s,what is the time required to decrease the initial concentration to 0.050 mol/L?
2A B rate = k[A]2
A) 710 s
B) 1100 s
C) 49.5 s
D) 3.57 s
E) 2100 s
2A B rate = k[A]2
A) 710 s
B) 1100 s
C) 49.5 s
D) 3.57 s
E) 2100 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For the zero-order reaction below,a graph of ____ versus time will generate a straight line.
A B + C rate = k[A]0
A) [A]t
B)![<strong>For the zero-order reaction below,a graph of ____ versus time will generate a straight line. A \to B + C ~~~~~~~~ rate = k[A]<sup>0</sup></strong> A) [A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) ln[A]<sub>t</sub> D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7c_06db_a16d_5ba0b94cbe49_TB4499_11.jpg)
C) ln[A]t
D)![<strong>For the zero-order reaction below,a graph of ____ versus time will generate a straight line. A \to B + C ~~~~~~~~ rate = k[A]<sup>0</sup></strong> A) [A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) ln[A]<sub>t</sub> D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7c_06dc_a16d_7ba59b0e098b_TB4499_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>For the zero-order reaction below,a graph of ____ versus time will generate a straight line. A \to B + C ~~~~~~~~ rate = k[A]<sup>0</sup></strong> A) [A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) ln[A]<sub>t</sub> D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7c_06dd_a16d_bfc531617fe7_TB4499_11.jpg)
A B + C rate = k[A]0
A) [A]t
B)
![<strong>For the zero-order reaction below,a graph of ____ versus time will generate a straight line. A \to B + C ~~~~~~~~ rate = k[A]<sup>0</sup></strong> A) [A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) ln[A]<sub>t</sub> D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7c_06db_a16d_5ba0b94cbe49_TB4499_11.jpg)
C) ln[A]t
D)
![<strong>For the zero-order reaction below,a graph of ____ versus time will generate a straight line. A \to B + C ~~~~~~~~ rate = k[A]<sup>0</sup></strong> A) [A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) ln[A]<sub>t</sub> D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7c_06dc_a16d_7ba59b0e098b_TB4499_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>For the zero-order reaction below,a graph of ____ versus time will generate a straight line. A \to B + C ~~~~~~~~ rate = k[A]<sup>0</sup></strong> A) [A]<sub>t</sub> B) C) ln[A]<sub>t</sub> D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7c_06dd_a16d_bfc531617fe7_TB4499_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In general,as temperature increases,the rate of a chemical reaction
A) decreases due to fewer collisions with proper molecular orientation.
B) increases for exothermic reactions,but decreases for endothermic reactions.
C) increases due to a greater number of effective collisions.
D) remains unchanged.
E) decreases due to an increase in the activation energy.
A) decreases due to fewer collisions with proper molecular orientation.
B) increases for exothermic reactions,but decreases for endothermic reactions.
C) increases due to a greater number of effective collisions.
D) remains unchanged.
E) decreases due to an increase in the activation energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Calculate the activation energy,Ea,for
N2O5(g) 2 NO2(g)+ 1/2 O2(g)
Given k (at 45.0 C)= 5.79 10-4 s-1 and k (at 60.0 C)= 3.83 10-3 s-1.(R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 0.256 kJ/mol
B) 2.83 kJ/mol
C) 31.1 kJ/mol
D) 111 kJ/mol
E) 389 kJ/mol
N2O5(g) 2 NO2(g)+ 1/2 O2(g)
Given k (at 45.0 C)= 5.79 10-4 s-1 and k (at 60.0 C)= 3.83 10-3 s-1.(R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 0.256 kJ/mol
B) 2.83 kJ/mol
C) 31.1 kJ/mol
D) 111 kJ/mol
E) 389 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Hydrogen peroxide decomposes into water and oxygen in a first-order process.H2O2(aq) H2O( 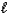 )+ 1/2 O2(g)
)+ 1/2 O2(g)
At 20.0 C,the half-life for the reaction is 3.92 104 seconds.If the initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide is 0.52 M,what is the concentration after 7.00 days?
A) 1.2 10-5 M
B) 0.034 M
C) 0.074 M
D) 0.22 M
E) 0.52 M
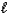 )+ 1/2 O2(g)
)+ 1/2 O2(g)At 20.0 C,the half-life for the reaction is 3.92 104 seconds.If the initial concentration of hydrogen peroxide is 0.52 M,what is the concentration after 7.00 days?
A) 1.2 10-5 M
B) 0.034 M
C) 0.074 M
D) 0.22 M
E) 0.52 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
For the second-order reaction below,the initial concentration of reactant A is 0.24 M.If the rate constant for the reaction is 1.5 10-2 M-1s-1,what is the concentration of A after 265 seconds?
2A B + C rate = k[A]2
A) 0.12 M
B) 0.19 M
C) 0.95 M
D) 4.0 M
E) 5.2 M
2A B + C rate = k[A]2
A) 0.12 M
B) 0.19 M
C) 0.95 M
D) 4.0 M
E) 5.2 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The rate constant for a first-order reaction is 1.4 10-2 s-1 at 716 K and 5.5 10-2 s-1 at 864 K.What is the activation energy? (R = 8.314 J/K.mol)
A) 27 kJ/mol
B) 21 kJ/mol
C) 47 kJ/mol
D) 5700 kJ/mol
E) 48 kJ/mol
A) 27 kJ/mol
B) 21 kJ/mol
C) 47 kJ/mol
D) 5700 kJ/mol
E) 48 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The Arrhenius equation, 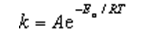 ,relates the rate constant of reaction and temperature.A plot of ____ versus 1/T will yield a straight line with a slope of -Ea/R.
,relates the rate constant of reaction and temperature.A plot of ____ versus 1/T will yield a straight line with a slope of -Ea/R.
A) k2/k1
B) -Ea
C) ln(k)
D)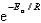
E) 1/RT
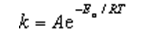 ,relates the rate constant of reaction and temperature.A plot of ____ versus 1/T will yield a straight line with a slope of -Ea/R.
,relates the rate constant of reaction and temperature.A plot of ____ versus 1/T will yield a straight line with a slope of -Ea/R.A) k2/k1
B) -Ea
C) ln(k)
D)
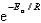
E) 1/RT

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
According to collision theory,which condition(s)must be met in order for molecules to react?
1)The reacting molecules must collide with sufficient energy to initiate the process of breaking and forming bonds.
2)A catalyst must be in contact with the reacting molecules for a reaction to occur.
3)The reacting molecules must collide with an orientation that can lead to rearrangement of the atoms.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1 and 3
1)The reacting molecules must collide with sufficient energy to initiate the process of breaking and forming bonds.
2)A catalyst must be in contact with the reacting molecules for a reaction to occur.
3)The reacting molecules must collide with an orientation that can lead to rearrangement of the atoms.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2
E) 1 and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A first-order reaction is 40.0% complete at the end of 23.9 minutes.What is the value of the rate constant?
A) 3.83 10-2 min-1
B) 2.14 10-2 min-1
C) 26.1 min-1
D) 46.8 min-1
E) none of these
A) 3.83 10-2 min-1
B) 2.14 10-2 min-1
C) 26.1 min-1
D) 46.8 min-1
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The rate constant for a reaction at 40.0°C is exactly 6 times that at 20.0°C.Calculate the Arrhenius energy of activation for the reaction.(R = 8.314 J/K.0mol)
A) 6.00 kJ/mol
B) 8.22 kJ/mol
C) 68.3 kJ/mol
D) 14.9 kJ/mol
E) none of these
A) 6.00 kJ/mol
B) 8.22 kJ/mol
C) 68.3 kJ/mol
D) 14.9 kJ/mol
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the half-life of a first-order reaction if it takes 4.4 10-2 seconds for the concentration to decrease from 0.50 M to 0.20 M?
A) 2.5 10-2 s
B) 3.3 10-2 s
C) 1.6 s
D) 21 s
E) 27 s
A) 2.5 10-2 s
B) 3.3 10-2 s
C) 1.6 s
D) 21 s
E) 27 s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A possible mechanism for the gas phase reaction of NO and H2 is as follows:
![<strong>A possible mechanism for the gas phase reaction of NO and H<sub>2</sub> is as follows: Which of the following statements concerning this mechanism is not directly supported by the information provided?</strong> A) Step 1 is the rate determining step. B) N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> is an intermediate. C) There is no catalyst in this reaction. D) The rate expression for step 1 is rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>. E) All steps are bimolecular reactions.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ec6bce_db57_0226_ac74_076589b58af3_TB4499_11.jpg)
Which of the following statements concerning this mechanism is not directly supported by the information provided?
A) Step 1 is the rate determining step.
B) N2O2 is an intermediate.
C) There is no catalyst in this reaction.
D) The rate expression for step 1 is rate = k[NO]2.
E) All steps are bimolecular reactions.
![<strong>A possible mechanism for the gas phase reaction of NO and H<sub>2</sub> is as follows: Which of the following statements concerning this mechanism is not directly supported by the information provided?</strong> A) Step 1 is the rate determining step. B) N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> is an intermediate. C) There is no catalyst in this reaction. D) The rate expression for step 1 is rate = k[NO]<sup>2</sup>. E) All steps are bimolecular reactions.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ec6bce_db57_0226_ac74_076589b58af3_TB4499_11.jpg)
Which of the following statements concerning this mechanism is not directly supported by the information provided?
A) Step 1 is the rate determining step.
B) N2O2 is an intermediate.
C) There is no catalyst in this reaction.
D) The rate expression for step 1 is rate = k[NO]2.
E) All steps are bimolecular reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Elementary steps in a reaction mechanism often include reaction ________.These (usually)short-lived species,which are at one point produced and then later consumed,do not appear in the overall chemical reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In a reaction coordinate diagram,reacting molecules are most unstable ______.
A) at their initial position
B) when they are about to collide
C) right after they collide
D) at the transition state
A) at their initial position
B) when they are about to collide
C) right after they collide
D) at the transition state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Nitrogen dioxide reacts with carbon monoxide to produce nitrogen monoxide and carbon dioxide.
NO2(g)+ CO(g) NO(g)+ CO2(g)
A proposed mechanism for this reaction is
![<strong>Nitrogen dioxide reacts with carbon monoxide to produce nitrogen monoxide and carbon dioxide. NO<sub>2</sub>(g)+ CO(g) \to NO(g)+ CO<sub>2</sub>(g) A proposed mechanism for this reaction is What is a rate law that is consistent with the proposed mechanism?</strong> A) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[CO] [NO]<sup>-1</sup> B) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[CO] C) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>][CO] D) rate = k[NO<sub>3</sub>][CO] E) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ec6bce_50b0_edc4_ac74_4345ebe789f1_TB4499_11.jpg)
What is a rate law that is consistent with the proposed mechanism?
A) rate = k[NO2]2[CO] [NO]-1
B) rate = k[NO2]2[CO]
C) rate = k[NO2][CO]
D) rate = k[NO3][CO]
E) rate = k[NO2]2
NO2(g)+ CO(g) NO(g)+ CO2(g)
A proposed mechanism for this reaction is
![<strong>Nitrogen dioxide reacts with carbon monoxide to produce nitrogen monoxide and carbon dioxide. NO<sub>2</sub>(g)+ CO(g) \to NO(g)+ CO<sub>2</sub>(g) A proposed mechanism for this reaction is What is a rate law that is consistent with the proposed mechanism?</strong> A) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[CO] [NO]<sup>-1</sup> B) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>[CO] C) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>][CO] D) rate = k[NO<sub>3</sub>][CO] E) rate = k[NO<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ec6bce_50b0_edc4_ac74_4345ebe789f1_TB4499_11.jpg)
What is a rate law that is consistent with the proposed mechanism?
A) rate = k[NO2]2[CO] [NO]-1
B) rate = k[NO2]2[CO]
C) rate = k[NO2][CO]
D) rate = k[NO3][CO]
E) rate = k[NO2]2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If a catalyst is present in a different phase from the reactants and products,it is referred to as a(n)________ catalyst.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The pre-exponential,A,in the Arrhenius equation is called the ________ factor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
For the overall reaction
2A + B C
Which of the following mechanisms is/are consistent with a rate equation of rate = k[A]2[B]?
A)![<strong>For the overall reaction 2A + B \to C Which of the following mechanisms is/are consistent with a rate equation of rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]? </strong> A) B) C) D) E) Answers a and d are both correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_ca2f_e01f_ac74_51473c110d54_TB34225555_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>For the overall reaction 2A + B \to C Which of the following mechanisms is/are consistent with a rate equation of rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]? </strong> A) B) C) D) E) Answers a and d are both correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_ca30_a270_ac74_0512c7349c45_TB34225555_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>For the overall reaction 2A + B \to C Which of the following mechanisms is/are consistent with a rate equation of rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]? </strong> A) B) C) D) E) Answers a and d are both correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_ca31_65c1_ac74_af5126028c27_TB34225555_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>For the overall reaction 2A + B \to C Which of the following mechanisms is/are consistent with a rate equation of rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]? </strong> A) B) C) D) E) Answers a and d are both correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_ca32_0202_ac74_ff7c4ff7ee33_TB34225555_11.jpg)
E) Answers a and d are both correct.
2A + B C
Which of the following mechanisms is/are consistent with a rate equation of rate = k[A]2[B]?
A)
![<strong>For the overall reaction 2A + B \to C Which of the following mechanisms is/are consistent with a rate equation of rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]? </strong> A) B) C) D) E) Answers a and d are both correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_ca2f_e01f_ac74_51473c110d54_TB34225555_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>For the overall reaction 2A + B \to C Which of the following mechanisms is/are consistent with a rate equation of rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]? </strong> A) B) C) D) E) Answers a and d are both correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_ca30_a270_ac74_0512c7349c45_TB34225555_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>For the overall reaction 2A + B \to C Which of the following mechanisms is/are consistent with a rate equation of rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]? </strong> A) B) C) D) E) Answers a and d are both correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_ca31_65c1_ac74_af5126028c27_TB34225555_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>For the overall reaction 2A + B \to C Which of the following mechanisms is/are consistent with a rate equation of rate = k[A]<sup>2</sup>[B]? </strong> A) B) C) D) E) Answers a and d are both correct.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_ca32_0202_ac74_ff7c4ff7ee33_TB34225555_11.jpg)
E) Answers a and d are both correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows:
![<strong>A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows: What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?</strong> A) Rate = B) Rate = k<sub>2</sub>[O] [O<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = D) Rate = E) Rate =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ec6bce_a19e_dad5_ac74_d95e3605a673_TB4499_11.jpg)
What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?
A) Rate =![<strong>A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows: What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?</strong> A) Rate = B) Rate = k<sub>2</sub>[O] [O<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = D) Rate = E) Rate =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7d_185b_a16d_3fb553d23082_TB4499_11.jpg)
B) Rate = k2[O] [O3]
C) Rate =![<strong>A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows: What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?</strong> A) Rate = B) Rate = k<sub>2</sub>[O] [O<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = D) Rate = E) Rate =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7d_185c_a16d_9f1071e65aef_TB4499_11.jpg)
D) Rate =![<strong>A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows: What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?</strong> A) Rate = B) Rate = k<sub>2</sub>[O] [O<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = D) Rate = E) Rate =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7d_185d_a16d_494ec2b275d1_TB4499_11.jpg)
E) Rate =![<strong>A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows: What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?</strong> A) Rate = B) Rate = k<sub>2</sub>[O] [O<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = D) Rate = E) Rate =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7d_185e_a16d_1fa7e3344ac0_TB4499_11.jpg)
![<strong>A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows: What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?</strong> A) Rate = B) Rate = k<sub>2</sub>[O] [O<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = D) Rate = E) Rate =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ec6bce_a19e_dad5_ac74_d95e3605a673_TB4499_11.jpg)
What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?
A) Rate =
![<strong>A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows: What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?</strong> A) Rate = B) Rate = k<sub>2</sub>[O] [O<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = D) Rate = E) Rate =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7d_185b_a16d_3fb553d23082_TB4499_11.jpg)
B) Rate = k2[O] [O3]
C) Rate =
![<strong>A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows: What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?</strong> A) Rate = B) Rate = k<sub>2</sub>[O] [O<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = D) Rate = E) Rate =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7d_185c_a16d_9f1071e65aef_TB4499_11.jpg)
D) Rate =
![<strong>A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows: What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?</strong> A) Rate = B) Rate = k<sub>2</sub>[O] [O<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = D) Rate = E) Rate =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7d_185d_a16d_494ec2b275d1_TB4499_11.jpg)
E) Rate =
![<strong>A suggested mechanism for the decomposition of ozone is as follows: What is the rate law predicted by this mechanism?</strong> A) Rate = B) Rate = k<sub>2</sub>[O] [O<sub>3</sub>] C) Rate = D) Rate = E) Rate =](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ea8937_ab7d_185e_a16d_1fa7e3344ac0_TB4499_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Radioactive isotopes decay by ________-order kinetics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The reaction,A + 2B B2 + A,proceeds by the following mechanism: (A is a catalyst.)
A + B AB (slow)
AB + B B2 + A (fast)
What is the rate law expression for this reaction?
A) Rate = k[A]
B) Rate = k[B]
C) Rate = k[A][B]
D) Rate = k[A][B]2
E) Rate = k[A]2[B]
A + B AB (slow)
AB + B B2 + A (fast)
What is the rate law expression for this reaction?
A) Rate = k[A]
B) Rate = k[B]
C) Rate = k[A][B]
D) Rate = k[A][B]2
E) Rate = k[A]2[B]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The ________ of an elementary step is defined as the number of reactant molecules that come together in the reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
How many mechanistic steps are depicted by in this potential energy diagram? 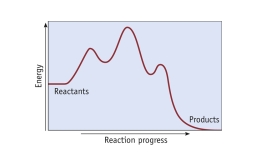
A) one step
B) two steps
C) three steps
D) four steps
E) five steps

A) one step
B) two steps
C) three steps
D) four steps
E) five steps

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Below is a proposed mechanism for the decomposition of H2O2.
H2O2 + I- H2O + IO- slow
H2O2 + IO- H2O + O2 + I- Fast
Which of the following statements is
A) IO- is a catalyst.
B) I- is a catalyst.
C) The net reaction is 2H2O2 2H2O + O2.
D) The reaction is first-order with respect to [I-].
E) The reaction is first-order with respect to [H2O2].
H2O2 + I- H2O + IO- slow
H2O2 + IO- H2O + O2 + I- Fast
Which of the following statements is
A) IO- is a catalyst.
B) I- is a catalyst.
C) The net reaction is 2H2O2 2H2O + O2.
D) The reaction is first-order with respect to [I-].
E) The reaction is first-order with respect to [H2O2].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The mechanism of a chemical reaction is given below.
(CH3)3CCl (CH3)3C+ + Cl- (slow)
(CH3)3C+ + OH- (CH3)3COH (fast)
Which of the following statements concerning the reaction is/are CORRECT?
1)The overall balanced reaction is: (CH3)3CCl + OH- (CH3)3COH + Cl-
2)Hydroxide ion is a reaction intermediate.
3)The following rate law is consistent with the mechanism: rate = k[(CH3)3CCl]OH-].
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3
(CH3)3CCl (CH3)3C+ + Cl- (slow)
(CH3)3C+ + OH- (CH3)3COH (fast)
Which of the following statements concerning the reaction is/are CORRECT?
1)The overall balanced reaction is: (CH3)3CCl + OH- (CH3)3COH + Cl-
2)Hydroxide ion is a reaction intermediate.
3)The following rate law is consistent with the mechanism: rate = k[(CH3)3CCl]OH-].
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The elementary steps for the catalyzed decomposition of dinitrogen monoxide are shown below.
N2O(g)+ NO(g) N2(g)+ NO2(g)
NO2(g) NO(g)+ 1/2 O2(g)
Which of the following statements is/are CORRECT?
1)The overall balanced reaction is N2O(g) N2(g)+ 1/2 O2(g).
2)NO2(g)is a catalyst for the reaction.
3)NO(g)is a reaction intermediate.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3
N2O(g)+ NO(g) N2(g)+ NO2(g)
NO2(g) NO(g)+ 1/2 O2(g)
Which of the following statements is/are CORRECT?
1)The overall balanced reaction is N2O(g) N2(g)+ 1/2 O2(g).
2)NO2(g)is a catalyst for the reaction.
3)NO(g)is a reaction intermediate.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 3
E) 1,2,and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A catalyst ____.
A) is used up in a chemical reaction
B) changes the potential energy change of the reaction
C) is always a solid
D) does not influence the reaction in any way
E) changes the activation energy of the reaction
A) is used up in a chemical reaction
B) changes the potential energy change of the reaction
C) is always a solid
D) does not influence the reaction in any way
E) changes the activation energy of the reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The effect of adding a catalyst to a reaction is to
A) increase the number of collisions between reactants.
B) lower the activation energy of a reaction.
C) increase the equilibrium constant of a reaction.
D) decrease the yield of the products.
E) increase the enthalpy change of a reaction.
A) increase the number of collisions between reactants.
B) lower the activation energy of a reaction.
C) increase the equilibrium constant of a reaction.
D) decrease the yield of the products.
E) increase the enthalpy change of a reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
For the overall reaction
A + 2B C
Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below?
Rate = k[A][B]
A)![<strong>For the overall reaction A + 2B \to C Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B] </strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_67a8_a3a9_ac74_c541cb93b8f8_TB34225555_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>For the overall reaction A + 2B \to C Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B] </strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_67a9_66fa_ac74_fdea6a67b88b_TB34225555_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>For the overall reaction A + 2B \to C Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B] </strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_67aa_2a4b_ac74_995e9afb3736_TB34225555_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>For the overall reaction A + 2B \to C Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B] </strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_67aa_c68c_ac74_a1a71a35bc27_TB34225555_11.jpg)
E)![<strong>For the overall reaction A + 2B \to C Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B] </strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_67ab_89dd_ac74_c11e1e8c2845_TB34225555_11.jpg)
A + 2B C
Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below?
Rate = k[A][B]
A)
![<strong>For the overall reaction A + 2B \to C Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B] </strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_67a8_a3a9_ac74_c541cb93b8f8_TB34225555_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>For the overall reaction A + 2B \to C Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B] </strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_67a9_66fa_ac74_fdea6a67b88b_TB34225555_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>For the overall reaction A + 2B \to C Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B] </strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_67aa_2a4b_ac74_995e9afb3736_TB34225555_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>For the overall reaction A + 2B \to C Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B] </strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_67aa_c68c_ac74_a1a71a35bc27_TB34225555_11.jpg)
E)
![<strong>For the overall reaction A + 2B \to C Which of the following mechanisms yields the correct overall chemical equation and is consistent with the rate equation below? Rate = k[A][B] </strong> A) B) C) D) E)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB34225555/11ec6bcf_67ab_89dd_ac74_c11e1e8c2845_TB34225555_11.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Consider the following proposed mechanism.If this mechanism for the overall reaction were correct,and if k1 were much less than k2,then the observed rate law would be
![<strong>Consider the following proposed mechanism.If this mechanism for the overall reaction were correct,and if k<sub>1</sub> were much less than k<sub>2</sub>,then the observed rate law would be </strong> A) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A] B) rate = k<sub>2</sub>[I][B] C) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup> D) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup> - k<sub>2</sub>[C][D] E) rate = k<sub>1</sub>k<sub>2</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup>[I][B]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ec6bce_2b15_3e43_ac74_5f85937b40b8_TB4499_11.jpg)
A) rate = k1[A]
B) rate = k2[I][B]
C) rate = k1[A]2
D) rate = k1[A]2 - k2[C][D]
E) rate = k1k2[A]2[I][B]
![<strong>Consider the following proposed mechanism.If this mechanism for the overall reaction were correct,and if k<sub>1</sub> were much less than k<sub>2</sub>,then the observed rate law would be </strong> A) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A] B) rate = k<sub>2</sub>[I][B] C) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup> D) rate = k<sub>1</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup> - k<sub>2</sub>[C][D] E) rate = k<sub>1</sub>k<sub>2</sub>[A]<sup>2</sup>[I][B]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4499/11ec6bce_2b15_3e43_ac74_5f85937b40b8_TB4499_11.jpg)
A) rate = k1[A]
B) rate = k2[I][B]
C) rate = k1[A]2
D) rate = k1[A]2 - k2[C][D]
E) rate = k1k2[A]2[I][B]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The reaction kinetics for a certain reaction are studied over several temperatures.Which of the following is/are effected by a change in reaction temperature?
A) the reaction rate
B) the rate constant,k
C) the energy of activation,Ea
D) a and b
E) a,b,and c
A) the reaction rate
B) the rate constant,k
C) the energy of activation,Ea
D) a and b
E) a,b,and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



