Deck 2: Chemistry of Life
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/112
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Chemistry of Life
1
The smallest unit of matter is the
A)molecule.
B)atom.
C)compound.
D)isotope.
A)molecule.
B)atom.
C)compound.
D)isotope.
B
2
If the atomic number of an element is 27 and the mass number is 60,how many neutrons does the atom have?
A)27
B)33
C)87
D)60
A)27
B)33
C)87
D)60
B
3
If the atomic number of an element is 9 and the mass number is 19,how many neutrons does the atom have?
A)10
B)9
C)19
D)28
A)10
B)9
C)19
D)28
A
4
The number of protons in an atom is called the
A)atomic number.
B)atomic weight.
C)mass number.
D)combining weight.
A)atomic number.
B)atomic weight.
C)mass number.
D)combining weight.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The positively charged particles in the nucleus of an atom are
A)neutrons.
B)electrons.
C)protons.
D)isotopes.
A)neutrons.
B)electrons.
C)protons.
D)isotopes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15 and a mass number of 31.How many protons,neutrons,and electrons does an atom of the element phosphorus have?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The atomic mass of a proton is
A)0 atomic mass units.
B)2 atomic mass units.
C)1 atomic mass units.
D)-1 atomic mass units.
A)0 atomic mass units.
B)2 atomic mass units.
C)1 atomic mass units.
D)-1 atomic mass units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which subatomic particle determines the identity of an atom?
A)Neutron
B)Proton
C)Electron
D)Prion
A)Neutron
B)Proton
C)Electron
D)Prion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The number of electrons in the outermost shell of an atom will determine the chemical activity of the atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Atoms with more than one shell are most stable when the outermost shell contains _____ electrons.
A)10
B)1
C)8
D)6
A)10
B)1
C)8
D)6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Exactly 6.02 x 1023 atoms of any element is called 1 ____ of that element.
A)atomic mass unit
B)isotope
C)mole
D)mouse
A)atomic mass unit
B)isotope
C)mole
D)mouse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which subatomic particle determines the chemical activity of an atom?
A)Neutron
B)Proton
C)Electron
D)Prion
A)Neutron
B)Proton
C)Electron
D)Prion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What makes an isotope radioactive?
A)It has more protons than electrons.
B)It releases energy to become stable.
C)It releases hydrogen ions into solution.
D)It breaks down into hydrogen and electrons.
A)It has more protons than electrons.
B)It releases energy to become stable.
C)It releases hydrogen ions into solution.
D)It breaks down into hydrogen and electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Describe each of the three subatomic particles with regard to charge,weight,and location in an atom.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
An element is any substance that contains one type of
A)molecule.
B)isotope.
C)atom.
D)proton.
A)molecule.
B)isotope.
C)atom.
D)proton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following subatomic particles are found in the nucleus of an atom?
A)Protons and electrons
B)Electrons and neutrons
C)Protons and shells
D)Neutrons and protons
A)Protons and electrons
B)Electrons and neutrons
C)Protons and shells
D)Neutrons and protons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Over 90% of the body is composed of four elements: carbon,nitrogen,chlorine,and hydrogen.
Over 90% of the body is composed of four elements: carbon,nitrogen,oxygen,and hydrogen.
Over 90% of the body is composed of four elements: carbon,nitrogen,oxygen,and hydrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
All radioactive isotopes are very dangerous and have no practical,safe uses.
Some radioactive isotopes are very dangerous and have no practical,safe uses.
Some radioactive isotopes are very dangerous and have no practical,safe uses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Different forms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called
A)molecules.
B)compounds.
C)isotopes.
D)lattices.
A)molecules.
B)compounds.
C)isotopes.
D)lattices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Low levels of radiation are commonly used to
A)sterilize dental products.
B)destroy cancer cells.
C)produce images of body parts.
D)All apply.
A)sterilize dental products.
B)destroy cancer cells.
C)produce images of body parts.
D)All apply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The most abundant molecule in living organisms is
A)water.
B)glucose.
C)oxygen.
D)ammonia.
A)water.
B)glucose.
C)oxygen.
D)ammonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A bond created from the sharing of electrons between two atoms is a(n)______ bond.
A)covalent
B)hydrogen
C)ionic
D)metallic
A)covalent
B)hydrogen
C)ionic
D)metallic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Molecules form from
A)the shape of the individual atoms.
B)the attraction between electrons.
C)the sharing of electrons.
D)a drive toward solubility.
A)the shape of the individual atoms.
B)the attraction between electrons.
C)the sharing of electrons.
D)a drive toward solubility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The ability of water molecules to cling to each other is _________,while the ability to cling to other surfaces is ___________.
A)cohesion;adhesion
B)dissolving;vaporization
C)adhesion;cohesion
D)cohesion;dissolving
A)cohesion;adhesion
B)dissolving;vaporization
C)adhesion;cohesion
D)cohesion;dissolving

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Substances that are water-loving are called
A)hydrophilic.
B)hydrophobic.
C)hydrophoriC.
D)hydrochromic.
A)hydrophilic.
B)hydrophobic.
C)hydrophoriC.
D)hydrochromic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When one atom has a stronger attraction for shared electrons in a bond than the other atom,a(n)___________ covalent bond is formed.
A)polar
B)nonpolar
C)ionic
D)metallic
A)polar
B)nonpolar
C)ionic
D)metallic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A molecule made of two or more different atoms bonded together is called a(n)
A)ion.
B)isotope.
C)atom.
D)compounD.
A)ion.
B)isotope.
C)atom.
D)compounD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Explain how hydrogen bonding contributes to the characteristics of the water molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms a ______ bond is formed.
A)single covalent
B)double covalent
C)triple covalent
D)double ionic
A)single covalent
B)double covalent
C)triple covalent
D)double ionic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen to a slightly negative oxygen of another molecule describes a(n)________ bond.
A)hydrogen
B)oxygen
C)nitrogen
D)ionic
A)hydrogen
B)oxygen
C)nitrogen
D)ionic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An ion is an atom or molecule that
A)is in a gaseous state.
B)carries an electrical charge.
C)is attracted to a north-seeking pole.
D)forms a visible glow.
A)is in a gaseous state.
B)carries an electrical charge.
C)is attracted to a north-seeking pole.
D)forms a visible glow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The ability of water to absorb large amounts of heat energy without changing its temperature is a
A)low specific heat capacity.
B)low heat of vaporization.
C)high specific heat capacity.
D)high heat of vaporization.
A)low specific heat capacity.
B)low heat of vaporization.
C)high specific heat capacity.
D)high heat of vaporization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An atom or group of atoms with a charge is called a(n)
A)molecule.
B)isotope.
C)compound.
D)ion.
A)molecule.
B)isotope.
C)compound.
D)ion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is NOT a property of water?
A)The ability to cling to other water molecules,yet flow.
B)The ability to facilitate chemical reactions.
C)The ability to insulate the body from temperature extremes.
D)The ability to dissolve nonpolar,hydrophobic molecules.
A)The ability to cling to other water molecules,yet flow.
B)The ability to facilitate chemical reactions.
C)The ability to insulate the body from temperature extremes.
D)The ability to dissolve nonpolar,hydrophobic molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is NOT a property of water?
A)High heat capacity
B)Low heat of vaporization
C)Solvent for polar and ionic compounds
D)Cohesiveness
A)High heat capacity
B)Low heat of vaporization
C)Solvent for polar and ionic compounds
D)Cohesiveness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A bond created from the attraction between positively and negatively charged ions is a(n)______ bond.
A)covalent
B)hydrogen
C)ionic
D)metallic
A)covalent
B)hydrogen
C)ionic
D)metallic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
High levels of radiation are NOT used
A)to sterilize medical equipment.
B)to kill cancer cells.
C)as tracers to detect molecular changes.
D)to sterilize from anthrax.
A)to sterilize medical equipment.
B)to kill cancer cells.
C)as tracers to detect molecular changes.
D)to sterilize from anthrax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Compounds that form ions when put into water are called
A)mixtures.
B)solvents.
C)electrolytes.
D)suspensions.
A)mixtures.
B)solvents.
C)electrolytes.
D)suspensions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Atoms bonded together to form a chemical unit are called
A)molecules.
B)ions.
C)radioisotopes.
D)buffers.
A)molecules.
B)ions.
C)radioisotopes.
D)buffers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Explain the difference between an ionic bond and a covalent bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The pH of the blood is slightly basic.Which of the following describes this pH?
A)6.4
B)12.6
C)4.7
D)7.4
A)6.4
B)12.6
C)4.7
D)7.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The removal of a water molecule during a reaction results in
A)breaking a bond.
B)forming an acid.
C)hydrolysis.
D)forming a bonD.
A)breaking a bond.
B)forming an acid.
C)hydrolysis.
D)forming a bonD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A weak base will accept many hydrogen ions.
A strong base will accept many hydrogen ions.
A strong base will accept many hydrogen ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A pH of 5.5 would be considered
A)acidic.
B)basic.
C)neutral.
A)acidic.
B)basic.
C)neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A substance that dissociates in water,releasing hydrogen ions is a(n)
A)salt.
B)base.
C)protein.
D)aciD.
A)salt.
B)base.
C)protein.
D)aciD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The subunit molecules for proteins are
A)atoms.
B)amino acids.
C)enzymes.
D)polymers.
A)atoms.
B)amino acids.
C)enzymes.
D)polymers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Chemicals that help keep body fluids within a normal pH range are called
A)acids.
B)bases.
C)buffers.
D)salts.
A)acids.
B)bases.
C)buffers.
D)salts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A pH of 7.0 would be considered
A)acidic.
B)basic.
C)neutral.
A)acidic.
B)basic.
C)neutral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Hydrochloric acid is considered a strong acid because it
A)produces very few hydrogen ions in water.
B)produces many hydroxide ions in water.
C)produces many hydrogen ions in water.
D)dissociates very little in water.
A)produces very few hydrogen ions in water.
B)produces many hydroxide ions in water.
C)produces many hydrogen ions in water.
D)dissociates very little in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The main monomer for carbohydrates is
A)sucrose.
B)nucleic acids.
C)glucose.
D)amino acids.
A)sucrose.
B)nucleic acids.
C)glucose.
D)amino acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The subunit building block of nucleic acids is the
A)monosaccharide.
B)nucleotide.
C)amino acid.
D)fatty aciD.
A)monosaccharide.
B)nucleotide.
C)amino acid.
D)fatty aciD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
List the four macromolecules found in cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Organic compounds always contain ___________ atoms.
A)water
B)carbon
C)nitrogen
D)oxygen
A)water
B)carbon
C)nitrogen
D)oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A substance that can take up hydrogen ions or release hydroxide ions in water is a(n)
A)salt.
B)base.
C)protein.
D)aciD.
A)salt.
B)base.
C)protein.
D)aciD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The addition of water in an enzyme catalyzed reaction is a ________ reaction.
A)dehydration
B)hydrolysis
C)exchange
D)neutralization
A)dehydration
B)hydrolysis
C)exchange
D)neutralization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What monomer is NOT correctly matched with its macromolecule?
A)carbohydrates - glucose
B)lipids - glycerol and citric acids
C)proteins - amino acids
D)nucleic acids - nucleotides
A)carbohydrates - glucose
B)lipids - glycerol and citric acids
C)proteins - amino acids
D)nucleic acids - nucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is NOT a macromolecule group found in cells?
A)Proteins
B)Organic acids
C)Carbohydrates
D)Nucleic acids
A)Proteins
B)Organic acids
C)Carbohydrates
D)Nucleic acids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The lower the pH,
A)the lesser the hydrogen ion concentration.
B)the more acidic the solution.
C)the lesser the hydrogen ion concentration and the more acidic the solution.
D)the greater the hydroxide ion concentration.
E)the more basic the solution and the greater the hydroxide ion concentration.
A)the lesser the hydrogen ion concentration.
B)the more acidic the solution.
C)the lesser the hydrogen ion concentration and the more acidic the solution.
D)the greater the hydroxide ion concentration.
E)the more basic the solution and the greater the hydroxide ion concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which arrow in the following equation represents dehydration? 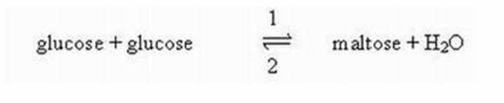
A)Arrow 1
B)Arrow 2
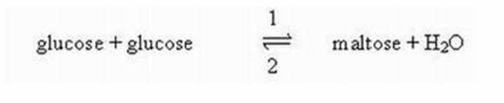
A)Arrow 1
B)Arrow 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The main function of carbohydrates is to provide
A)cellular energy.
B)insulation.
C)transport molecules.
D)hereditary information.
A)cellular energy.
B)insulation.
C)transport molecules.
D)hereditary information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins?
A)They form structural components such as collagen.
B)They form many hormones.
C)They form actin and myosin needed for muscular movement.
D)They form important energy molecules.
A)They form structural components such as collagen.
B)They form many hormones.
C)They form actin and myosin needed for muscular movement.
D)They form important energy molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Fats are usually liquid at room temperature and oils are solids.
Fats are usually solid at room temperature and oils are liquid.
Fats are usually solid at room temperature and oils are liquid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If you need quick energy,would you eat foods high in carbohydrates,fats,or proteins? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Glycogen is
A)a monosaccharide used for quick energy.
B)a protein found in cell membranes.
C)a polysaccharide used as stored energy in animals.
D)a fat found in margarine.
A)a monosaccharide used for quick energy.
B)a protein found in cell membranes.
C)a polysaccharide used as stored energy in animals.
D)a fat found in margarine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is NOT a monosaccharide?
A)Glucose
B)Fructose
C)Sucrose
D)Galactose
A)Glucose
B)Fructose
C)Sucrose
D)Galactose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following contains glucose?
A)Protein
B)Fat
C)Nucleic acid
D)Starch
A)Protein
B)Fat
C)Nucleic acid
D)Starch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The lipid molecules that are the main component of cell membranes are
A)steroids.
B)triglycerides.
C)phospholipids.
D)prostaglandins.
A)steroids.
B)triglycerides.
C)phospholipids.
D)prostaglandins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Triglycerides are composed of glycerol and three fatty acids.When the fatty acids contain one or more double bonds,the fat is considered
A)saturated.
B)unsaturated.
C)emulsified.
D)synthesizeD.
A)saturated.
B)unsaturated.
C)emulsified.
D)synthesizeD.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Organic compounds that are always insoluble in water are called
A)sugars.
B)lipids.
C)nucleotides.
D)proteins.
A)sugars.
B)lipids.
C)nucleotides.
D)proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following is NOT a function of lipids?
A)Long-term energy storage
B)Formation of antibodies
C)Formation of cell membranes
D)Formation of sex hormones
A)Long-term energy storage
B)Formation of antibodies
C)Formation of cell membranes
D)Formation of sex hormones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is NOT a function of proteins?
A)They form enzymes to speed up reactions.
B)They form the backbone of cell membranes.
C)They form hemoglobin to transport oxygen in the blood.
D)They form antibodies to protect the body from disease.
A)They form enzymes to speed up reactions.
B)They form the backbone of cell membranes.
C)They form hemoglobin to transport oxygen in the blood.
D)They form antibodies to protect the body from disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
How many different amino acids compose all human polypeptides (proteins)?
A)10
B)15
C)20
D)25
A)10
B)15
C)20
D)25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The process that allows fats to mix with water,particularly so digestion can occur is called
A)hydrolysis.
B)degradation.
C)dehydration.
D)emulsification.
A)hydrolysis.
B)degradation.
C)dehydration.
D)emulsification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The coiling or folding of a polypeptide chain is the ________ structure of a protein.
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is NOT a disaccharide?
A)Maltose
B)Galactose
C)Lactose
D)Sucrose
A)Maltose
B)Galactose
C)Lactose
D)Sucrose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What makes a phospholipid different from a fat?
A)Fats are neutral while phospholipids are ionized.
B)Fats are solid while phospholiopids are liquid.
C)Fats are ionized while phospholipids are neutral.
D)Fats are basic while phospholipids are acidic.
A)Fats are neutral while phospholipids are ionized.
B)Fats are solid while phospholiopids are liquid.
C)Fats are ionized while phospholipids are neutral.
D)Fats are basic while phospholipids are acidic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following is the main component of fiber in our diet?
A)Glycogen
B)Protein
C)Cellulose
D)Starch
A)Glycogen
B)Protein
C)Cellulose
D)Starch

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Steroids differ in structure from other lipids in that they have a backbone of
A)four fused carbon rings.
B)branched chains of carbons.
C)saturated carbon chains.
D)unsaturated carbon chains.
A)four fused carbon rings.
B)branched chains of carbons.
C)saturated carbon chains.
D)unsaturated carbon chains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The sequence of amino acids makes up the ______ structure of a protein.
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)quaternary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A monosaccharide of five carbons is a
A)hexose sugar.
B)glycerol.
C)fatty acid.
D)pentose sugar.
A)hexose sugar.
B)glycerol.
C)fatty acid.
D)pentose sugar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 112 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



