Deck 17: Monetary Theory and Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/186
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Monetary Theory and Policy
1
The demand for money varies
A)directly with both the price level and the level of real GDP
B)inversely with both the price level and the level of real GDP
C)inversely with the price level and directly with the level of real GDP
D)directly with the price level and inversely with the level of real GDP
E)inversely with the level of nominal GDP
A)directly with both the price level and the level of real GDP
B)inversely with both the price level and the level of real GDP
C)inversely with the price level and directly with the level of real GDP
D)directly with the price level and inversely with the level of real GDP
E)inversely with the level of nominal GDP
A
2
The demand for money
A)d and e are correct
B)all of the following are correct
C)decreases as the average selling price of a unit of output increases
D)increases as GDP increases
E)is increased by credit card usage
A)d and e are correct
B)all of the following are correct
C)decreases as the average selling price of a unit of output increases
D)increases as GDP increases
E)is increased by credit card usage
D
3
The demand for money is based primarily on money's role as a(n)
A)store of wealth
B)medium of exchange
C)standard of value
D)interest-bearing asset
E)non-interest-bearing asset
A)store of wealth
B)medium of exchange
C)standard of value
D)interest-bearing asset
E)non-interest-bearing asset
B
4
In deciding how much money to hold, you should compare the
A)disadvantage of liquidity with the advantage of earning more interest
B)advantage of liquidity with the disadvantage of losing interest
C)disadvantage of storing wealth with the advantage of having a medium of exchange
D)advantage of storing wealth with the advantage of having a medium of exchange
E)advantage of liquidity with the disadvantage of storing wealth
A)disadvantage of liquidity with the advantage of earning more interest
B)advantage of liquidity with the disadvantage of losing interest
C)disadvantage of storing wealth with the advantage of having a medium of exchange
D)advantage of storing wealth with the advantage of having a medium of exchange
E)advantage of liquidity with the disadvantage of storing wealth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
People will hold __________ money as the interest rate __________ because they will __________ other financial assets.
A)more; decreases; buy
B)more; increases; sell
C)more; decreases; sell
D)less; increases; sell
E)less; decreases; buy
A)more; decreases; buy
B)more; increases; sell
C)more; decreases; sell
D)less; increases; sell
E)less; decreases; buy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When the demand for money is shown on a graph, the __________ is on the vertical axis, and the __________ is on the horizontal axis.
A)quantity of money; interest rate
B)interest rate; quantity of money
C)real GDP; quantity of money
D)nominal GDP; quantity of money
E)price level; quantity of money
A)quantity of money; interest rate
B)interest rate; quantity of money
C)real GDP; quantity of money
D)nominal GDP; quantity of money
E)price level; quantity of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Speaking of the demand for money
A)makes no sense in a modern society in which most people use credit cards
B)makes no sense in a modern society in which most people use checks
C)makes sense in a modern society in which most people use checks, since demand deposits are included in M1, but it does not make sense in a society in which the primary payment is by credit card
D)makes sense in a modern society in which most people use credit cards, since credit cards are included in M1, but it does not make sense in a society in which the primary payment is by check
E)is relevant even in a society in which primary payment is by credit card, since eventually all accounts must be settled with money
A)makes no sense in a modern society in which most people use credit cards
B)makes no sense in a modern society in which most people use checks
C)makes sense in a modern society in which most people use checks, since demand deposits are included in M1, but it does not make sense in a society in which the primary payment is by credit card
D)makes sense in a modern society in which most people use credit cards, since credit cards are included in M1, but it does not make sense in a society in which the primary payment is by check
E)is relevant even in a society in which primary payment is by credit card, since eventually all accounts must be settled with money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The money demand curve shifts to the right whenever there is a decrease in the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The opportunity cost of holding money is measured by the
A)interest rate
B)liquidity lost by holding money
C)money supply curve
D)inflation rate
E)cost of cashing in financial assets
A)interest rate
B)liquidity lost by holding money
C)money supply curve
D)inflation rate
E)cost of cashing in financial assets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the opportunity cost of holding money rather than some other financial asset?
A)the forgone interest income
B)the forgone utility
C)time
D)the forgone leisure
E)the forgone profit
A)the forgone interest income
B)the forgone utility
C)time
D)the forgone leisure
E)the forgone profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following best explains why the demand for money depends upon the interest rate?
A)Money is an interest-earning asset.
B)Money is not an interest-earning asset.
C)The alternatives to holding money are not interest-earning assets.
D)The alternatives to holding money earn more interest than money does.
E)People must pay interest on loans.
A)Money is an interest-earning asset.
B)Money is not an interest-earning asset.
C)The alternatives to holding money are not interest-earning assets.
D)The alternatives to holding money earn more interest than money does.
E)People must pay interest on loans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The money demand curve slopes
A)downward because the cost of holding money decreases as the interest rate decreases
B)downward because the cost of holding money increases as the interest rate decreases
C)upward because people demand more money as GDP increases
D)upward because people demand more money as GDP decreases
E)downward because people demand more money as the price level increases
A)downward because the cost of holding money decreases as the interest rate decreases
B)downward because the cost of holding money increases as the interest rate decreases
C)upward because people demand more money as GDP increases
D)upward because people demand more money as GDP decreases
E)downward because people demand more money as the price level increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The relationship between the interest rate and the quantity of money demanded
A)is a direct relationship
B)is an inverse relationship
C)is nonexistent
D)is a direct relationship when the interest rate is low and an inverse relationship when the interest rate is high
E)is an inverse relationship when the interest rate is low and a direct relationship when the interest rate is high
A)is a direct relationship
B)is an inverse relationship
C)is nonexistent
D)is a direct relationship when the interest rate is low and an inverse relationship when the interest rate is high
E)is an inverse relationship when the interest rate is low and a direct relationship when the interest rate is high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The opportunity cost of holding money increases when
A)the interest rate rises
B)the interest rate falls
C)the price level falls
D)nominal GDP rises
E)nominal GDP falls
A)the interest rate rises
B)the interest rate falls
C)the price level falls
D)nominal GDP rises
E)nominal GDP falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The money demand curve describes how the quantity of money demanded varies with
A)nominal GDP
B)real GDP
C)the price level
D)the interest rate
E)consumption
A)nominal GDP
B)real GDP
C)the price level
D)the interest rate
E)consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An increase in the price level will
A)shift the money demand curve to the right
B)shift the money demand curve to the left
C)increase the quantity of money people want to hold
D)decrease the quantity of money people want to hold
E)have no impact on the money demand curve
A)shift the money demand curve to the right
B)shift the money demand curve to the left
C)increase the quantity of money people want to hold
D)decrease the quantity of money people want to hold
E)have no impact on the money demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The money demand curve will shift when there is a change in
A)interest rates
B)velocity
C)the money supply
D)the opportunity cost of holding money
E)nominal GDP
A)interest rates
B)velocity
C)the money supply
D)the opportunity cost of holding money
E)nominal GDP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The higher the interest rate, the more of their wealth people will hold as money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
If the price level rises, the money demand curve will shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The demand for money is depicted by a curve downward sloping curve because if the interest rate falls, the opportunity cost of holding assets in the form of money decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If the demand for money increases,
A)the interest rate will fall
B)there will be a movement downward along the money demand curve
C)there will be a movement upward (to the left) along the money demand curve
D)there will be a rightward shift of the money demand curve
E)there will be a leftward shift of the money demand curve
A)the interest rate will fall
B)there will be a movement downward along the money demand curve
C)there will be a movement upward (to the left) along the money demand curve
D)there will be a rightward shift of the money demand curve
E)there will be a leftward shift of the money demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Exhibit 16-1
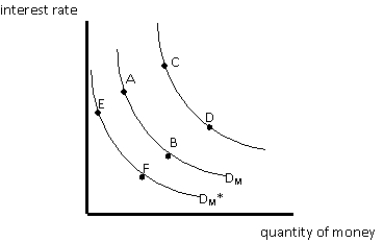
Referring to Exhibit 16-1, an increase in the price level will cause a move from
A)B to A
B)A to B
C)DM to DM'
D)DM to DM*
E)E to F

Referring to Exhibit 16-1, an increase in the price level will cause a move from
A)B to A
B)A to B
C)DM to DM'
D)DM to DM*
E)E to F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A decrease in the interest rate will
A)shift the money demand curve to the right
B)shift the money demand curve to the left
C)increase the quantity of money people want to hold
D)decrease the quantity of money people want to hold
E)have no impact on the money demand curve
A)shift the money demand curve to the right
B)shift the money demand curve to the left
C)increase the quantity of money people want to hold
D)decrease the quantity of money people want to hold
E)have no impact on the money demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the price level rises, then the
A)money supply will increase
B)money supply will decrease
C)quantity of money supplied will increase
D)quantity of money supplied will decrease
E)demand for money will increase
A)money supply will increase
B)money supply will decrease
C)quantity of money supplied will increase
D)quantity of money supplied will decrease
E)demand for money will increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the money supply increases, the interest rate will __________ and people will want to hold a __________ quantity of money.
A)rise; greater
B)rise; smaller
C)not change; greater
D)fall; greater
E)fall; smaller
A)rise; greater
B)rise; smaller
C)not change; greater
D)fall; greater
E)fall; smaller

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A movement upward and to the left along the money demand curve is caused by
A)an increase in the interest rate
B)a decrease in the interest rate
C)a decrease in real GDP
D)an increase in real GDP
E)an increase in the average price level
A)an increase in the interest rate
B)a decrease in the interest rate
C)a decrease in real GDP
D)an increase in real GDP
E)an increase in the average price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not assumed to be constant along the money demand curve?
A)the price level
B)the interest rate
C)real GDP
D)nominal GDP
E)individual's tastes and preferences
A)the price level
B)the interest rate
C)real GDP
D)nominal GDP
E)individual's tastes and preferences

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following, other things constant, will shift the money demand curve to the left?
A)an increase in the interest rate
B)a decrease in the interest rate
C)a decrease in real GDP
D)an increase in real GDP
E)an increase in the price level
A)an increase in the interest rate
B)a decrease in the interest rate
C)a decrease in real GDP
D)an increase in real GDP
E)an increase in the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When people exchange money for financial assets, the interest rate rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following would cause a downward movement along the money demand curve?
A)an increase in the interest rate
B)a decrease in the interest rate
C)a decrease in real GDP
D)an increase in real GDP
E)an increase in the price level
A)an increase in the interest rate
B)a decrease in the interest rate
C)a decrease in real GDP
D)an increase in real GDP
E)an increase in the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
As the price level rises, money __________ causing interest rates to __________ and investment spending to __________.
A)demand rises; fall; fall
B)demand rises; rise; fall
C)demand falls; rise; rise
D)supply rises; rise; fall
E)supply falls; fall; rise
A)demand rises; fall; fall
B)demand rises; rise; fall
C)demand falls; rise; rise
D)supply rises; rise; fall
E)supply falls; fall; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The opportunity cost of holding money
A)includes bank service charges
B)is the interest foregone on potential interest-earning assets
C)varies inversely with the rate of interest
D)affects relatively few individuals
E)is determined exclusively by the Fed
A)includes bank service charges
B)is the interest foregone on potential interest-earning assets
C)varies inversely with the rate of interest
D)affects relatively few individuals
E)is determined exclusively by the Fed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the interest rate rises, people hold
A)less money because its opportunity cost has increased
B)more money because its opportunity cost has increased
C)less money because its opportunity cost has declined
D)more money because its opportunity cost has declined
E)the same amount of money
A)less money because its opportunity cost has increased
B)more money because its opportunity cost has increased
C)less money because its opportunity cost has declined
D)more money because its opportunity cost has declined
E)the same amount of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The supply of money is depicted diagrammatically as a vertical line because the quantity of money supplied is totally dependent on the rate of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Exhibit 16-1

Referring to Exhibit 16-1, an increase in the interest rate will cause a move from
A)B to A
B)A to B
C)DM to DM'
D)DM to DM*
E)C to D

Referring to Exhibit 16-1, an increase in the interest rate will cause a move from
A)B to A
B)A to B
C)DM to DM'
D)DM to DM*
E)C to D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the money supply decreases, the opportunity cost of holding money __________ and people will want to hold __________ quantity of money.
A)rises; a greater
B)rises; a smaller
C)does not change; the same
D)falls; a greater
E)falls; a smaller
A)rises; a greater
B)rises; a smaller
C)does not change; the same
D)falls; a greater
E)falls; a smaller

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The equilibrium interest rate is determined by
A)the Fed
B)Congress
C)the demand for money alone
D)the supply of money alone
E)both the supply of and demand for money
A)the Fed
B)Congress
C)the demand for money alone
D)the supply of money alone
E)both the supply of and demand for money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Exhibit 16-1

Referring to Exhibit 16-1, an increase in the level of real GDP will cause a move from
A)B to A
B)A to B
C)DM to DM'
D)DM to DM*
E)E to F

Referring to Exhibit 16-1, an increase in the level of real GDP will cause a move from
A)B to A
B)A to B
C)DM to DM'
D)DM to DM*
E)E to F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following, other things constant, will shift the money demand curve to the right?
A)an increase in the interest rate
B)a decrease in the interest rate
C)an increase in real GDP
D)a decrease in real GDP
E)a decrease in the price level
A)an increase in the interest rate
B)a decrease in the interest rate
C)an increase in real GDP
D)a decrease in real GDP
E)a decrease in the price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When the money supply increases, people get rid of their excess money by buying real assets, such as durable goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, an increase in the money supply will cause in the short run a(n)
A)increase in both the price level and real GDP
B)decrease in both the price level and real GDP
C)increase in real GDP and a decrease in the price level
D)decrease in real GDP and an increase in the price level
E)increase in the price level only
A)increase in both the price level and real GDP
B)decrease in both the price level and real GDP
C)increase in real GDP and a decrease in the price level
D)decrease in real GDP and an increase in the price level
E)increase in the price level only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Exhibit 16-2
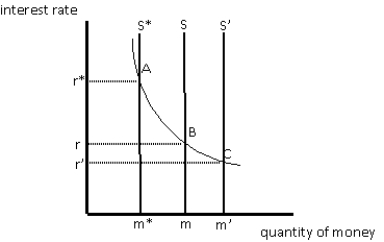
Given the demand for money in Exhibit 16-2, if the supply of money is given by the supply curve labelled S, the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money would be
A)r and m
B)r* and m*
C)r' and m'
D)r and m'
E)cannot tell from the information given

Given the demand for money in Exhibit 16-2, if the supply of money is given by the supply curve labelled S, the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money would be
A)r and m
B)r* and m*
C)r' and m'
D)r and m'
E)cannot tell from the information given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the Fed increases the money supply, then
A)the interest rate declines and the quantity of money demanded increases
B)the interest rate declines and the quantity of money demanded declines
C)the interest rate increases and the quantity of money demanded increases
D)the interest rate increases and the quantity of money demanded declines
E)nothing happens to the quantity of money demanded
A)the interest rate declines and the quantity of money demanded increases
B)the interest rate declines and the quantity of money demanded declines
C)the interest rate increases and the quantity of money demanded increases
D)the interest rate increases and the quantity of money demanded declines
E)nothing happens to the quantity of money demanded

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In a macroeconomic model, increases in the money supply decrease the interest rate, increase investment, and thus raise employment and real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An increase in the money supply will
A)increase the demand for money at each interest rate
B)decrease the demand for money at each interest rate
C)lead people to try to exchange money for interest-bearing assets
D)lead people to try to exchange interest-bearing assets for money
E)increase the interest rate
A)increase the demand for money at each interest rate
B)decrease the demand for money at each interest rate
C)lead people to try to exchange money for interest-bearing assets
D)lead people to try to exchange interest-bearing assets for money
E)increase the interest rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the Fed wanted to stimulate the economy, it might
A)buy bonds to lower the money supply
B)sell bonds to lower the money supply
C)raise the discount rate to increase the money supply
D)lower the discount rate to increase the money supply
E)increase the required reserve ratio to lower the money supply
A)buy bonds to lower the money supply
B)sell bonds to lower the money supply
C)raise the discount rate to increase the money supply
D)lower the discount rate to increase the money supply
E)increase the required reserve ratio to lower the money supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the short run, a decrease in the money supply will cause a decrease in Gross Domestic Product and a decrease in the price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which one of the following statements is correct?
A)The lower the interest rate, the higher the opportunity cost of holding assets in the form of money.
B)A vertical money supply curve means that the quantity of money supplied is independent of the interest rate.
C)The larger the supply of money, the higher the interest rate, all things equal.
D)Travelers checks and government bonds are equally liquid assets.
E)The transactions demand for money increases whenever the price level decreases.
A)The lower the interest rate, the higher the opportunity cost of holding assets in the form of money.
B)A vertical money supply curve means that the quantity of money supplied is independent of the interest rate.
C)The larger the supply of money, the higher the interest rate, all things equal.
D)Travelers checks and government bonds are equally liquid assets.
E)The transactions demand for money increases whenever the price level decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Of the following, the major influence on the supply of money is
A)interest rates
B)prices
C)the transactions demand for money
D)GDP
E)the Fed
A)interest rates
B)prices
C)the transactions demand for money
D)GDP
E)the Fed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
As the interest rate decreases,
A)the demand for investment curve shifts to the right
B)the demand for investment curve shifts to the left
C)there is a downward movement along the demand for investment curve
D)there is an upward movement along the demand for investment curve
E)GDP decreases
A)the demand for investment curve shifts to the right
B)the demand for investment curve shifts to the left
C)there is a downward movement along the demand for investment curve
D)there is an upward movement along the demand for investment curve
E)GDP decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
In the aggregate demand-aggregate supply model, a decrease in the money supply will cause a short-run
A)increase in both the price level and real GDP
B)decrease in both the price level and real GDP
C)increase in real GDP and a decrease in the price level
D)decrease in real GDP and an increase in the price level
E)increase in the price level only
A)increase in both the price level and real GDP
B)decrease in both the price level and real GDP
C)increase in real GDP and a decrease in the price level
D)decrease in real GDP and an increase in the price level
E)increase in the price level only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An increase in the money supply will cause a decrease in planned investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
As the interest rate increases,
A)the demand for investment curve shifts to the right
B)the demand for investment curve shifts to the left
C)there is a movement downward along the demand for investment curve
D)there is a movement upward along the demand for investment curve
E)GDP increases
A)the demand for investment curve shifts to the right
B)the demand for investment curve shifts to the left
C)there is a movement downward along the demand for investment curve
D)there is a movement upward along the demand for investment curve
E)GDP increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If there is a decrease in the supply of money, which one of the following is most likely to happen?
A)the demand for money will increase
B)planned investment spending will increase
C)interest rates will rise
D)aggregate expenditure will increase
E)the demand for money will decrease
A)the demand for money will increase
B)planned investment spending will increase
C)interest rates will rise
D)aggregate expenditure will increase
E)the demand for money will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The demand curve for investment is graphed with __________ on the vertical axis and __________ on the horizontal axis.
A)the interest rate; investment
B)investment; the interest rate
C)the price level; investment
D)investment; the price level
E)real GDP; investment
A)the interest rate; investment
B)investment; the interest rate
C)the price level; investment
D)investment; the price level
E)real GDP; investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When an increase in the money supply reduces the interest rate, investment and nominal GDP increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the quantity of money supplied exceeds the quantity of money demanded,
A)this is evidence of a failed fiscal policy
B)this indicates that the supply of money curve is horizontal
C)the interest rate will fall
D)the quantity of money demanded will increase
E)the transactions money demand curve will shift to the right
A)this is evidence of a failed fiscal policy
B)this indicates that the supply of money curve is horizontal
C)the interest rate will fall
D)the quantity of money demanded will increase
E)the transactions money demand curve will shift to the right

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If the Fed buys bonds, then the money supply
A)increases, the interest rate falls, and the quantity of money demanded increases
B)falls, the interest rate falls, and the quantity of money demanded increases
C)increases, the interest rate increases, and the quantity of money demanded increases
D)falls, the interest rate increases, and the quantity of money demanded falls
E)falls, the interest rate falls, and the quantity of money demanded falls
A)increases, the interest rate falls, and the quantity of money demanded increases
B)falls, the interest rate falls, and the quantity of money demanded increases
C)increases, the interest rate increases, and the quantity of money demanded increases
D)falls, the interest rate increases, and the quantity of money demanded falls
E)falls, the interest rate falls, and the quantity of money demanded falls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An increase in the interest rate will
A)have no effect on investment, since investment is autonomous
B)increase investment, since it will be more profitable to hold stocks and bonds
C)increase investment, since people will be less willing to hold money
D)decrease investment only if firms have to borrow money to make investments
E)decrease investment regardless of whether firms have to borrow money to make an investment
A)have no effect on investment, since investment is autonomous
B)increase investment, since it will be more profitable to hold stocks and bonds
C)increase investment, since people will be less willing to hold money
D)decrease investment only if firms have to borrow money to make investments
E)decrease investment regardless of whether firms have to borrow money to make an investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Exhibit 16-2

Each of the following can cause the supply of money to shift from S to S* in Exhibit 16-2, except
A)an increase in the required reserve ratio
B)the sale of US Treasury securities by the Fed
C)a decrease in the required reserve ratio
D)a decrease in the discount rate
E)an increase in excess reserves in the banking system

Each of the following can cause the supply of money to shift from S to S* in Exhibit 16-2, except
A)an increase in the required reserve ratio
B)the sale of US Treasury securities by the Fed
C)a decrease in the required reserve ratio
D)a decrease in the discount rate
E)an increase in excess reserves in the banking system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If interest rates are __________ to changes in the money supply and planned investment expenditures are __________ to interest rate changes, then monetary policy will be ineffective in changing aggregate demand.
A)responsive; sensitive
B)responsive; insensitive
C)not responsive; sensitive
D)not responsive; insensitive
E)none of the above
A)responsive; sensitive
B)responsive; insensitive
C)not responsive; sensitive
D)not responsive; insensitive
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
If the Fed decreases the money supply, causing the interest rate to rise, GDP
A)increases by the same amount as the increase in the interest rate
B)decreases by more than the increase in the interest rate because of the multiplier
C)decreases by the same amount as the decrease in investment
D)decreases by more than the decrease in investment because of the multiplier
E)decreases by less than the decrease in investment because of the multiplier
A)increases by the same amount as the increase in the interest rate
B)decreases by more than the increase in the interest rate because of the multiplier
C)decreases by the same amount as the decrease in investment
D)decreases by more than the decrease in investment because of the multiplier
E)decreases by less than the decrease in investment because of the multiplier

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
What would be the ultimate effect of a reduction in the money supply?
A)a leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve
B)a rightward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve
C)a movement upward along the aggregate demand curve
D)a movement downward along the aggregate demand curve
E)such a monetary policy would have no impact at all
A)a leftward shift of the aggregate demand curve
B)a rightward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve
C)a movement upward along the aggregate demand curve
D)a movement downward along the aggregate demand curve
E)such a monetary policy would have no impact at all

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A decrease in the money supply causes interest rates to __________, investment spending to __________ and Gross Domestic Product to __________.
A)fall; rise; fall
B)fall; fall; rise
C)rise; rise; rise
D)rise; fall; fall
E)rise; fall; rise
A)fall; rise; fall
B)fall; fall; rise
C)rise; rise; rise
D)rise; fall; fall
E)rise; fall; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If the Fed sells government securities to banks, eventually we expect
A)aggregate demand to increase
B)short-run aggregate supply to decrease
C)interest rates to decrease
D)planned investment expenditures to decrease
E)real Gross Domestic Product to increase
A)aggregate demand to increase
B)short-run aggregate supply to decrease
C)interest rates to decrease
D)planned investment expenditures to decrease
E)real Gross Domestic Product to increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An increase in the money supply causes interest rates to __________, investment spending to __________ and aggregate demand to __________.
A)rise; rise; rise
B)rise; fall; rise
C)rise; fall; fall
D)fall; rise; fall
E)fall; rise; rise
A)rise; rise; rise
B)rise; fall; rise
C)rise; fall; fall
D)fall; rise; fall
E)fall; rise; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
As a result of expansionary monetary policy,
A)both aggregate expenditure and aggregate demand increase
B)both aggregate expenditure and aggregate demand decrease
C)aggregate expenditure increases and aggregate demand decreases
D)aggregate expenditure decreases and aggregate demand increases
E)aggregate expenditure remains unchanged; aggregate demand increases
A)both aggregate expenditure and aggregate demand increase
B)both aggregate expenditure and aggregate demand decrease
C)aggregate expenditure increases and aggregate demand decreases
D)aggregate expenditure decreases and aggregate demand increases
E)aggregate expenditure remains unchanged; aggregate demand increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
For monetary policy to be effective in changing planned investment spending,
A)interest rates must not be responsive to changes in the money supply
B)interest rates must be sensitive to changes in Gross Domestic Product
C)investment must be sensitive to changes in interest rates
D)investment must be sensitive to changes in the spending multiplier
E)the spending multiplier must be stable
A)interest rates must not be responsive to changes in the money supply
B)interest rates must be sensitive to changes in Gross Domestic Product
C)investment must be sensitive to changes in interest rates
D)investment must be sensitive to changes in the spending multiplier
E)the spending multiplier must be stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If interest rates are __________ to changes in the money supply and planned investment expenditures are __________ to interest rates, then monetary policy will be __________ in changing Gross Domestic Product.
A)sensitive; sensitive; effective
B)responsive; insensitive; ineffective
C)responsive; insensitive; effective
D)not responsive; sensitive; effective
E)not responsive; insensitive; effective
A)sensitive; sensitive; effective
B)responsive; insensitive; ineffective
C)responsive; insensitive; effective
D)not responsive; sensitive; effective
E)not responsive; insensitive; effective

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If investment is not sensitive to changes in the interest rate, then changes in the money supply
A)will have no effect on interest rates
B)will have a major impact on investment
C)will have no effect on aggregate demand
D)will have a major impact on aggregate demand
E)mean the money supply curve will not be vertical
A)will have no effect on interest rates
B)will have a major impact on investment
C)will have no effect on aggregate demand
D)will have a major impact on aggregate demand
E)mean the money supply curve will not be vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Planned investment expenditures will eventually decrease after
A)the money supply decreases
B)the demand for money decreases
C)the interest rate falls
D)the Fed buys government securities
E)business managers become more optimistic about future market conditions for their products
A)the money supply decreases
B)the demand for money decreases
C)the interest rate falls
D)the Fed buys government securities
E)business managers become more optimistic about future market conditions for their products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If the Fed sells U.S. government securities to drain reserves from banks, which of the following will probably occur?
A)The demand for money will increase and the interest rate will rise.
B)The money supply will increase and the interest rate will fall.
C)The interest rate will rise and the quantity of money demanded will fall.
D)The money supply will decrease and the interest rate will fall.
E)The interest rate will fall and the quantity of money demanded will increase.
A)The demand for money will increase and the interest rate will rise.
B)The money supply will increase and the interest rate will fall.
C)The interest rate will rise and the quantity of money demanded will fall.
D)The money supply will decrease and the interest rate will fall.
E)The interest rate will fall and the quantity of money demanded will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the Fed increases the money supply, GDP
A)increases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to a decrease in investment
B)increases because the resulting decrease in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment
C)decreases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to a decrease in investment
D)decreases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment
E)decreases because the resulting decrease in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment
A)increases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to a decrease in investment
B)increases because the resulting decrease in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment
C)decreases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to a decrease in investment
D)decreases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment
E)decreases because the resulting decrease in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An increase in the money supply leads to a(n)
A)decline in interest rates, an increase in investment, and an increase in aggregate demand
B)decline in interest rates, a decrease in investment, and an increase in aggregate demand
C)decline in interest rates, an increase in investment, and a decline in aggregate demand
D)increase in interest rates, an increase in investment, and an increase in aggregate demand
E)decline in interest rates, a decline in investment, and a decline in aggregate demand
A)decline in interest rates, an increase in investment, and an increase in aggregate demand
B)decline in interest rates, a decrease in investment, and an increase in aggregate demand
C)decline in interest rates, an increase in investment, and a decline in aggregate demand
D)increase in interest rates, an increase in investment, and an increase in aggregate demand
E)decline in interest rates, a decline in investment, and a decline in aggregate demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
If the Fed sells government securities to banks, eventually we expect
A)the price level to increase
B)planned investment expenditures to increase
C)aggregate demand to increase
D)short-run aggregate supply to increase
E)interest rates to increase
A)the price level to increase
B)planned investment expenditures to increase
C)aggregate demand to increase
D)short-run aggregate supply to increase
E)interest rates to increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
To eliminate a contractionary gap, the Fed can __________ the money supply, which would __________.
A)increase; increase the interest rate and investment
B)increase; decrease the interest rate and increase investment
C)decrease; increase the interest rate and investment
D)decrease; decrease the interest rate and investment
E)decrease; increase the interest rate and decrease investment
A)increase; increase the interest rate and investment
B)increase; decrease the interest rate and increase investment
C)decrease; increase the interest rate and investment
D)decrease; decrease the interest rate and investment
E)decrease; increase the interest rate and decrease investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the Fed decreases the money supply, GDP
A)increases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to a decrease in investment
B)increases because the resulting decrease in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment
C)decreases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to a decrease in investment
D)decreases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment
E)decreases because the resulting decrease in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment
A)increases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to a decrease in investment
B)increases because the resulting decrease in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment
C)decreases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to a decrease in investment
D)decreases because the resulting increase in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment
E)decreases because the resulting decrease in the interest rate leads to an increase in investment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
What is the effect of an expansionary monetary policy on the demand for investment curve?
A)It causes the curve to shift left.
B)It causes the curve to shift right.
C)It causes downward movement along the curve.
D)It causes an upward movement along the curve.
E)It has no effect on the quantity of investment demanded.
A)It causes the curve to shift left.
B)It causes the curve to shift right.
C)It causes downward movement along the curve.
D)It causes an upward movement along the curve.
E)It has no effect on the quantity of investment demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If interest rates are __________ to changes in the money supply and planned investment expenditures are __________ to interest rate changes, then monetary policy will be effective in changing aggregate demand.
A)responsive; sensitive
B)responsive; insensitive
C)not responsive; sensitive
D)not responsive; insensitive
E)none of the above
A)responsive; sensitive
B)responsive; insensitive
C)not responsive; sensitive
D)not responsive; insensitive
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Planned investment expenditures will eventually increase after
A)the money supply decreases
B)the demand for money increases
C)the interest rate falls
D)the Fed sells government securities
E)business managers are pessimistic about future market conditions for their product
A)the money supply decreases
B)the demand for money increases
C)the interest rate falls
D)the Fed sells government securities
E)business managers are pessimistic about future market conditions for their product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 186 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



