Deck 9: Productivity and Growth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/119
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Productivity and Growth
1
Which is the resource whose quality is most often enhanced by technological change
A)capital
B)land
C)labor
D)entrepreneurship
E)credit
A)capital
B)land
C)labor
D)entrepreneurship
E)credit
A
2
What is the definition of productivity?
A)output plus quantity of input
B)output minus quantity of input
C)quantity of input divided by output
D)output divided by quantity of input
E)output times quantity of input
A)output plus quantity of input
B)output minus quantity of input
C)quantity of input divided by output
D)output divided by quantity of input
E)output times quantity of input
D
3
Labor productivity is measured by
A)total employment/total output
B)total output/total employment
C)labor force/total output
D)total output/labor force
E)total output/potential employment
A)total employment/total output
B)total output/total employment
C)labor force/total output
D)total output/labor force
E)total output/potential employment
B
4
Labor productivity measures
A)input per unit of labor
B)output per unit of labor
C)average input per unit of labor
D)units of capital per unit of labor
E)output per unit of capital
A)input per unit of labor
B)output per unit of labor
C)average input per unit of labor
D)units of capital per unit of labor
E)output per unit of capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If Q is total real output, K is capital in use, L is labor employed, and the productivity of labor grows, other things constant, then
A)K/L rises
B)L/K rises
C)Q/L rises
D)Q/K falls
E)(Q + K)/L falls
A)K/L rises
B)L/K rises
C)Q/L rises
D)Q/K falls
E)(Q + K)/L falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An example of an increase in human capital would be
A)a new machine that humans use to produce more capital
B)an increase in wealth
C)a more educated labor force
D)all of the above
E)both a and c
A)a new machine that humans use to produce more capital
B)an increase in wealth
C)a more educated labor force
D)all of the above
E)both a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If on-the-job experience causes labor productivity to increase, that is the result of an improvement in human capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Labor productivity is measured as
A)the value of total output times total employment
B)total output of all workers employed
C)total output divided by the number of units of labor employed
D)total labor input divided by output
E)average output per unit of capital
A)the value of total output times total employment
B)total output of all workers employed
C)total output divided by the number of units of labor employed
D)total labor input divided by output
E)average output per unit of capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Labor productivity tends to fall as the capital-labor ratio rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If Q is total real output, K is capital in use, and L is labor employed, the productivity of labor is measured by
A)K/L
B)L/K
C)Q/L
D)Q/K
E)(Q + K)/L
A)K/L
B)L/K
C)Q/L
D)Q/K
E)(Q + K)/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The rules of the game refer to
A)any factor that facilitates production and exchange, such as tax laws and property rights
B)a gradual but consistent change in the price level until a fair price is attained
C)the set of election laws that ensure that all elections are fair
D)the requirements placed on firms in earning a profit
E)the requirements that households must supply labor to firms
A)any factor that facilitates production and exchange, such as tax laws and property rights
B)a gradual but consistent change in the price level until a fair price is attained
C)the set of election laws that ensure that all elections are fair
D)the requirements placed on firms in earning a profit
E)the requirements that households must supply labor to firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The difference between human capital and physical capital is that
A)human capital is used by humans whereas physical capital is not
B)only human capital increases labor productivity
C)human capital is not physical; an example of human capital is education
D)physical capital requires investment, whereas human capital does not
E)only physical capital increases labor productivity
A)human capital is used by humans whereas physical capital is not
B)only human capital increases labor productivity
C)human capital is not physical; an example of human capital is education
D)physical capital requires investment, whereas human capital does not
E)only physical capital increases labor productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Human capital includes the machinery, equipment and other manufactured creations used to produce goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If the ratio of capital to labor increases, we can expect that labor productivity will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
"The most important factor in determining a nation's standard of living in the long run is the productivity of its resources."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following does not contribute to an improved standard of living?
A)increases in the amount and quality of available resources
B)better technology
C)lower prices for the necessities of life
D)improvements in the "rules of the game"
E)increases in the quality of labor
A)increases in the amount and quality of available resources
B)better technology
C)lower prices for the necessities of life
D)improvements in the "rules of the game"
E)increases in the quality of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The resource whose productivity is most commonly measured is
A)labor
B)capital
C)land
D)energy
E)money
A)labor
B)capital
C)land
D)energy
E)money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Productivity is defined as
A)the ratio of a specific measure of output to a specific measure of input
B)the production of worthwhile goods and services
C)the market value of goods, services, and resources produced per time period (e.g., per year)
D)the average input divided by average output
E)total input divided by average output
A)the ratio of a specific measure of output to a specific measure of input
B)the production of worthwhile goods and services
C)the market value of goods, services, and resources produced per time period (e.g., per year)
D)the average input divided by average output
E)total input divided by average output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Human capital represents
A)the equipment that labor uses on-the-job to improve labor productivity
B)a direct method of measuring output-per-worker
C)the education, skills and training embodied in workers
D)the technology, developed by humans, that is embodied in equipment
E)the social institutions created by people which promote the accumulation of equipment for production
A)the equipment that labor uses on-the-job to improve labor productivity
B)a direct method of measuring output-per-worker
C)the education, skills and training embodied in workers
D)the technology, developed by humans, that is embodied in equipment
E)the social institutions created by people which promote the accumulation of equipment for production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Long-term growth in production can be explained by
A)an improvement in the quality of resources available
B)a gradual but consistent rise in the price level
C)a rapid and accelerating increase in the price level
D)a trade surplus that leads to the accumulation of gold
E)the peaks and troughs of economic fluctuations
A)an improvement in the quality of resources available
B)a gradual but consistent rise in the price level
C)a rapid and accelerating increase in the price level
D)a trade surplus that leads to the accumulation of gold
E)the peaks and troughs of economic fluctuations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The law of diminishing marginal returns states that as the quantity of capital per worker increases, other things constant, output per worker eventually
A)increases at a constant rate
B)increases at a decreasing rate
C)increases at an increasing rate
D)decreases
E)remains constant
A)increases at a constant rate
B)increases at a decreasing rate
C)increases at an increasing rate
D)decreases
E)remains constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Exhibit 8-1
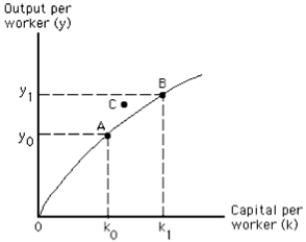
The movement from point A to point B in Exhibit 8-1 could illustrate the result of
A)an increase in the capital stock relative to the work force
B)an increase in the labor productivity growth rate
C)an increase in labor productivity because of higher quality capital
D)all of the above
E)a and b only

The movement from point A to point B in Exhibit 8-1 could illustrate the result of
A)an increase in the capital stock relative to the work force
B)an increase in the labor productivity growth rate
C)an increase in labor productivity because of higher quality capital
D)all of the above
E)a and b only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An increase in the quantity of capital per worker would
A)rotate the per-worker production function outward
B)rotate the per-worker production function inward
C)shift the per-worker production function downwards
D)shift the per-worker production function upwards
E)result in movement along the current per-worker production function
A)rotate the per-worker production function outward
B)rotate the per-worker production function inward
C)shift the per-worker production function downwards
D)shift the per-worker production function upwards
E)result in movement along the current per-worker production function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Exhibit 8-1

A technological improvement would make point C in Exhibit 8-1 attainable.

A technological improvement would make point C in Exhibit 8-1 attainable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a nation moves upward along its per-worker production function relating output per worker to capital per worker,
A)labor productivity rises
B)labor productivity falls
C)the amount of capital decreases, other things constant
D)labor input decreases
E)none of the above
A)labor productivity rises
B)labor productivity falls
C)the amount of capital decreases, other things constant
D)labor input decreases
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Exhibit 8-1

Point C in Exhibit 8-1 represents an unatainable output per worker with current technology.

Point C in Exhibit 8-1 represents an unatainable output per worker with current technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A decrease in the capital-labor ratio means
A)higher labor productivity because labor does more work
B)lower labor productivity because labor is working with relatively less capital
C)higher labor productivity because labor is producing less capital and more of other goods
D)lower labor productivity because more capital is available
E)higher labor productivity because more capital is available
A)higher labor productivity because labor does more work
B)lower labor productivity because labor is working with relatively less capital
C)higher labor productivity because labor is producing less capital and more of other goods
D)lower labor productivity because more capital is available
E)higher labor productivity because more capital is available

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If increases in capital per worker lead to increased output per worker, but by decreasing amounts as capital increases, the per-worker production function
A)is linear
B)has a decreasing slope
C)has an increasing slope
D)has a negative slope
E)is horizontal
A)is linear
B)has a decreasing slope
C)has an increasing slope
D)has a negative slope
E)is horizontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The per-worker production function illustrates the fact that as the amount of capital per worker increases, output per worker
A)increases at an increasing rate
B)increases then decreases
C)decreases but at an increasing rate
D)decreases
E)increases but at a decreasing rate
A)increases at an increasing rate
B)increases then decreases
C)decreases but at an increasing rate
D)decreases
E)increases but at a decreasing rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Exhibit 8-1

The bowed shape of the per-worker production function in Exhibit 8-1 illustrates the law of diminishing marginal returns from capital.

The bowed shape of the per-worker production function in Exhibit 8-1 illustrates the law of diminishing marginal returns from capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Improvements in technology shift the per-worker production function downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The slope of the per-worker production function diminishes as the amount of capital per worker increases. This is a reflection of the law of
A)increasing marginal returns
B)diminishing marginal returns
C)constant marginal returns
D)first diminishing then increasing marginal returns
E)demand
A)increasing marginal returns
B)diminishing marginal returns
C)constant marginal returns
D)first diminishing then increasing marginal returns
E)demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The diminishing slope of the per-worker production function reflects the law of diminishing marginal returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An improvement in the quality of capital would
A)rotate the per-worker production function upward
B)make the per-worker production function flatter
C)shift the per-worker production function downward
D)rotate the per-worker production function downward
E)have no effect on the per-worker production function
A)rotate the per-worker production function upward
B)make the per-worker production function flatter
C)shift the per-worker production function downward
D)rotate the per-worker production function downward
E)have no effect on the per-worker production function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An increase in the amount of capital per worker will
A)increase labor productivity but not capital productivity
B)increase capital productivity but not labor productivity
C)increase both labor and capital productivity
D)shift the per-worker production function upward
E)increase total output but not the productivity levels of individual workers
A)increase labor productivity but not capital productivity
B)increase capital productivity but not labor productivity
C)increase both labor and capital productivity
D)shift the per-worker production function upward
E)increase total output but not the productivity levels of individual workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following does not contribute to labor productivity growth?
A)a steepening of the per-worker production function
B)an increase in amount of capital per unit of labor
C)growth of the labor force
D)an improvement in the quality of capital
E)a decrease in the labor-capital ratio
A)a steepening of the per-worker production function
B)an increase in amount of capital per unit of labor
C)growth of the labor force
D)an improvement in the quality of capital
E)a decrease in the labor-capital ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following would not increase labor productivity?
A)technological change
B)an increased amount of capital per unit of labor
C)a lower unemployment rate
D)greater job experience for the work force
E)all of the above increase labor productivity
A)technological change
B)an increased amount of capital per unit of labor
C)a lower unemployment rate
D)greater job experience for the work force
E)all of the above increase labor productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
According to Simon Kuznets,
A)the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quantity of labor
B)the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quantity of capital
C)the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quality of inputs
D)government regulations increase labor productivity
E)government regulations decrease labor productivity
A)the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quantity of labor
B)the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quantity of capital
C)the main force behind economic growth is increases in the quality of inputs
D)government regulations increase labor productivity
E)government regulations decrease labor productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following would increase labor productivity?
A)a decrease in amount of capital per unit of labor
B)technological change
C)a decrease in the unemployment rate
D)an increase in the number of inexperienced workers entering the labor force
E)a decrease in the quality of capital
A)a decrease in amount of capital per unit of labor
B)technological change
C)a decrease in the unemployment rate
D)an increase in the number of inexperienced workers entering the labor force
E)a decrease in the quality of capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Exhibit 8-1

The shape of the per-worker production function in Exhibit 8-1 illustrates the law of diminishing marginal returns to labor.

The shape of the per-worker production function in Exhibit 8-1 illustrates the law of diminishing marginal returns to labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Over the last 100 years, U.S. labor productivity grew the fastest
A)during the Depression
B)in the 1940s
C)in the first half of the period
D)during the 1960s
E)during the 1980s
A)during the Depression
B)in the 1940s
C)in the first half of the period
D)during the 1960s
E)during the 1980s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Since 1870, U.S. labor productivity growth has averaged roughly 2.1 percent annually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Productivity growth is important because
A)it is the only way an economy can increase GDP
B)a small decrease in productivity growth causes a large decline in GDP
C)a large increase in productivity growth causes a small decrease in GDP
D)it causes an increase in the quantity of all resources available to an economy
E)it ultimately increases a nation's standard of living
A)it is the only way an economy can increase GDP
B)a small decrease in productivity growth causes a large decline in GDP
C)a large increase in productivity growth causes a small decrease in GDP
D)it causes an increase in the quantity of all resources available to an economy
E)it ultimately increases a nation's standard of living

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Labor productivity in the United States has been
A)growing at ever-increasing rates since World War II
B)growing but at lower rates in the last 25 years compared to the 25 years immediately after World War II
C)falling for the last 50 years
D)largely unchanged over the last 50 years
E)growing more rapidly in the last 50 years than in most other developed economies
A)growing at ever-increasing rates since World War II
B)growing but at lower rates in the last 25 years compared to the 25 years immediately after World War II
C)falling for the last 50 years
D)largely unchanged over the last 50 years
E)growing more rapidly in the last 50 years than in most other developed economies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Labor productivity the United States has never fallen has never fallen from one year to the next.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What was the average yearly increase in U.S. labor productivity growth between the 1870s and the early years of the 21st century?
A)about 1 percent
B)about 2 percent
C)about 5 percent
D)about 10 percent
E)between 0 and 1 percent
A)about 1 percent
B)about 2 percent
C)about 5 percent
D)about 10 percent
E)between 0 and 1 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Between the 1880s and the early 21st century, U.S. productivity increased at a constant annual rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following would not be considered a developed country?
A)Pakistan
B)the United States
C)Japan
D)Australia
E)Belgium
A)Pakistan
B)the United States
C)Japan
D)Australia
E)Belgium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The rules of the game refer to
A)any factor that facilitates production and exchange
B)a gradual but consistent change in the price level until a fair price is attained
C)the set of election laws that ensure that all votes are counted in every election
D)the requirements place on firms earning a profit
E)the requirements that households must provide funding for the investments that firms need to make
A)any factor that facilitates production and exchange
B)a gradual but consistent change in the price level until a fair price is attained
C)the set of election laws that ensure that all votes are counted in every election
D)the requirements place on firms earning a profit
E)the requirements that households must provide funding for the investments that firms need to make

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The rules of the game include all of the following except one. Which is the exception?
A)the laws, customs, conventions and other institutional elements associated with trade
B)property rights
C)ensuring that the market process generates a fair price to all
D)a stable political environment
E)a stable legal system
A)the laws, customs, conventions and other institutional elements associated with trade
B)property rights
C)ensuring that the market process generates a fair price to all
D)a stable political environment
E)a stable legal system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Over the last century, U.S. labor productivity has
A)fallen
B)been constant, on average
C)grown at about 2 percent per year
D)grown at about 8 percent per year
E)grown at about 15 percent per year
A)fallen
B)been constant, on average
C)grown at about 2 percent per year
D)grown at about 8 percent per year
E)grown at about 15 percent per year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Over the last 100 years, the U.S. labor productivity growth rate experienced its largest declines
A)during the Great Depression
B)in the 1940s
C)during the 1950s
D)during the 1980s
E)a and c
A)during the Great Depression
B)in the 1940s
C)during the 1950s
D)during the 1980s
E)a and c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following did Simon Kuznets find to be the driving force behind modern economic growth?
A)changes in the quantity of labor
B)changes in the quantity of capital
C)changes in the quantities of labor and capital
D)about half the growth is due to changes in quantity of inputs; the other half is due to changes in quality of inputs
E)nearly all was due to improvements in input quality
A)changes in the quantity of labor
B)changes in the quantity of capital
C)changes in the quantities of labor and capital
D)about half the growth is due to changes in quantity of inputs; the other half is due to changes in quality of inputs
E)nearly all was due to improvements in input quality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The reason why productivity growth is so important is that
A)it is the key to long-run increases in the standard of living
B)per capita GDP ultimately depends on labor productivity
C)total GDP cannot increase without increases in resource productivity levels
D)all of the above
E)both a and b
A)it is the key to long-run increases in the standard of living
B)per capita GDP ultimately depends on labor productivity
C)total GDP cannot increase without increases in resource productivity levels
D)all of the above
E)both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
According to Nobel prize winner Simon Kuznets, the greatest increase in output and economic growth comes from changes in the
A)quantities of resources
B)quantities of natural resources (land)
C)quantities of labor
D)qualities of resources
E)quantities of capital
A)quantities of resources
B)quantities of natural resources (land)
C)quantities of labor
D)qualities of resources
E)quantities of capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The reason why small changes in productivity growth rates have large long-term effects on economic growth over the long run is that
A)lower productivity growth makes labor discouraged, compounding the problem
B)lower productivity growth effects on the economy are compounded over the years, leading to large cumulative effects
C)when the productivity growth rate falls, output actually falls
D)lower productivity growth for one resource means lower productivity growth for all resources
E)output usually falls when productivity grows
A)lower productivity growth makes labor discouraged, compounding the problem
B)lower productivity growth effects on the economy are compounded over the years, leading to large cumulative effects
C)when the productivity growth rate falls, output actually falls
D)lower productivity growth for one resource means lower productivity growth for all resources
E)output usually falls when productivity grows

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Over the past century in the United States, the growth of labor productivity was highest in the
A)1940s
B)1950s
C)1960s
D)1970s
E)1980s
A)1940s
B)1950s
C)1960s
D)1970s
E)1980s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is most likely to increase productivity growth, as measured using GDP statistics?
A)reduced capital formation
B)decreased human capital
C)increased research and development
D)increased government regulation
E)higher prices for raw materials
A)reduced capital formation
B)decreased human capital
C)increased research and development
D)increased government regulation
E)higher prices for raw materials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Productivity growth averaged approximately 3 percent per year between 1948 and 1973; since that time it has averaged approximately 5 percent annually.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A small change in the rate of productivity growth will have
A)a small impact on output in both the short run and the long run
B)a large impact on output in both the short run and the long run
C)a small impact on output in the short run but a large impact in the long run
D)a large impact on output in the short run but a small impact in the long run
E)no effect on output at all
A)a small impact on output in both the short run and the long run
B)a large impact on output in both the short run and the long run
C)a small impact on output in the short run but a large impact in the long run
D)a large impact on output in the short run but a small impact in the long run
E)no effect on output at all

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Most economists agree that the most important factor contributing to the recent reduction in U.S. labor productivity growth rate has been the increased level of government regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following would not slow down productivity growth?
A)The composition of the work force changes so that more young people and fewer middle-aged people are working.
B)The composition of the work force changes so that more women, who enter and leave the work force more frequently than men, are included.
C)The quality of education decreases.
D)Investment declines.
E)Firms switch from providing services to producing goods.
A)The composition of the work force changes so that more young people and fewer middle-aged people are working.
B)The composition of the work force changes so that more women, who enter and leave the work force more frequently than men, are included.
C)The quality of education decreases.
D)Investment declines.
E)Firms switch from providing services to producing goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following would be likely to cause a decrease in the labor productivity growth rate?
A)an increase in student achievement scores
B)a service sector that is growing as a percentage of GDP
C)increased spending on research and development
D)increases in capital formation
E)technological change
A)an increase in student achievement scores
B)a service sector that is growing as a percentage of GDP
C)increased spending on research and development
D)increases in capital formation
E)technological change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is not likely to cause a decrease in labor productivity?
A)a decline in student achievement scores
B)a service sector that is growing as a percentage of GDP
C)decreased spending on research and development
D)increases in capital formation
E)high federal budget deficits
A)a decline in student achievement scores
B)a service sector that is growing as a percentage of GDP
C)decreased spending on research and development
D)increases in capital formation
E)high federal budget deficits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If population increases, which of the following must be true?
A)GDP will increase.
B)GDP per capita will fall.
C)GDP must increase if the same standard of living is to be maintained.
D)The labor force must increase if the same standard of living is to be maintained.
E)Overall demand increases, but per capita aggregate demand remains constant.
A)GDP will increase.
B)GDP per capita will fall.
C)GDP must increase if the same standard of living is to be maintained.
D)The labor force must increase if the same standard of living is to be maintained.
E)Overall demand increases, but per capita aggregate demand remains constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If both total employment and total output always grew by 2 percent each year, what would the annual growth in labor productivity in an economy be over a decade?
A)0 percent
B)2 percent
C)10 percent
D)20 percent
E)2 percent times the size of the labor force
A)0 percent
B)2 percent
C)10 percent
D)20 percent
E)2 percent times the size of the labor force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The productivity growth slowdown of the late 1970s and early 1980s may have been due, in part, to the environmental and workplace safety legislation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following is the best indicator of the standard of living?
A)nominal GDP
B)real GDP
C)real GDP per capita
D)productivity
E)productivity per unit of labor
A)nominal GDP
B)real GDP
C)real GDP per capita
D)productivity
E)productivity per unit of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the period 2005-2012, the annual productivity growth rate was approximately
A)1.6 percent per year
B)3 percent per year
C)4.2 percent per year
D)5 percent per year
E)6 percent per year
A)1.6 percent per year
B)3 percent per year
C)4.2 percent per year
D)5 percent per year
E)6 percent per year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The only way the standard of living can increase is for labor productivity to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The impact of computers on U.S. productivity growth
A)has been disappointingly small--about one-half percentage point annually between 1972 and 1996
B)has been dramatic, contributing to significant growth during the early years of the 21st century
C)has been significant in the health care sector, but not elsewhere
D)has actually been negative in most industries
E)was greater during the period 1972-1990 than it has been since that time
A)has been disappointingly small--about one-half percentage point annually between 1972 and 1996
B)has been dramatic, contributing to significant growth during the early years of the 21st century
C)has been significant in the health care sector, but not elsewhere
D)has actually been negative in most industries
E)was greater during the period 1972-1990 than it has been since that time

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Per capita GDP in the United States has declined since 1950.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If labor productivity growth slows, the standard of living must decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Technological change leads to unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Declining growth in productivity means that the standard of living has been falling over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The growing use of computers led to a substantial increase in overall U.S. productivity growth in the era from 1995-2005.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Between 1982 and 2002, U.S. GDP per capita grew at an average rate of 2.2 percent per year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Since 1996,
A)U.S. productivity growth skyrocketed, at least intitially, as more computers were installed
B)the computer sector has grown faster than the U.S. economy as a whole
C)spending on computers has been approximately constant as a fraction of total U.S. investment spending
D)the contribution of computers to U.S. productivity growth has been negative
E)computing technology did not improve enough to have a measurable impact on U.S. productivity
A)U.S. productivity growth skyrocketed, at least intitially, as more computers were installed
B)the computer sector has grown faster than the U.S. economy as a whole
C)spending on computers has been approximately constant as a fraction of total U.S. investment spending
D)the contribution of computers to U.S. productivity growth has been negative
E)computing technology did not improve enough to have a measurable impact on U.S. productivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Physical capital includes all of the following except
A)roads and bridges
B)machinery and factories
C)communications networks
D)high school diploma or college degree
E)a new dump truck
A)roads and bridges
B)machinery and factories
C)communications networks
D)high school diploma or college degree
E)a new dump truck

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The process of adding more capital per worker is known as "capital deepening."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



