Deck 2: Applying Graphs to Economics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/37
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Applying Graphs to Economics
1
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.3 Straight line 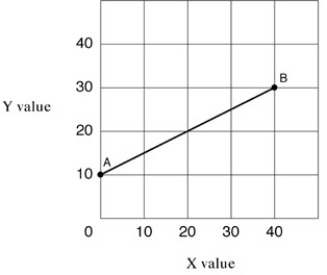 Narrend
Narrend
As shown in Exhibit A1.3, the intercept of straight line AB is:
A)1.
B)10.
C)20.
D)30.
E) not determinable from the information provided.
 Narrend
NarrendAs shown in Exhibit A1.3, the intercept of straight line AB is:
A)1.
B)10.
C)20.
D)30.
E) not determinable from the information provided.
B
2
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.2 Straight line 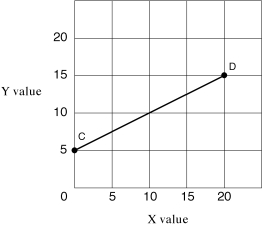 Narrend
Narrend
Straight line CD in Exhibit A1.2 shows which of the following?
A) The relationship between X and Y is unknown.
B) The values of Y are independent from the values of X.
C) There is an inverse relationship between X and Y.
D) There is a negative relationship between X and Y.
 Narrend
NarrendStraight line CD in Exhibit A1.2 shows which of the following?
A) The relationship between X and Y is unknown.
B) The values of Y are independent from the values of X.
C) There is an inverse relationship between X and Y.
D) There is a negative relationship between X and Y.
D
3
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.1 Straight line 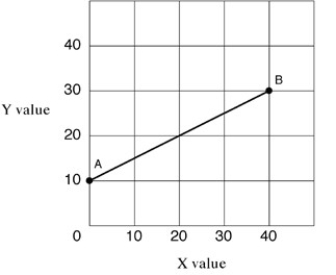 Narrend
Narrend
In Exhibit A1.1, as X increases along the horizontal axis, corresponding to points A-B on the line, the Y values increase. The relationship between the X and Y variables is:
A) positive.
B) inverse.
C) independent.
D) variable.
 Narrend
NarrendIn Exhibit A1.1, as X increases along the horizontal axis, corresponding to points A-B on the line, the Y values increase. The relationship between the X and Y variables is:
A) positive.
B) inverse.
C) independent.
D) variable.
A
4
If the coordinates are x1=3, y1=6 and x2=1, y2=2, the slope of the line is:
A)1.
B)2
C)3
D)6.
A)1.
B)2
C)3
D)6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When one variable increases, the other variable increases - it is called:
A) an inverse relationship.
B) causation.
C) horizontal line.
D) a positive relationship.
A) an inverse relationship.
B) causation.
C) horizontal line.
D) a positive relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A positive relationship exists when:
A) there is no association between two variables.
B) one variable increases and there is no change in the other variable.
C) one variable increases and the other variable increases too.
D) one variable increases and the other variable decreases.
A) there is no association between two variables.
B) one variable increases and there is no change in the other variable.
C) one variable increases and the other variable increases too.
D) one variable increases and the other variable decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.3 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
As shown in Exhibit A1.3, the slope of straight line AB:
A) decreases with increases in X.
B) increases with increases in X.
C) increases with decreases in X.
D) remains constant with changes in X.
 Narrend
NarrendAs shown in Exhibit A1.3, the slope of straight line AB:
A) decreases with increases in X.
B) increases with increases in X.
C) increases with decreases in X.
D) remains constant with changes in X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A) The slope is the ration of the rise to the run.
B) A direct relationship is one in which two variables change in the same direction.
C) Slope is the ratio of the change in the variable on the horizontal axis to the change in the variable on the vertical axis.
D) An independent relationship is one in which two variables are unrelated.
A) The slope is the ration of the rise to the run.
B) A direct relationship is one in which two variables change in the same direction.
C) Slope is the ratio of the change in the variable on the horizontal axis to the change in the variable on the vertical axis.
D) An independent relationship is one in which two variables are unrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.3 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
In Exhibit A1.3, the slope of straight line AB is:
A) variable.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) positive.
E) not determinable from the information provided.
 Narrend
NarrendIn Exhibit A1.3, the slope of straight line AB is:
A) variable.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) positive.
E) not determinable from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An upward-sloping line or curve is used to illustrate:
A) the ceteris paribus assumption.
B) an inverse relationship.
C) two unrelated variables.
D) a positive relationship.
A) the ceteris paribus assumption.
B) an inverse relationship.
C) two unrelated variables.
D) a positive relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Measured between two points on a curve, the ratio of the change in the variable on the vertical axis to the change in the variable on the horizontal axis is the:
A) axis.
B) slope.
C) dependent curve.
D) independent curve.
A) axis.
B) slope.
C) dependent curve.
D) independent curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.4 Straight line 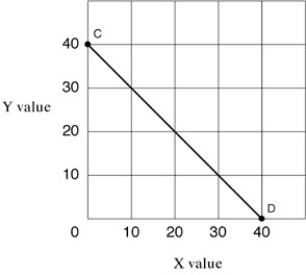 Narrend
Narrend
Straight line CD in Exhibit A1.4 shows which of the following?
A) Increasing values for X increases the value of Y.
B) Decreasing values for X decreases the value of Y.
C) There is no association between X and Y.
D) Variables X and Y are negatively related.
 Narrend
NarrendStraight line CD in Exhibit A1.4 shows which of the following?
A) Increasing values for X increases the value of Y.
B) Decreasing values for X decreases the value of Y.
C) There is no association between X and Y.
D) Variables X and Y are negatively related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.1 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
Straight line AB in Exhibit A1.1 shows which of the following?
A) X and Y have negative causation.
B) The higher the values of X, the higher the values of Y.
C) There is an inverse relationship between X and Y.
D) When values of X increase, values of Y are constant.
 Narrend
NarrendStraight line AB in Exhibit A1.1 shows which of the following?
A) X and Y have negative causation.
B) The higher the values of X, the higher the values of Y.
C) There is an inverse relationship between X and Y.
D) When values of X increase, values of Y are constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.4 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
In Exhibit A1.4, the slope of straight line CD is:
A) positive.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) variable.
 Narrend
NarrendIn Exhibit A1.4, the slope of straight line CD is:
A) positive.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.4 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
In Exhibit A1.4, as X increases along the horizontal axis, corresponding to points C-D on the line, the Y values decrease. The relationship between the X and Y variables is:
A) direct.
B) inverse.
C) independent.
D) variable.
 Narrend
NarrendIn Exhibit A1.4, as X increases along the horizontal axis, corresponding to points C-D on the line, the Y values decrease. The relationship between the X and Y variables is:
A) direct.
B) inverse.
C) independent.
D) variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.2 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
In Exhibit A1.2, as X increases along the horizontal axis, corresponding to points C-D on the line, the Y values decrease. The relationship between the X and Y variables is:
A) direct.
B) inverse.
C) independent.
D) variable.
 Narrend
NarrendIn Exhibit A1.2, as X increases along the horizontal axis, corresponding to points C-D on the line, the Y values decrease. The relationship between the X and Y variables is:
A) direct.
B) inverse.
C) independent.
D) variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Basic economic analysis typically concerns:
A) the relationship between two variables, one of which has negative values.
B) the relationship between two variables, both of which have negative values.
C) the relationship between two variables, both of which have positive values.
D) the relationship between two variables, one variable always increases and the other variable always decreases.
A) the relationship between two variables, one of which has negative values.
B) the relationship between two variables, both of which have negative values.
C) the relationship between two variables, both of which have positive values.
D) the relationship between two variables, one variable always increases and the other variable always decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.1 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
Straight line AB in Exhibit A1.1 shows which of the following?
A) There is no relationship between variable X and variable Y.
B) Decreasing values for X will cause the values of Y to increase.
C) There is a positive relationship between X and Y.
D) There is a negative relationship between X and Y.
 Narrend
NarrendStraight line AB in Exhibit A1.1 shows which of the following?
A) There is no relationship between variable X and variable Y.
B) Decreasing values for X will cause the values of Y to increase.
C) There is a positive relationship between X and Y.
D) There is a negative relationship between X and Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following pairs is the most likely to exhibit an inverse relationship?
A) The amount of time you spend studying and your final marks.
B) Waiter's tips and his/her service.
C) The annual income and demand for overseas travel.
D) People's annual income and their expenditure on second-hand clothes.
A) The amount of time you spend studying and your final marks.
B) Waiter's tips and his/her service.
C) The annual income and demand for overseas travel.
D) People's annual income and their expenditure on second-hand clothes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.3 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
In Exhibit A1.3, the slope of straight line AB is:
A)1.
B)5.
C) 1/2.
D) -1.
E) not determinable from the information provided.
 Narrend
NarrendIn Exhibit A1.3, the slope of straight line AB is:
A)1.
B)5.
C) 1/2.
D) -1.
E) not determinable from the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.4 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
In Exhibit A1.4, the slope for straight line CD is:
A)5.
B)1.
C) -1.
D) -5.
 Narrend
NarrendIn Exhibit A1.4, the slope for straight line CD is:
A)5.
B)1.
C) -1.
D) -5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A change in a third variable, not on either axis of a graph, is illustrated with:
A) a horizontal or vertical line.
B) a movement along a curve.
C) a shift of a curve.
D) a point of intersection.
A) a horizontal or vertical line.
B) a movement along a curve.
C) a shift of a curve.
D) a point of intersection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.5 Straight line 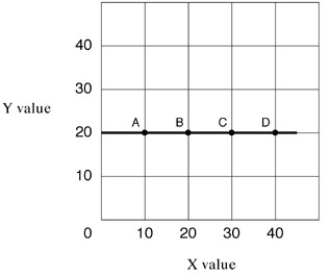 Narrend
Narrend
In Exhibit A1.5, the slope of the straight line A-D is:
A) zero.
B)1.
C) 1/2.
D) -1.
 Narrend
NarrendIn Exhibit A1.5, the slope of the straight line A-D is:
A) zero.
B)1.
C) 1/2.
D) -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
An inverse relationship is a negative causation between two variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.6 Straight-line relationship 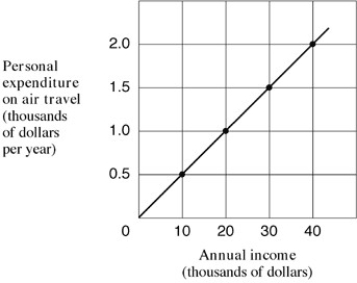 Narrend
Narrend
What is the slope of the line shown in Exhibit A1.6?
A) 1/20.
B) 1/10.
C) 1/5.
D) 1/2.
 Narrend
NarrendWhat is the slope of the line shown in Exhibit A1.6?
A) 1/20.
B) 1/10.
C) 1/5.
D) 1/2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Direct relationships are illustrated using upward-sloping lines and curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A direct relationship is a relationship between two variables in which they move in different directions (if one increases, the other decreases).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.5 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
Straight line A-D in Exhibit A1.5 shows which of the following?
A) Increasing values for X will increase the value of Y.
B) Increasing values for X will decrease the value of Y.
C) Increasing values for X does not affect the value of Y.
D) All of the above.
 Narrend
NarrendStraight line A-D in Exhibit A1.5 shows which of the following?
A) Increasing values for X will increase the value of Y.
B) Increasing values for X will decrease the value of Y.
C) Increasing values for X does not affect the value of Y.
D) All of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In a graphic relationship, shifts in a curve are caused by a change in:
A) the slope of the curve.
B) a factor not measured on the axes of the graph.
C) one of the factors measured on either axes of the graph.
D) any factor, whether measured on the axes of the graph or not.
A) the slope of the curve.
B) a factor not measured on the axes of the graph.
C) one of the factors measured on either axes of the graph.
D) any factor, whether measured on the axes of the graph or not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.5 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
In Exhibit A1.5, as X increases along the horizontal axis, corresponding to points A-D on the line, the Y values remain unchanged at 20 units. The relationship between the X and Y variables is:
A) direct.
B) inverse.
C) independent.
D) undefined.
 Narrend
NarrendIn Exhibit A1.5, as X increases along the horizontal axis, corresponding to points A-D on the line, the Y values remain unchanged at 20 units. The relationship between the X and Y variables is:
A) direct.
B) inverse.
C) independent.
D) undefined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A downward-sloping line has a negative slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A graph can be used to illustrate the relationship between the price of compact discs and the quantity of compact discs demanded. If there is evidence that buyers' income also influences the demand for compact discs, then a movement along the curve can be caused by a change in the price of compact discs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.5 Straight line  Narrend
Narrend
In Exhibit A1.5, the slope of straight line A-D is:
A) positive.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) variable.
 Narrend
NarrendIn Exhibit A1.5, the slope of straight line A-D is:
A) positive.
B) zero.
C) negative.
D) variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A horizontal line indicates an independent relationship between two variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The graph of a direct relationship will have a negative slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Narrbegin Exhibit A1.6 Straight-line relationship  Narrend
Narrend
Which of the following would cause a shift in the relationship shown in Exhibit A1.6?
A) A change in people's annual income.
B) A rise in people's expenditure on air travel.
C) Both a rise in income and a rise in expenditure on air travel.
D) A change in people's preferences in favour of air travel.
 Narrend
NarrendWhich of the following would cause a shift in the relationship shown in Exhibit A1.6?
A) A change in people's annual income.
B) A rise in people's expenditure on air travel.
C) Both a rise in income and a rise in expenditure on air travel.
D) A change in people's preferences in favour of air travel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Adding a third variable to a two dimensional graph:
A) makes it impossible to interpret the graph.
B) helps to show the effect of factors that are not on the graph.
C) creates unnecessary complexity and should be avoided.
D) provides a point of intersection.
A) makes it impossible to interpret the graph.
B) helps to show the effect of factors that are not on the graph.
C) creates unnecessary complexity and should be avoided.
D) provides a point of intersection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 37 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



