Deck 11: Fiscal Policy and the Public Debt
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/116
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Fiscal Policy and the Public Debt
1
Suppose the economy is experiencing a inflationary gap and the government increases spending to close the gap.In the short run one would expect
A)output and the price level to remain constant.
B)output to increase and the price level to remain constant.
C)output and the price level to rise even further .
D)output to remain constant and the price level to rise.
A)output and the price level to remain constant.
B)output to increase and the price level to remain constant.
C)output and the price level to rise even further .
D)output to remain constant and the price level to rise.
output and the price level to rise even further .
2
If the government wants to decrease real GDP levels,it could
A)increase government expenditures.
B)increase taxes.
C)wait for inflationary pressure to come.
D)decrease government expenditures and increase taxes.
A)increase government expenditures.
B)increase taxes.
C)wait for inflationary pressure to come.
D)decrease government expenditures and increase taxes.
increase taxes.
3
An inflationary gap is
A)the difference between aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
B)the amount of unwanted inventory accumulation.
C)the amount by which taxes should be increased in order to put the brakes on run-away inflation.
D)the amount by which the equilibrium level of real GDP exceeds the long-run equilibrium level as given by LRAS.
A)the difference between aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
B)the amount of unwanted inventory accumulation.
C)the amount by which taxes should be increased in order to put the brakes on run-away inflation.
D)the amount by which the equilibrium level of real GDP exceeds the long-run equilibrium level as given by LRAS.
the amount by which the equilibrium level of real GDP exceeds the long-run equilibrium level as given by LRAS.
4
A contractionary gap is
A)the difference between aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
B)the amount of unwanted inventory accumulation.
C)the amount by which taxes should be increased in order to put the brakes on run-away inflation.
D)the amount by which the equilibrium level of real GDP is less than the long-run equilibrium level as given by LRAS.
A)the difference between aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
B)the amount of unwanted inventory accumulation.
C)the amount by which taxes should be increased in order to put the brakes on run-away inflation.
D)the amount by which the equilibrium level of real GDP is less than the long-run equilibrium level as given by LRAS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The amount by which the equilibrium level of real GDP is less than the long-run equilibrium level as given by LRAS is referred to as
A)a contractionary gap.
B)economic growth.
C)the amount by which taxes should be increased in order to put the brakes on run-away inflation.
D)an inflationary gap.
A)a contractionary gap.
B)economic growth.
C)the amount by which taxes should be increased in order to put the brakes on run-away inflation.
D)an inflationary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Fiscal policy refers to the
A)manipulation of the money supply so as to increase the amount of paper currency in circulation.
B)adjustment of government spending and taxes in order to achieve certain national economic goals.
C)adjustment of national income data for price level changes.
D)adjustment of the manner in which unemployment data is calculated so as to make it appear that unemployment is lower than it actually is.
A)manipulation of the money supply so as to increase the amount of paper currency in circulation.
B)adjustment of government spending and taxes in order to achieve certain national economic goals.
C)adjustment of national income data for price level changes.
D)adjustment of the manner in which unemployment data is calculated so as to make it appear that unemployment is lower than it actually is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the government wants to increase real GDP levels,it could
A)decrease government expenditures.
B)decrease taxes.
C)decrease government expenditures and increase taxes.
A)decrease government expenditures.
B)decrease taxes.
C)decrease government expenditures and increase taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If the government wants to engage in fiscal policy to close a recessionary gap,it should
A)increase government spending in order to increase aggregate supply.
B)decrease government spending in order to increase aggregate supply.
C)increase government spending in order to increase aggregate demand.
D)decrease government spending in order to decrease aggregate demand.
A)increase government spending in order to increase aggregate supply.
B)decrease government spending in order to increase aggregate supply.
C)increase government spending in order to increase aggregate demand.
D)decrease government spending in order to decrease aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the government wants to engage in fiscal policy to close an inflationary gap,it should
A)increase government spending in order to increase aggregate supply.
B)decrease government spending in order to increase aggregate supply.
C)increase government spending in order to increase aggregate demand.
D)decrease government spending in order to decrease aggregate demand.
A)increase government spending in order to increase aggregate supply.
B)decrease government spending in order to increase aggregate supply.
C)increase government spending in order to increase aggregate demand.
D)decrease government spending in order to decrease aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the government increases spending to move the economy closer to full employment,the government is most likely trying to
A)close a contractionary gap by increasing aggregate demand.
B)close a contractionary gap by raising the price level.
C)close an expansionary gap by increasing aggregate demand.
D)close an expansionary gap by increasing aggregate supply.
A)close a contractionary gap by increasing aggregate demand.
B)close a contractionary gap by raising the price level.
C)close an expansionary gap by increasing aggregate demand.
D)close an expansionary gap by increasing aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Suppose the economy is experiencing a contractionary gap and the government increases spending to close the gap.In the short run one would expect
A)output and the price level to remain constant.
B)output to increase and the price level to remain constant.
C)output and the price level to rise.
D)output to remain constant and the price level to rise.
A)output and the price level to remain constant.
B)output to increase and the price level to remain constant.
C)output and the price level to rise.
D)output to remain constant and the price level to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The amount by which the equilibrium level of real GDP exceeds the long-run equilibrium level as given by LRAS is referred to as
A)a contractionary gap.
B)economic growth.
C)the amount by which taxes should be increased in order to put the brakes on run-away inflation.
D)an inflationary gap.
A)a contractionary gap.
B)economic growth.
C)the amount by which taxes should be increased in order to put the brakes on run-away inflation.
D)an inflationary gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Suppose the economy is experiencing a inflationary gap and the government decreases spending to close the gap.In the short run one would expect
A)output and the price level to remain constant.
B)output to increase and the price level to remain constant.
C)output and the price level to fall.
D)output to remain constant and the price level to rise.
A)output and the price level to remain constant.
B)output to increase and the price level to remain constant.
C)output and the price level to fall.
D)output to remain constant and the price level to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The adjustment of government spending and taxes in order to achieve certain national economic goals refers to
A)monetary policy.
B)fiscal policy.
C)the national debt.
D)seignorage
A)monetary policy.
B)fiscal policy.
C)the national debt.
D)seignorage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Suppose the economy is experiencing a contractionary gap and the government decreases spending to close the gap.In the short run one would expect
A)output and the price level to remain constant.
B)output to increase and the price level to remain constant.
C)output and the price level to fall.
D)output to remain constant and the price level to rise.
A)output and the price level to remain constant.
B)output to increase and the price level to remain constant.
C)output and the price level to fall.
D)output to remain constant and the price level to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Expansionary fiscal policy is designed to
A)increase real national income and increase the price level.
B)reduce real national income and reduce the price level.
C)raise both real national income and the price level.
D)raise the price level only.
A)increase real national income and increase the price level.
B)reduce real national income and reduce the price level.
C)raise both real national income and the price level.
D)raise the price level only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the government decreases spending to move the economy closer to full employment,the government is most likely trying to
A)close a contractionary gap by increasing aggregate demand.
B)close a contractionary gap by raising the price level.
C)close an expansionary gap by decreasing aggregate demand.
D)close an expansionary gap by increasing aggregate supply.
A)close a contractionary gap by increasing aggregate demand.
B)close a contractionary gap by raising the price level.
C)close an expansionary gap by decreasing aggregate demand.
D)close an expansionary gap by increasing aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Contractionary fiscal policy is designed to
A)reduce real national income and increase the price level.
B)reduce real national income and reduce the price level.
C)raise both real national income and the price level.
D)raise the price level only.
A)reduce real national income and increase the price level.
B)reduce real national income and reduce the price level.
C)raise both real national income and the price level.
D)raise the price level only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the government wants to increase real GDP levels,it could
A)increase government expenditures.
B)increase taxes.
C)decrease government expenditures.
D)decrease government expenditures and increase taxes.
A)increase government expenditures.
B)increase taxes.
C)decrease government expenditures.
D)decrease government expenditures and increase taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements about fiscal policy is TRUE?
A)Real GDP can be increased above its long-run equilibrium only in the short run.
B)Real GDP can never be increased above its long-run equilibrium,even for a brief period of time.
C)Government can shift the aggregate demand curve inward by increasing spending.
D)Government can shift the aggregate demand curve outward by reducing spending.
A)Real GDP can be increased above its long-run equilibrium only in the short run.
B)Real GDP can never be increased above its long-run equilibrium,even for a brief period of time.
C)Government can shift the aggregate demand curve inward by increasing spending.
D)Government can shift the aggregate demand curve outward by reducing spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the government decreases aggregate demand when the economy is at both short-run and long-run equilibrium,the full long-run effect of this fiscal policy will be to
A)decrease real GDP.
B)decrease the price level.
C)decrease either the real GDP or the price level,depending on the length of the time lag.
D)decrease both real GDP and the price level.
A)decrease real GDP.
B)decrease the price level.
C)decrease either the real GDP or the price level,depending on the length of the time lag.
D)decrease both real GDP and the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Suppose the economy is at a short run equilibrium and is beyond the economy's long run potential level of real GDP.Which of the following fiscal policies would reduce output and prices in the short run?
A)an increase in government spending
B)a reduction in taxes
C)an increase in taxes
D)an increase in interest rates
A)an increase in government spending
B)a reduction in taxes
C)an increase in taxes
D)an increase in interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose the economy is at an equilibrium on the LRAS curve and the government decreases spending.In the short run one would expect
A)output and prices to decrease.
B)output to remain constant and prices to increase.
C)output to increase and prices to remain constant.
D)output and prices to remain constant.
A)output and prices to decrease.
B)output to remain constant and prices to increase.
C)output to increase and prices to remain constant.
D)output and prices to remain constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Suppose the economy is at a short run equilibrium in recession.Which of the following fiscal policies would increase output and prices in the short run?
A)a decrease in government spending
B)a reduction in taxes
C)an increase in taxes
D)an increase in interest rates
A)a decrease in government spending
B)a reduction in taxes
C)an increase in taxes
D)an increase in interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the government decreases government spending,then the
A)short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
B)long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
C)aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
D)aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
A)short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
B)long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
C)aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
D)aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose there is a contractionary gap and the economy is in equilibrium on the SRAS at an output level beyond the economy's long-run real GDP.In the short run,if the government increases spending then
A)output will decrease but prices will rise.
B)output will increase but prices will fall.
C)output and prices will fall.
D)output and prices will rise.
A)output will decrease but prices will rise.
B)output will increase but prices will fall.
C)output and prices will fall.
D)output and prices will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the government increases government spending,then the
A)short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
B)long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
C)aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
D)aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
A)short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
B)long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
C)aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
D)aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the government increases taxes,then the
A)short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
B)long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
C)aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
D)aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
A)short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
B)long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
C)aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
D)aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following statements about fiscal policy is FALSE?
A)Real GDP can be increased above its long-run equilibrium only in the short run.
B)Real GDP is expanding over time in the long-run.
C)Government can shift the aggregate demand curve inward by decreasing spending.
D)Government can shift the aggregate demand curve outward by reducing spending.
A)Real GDP can be increased above its long-run equilibrium only in the short run.
B)Real GDP is expanding over time in the long-run.
C)Government can shift the aggregate demand curve inward by decreasing spending.
D)Government can shift the aggregate demand curve outward by reducing spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose the economy is in equilibrium on the LRAS curve and government spending increases.In the long run
A)prices and output will return to the original levels.
B)prices will increase,but output will return to the original level.
C)prices and output will increase.
D)output will increase and prices will decrease.
A)prices and output will return to the original levels.
B)prices will increase,but output will return to the original level.
C)prices and output will increase.
D)output will increase and prices will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
According to traditional Keynesian analysis,fiscal policy operates by
A)informing consumers and business people about its plans for the economy so they will know how to adjust their behaviour.
B)indirectly affecting aggregate demand through its effect on interest rates.
C)directly affecting aggregate demand.
D)directly affecting aggregate supply.
A)informing consumers and business people about its plans for the economy so they will know how to adjust their behaviour.
B)indirectly affecting aggregate demand through its effect on interest rates.
C)directly affecting aggregate demand.
D)directly affecting aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If the government decreases taxes,then the
A)short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
B)long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
C)aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
D)aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.
A)short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right.
B)long-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the left.
C)aggregate demand curve shifts to the right.
D)aggregate demand curve shifts to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose the economy is at a short run equilibrium in recession.Which of the following fiscal policies would decrease output and prices in the short run?
A)an increase in government spending
B)a reduction in taxes
C)an increase in taxes
D)an increase in interest rates
A)an increase in government spending
B)a reduction in taxes
C)an increase in taxes
D)an increase in interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose there is a contractionary gap and the economy is in equilibrium on the SRAS at an output level beyond the economy's long-run real GDP.In the short run,if the government decreases spending then
A)output will decrease but prices will rise.
B)output will increase but prices will fall.
C)output and prices will fall.
D)output and prices will rise.
A)output will decrease but prices will rise.
B)output will increase but prices will fall.
C)output and prices will fall.
D)output and prices will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Suppose the economy is at a short run equilibrium and is beyond the economy's long run potential level of real GDP.Which of the following fiscal policies would increase output and prices in the short run?
A)a decrease in government spending
B)a reduction in taxes
C)an increase in taxes
D)an increase in interest rates
A)a decrease in government spending
B)a reduction in taxes
C)an increase in taxes
D)an increase in interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
To close a recessionary gap through fiscal policy,the government should
A)decrease government spending in order to increase aggregate supply.
B)increase government spending in order to increase aggregate demand.
C)reduce taxes in order to stimulate investment,and thus increase aggregate supply.
D)increase government spending and taxes in order to both increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
A)decrease government spending in order to increase aggregate supply.
B)increase government spending in order to increase aggregate demand.
C)reduce taxes in order to stimulate investment,and thus increase aggregate supply.
D)increase government spending and taxes in order to both increase aggregate demand and aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the government increases aggregate demand when the economy is at both short-run and long-run equilibrium,the full long-run effect of this fiscal policy will be to
A)increase real GDP.
B)increase the price level.
C)increase either the real GDP or the price level,depending on the length of the time lag.
D)decrease both real GDP and the price level.
A)increase real GDP.
B)increase the price level.
C)increase either the real GDP or the price level,depending on the length of the time lag.
D)decrease both real GDP and the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
To shift the aggregate demand curve inward and thereby reduce an expansionary gap,the government could
A)increase taxes.
B)increase government spending.
C)decrease government spending.
D)increase Social Security benefits.
A)increase taxes.
B)increase government spending.
C)decrease government spending.
D)increase Social Security benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
To shift the aggregate demand curve outward and thereby reduce a contractionary gap,the government could
A)increase taxes.
B)increase government spending.
C)decrease government spending.
D)increase Social Security benefits.
A)increase taxes.
B)increase government spending.
C)decrease government spending.
D)increase Social Security benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose the economy is at an equilibrium on the LRAS curve and the government increases spending.In the short run one would expect
A)output and prices to increase.
B)output to remain constant and prices to increase.
C)output to increase and prices to remain constant.
D)output and prices to remain constant.
A)output and prices to increase.
B)output to remain constant and prices to increase.
C)output to increase and prices to remain constant.
D)output and prices to remain constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure 11-1 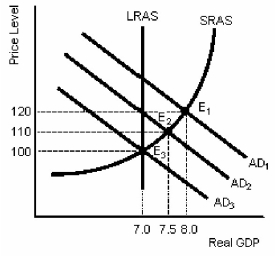
In Figure 11-1,assume that the economy is originally at E₁.If the government imposes contractionary economic policies,it is likely that
A)the new equilibrium will be E₃.
B)the new equilibrium will be E₂.
C)the price level will fall to 110.
D)aggregate demand will be represented by the A D₂ line.

In Figure 11-1,assume that the economy is originally at E₁.If the government imposes contractionary economic policies,it is likely that
A)the new equilibrium will be E₃.
B)the new equilibrium will be E₂.
C)the price level will fall to 110.
D)aggregate demand will be represented by the A D₂ line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the government increases spending while holding taxes constant,we expect
A)an increase in investment spending by businesses too,as they anticipate future economic growth.
B)a decrease in saving as consumers follow suit and also increase borrowing.
C)investment spending by businesses to increase.
D)interest rates to rise.
A)an increase in investment spending by businesses too,as they anticipate future economic growth.
B)a decrease in saving as consumers follow suit and also increase borrowing.
C)investment spending by businesses to increase.
D)interest rates to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The tendency for expansionary fiscal policy to cause a reduction in planned investment spending by the private sector is called
A)the indirect effect.
B)the interest rate effect.
C)the crowding-out effect.
D)the Laffer effect.
A)the indirect effect.
B)the interest rate effect.
C)the crowding-out effect.
D)the Laffer effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When the economy is operating on the LRAS curve,then expansionary fiscal policy will
A)generate higher prices in the short run,but will induce aggregate supply to increase in the long run.
B)generate an increase in real national income and higher prices in both the short run and the long run.
C)generate an increase in real national income without higher prices in the short run,but then real national income will return to its long-run level and the price level will increase.
D)generate an increase in real national income and higher prices in the short run,but then real national income will decrease to its long-run level and the price level will increase some more.
A)generate higher prices in the short run,but will induce aggregate supply to increase in the long run.
B)generate an increase in real national income and higher prices in both the short run and the long run.
C)generate an increase in real national income without higher prices in the short run,but then real national income will return to its long-run level and the price level will increase.
D)generate an increase in real national income and higher prices in the short run,but then real national income will decrease to its long-run level and the price level will increase some more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Expansionary fiscal policy falls short of its goal.Some economists claim it is due to indirect crowding out.What evidence is consistent with this claim?
A)A reduction in consumer spending
B)The interest rate increased
C)Saving increased
D)The price level increased
A)A reduction in consumer spending
B)The interest rate increased
C)Saving increased
D)The price level increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If other factors are held constant and the federal government increases its borrowing from the private sector in order to pay for an increased budget deficit,the result will be
A)an overall increase in the interest rate.
B)an overall decrease in the interest rate.
C)a cancelling of the crowding out effect.
D)an increase in net exports.
A)an overall increase in the interest rate.
B)an overall decrease in the interest rate.
C)a cancelling of the crowding out effect.
D)an increase in net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the economy is experiencing an inflationary gap and the government wants to speed up the adjustment to full employment,the government should
A)increase aggregate supply by cutting spending.
B)reduce aggregate supply by cutting spending or raising taxes.
C)reduce aggregate demand by cutting taxes or raising spending.
D)reduce aggregate demand by cutting spending or raising taxes.
A)increase aggregate supply by cutting spending.
B)reduce aggregate supply by cutting spending or raising taxes.
C)reduce aggregate demand by cutting taxes or raising spending.
D)reduce aggregate demand by cutting spending or raising taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If the government holds spending constant while decreasing taxes,we expect
A)an increase in investment spending by businesses too,as they anticipate future economic growth.
B)a decrease in saving as consumers follow suit and also increase borrowing.
C)investment spending by businesses to increase.
D)interest rates to rise.
A)an increase in investment spending by businesses too,as they anticipate future economic growth.
B)a decrease in saving as consumers follow suit and also increase borrowing.
C)investment spending by businesses to increase.
D)interest rates to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the government increases spending but doesn't raise taxes,
A)aggregate demand will increase without any effect on the price level.
B)borrowing by the government will take place.
C)the government will have to sell some assets,such as oil and national parks.
D)the government will have to either lower expenditures or raise taxes the next year.
A)aggregate demand will increase without any effect on the price level.
B)borrowing by the government will take place.
C)the government will have to sell some assets,such as oil and national parks.
D)the government will have to either lower expenditures or raise taxes the next year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If the economy is experiencing a recessionary gap and the government wants to speed up the adjustment to full employment,the government should
A)increase aggregate supply by cutting spending.
B)reduce aggregate supply by cutting spending or raising taxes.
C)increase aggregate demand by cutting taxes or raising spending.
D)reduce aggregate demand by cutting spending or raising taxes.
A)increase aggregate supply by cutting spending.
B)reduce aggregate supply by cutting spending or raising taxes.
C)increase aggregate demand by cutting taxes or raising spending.
D)reduce aggregate demand by cutting spending or raising taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the economy is at an output level below the LRAS curve,which of the following fiscal policies would likely lead to a higher equilibrium level of real GDP in the short run?
A)decrease government spending
B)increase taxes
C)increase government spending and/or reduce taxes
D)decrease government spending and/or increase taxes
A)decrease government spending
B)increase taxes
C)increase government spending and/or reduce taxes
D)decrease government spending and/or increase taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
"Expansionary fiscal policy is always 100 percent effective when the short-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal." Is this statement true?
A)Yes
B)Yes,when the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal too
C)No,because crowding out could take place
D)No,because the increased spending may cause the price level to increase
A)Yes
B)Yes,when the long-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal too
C)No,because crowding out could take place
D)No,because the increased spending may cause the price level to increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
To reduce an expansionary gap,the government could
A)decrease taxes.
B)increase taxes.
C)increase spending on goods and services.
D)increase military spending.
A)decrease taxes.
B)increase taxes.
C)increase spending on goods and services.
D)increase military spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose the government decreases lump-sum taxes.This causes
A)disposable income to increase,which causes consumption spending to increase and aggregate demand to increase.
B)government spending to increase,which causes aggregate demand to increase.
C)consumption spending to decrease and spending on imports to increase.The effect on aggregate demand depends on whether domestic spending or spending on imports decreased the most.
D)disposable income to increase,which causes aggregate supply to increase.
A)disposable income to increase,which causes consumption spending to increase and aggregate demand to increase.
B)government spending to increase,which causes aggregate demand to increase.
C)consumption spending to decrease and spending on imports to increase.The effect on aggregate demand depends on whether domestic spending or spending on imports decreased the most.
D)disposable income to increase,which causes aggregate supply to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Three candidates for political office disagree over the benefits of enlarging the federal budget deficit.Candidate C says the stimulation package is needed to increase employment and national income;Candidate D says it will only cause higher prices;and Candidate F says it will have no real effect.How do the three candidates differ with respect to the condition of the economy and the effects of fiscal policy?
A)Candidate C thinks the simple Keynesian model is applicable,while D thinks the expansionary policy will crowd out private investment.F believes the economy is at full employment.
B)Candidate C thinks the simple Keynesian model is applicable;D thinks the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping;and F thinks the expansionary policy will generate lower interest rates.
C)Candidate C thinks the economy is at less than full employment and that the short-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.Candidate D believes the economy is at full employment,while Candidate F believes the expansionary policy will be offset completely.
D)Candidate C thinks the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping;D thinks interest rates will rise;and F thinks the economy is at full employment.
A)Candidate C thinks the simple Keynesian model is applicable,while D thinks the expansionary policy will crowd out private investment.F believes the economy is at full employment.
B)Candidate C thinks the simple Keynesian model is applicable;D thinks the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping;and F thinks the expansionary policy will generate lower interest rates.
C)Candidate C thinks the economy is at less than full employment and that the short-run aggregate supply curve is horizontal.Candidate D believes the economy is at full employment,while Candidate F believes the expansionary policy will be offset completely.
D)Candidate C thinks the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping;D thinks interest rates will rise;and F thinks the economy is at full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the government began providing free textbooks to college students who were already buying textbooks from the private sector,the government's action would result in
A)an increase in real GDP.
B)crowding out the private sector.
C)a ricardian dilemma.
D)a reduction of the government deficit.
A)an increase in real GDP.
B)crowding out the private sector.
C)a ricardian dilemma.
D)a reduction of the government deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Figure 11-1 
In Figure 11-1,assume that the economy is originally at E₂.If the government imposes contractionary economic policies,it is likely that
A)the new equilibrium will be E₃.
B)the new equilibrium will be E₁.
C)the price level will rise to 120.
D)aggregate demand will be represented by the A D₁ line.

In Figure 11-1,assume that the economy is originally at E₂.If the government imposes contractionary economic policies,it is likely that
A)the new equilibrium will be E₃.
B)the new equilibrium will be E₁.
C)the price level will rise to 120.
D)aggregate demand will be represented by the A D₁ line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If the economy is at an output level above the LRAS curve,which of the following fiscal policies would likely lead to a lower equilibrium level of real GDP in the short run?
A)increase government spending
B)decrease taxes
C)increase government spending and/or reduce taxes
D)decrease government spending and/or increase taxes
A)increase government spending
B)decrease taxes
C)increase government spending and/or reduce taxes
D)decrease government spending and/or increase taxes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Suppose the government increases lump-sum taxes.This causes
A)disposable income to decrease,which causes consumption spending to decrease and aggregate demand to decrease.
B)government spending to decrease,which causes aggregate demand to decrease.
C)consumption spending to decrease and spending on imports to increase.The effect on aggregate demand depends on whether domestic spending or spending on imports decreased the most.
D)disposable income to decrease,which causes aggregate supply to decrease.
A)disposable income to decrease,which causes consumption spending to decrease and aggregate demand to decrease.
B)government spending to decrease,which causes aggregate demand to decrease.
C)consumption spending to decrease and spending on imports to increase.The effect on aggregate demand depends on whether domestic spending or spending on imports decreased the most.
D)disposable income to decrease,which causes aggregate supply to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When the economy is operating on its long-run aggregate supply curve and the government initiates an expansionary fiscal policy,the result is
A)a permanent increase in real national income and a permanent increase in the price level.
B)a temporary increase in real national income and a temporary increase in the price level.
C)a temporary increase in real national income and an increase in the price level,followed by a reduction of real national income to its original level and a further increase in the price level.
D)a temporary increase in real national income and an increase in the price level,followed by a further increase in the price level.
A)a permanent increase in real national income and a permanent increase in the price level.
B)a temporary increase in real national income and a temporary increase in the price level.
C)a temporary increase in real national income and an increase in the price level,followed by a reduction of real national income to its original level and a further increase in the price level.
D)a temporary increase in real national income and an increase in the price level,followed by a further increase in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When interest rates increase in Canada,the value of the dollar is likely to
A)increase and net exports are likely to decline.
B)decrease and net exports are likely to decline.
C)increase and net exports are likely to increase.
D)remain constant and net exports are likely to remain unchanged.
A)increase and net exports are likely to decline.
B)decrease and net exports are likely to decline.
C)increase and net exports are likely to increase.
D)remain constant and net exports are likely to remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Suppose the government lowered marginal tax rates from 50 percent to 30 percent.This would be an example of
A)crowding out.
B)demand-side economics.
C)an expansionary fiscal policy.
D)a contractionary fiscal policy.
A)crowding out.
B)demand-side economics.
C)an expansionary fiscal policy.
D)a contractionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If the economy is below its full-employment level of real national income,a supply-side economist would argue the appropriate policy is
A)expansionary fiscal policy by lowering marginal tax rates.
B)expansionary fiscal policy of increasing government spending.
C)lowering marginal tax rates on people and raising them on corporations.
D)leaving the economy alone and letting the natural forces bring it into a long-run equilibrium.
A)expansionary fiscal policy by lowering marginal tax rates.
B)expansionary fiscal policy of increasing government spending.
C)lowering marginal tax rates on people and raising them on corporations.
D)leaving the economy alone and letting the natural forces bring it into a long-run equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Figure 11-2 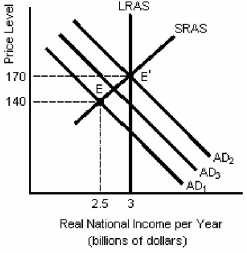
In Figure 11-2,if the government increases government spending to shift aggregate demand from A D₁ to A D₂,but aggregate demand only increases to AD₃,then it is likely that
A)price increases are preventing the full multiplier effect from taking place.
B)consumers have increased saving to prepare for higher taxes in the future.
C)investment spending has fallen by an amount equal to the increase in government spending.
D)the government also reduced taxes.

In Figure 11-2,if the government increases government spending to shift aggregate demand from A D₁ to A D₂,but aggregate demand only increases to AD₃,then it is likely that
A)price increases are preventing the full multiplier effect from taking place.
B)consumers have increased saving to prepare for higher taxes in the future.
C)investment spending has fallen by an amount equal to the increase in government spending.
D)the government also reduced taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
When private expenditures decrease as a result of increased government spending,it is known as
A)the stabilizer effect.
B)the crowding out effect.
C)the multiplier effect.
D)government deficit spending.
A)the stabilizer effect.
B)the crowding out effect.
C)the multiplier effect.
D)government deficit spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A recent government proposal to increase marginal taxes on those making over $200,000 a year will generate $100 billion in new tax revenues.A supply-side economist would argue that the actual revenue raised will be
A)less than $100 billion because some people will respond by working less.
B)exactly $100 billion because there are no offsetting factors to a tax increase.
C)more than $100 billion because lower income people will work harder when they perceive the tax system is more fair.
D)more than $100 billion because interest rates will also be affected.
A)less than $100 billion because some people will respond by working less.
B)exactly $100 billion because there are no offsetting factors to a tax increase.
C)more than $100 billion because lower income people will work harder when they perceive the tax system is more fair.
D)more than $100 billion because interest rates will also be affected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The possibility of indirect crowding out suggests that,if the government wants to engage in expansionary policy,it must
A)increase spending less than the simple Keynesian model would predict.
B)increase spending more than the simple Keynesian model would predict.
C)reduce taxes rather than increase government spending.
D)both reduce taxes and reduce spending to be able to achieve full employment.
A)increase spending less than the simple Keynesian model would predict.
B)increase spending more than the simple Keynesian model would predict.
C)reduce taxes rather than increase government spending.
D)both reduce taxes and reduce spending to be able to achieve full employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The crowding out effect is usually associated with
A)a temporary change in taxes.
B)an increase in the rate of interest following government borrowing.
C)the reinforcing impact of provincial tax changes on federal tax changes.
D)the impact of a tax cut when the aggregate supply function is horizontal.
A)a temporary change in taxes.
B)an increase in the rate of interest following government borrowing.
C)the reinforcing impact of provincial tax changes on federal tax changes.
D)the impact of a tax cut when the aggregate supply function is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Suppose the government increased marginal tax rates from 30 percent to 50 percent.This would be an example of
A)crowding out.
B)demand-side economics.
C)an expansionary fiscal policy.
D)a contractionary fiscal policy.
A)crowding out.
B)demand-side economics.
C)an expansionary fiscal policy.
D)a contractionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
According to supply-side economists,lower marginal tax rates will not necessarily lead to lower tax revenues because
A)the crowding out effect does not apply to taxes.
B)an increase in tax rates increases the opportunity cost of labour.
C)the aggregate supply curve will shift inward to the left if the tax rates are lowered.
D)the lower marginal tax rates will be applied to a growing tax base due to economic growth.
A)the crowding out effect does not apply to taxes.
B)an increase in tax rates increases the opportunity cost of labour.
C)the aggregate supply curve will shift inward to the left if the tax rates are lowered.
D)the lower marginal tax rates will be applied to a growing tax base due to economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
According to the new classical economists,increases in government spending unaccompanied by tax increases will not necessarily increase aggregate demand because
A)consumers will consume less and save more to prepare for increased taxes in the future.
B)the private sector is more likely than the public sector to spend any extra income on national defense.
C)consumers will increase their consumption proportionately more than Keynesian economists believe they will.
D)consumers will save less than they otherwise would have.
A)consumers will consume less and save more to prepare for increased taxes in the future.
B)the private sector is more likely than the public sector to spend any extra income on national defense.
C)consumers will increase their consumption proportionately more than Keynesian economists believe they will.
D)consumers will save less than they otherwise would have.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When interest rates decrease in Canada,the value of the dollar is likely to
A)increase and net exports are likely to decline.
B)decrease and net exports are likely to increase.
C)increase and net exports are likely to increase.
D)remain constant and net exports are likely to remain unchanged.
A)increase and net exports are likely to decline.
B)decrease and net exports are likely to increase.
C)increase and net exports are likely to increase.
D)remain constant and net exports are likely to remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If increased government spending has no effect on either the level of real national income or the price level,we know that
A)the economy was already at full employment.
B)the crowding out of private sector investment spending and consumption spending was complete.
C)the interest rate effect was small.
D)the government spending was on goods and services the people didn't value.
A)the economy was already at full employment.
B)the crowding out of private sector investment spending and consumption spending was complete.
C)the interest rate effect was small.
D)the government spending was on goods and services the people didn't value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Supply side economics refers to
A)attempts at increasing aggregate demand to coincide with the long-run aggregate supply.
B)attempts at creating incentives that will generate increased productivity and output.
C)selecting fiscal policy so that the revenues of the federal government are maximized.
D)all attempts at increasing government spending and narrowing the budget deficit.
A)attempts at increasing aggregate demand to coincide with the long-run aggregate supply.
B)attempts at creating incentives that will generate increased productivity and output.
C)selecting fiscal policy so that the revenues of the federal government are maximized.
D)all attempts at increasing government spending and narrowing the budget deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If government spending is increased without a raise in taxes,net exports will eventually decrease due to a rise in interest rates.This phenomenon is known as the
A)supply-side effect.
B)marginal boost.
C)Paris factor.
D)net export effect.
A)supply-side effect.
B)marginal boost.
C)Paris factor.
D)net export effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The crowding-out effect refers to the tendency of expansionary fiscal policy to
A)cause decreases in planned investment or planned consumption in the private sector.
B)cause households to save less.
C)replace low skilled labour with higher skilled labour.
D)cause firms to produce beyond capacity.
A)cause decreases in planned investment or planned consumption in the private sector.
B)cause households to save less.
C)replace low skilled labour with higher skilled labour.
D)cause firms to produce beyond capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The Ricardian equivalence theorem states that
A)an increase in government spending has no effect on aggregate supply.
B)increases in government spending have a larger impact on real national income than decreases in taxes.
C)an increase in the government budget deficit created by a current tax cut has no effect on aggregate demand.
D)an increase in the government budget deficit has no effect on real national income because it only affects the price index.
A)an increase in government spending has no effect on aggregate supply.
B)increases in government spending have a larger impact on real national income than decreases in taxes.
C)an increase in the government budget deficit created by a current tax cut has no effect on aggregate demand.
D)an increase in the government budget deficit has no effect on real national income because it only affects the price index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Lower marginal tax rates can increase total tax revenues is a tenet of
A)deficit financing.
B)the supply-side economics argument.
C)the flat -tax proposition.
D)mercantilism.
A)deficit financing.
B)the supply-side economics argument.
C)the flat -tax proposition.
D)mercantilism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Figure 11-2 
Assume the economy was at E in Figure 11-2 and the government increased spending.If the aggregate demand curve initially shifted to A D₂,but then fell back to AD₃,then we know that
A)the multiplier is larger than the government thought.
B)the economy will experience an expansionary gap.
C)some planned private investment spending has been crowded out.
D)planned private investment spending unexpectedly increased.

Assume the economy was at E in Figure 11-2 and the government increased spending.If the aggregate demand curve initially shifted to A D₂,but then fell back to AD₃,then we know that
A)the multiplier is larger than the government thought.
B)the economy will experience an expansionary gap.
C)some planned private investment spending has been crowded out.
D)planned private investment spending unexpectedly increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
One part of the supply-side economics argument is that
A)lower marginal tax rates are needed to get Parliament to spend less money.
B)lower marginal tax rates can increase total tax revenues.
C)the marginal tax rate should be set at 50 percent.
D)the relevant aggregate supply curve is close to horizontal.
A)lower marginal tax rates are needed to get Parliament to spend less money.
B)lower marginal tax rates can increase total tax revenues.
C)the marginal tax rate should be set at 50 percent.
D)the relevant aggregate supply curve is close to horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 116 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



