Deck 14: The Bank of Canada and Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/131
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: The Bank of Canada and Monetary Policy
1
The Canadian Payments Association
A)monitors the chartered banks.
B)handles cheque clearing.
C)monitors the Bank of Canada.
D)loans chartered banks money.
A)monitors the chartered banks.
B)handles cheque clearing.
C)monitors the Bank of Canada.
D)loans chartered banks money.
handles cheque clearing.
2
Open market operations are
A)the buying of existing corporate securities in secondary markets by private citizens,banks and the Bank of Canada.
B)the buying and selling of existing government securities in open private markets by the Bank of Canada.
C)the actions of the Bank of Canada that are used to finance deficit financing by the government.
D)the selling of new government securities in order to increase the money supply.
A)the buying of existing corporate securities in secondary markets by private citizens,banks and the Bank of Canada.
B)the buying and selling of existing government securities in open private markets by the Bank of Canada.
C)the actions of the Bank of Canada that are used to finance deficit financing by the government.
D)the selling of new government securities in order to increase the money supply.
the buying and selling of existing government securities in open private markets by the Bank of Canada.
3
When the Bank of Canada sells a government security to a commercial bank,
A)the cash reserves of the commercial bank decrease.
B)the net worth of the commercial bank increases.
C)the loans of the commercial bank will increase.
D)the balance sheet of the commercial bank is thrown off balance.
A)the cash reserves of the commercial bank decrease.
B)the net worth of the commercial bank increases.
C)the loans of the commercial bank will increase.
D)the balance sheet of the commercial bank is thrown off balance.
the cash reserves of the commercial bank decrease.
4
The initial impact of the Bank of Canada's open market sale of government securities to commercial banks is
A)an increase in the money supply by some multiple of the dollar volume of the sale.
B)an increase in commercial bank deposits at the Bank of Canada.
C)a fall in the money supply by some multiple of the dollar volume of the sale.
D)a reduction of the commercial banking system's reserve deposits at the Bank of Canada.
A)an increase in the money supply by some multiple of the dollar volume of the sale.
B)an increase in commercial bank deposits at the Bank of Canada.
C)a fall in the money supply by some multiple of the dollar volume of the sale.
D)a reduction of the commercial banking system's reserve deposits at the Bank of Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
To increase the money supply
A)the Bank of Canada should sell government securities.
B)the commercial banks should reduce their loans.
C)the Bank of Canada should buy government securities from commercial banks.
D)the Bank of Canada should increase reserve requirements.
A)the Bank of Canada should sell government securities.
B)the commercial banks should reduce their loans.
C)the Bank of Canada should buy government securities from commercial banks.
D)the Bank of Canada should increase reserve requirements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
With respect to the nation's money supply,the Bank of Canada
A)has no ability to influence its magnitude or its rate of growth.
B)precisely sets the amount of money in circulation in consultation with Parliament.
C)can influence its future growth.
D)has disavowed any intention to influence the money supply.
A)has no ability to influence its magnitude or its rate of growth.
B)precisely sets the amount of money in circulation in consultation with Parliament.
C)can influence its future growth.
D)has disavowed any intention to influence the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Board of Directors of the Bank of Canada is
A)appointed by the Prime Minister.
B)elected by the public.
C)appointed by Parliament.
D)elected by members of the Canadian Banking Association.
A)appointed by the Prime Minister.
B)elected by the public.
C)appointed by Parliament.
D)elected by members of the Canadian Banking Association.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The Bank of Canada accepts deposits from
A)the general public.
B)chartered banks only.
C)the Bank of Canada and chartered banks.
D)the Board of Directors.
A)the general public.
B)chartered banks only.
C)the Bank of Canada and chartered banks.
D)the Board of Directors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Bank of Canada acts as the government's fiscal agent by
A)auditing taxpayers.
B)providing chequing account services for the government.
C)preparing the budget the Prime Minister presents to Parliament every year.
D)determining how to finance a deficit.
A)auditing taxpayers.
B)providing chequing account services for the government.
C)preparing the budget the Prime Minister presents to Parliament every year.
D)determining how to finance a deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The Bank of Canada is said to be the "lender of last resort" in that
A)it stands ready to "bail out" any chartered bank that it has decided should not fail.
B)it makes loans to individuals whom commercial banks do not believe are credit-worthy.
C)it charges a higher interest rate to borrowers than does any other bank.
D)it functions as the government's bank only when commercial banks fail to do so.
A)it stands ready to "bail out" any chartered bank that it has decided should not fail.
B)it makes loans to individuals whom commercial banks do not believe are credit-worthy.
C)it charges a higher interest rate to borrowers than does any other bank.
D)it functions as the government's bank only when commercial banks fail to do so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the money multiplier is 2.4 and the Bank of Canada buys $8 million in securities on the open market,demand deposits could potentially
A)increase by $19.2 million.
B)increase by $8 million.
C)decrease by $19.2 million.
D)decrease by $16.5 million.
A)increase by $19.2 million.
B)increase by $8 million.
C)decrease by $19.2 million.
D)decrease by $16.5 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All depository institutions
A)keep all of their deposits at the Bank of Canada district bank except their vault cash.
B)keep a certain percentage of their deposits at the Bank of Canada district bank or as vault cash.
C)charge the interest rates and pay the interest rates determined by their Bank of Canada district bank.
D)limit their loans to households to a certain percentage of all their loans,and the limit is set by the Bank of Canada.
A)keep all of their deposits at the Bank of Canada district bank except their vault cash.
B)keep a certain percentage of their deposits at the Bank of Canada district bank or as vault cash.
C)charge the interest rates and pay the interest rates determined by their Bank of Canada district bank.
D)limit their loans to households to a certain percentage of all their loans,and the limit is set by the Bank of Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the Bank of Canada buys $500 of government securities when the desired reserve ratio is 20 percent,the money supply may ultimately
A)increase by $100.
B)increase by $2,500.
C)decrease by $100.
D)decrease by $2,500.
A)increase by $100.
B)increase by $2,500.
C)decrease by $100.
D)decrease by $2,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the Bank of Canada wishes to increase the money supply by $500 when the desired reserve ratio is 10 percent,it should
A)sell $50 of government bonds.
B)buy $50 of government bonds.
C)sell $5,000 of government bonds.
D)buy $5,000 of government bonds.
A)sell $50 of government bonds.
B)buy $50 of government bonds.
C)sell $5,000 of government bonds.
D)buy $5,000 of government bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When the Bank of Canada wants to undertake open market operations,it
A)can require all commercial banks to buy from or sell to it.
B)can require all member banks to buy from or sell to it.
C)buys or sells securities by writing a cheque.
D)buys from or sells to the Canadian Treasury.
A)can require all commercial banks to buy from or sell to it.
B)can require all member banks to buy from or sell to it.
C)buys or sells securities by writing a cheque.
D)buys from or sells to the Canadian Treasury.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Board of Directors of the Bank of Canada is
A)elected by the general public.
B)appointed for three year terms.
C)composed of representatives from the country's 12 largest commercial banks.
D)composed of 12 members of the Parliament.
A)elected by the general public.
B)appointed for three year terms.
C)composed of representatives from the country's 12 largest commercial banks.
D)composed of 12 members of the Parliament.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
It can be argued that the Bank of Canada's most important function is
A)to provide for check collection and clearing.
B)to create stability in the Canadian banking system.
C)to set the legal,controlled consumer interest rates.
D)to lend to risky customers.
A)to provide for check collection and clearing.
B)to create stability in the Canadian banking system.
C)to set the legal,controlled consumer interest rates.
D)to lend to risky customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Assume that desired reserves are 20 percent.If the Bank of Canada buys $1,000 worth of bonds from a member bank,then the banking system can
A)increase loans by a maximum of $5,000.
B)increase loans by a maximum of $4,000.
C)decrease loans by a maximum of $5,000.
D)decrease loans by a maximum of $4,000.
A)increase loans by a maximum of $5,000.
B)increase loans by a maximum of $4,000.
C)decrease loans by a maximum of $5,000.
D)decrease loans by a maximum of $4,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the commercial banking system's excess reserves are zero and the reserve requirement is 10 percent,in order for the banking system to increase deposits by $2.5 million,the Bank of Canada must
A)permit the system to have prolonged reserve deficiencies.
B)sell $2.5 million of government securities to the general public.
C)sell $250,000 of government securities to the general public.
D)buy $250,000 of government securities from the public.
A)permit the system to have prolonged reserve deficiencies.
B)sell $2.5 million of government securities to the general public.
C)sell $250,000 of government securities to the general public.
D)buy $250,000 of government securities from the public.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The central bank for Canada is
A)the Bank of Montreal.
B)the Parliamentary Bank.
C)the Bank of Canada.
D)the First National Bank of Canada.
A)the Bank of Montreal.
B)the Parliamentary Bank.
C)the Bank of Canada.
D)the First National Bank of Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The desired reserve ratio is 10 percent but banks have decided they want to keep 20 percent of deposits as reserves.There are no currency drains.If the Bank of Canada buys $1 million of government securities,the money supply will
A)not change because of the excess reserves banks keep on hand.
B)increase by $1 million.
C)increase by $5 million.
D)increase by $10 million.
A)not change because of the excess reserves banks keep on hand.
B)increase by $1 million.
C)increase by $5 million.
D)increase by $10 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The desired reserve ratio equals 20 percent and all banks initially have zero excess reserves.The Bank of Canada buys $1 million in Canadian government securities.The most the money supply can increase is
A)$1 million.
B)$4 million.
C)$5 million.
D)$10 million.
A)$1 million.
B)$4 million.
C)$5 million.
D)$10 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the Bank of Canada wishes to reduce the money supply by $1,000 when desired reserves are 20 percent,it should
A)sell $200 of government securities.
B)buy $200 of government securities.
C)sell $5,000 of government securities.
D)buy $5,000 of government securities.
A)sell $200 of government securities.
B)buy $200 of government securities.
C)sell $5,000 of government securities.
D)buy $5,000 of government securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When the Bank of Canada buys a Canadian bond in the open market
A)it has no effect on the total reserves or the money supply because the cheque it writes increases reserves at one bank but they fall at another.
B)total reserves increase by the amount of the purchase but the money supply stays the same.
C)it expands total reserves and the money supply.
D)it contracts total reserves and the money supply.
A)it has no effect on the total reserves or the money supply because the cheque it writes increases reserves at one bank but they fall at another.
B)total reserves increase by the amount of the purchase but the money supply stays the same.
C)it expands total reserves and the money supply.
D)it contracts total reserves and the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Bank of Canada sells a Canadian government security and a bank dealer writes a cheque for the amount.When the cheque clears,
A)reserves remain unchanged because the decrease of reserves at the dealer's bank are offset by an increase in the reserves at the Bank of Canada.
B)reserves have fallen by the amount of the cheque because the Bank of Canada clears the cheque by reducing the bank's deposits at the Bank of Canada.
C)reserves increase by the amount of the cheque because the Bank of Canada clears the cheque by increasing the amount of the bank's deposits with the Bank of Canada.
D)reserves have fallen by the amount of the reserves times the desired reserve ratio,and the money supply falls by the difference between the amount of the cheque and the fall in the reserves.
A)reserves remain unchanged because the decrease of reserves at the dealer's bank are offset by an increase in the reserves at the Bank of Canada.
B)reserves have fallen by the amount of the cheque because the Bank of Canada clears the cheque by reducing the bank's deposits at the Bank of Canada.
C)reserves increase by the amount of the cheque because the Bank of Canada clears the cheque by increasing the amount of the bank's deposits with the Bank of Canada.
D)reserves have fallen by the amount of the reserves times the desired reserve ratio,and the money supply falls by the difference between the amount of the cheque and the fall in the reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a bank's deposits at the Bank of Canada increase by $1 million,then
A)the bank's assets increase by $1 million and the Bank of Canada's assets in the form of depository institution's reserves increase by $1 million.
B)the bank's assets increase by $1 million and the Bank of Canada's liabilities increase by $1 million.
C)the bank's assets increase by $1 million but there is no change at the Bank of Canada.
D)the net effect on the Bank of Canada and the bank is zero because assets always equal liabilities.
A)the bank's assets increase by $1 million and the Bank of Canada's assets in the form of depository institution's reserves increase by $1 million.
B)the bank's assets increase by $1 million and the Bank of Canada's liabilities increase by $1 million.
C)the bank's assets increase by $1 million but there is no change at the Bank of Canada.
D)the net effect on the Bank of Canada and the bank is zero because assets always equal liabilities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When the Bank of Canada buys Canadian government securities,the money supply
A)decreases because excess reserves are now held by the bond dealer's bank.
B)decreases because there is a decrease in demand deposits at the bank of the bond dealer,but there is no offsetting increase at any other bank.
C)increases because there is an increase in demand deposits at the bank of the bond dealer,but there is no decrease in demand deposits at any other bank.
D)stays the same until the bank starts to make some loans.
A)decreases because excess reserves are now held by the bond dealer's bank.
B)decreases because there is a decrease in demand deposits at the bank of the bond dealer,but there is no offsetting increase at any other bank.
C)increases because there is an increase in demand deposits at the bank of the bond dealer,but there is no decrease in demand deposits at any other bank.
D)stays the same until the bank starts to make some loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
To decrease the money supply
A)the Bank of Canada should sell government securities.
B)the Bank of Canada should decrease reserve requirements.
C)commercial banks should increase their loans.
D)commercial banks should sell government securities.
A)the Bank of Canada should sell government securities.
B)the Bank of Canada should decrease reserve requirements.
C)commercial banks should increase their loans.
D)commercial banks should sell government securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The desired reserve ratio is 10 percent,Bank A has $1 million in excess reserves,and all other banks have zero excess reserves.If the Bank of Canada buys $1 million of government securities and the cheque is deposited in Bank A,but Bank A refuses to grant any loans or buy any financial securities,then
A)the money supply does not increase.
B)the money supply increases by $900,000.
C)the money supply increases by $1 million.
D)the money supply increases by more than $1 million.
A)the money supply does not increase.
B)the money supply increases by $900,000.
C)the money supply increases by $1 million.
D)the money supply increases by more than $1 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Currently there are zero excess reserves in the Canadian banking system.If the required reserve ratio is 20 percent and the Bank of Canada sells 20 million in bonds,the maximum amount that the money supply can change is
A)$20 million.
B)$40 million.
C)$100 million.
D)$400 million.
A)$20 million.
B)$40 million.
C)$100 million.
D)$400 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Bank of Canada buys $1 million in bonds from a bond dealer.The bond dealer's bank experiences
A)an increase in assets of $1 million as its reserves increase and a decrease in liabilities as its deposits fall.
B)no change in assets or liabilities.Assets both increased and decreased by the amount of the cheque.
C)a decrease in assets of $1 million as the chequing account of the bond dealer increased,and a decrease in liabilities as the bank's deposits with the Bank of Canada increased by $1 million.
D)an increase in assets of $1 million as its reserves increase and an increase in liabilities of $1 million as the deposits in the bond dealer's chequing account increases by $1 million.
A)an increase in assets of $1 million as its reserves increase and a decrease in liabilities as its deposits fall.
B)no change in assets or liabilities.Assets both increased and decreased by the amount of the cheque.
C)a decrease in assets of $1 million as the chequing account of the bond dealer increased,and a decrease in liabilities as the bank's deposits with the Bank of Canada increased by $1 million.
D)an increase in assets of $1 million as its reserves increase and an increase in liabilities of $1 million as the deposits in the bond dealer's chequing account increases by $1 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The desired reserve ratio is 10%,and originally there are no excess reserves in any bank.If the Bank of Canada buys $1 million of Canadian government securities from a bond dealer,and the dealer deposits the Bank of Canada's cheque in her bank,then
A)the bank can make additional loans up to $1 million.
B)the bank can make additional loans up to $900,000.
C)the bank can make additional loans up to $90,000.
D)the bank has to call in loans of at least $1 million.
A)the bank can make additional loans up to $1 million.
B)the bank can make additional loans up to $900,000.
C)the bank can make additional loans up to $90,000.
D)the bank has to call in loans of at least $1 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the Bank of Canada sells $100 of securities through a commercial bank when the reserve requirement is 10 percent,the money supply may ultimately
A)increase by $100.
B)increase by $1,000.
C)decrease by $100.
D)decrease by $1,000.
A)increase by $100.
B)increase by $1,000.
C)decrease by $100.
D)decrease by $1,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The transactions demand for money
A)varies inversely with the velocity of money.
B)varies directly with the rate of interest.
C)is a function of national income.
D)is determined by the Bank of Canada.
A)varies inversely with the velocity of money.
B)varies directly with the rate of interest.
C)is a function of national income.
D)is determined by the Bank of Canada.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The transactions demand for money will increase when
A)the rate of interest increases.
B)the price level falls.
C)national income increases.
D)national income decreases.
A)the rate of interest increases.
B)the price level falls.
C)national income increases.
D)national income decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The interest rate that the Bank of Canada charges depository institutions when they borrow reserves directly from the Bank of Canada is the
A)prime rate.
B)aggregate rate.
C)bank rate.
D)expansionary rate.
A)prime rate.
B)aggregate rate.
C)bank rate.
D)expansionary rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The primary tool the Bank of Canada uses to control the money supply is
A)open market operations.
B)changing the desired reserve ratio.
C)changing the bank rate.
D)changing the federal funds rate.
A)open market operations.
B)changing the desired reserve ratio.
C)changing the bank rate.
D)changing the federal funds rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Initially,all banks have zero excess reserves and the desired reserve ratio is 10%.The Bank of Canada buys $1 million in government securities from a bond dealer who deposits the cheque in Bank A.The bank makes as large a loan as it can to a construction company,which buys materials from a lumber company who deposits the cheque in Bank B.Bank B makes as large a loan as possible to a car dealership.By how much has the money supply grown to this point?
A)$3 million.
B)$2.71 million.
C)$1.81 million.
D)$1.71 million.
A)$3 million.
B)$2.71 million.
C)$1.81 million.
D)$1.71 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The desired reserve ratio is 10%.The bank of a bond dealer has $100 million in deposits,$8 million in vault cash,and $7 million in deposits at the Bank of Canada.The Bank of Canada sells $1 million in securities to the bond dealer.As a result of the transaction,
A)the money supply falls by $1 million,total reserves fall by $1 million,and excess reserves fall by $900,000.
B)the money supply falls by $1 million,total reserves fall by $1 million and excess reserves fall by $1 million.
C)the money supply falls by $1 million,total reserves fall by $900,000 and excess reserves fall by $900,000.
D)the money supply falls by $1 million,but reserves don't change since the bank had $5 million in excess reserves before the transaction.
A)the money supply falls by $1 million,total reserves fall by $1 million,and excess reserves fall by $900,000.
B)the money supply falls by $1 million,total reserves fall by $1 million and excess reserves fall by $1 million.
C)the money supply falls by $1 million,total reserves fall by $900,000 and excess reserves fall by $900,000.
D)the money supply falls by $1 million,but reserves don't change since the bank had $5 million in excess reserves before the transaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose the economy is initially in long-run and short-run equilibrium.If the Bank of Canada decides to pursue a contractionary monetary policy,we will see
A)bond prices fall,interest rates fall,aggregate demand remain unchanged as consumption spending decreases,but investment spending increases.Real national income remains constant in both the short run and the long run,but the price level falls in both.
B)bond prices fall,interest rates rise,aggregate demand fall as investment and consumption spending decrease,and real national income and the price level decreasing in the short-run,but only the price level decreasing in the long run.
C)bond prices fall,interest rates rise,aggregate demand falls as investment spending decreases and consumption spending remains unchanged,and real national income and the price level decrease in the short run,but only the price level fall in the short run.
D)interest rates rise but no change in bond prices.Aggregate demand falls as consumption spending and investment spending decrease,and the price level and real national income fall in both the short run and the long run.
A)bond prices fall,interest rates fall,aggregate demand remain unchanged as consumption spending decreases,but investment spending increases.Real national income remains constant in both the short run and the long run,but the price level falls in both.
B)bond prices fall,interest rates rise,aggregate demand fall as investment and consumption spending decrease,and real national income and the price level decreasing in the short-run,but only the price level decreasing in the long run.
C)bond prices fall,interest rates rise,aggregate demand falls as investment spending decreases and consumption spending remains unchanged,and real national income and the price level decrease in the short run,but only the price level fall in the short run.
D)interest rates rise but no change in bond prices.Aggregate demand falls as consumption spending and investment spending decrease,and the price level and real national income fall in both the short run and the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Keynesians argue that for a change in the money supply (with constant prices),the mechanism through which aggregate demand changes is
A)change in the money supply → change in speculative balances → change in transactions balances → change in planned investment → change in aggregate demand.
B)change in the money supply → change in planned investment → change in government spending → change in aggregate demand.
C)change in the money supply → change in interest rates → change in planned investment → change in aggregate demand.
D)change in the money supply → change in interest rates → change in transactions balances → change in government spending → change in aggregate demand.
A)change in the money supply → change in speculative balances → change in transactions balances → change in planned investment → change in aggregate demand.
B)change in the money supply → change in planned investment → change in government spending → change in aggregate demand.
C)change in the money supply → change in interest rates → change in planned investment → change in aggregate demand.
D)change in the money supply → change in interest rates → change in transactions balances → change in government spending → change in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The transactions demand for money
A)varies directly with nominal national income.
B)varies inversely with nominal national income.
C)varies inversely with real national income.
D)has no relationship with nominal or real national income.
A)varies directly with nominal national income.
B)varies inversely with nominal national income.
C)varies inversely with real national income.
D)has no relationship with nominal or real national income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The asset demand for money is related to the function of money called
A)medium of exchange.
B)unit of account.
C)store of value.
D)standard of deferred payment.
A)medium of exchange.
B)unit of account.
C)store of value.
D)standard of deferred payment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When households hold money (currency)for unplanned expenditures and emergencies,it is called
A)the speculative demand for money.
B)the transactions demand for money.
C)the demand for "hot" money.
D)the precautionary demand for money.
A)the speculative demand for money.
B)the transactions demand for money.
C)the demand for "hot" money.
D)the precautionary demand for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Suppose a family is holding $1,000 in its checking account for normal transactions,$500 in cash for emergencies,and $1,500 as a store of value when the interest rate is 4 percent.If the interest rate rises to 10 percent,which of the following patterns of holding money would be most likely and why?
A)Transaction demand $800;Precautionary demand $350;Asset demand $500,because the opportunity cost of holding money has increased.The reduction money balances held as an asset is greatest because interest-bearing assets are much more attractive when interest rates are higher.
B)Transaction demand $500;Precautionary demand $500;Asset demand $1,400,because the opportunity cost of holding money balances has risen.The reduction in money balances held for transaction purposes falls the most because people start using credit cards more when the opportunity cost of holding money increases.
C)Transaction demand $1,000;Precautionary demand $500;Asset demand $500,because only the asset demand is responsive to changes in the interest rate.
D)Transaction demand $800;Precautionary demand $600;Asset demand $1,500,because people can economize on their money balances for making transactions,but the possibility of an emergency increases with the interest rate.People will also expect rates to go higher,so they will hold money as an asset until the rates increase further.
A)Transaction demand $800;Precautionary demand $350;Asset demand $500,because the opportunity cost of holding money has increased.The reduction money balances held as an asset is greatest because interest-bearing assets are much more attractive when interest rates are higher.
B)Transaction demand $500;Precautionary demand $500;Asset demand $1,400,because the opportunity cost of holding money balances has risen.The reduction in money balances held for transaction purposes falls the most because people start using credit cards more when the opportunity cost of holding money increases.
C)Transaction demand $1,000;Precautionary demand $500;Asset demand $500,because only the asset demand is responsive to changes in the interest rate.
D)Transaction demand $800;Precautionary demand $600;Asset demand $1,500,because people can economize on their money balances for making transactions,but the possibility of an emergency increases with the interest rate.People will also expect rates to go higher,so they will hold money as an asset until the rates increase further.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The type of analysis that assumes that money supply growth stimulates the economy primarily by lowering the interest rate and encouraging investment is
A)Keynesian analysis.
B)classical monetary analysis.
C)modern monetary analysis.
D)pre-Keynesian analysis.
A)Keynesian analysis.
B)classical monetary analysis.
C)modern monetary analysis.
D)pre-Keynesian analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the classical model,the demand for money curve
A)slopes upward with respect to the rate of interest.
B)is not affected by the price level.
C)slopes downward with respect to the rate of interest.
D)is vertical.
A)slopes upward with respect to the rate of interest.
B)is not affected by the price level.
C)slopes downward with respect to the rate of interest.
D)is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose the typical household holds $1,000 when the interest rate is 5 percent.When the interest rate rises to 6 percent,the typical household would most likely hold
A)more money because the opportunity cost of holding money is lower.
B)less money because the opportunity cost of holding money is lower.
C)more money because the opportunity cost of holding money is higher.
D)less money because the opportunity cost of holding money is higher.
A)more money because the opportunity cost of holding money is lower.
B)less money because the opportunity cost of holding money is lower.
C)more money because the opportunity cost of holding money is higher.
D)less money because the opportunity cost of holding money is higher.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The transactions demand for money varies
A)directly with real national income.
B)inversely with nominal national income.
C)directly with nominal national income.
D)inversely with real national income.
A)directly with real national income.
B)inversely with nominal national income.
C)directly with nominal national income.
D)inversely with real national income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
When a person holds money,they give up
A)the pleasure associated with spending money.
B)the pleasure associated with saving money.
C)the interest that could have been earned if the money had been changed into an interest-bearing asset.
D)nothing,since the person can always use the money to buy goods or services or interest-bearing assets.
A)the pleasure associated with spending money.
B)the pleasure associated with saving money.
C)the interest that could have been earned if the money had been changed into an interest-bearing asset.
D)nothing,since the person can always use the money to buy goods or services or interest-bearing assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The transactions demand for money exists because households
A)are insensitive to interest rate changes.
B)must save for unexpected emergencies.
C)do not like the fact that money is a liquid asset.
D)do not receive their incomes at the same time they wish to make purchases.
A)are insensitive to interest rate changes.
B)must save for unexpected emergencies.
C)do not like the fact that money is a liquid asset.
D)do not receive their incomes at the same time they wish to make purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The precautionary demand for holding money arises because
A)people want to hold money to make unexpected purchases or to meet emergencies.
B)credit cards charge low interest rates,which makes money more attractive than credit.
C)people would rather hold money in the form of time deposits than in the form of hard currency.
D)everyday,expected transactions are more easily transacted with debit cards than with credit cards.
A)people want to hold money to make unexpected purchases or to meet emergencies.
B)credit cards charge low interest rates,which makes money more attractive than credit.
C)people would rather hold money in the form of time deposits than in the form of hard currency.
D)everyday,expected transactions are more easily transacted with debit cards than with credit cards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The desire by households to hold a certain amount of money as a store of value,rather to hold assets such as certificates of deposit,stocks,and bonds,results in the
A)liquidity demand.
B)transactions demand.
C)precautionary demand.
D)asset demand.
A)liquidity demand.
B)transactions demand.
C)precautionary demand.
D)asset demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
One of the economic costs of holding currency is that
A)it is cumbersome to carry.
B)it requires constant attention.
C)it earns no interest income.
D)its real value always increases.
A)it is cumbersome to carry.
B)it requires constant attention.
C)it earns no interest income.
D)its real value always increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An increase in the money supply typically leads to
A)a reduction in the rate of interest.
B)a decrease in the price level.
C)a reduction in the velocity of money.
D)an inward shift in money demand.
A)a reduction in the rate of interest.
B)a decrease in the price level.
C)a reduction in the velocity of money.
D)an inward shift in money demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The transactions demand for money refers to
A)the desire for wealth.
B)the demand to hold money because money is used in all non-barter transactions.
C)the desire for income.
D)the demand to hold money as a long-term store of value.
A)the desire for wealth.
B)the demand to hold money because money is used in all non-barter transactions.
C)the desire for income.
D)the demand to hold money as a long-term store of value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A person is preparing for a long automobile trip and cashes in a CD for cash in case of emergencies along the way.This is an example of the
A)transaction demand for money.
B)precautionary demand for money.
C)wealth demand for money.
D)asset demand for money.
A)transaction demand for money.
B)precautionary demand for money.
C)wealth demand for money.
D)asset demand for money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
As nominal national income rises,the transactions demand for money
A)increases and the money demand curve shifts to the left.
B)decreases and the money demand curve shifts to the left.
C)increases and the money demand curve shifts to the right.
D)remains constant and the money demand curve remains the same.
A)increases and the money demand curve shifts to the left.
B)decreases and the money demand curve shifts to the left.
C)increases and the money demand curve shifts to the right.
D)remains constant and the money demand curve remains the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When interest rates rise,the transactions demand for money usually
A)decreases.
B)increases.
C)decreases initially and then increases to the original position.
D)does not change.
A)decreases.
B)increases.
C)decreases initially and then increases to the original position.
D)does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The transaction demand for money is the demand to hold money to
A)make regular,expected purchases.
B)meet unplanned expenditures.
C)store one's wealth.
D)purchase bonds when interest rates increase.
A)make regular,expected purchases.
B)meet unplanned expenditures.
C)store one's wealth.
D)purchase bonds when interest rates increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
According to the equation of exchange,if M = $400,P = $8,and Q = $200,then
A)NNP is $800.
B)V is 4.
C)the price level must fall.
D)V cannot be determined.
A)NNP is $800.
B)V is 4.
C)the price level must fall.
D)V cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The equation of exchange is
A)M = Q.
B)M = VPQ.
C)MV = PQ.
D)M/P = Q.
A)M = Q.
B)M = VPQ.
C)MV = PQ.
D)M/P = Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An increase in the supply of money,other things constant,
A)stimulates an increase in demand for money.
B)reduces the purchasing power of money.
C)reduces the rate of growth of the price level.
D)generates significant changes in relative prices.
A)stimulates an increase in demand for money.
B)reduces the purchasing power of money.
C)reduces the rate of growth of the price level.
D)generates significant changes in relative prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In the Keynesian view,
A)an increase in money supply will increase interest rates.
B)an increase in money supply will decrease interest rates.
C)a decrease in money supply will decrease interest rates.
D)a decrease in money supply will not change interest rates.
A)an increase in money supply will increase interest rates.
B)an increase in money supply will decrease interest rates.
C)a decrease in money supply will decrease interest rates.
D)a decrease in money supply will not change interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The velocity of money
A)is calculated as P/M.
B)indicates the number of times per year a dollar is spent on final goods and services.
C)is equal to 2k in the Cambridge equation.
D)indicates the speed with which the Canadian Treasury can mint new currency.
A)is calculated as P/M.
B)indicates the number of times per year a dollar is spent on final goods and services.
C)is equal to 2k in the Cambridge equation.
D)indicates the speed with which the Canadian Treasury can mint new currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Assume (other things constant)that the Bank of Canada increases the money supply.The mechanism through which aggregate demand increases is,according to Keynesians,
A)increase in the money supply → fall in money balances held → increase in interest rates → decrease in planned investment spending → increase in aggregate demand.
B)increase in money supply → increase in money balances held → decrease in interest rates → decrease in planned investment spending → increase in aggregate demand.
C)increase in money supply → decrease in money balances held → decrease in interest rates → increase in planned investment spending → increase in aggregate demand.
D)increase in money supply → decrease in interest rates → increase in planned investment spending → increase in aggregate demand.
A)increase in the money supply → fall in money balances held → increase in interest rates → decrease in planned investment spending → increase in aggregate demand.
B)increase in money supply → increase in money balances held → decrease in interest rates → decrease in planned investment spending → increase in aggregate demand.
C)increase in money supply → decrease in money balances held → decrease in interest rates → increase in planned investment spending → increase in aggregate demand.
D)increase in money supply → decrease in interest rates → increase in planned investment spending → increase in aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the Bank of Canada wants to target a rate of growth of the money supply faster than what currently exists,it must
A)also push for higher interest rates.
B)accept a lower interest rate.
C)accept lower bond prices.
D)permit price deflation.
A)also push for higher interest rates.
B)accept a lower interest rate.
C)accept lower bond prices.
D)permit price deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Suppose that the nominal money supply (M)is $200 million and the value of aggregate output (PQ)is $1 billion.It must be the case that
A)the economy is suffering from inflation.
B)the average price paid for a "typical" good is $5.
C)there will be a shortage of money balances in the economy.
D)the income velocity of money is 5.
A)the economy is suffering from inflation.
B)the average price paid for a "typical" good is $5.
C)there will be a shortage of money balances in the economy.
D)the income velocity of money is 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Figure 14-1 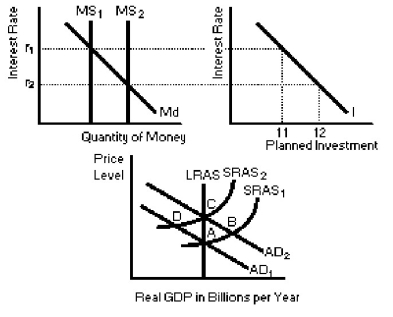
In Figure 14-1,suppose the economy is at a short run equilibrium at point B and the interest rate is r₂.Which of the following policy options for the Bank of Canada will help solve the short run situation?
A)lowering the bank rate
B)open market purchase of bonds
C)moral suasion
D)open market sale of bonds

In Figure 14-1,suppose the economy is at a short run equilibrium at point B and the interest rate is r₂.Which of the following policy options for the Bank of Canada will help solve the short run situation?
A)lowering the bank rate
B)open market purchase of bonds
C)moral suasion
D)open market sale of bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
In the Keynesian view,
A)an increase in reserve requirements will lower interest rates.
B)a decrease in reserve requirements will lower interest rates.
C)a decrease in reserve requirements will not affect interest rates.
D)an increase in reserve requirements will not affect interest rates.
A)an increase in reserve requirements will lower interest rates.
B)a decrease in reserve requirements will lower interest rates.
C)a decrease in reserve requirements will not affect interest rates.
D)an increase in reserve requirements will not affect interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The direct effect of an increase in the money supply is to
A)raise interest rates as people increase their saving.
B)increase interest rates as people anticipate higher inflation in the future.
C)increase aggregate demand as people try to spend their excess money balances.
D)decrease aggregate demand as people anticipate future economic problems.
A)raise interest rates as people increase their saving.
B)increase interest rates as people anticipate higher inflation in the future.
C)increase aggregate demand as people try to spend their excess money balances.
D)decrease aggregate demand as people anticipate future economic problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
According to the quantity theory of money,any change in the price level may be explained by changes in the
A)prime rate.
B)real interest rate.
C)money supply.
D)velocity of money.
A)prime rate.
B)real interest rate.
C)money supply.
D)velocity of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Figure 14-1 
In Figure 14-1,if the economy is initially at an equilibrium output at point A and the interest rate is r₁,then an open market purchase of bonds by the Bank of Canada will
A)cause interest rates to increase and output to decline.
B)cause interest rates to decline to r₂,investment to increase to I2 and the AD curve to shift upward to the right.
C)cause interest rates to decline to r₂,investment to decline,and aggregate demand to shift inward to the left.
D)not have any impact on the short or long run equilibrium output level.

In Figure 14-1,if the economy is initially at an equilibrium output at point A and the interest rate is r₁,then an open market purchase of bonds by the Bank of Canada will
A)cause interest rates to increase and output to decline.
B)cause interest rates to decline to r₂,investment to increase to I2 and the AD curve to shift upward to the right.
C)cause interest rates to decline to r₂,investment to decline,and aggregate demand to shift inward to the left.
D)not have any impact on the short or long run equilibrium output level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
According to both the equation of exchange and the quantity theory of money,
A)an increase in the money supply will increase real output.
B)an increase in the money supply will decrease real output.
C)a decrease in the money supply will decrease the velocity of money.
D)a decrease in the money supply will decrease the price level.
A)an increase in the money supply will increase real output.
B)an increase in the money supply will decrease real output.
C)a decrease in the money supply will decrease the velocity of money.
D)a decrease in the money supply will decrease the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If M = $100,Q = 500 and P = $2,then V is equal to
A)0)10.
B)1)0.
C)10.
D)50.
A)0)10.
B)1)0.
C)10.
D)50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An increase in the money supply will affect aggregate demand
A)only if the increase in the money supply causes interest rates to rise.
B)only if the increase in the money supply causes people to buy less goods and services.
C)only if the increase in the money supply causes people to increase their saving.
D)if the increase in the money supply causes interest rates to fall and/or causes people to buy more goods and services.
A)only if the increase in the money supply causes interest rates to rise.
B)only if the increase in the money supply causes people to buy less goods and services.
C)only if the increase in the money supply causes people to increase their saving.
D)if the increase in the money supply causes interest rates to fall and/or causes people to buy more goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If V = 5,P = $3,and Q = 50,then the money supply equals
A)$10.
B)$30.
C)$150.
D)$300.
A)$10.
B)$30.
C)$150.
D)$300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Other things constant,the crude quantity theory of money suggests that any increase in the money supply
A)causes a reduction in the demand for money.
B)results in a decrease in the aggregate price level.
C)causes the aggregate level of nominal income to fall.
D)results in a proportional increase in the price level.
A)causes a reduction in the demand for money.
B)results in a decrease in the aggregate price level.
C)causes the aggregate level of nominal income to fall.
D)results in a proportional increase in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 14-1 
In Figure 14-1,suppose the economy is at a short run equilibrium at point D.Which of the following is the best policy option for the Bank of Canada?
A)moral suasion
B)increase the bank rate
C)increase taxes
D)open market purchase of bonds

In Figure 14-1,suppose the economy is at a short run equilibrium at point D.Which of the following is the best policy option for the Bank of Canada?
A)moral suasion
B)increase the bank rate
C)increase taxes
D)open market purchase of bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Keynesian theorists argue that any increase in the money supply
A)is effective in increasing GDP only if it causes an outward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
B)will increase GDP only if interest rates fall and investment is sensitive to decreasing interest rates.
C)causes velocity to increase,and so in the short run nominal output must increase.
D)will move the economy from the "liquidity trap" during times of recession if interest rates fall enough to stimulate private investment.
A)is effective in increasing GDP only if it causes an outward shift of the aggregate supply curve.
B)will increase GDP only if interest rates fall and investment is sensitive to decreasing interest rates.
C)causes velocity to increase,and so in the short run nominal output must increase.
D)will move the economy from the "liquidity trap" during times of recession if interest rates fall enough to stimulate private investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



