Deck 9: Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/150
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Monopoly
1
Total deadweight loss in society is reduced through rent seeking by monopolists.
False
2
A monopolist's marginal revenue curve is flatter than its demand curve.
False
3
A profit-maximizing monopoly will always produce at the minimum point of its average total cost (ATC) curve.
False
4
Assuming a constant cost industry, consumer surplus would be greater under monopoly than if the industry were perfectly competitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A monopolist that earns a profit in the short run will always earn a profit in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Anything that prevents new firms from competing on an equal basis with existing firms in an industry is called a barrier to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Price-discriminating, profit-maximizing monopolists charge higher prices to buyers who have more elastic demand curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Rent-seeking activities are socially wasteful because they use scarce resources but do not add to society's output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A profit-maximizing monopolist will always operate where demand is unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Monopolists always earn positive short-run economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A natural monopoly emerges from legal restrictions imposed by a government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A monopolist maximizes profit at the output rate where its total revenue equals total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A monopolist maximizes profit at the quantity where the slope of its total revenue curve equals the slope of its total cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Average revenue, demand, and price are all depicted by the same curve for a monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A monopolist that fails to recover a short-run loss in the long run generally leaves the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
DeBeers Consolidated Mines is a natural monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Identify a distinguishing feature of monopoly.
A)There are no barriers to entry in a monopolized market.
B)A monopolist is a price taker.
C)There are no close substitutes for a monopolist's product.
D)There are many firms in a monopolized industry.
E)A monopolist faces a horizontal demand curve.
A)There are no barriers to entry in a monopolized market.
B)A monopolist is a price taker.
C)There are no close substitutes for a monopolist's product.
D)There are many firms in a monopolized industry.
E)A monopolist faces a horizontal demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Price discrimination will occur whenever a firm faces an upward-sloping demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Monopolists can earn positive economic profits in the long run because they are more productively efficient than perfectly competitive firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A monopolist's supply curve is the portion of its marginal cost curve that lies above its average variable cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A natural monopoly forms when a firm has:
A)a license.
B)a patent.
C)a U-shaped long-run average cost curve.
D)a downward-sloping long-run average cost curve.
E)a right to exclusively use a natural resource.
A)a license.
B)a patent.
C)a U-shaped long-run average cost curve.
D)a downward-sloping long-run average cost curve.
E)a right to exclusively use a natural resource.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Given the information in the table below, marginal revenue from the fourth unit of output is:

A)$12.
B)$3.
C)$4.
D)−$4.
E)$0.

A)$12.
B)$3.
C)$4.
D)−$4.
E)$0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The table below shows the demand schedule for a monopolist. Marginal revenue associated with the sale of the fourth unit of output is _____.
Table 9.3
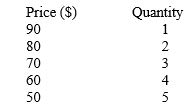
A)$10
B)$30
C)$60
D)$240
E)$210
Table 9.3
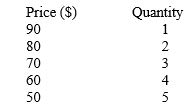
A)$10
B)$30
C)$60
D)$240
E)$210

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The demand curve a monopolist uses in making an output decision is:
A)the same as the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
B)positively sloped as it produces a highly differentiated product.
C)vertical as there are no close substitutes for its product.
D)the same as the market demand curve.
E)perfectly price inelastic.
A)the same as the demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm.
B)positively sloped as it produces a highly differentiated product.
C)vertical as there are no close substitutes for its product.
D)the same as the market demand curve.
E)perfectly price inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is most likely to be considered a natural monopoly?
A)A municipal water company
B)The mobile telephone industry
C)The baby care product industry
D)The cotton textile industry
E)The automobile industry
A)A municipal water company
B)The mobile telephone industry
C)The baby care product industry
D)The cotton textile industry
E)The automobile industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is true of marginal revenue earned by a non price-discriminating monopolist that charges a single price?
A)Marginal revenue earned by a monopolist is equal to the average cost incurred by it.
B)Marginal revenue earned by a monopolist is more than the price of its product.
C)Marginal revenue earned by a monopolist is less than the price of its product.
D)Marginal revenue earned by a monopolist is equal to the average revenue earned by it.
E)Marginal revenue earned by a monopolist is equal to price of its product.
A)Marginal revenue earned by a monopolist is equal to the average cost incurred by it.
B)Marginal revenue earned by a monopolist is more than the price of its product.
C)Marginal revenue earned by a monopolist is less than the price of its product.
D)Marginal revenue earned by a monopolist is equal to the average revenue earned by it.
E)Marginal revenue earned by a monopolist is equal to price of its product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A natural monopoly forms when:
A)small firms merge to form larger firms.
B)one firm has control over the entire supply of a basic input required to produce the product.
C)one firm's monopoly position is created and enforced by the government.
D)one firm receives patent protection for certain basic production processes.
E)the long-run average cost incurred by a firm declines as the firm expands output.
A)small firms merge to form larger firms.
B)one firm has control over the entire supply of a basic input required to produce the product.
C)one firm's monopoly position is created and enforced by the government.
D)one firm receives patent protection for certain basic production processes.
E)the long-run average cost incurred by a firm declines as the firm expands output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following prevents potential competitors from entering a monopolized market?
A)Legal restrictions
B)Diseconomies of scale
C)Product differentiation
D)Stable market demand
E)An abundant supply of resources
A)Legal restrictions
B)Diseconomies of scale
C)Product differentiation
D)Stable market demand
E)An abundant supply of resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to the information provided in the table below, total revenue from selling 5 units is:
Table 9.1

A)$20.
B)$140.
C)$100.
D)$10.
E)$5.
Table 9.1

A)$20.
B)$140.
C)$100.
D)$10.
E)$5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
For a monopolist, average revenue is:
A)equal to marginal revenue at all output levels.
B)greater than price at all output levels.
C)less than price at all output levels.
D)represented by a horizontal curve at all output levels.
E)more than marginal revenue at all output levels.
A)equal to marginal revenue at all output levels.
B)greater than price at all output levels.
C)less than price at all output levels.
D)represented by a horizontal curve at all output levels.
E)more than marginal revenue at all output levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A monopolist's demand curve is:
A)its marginal cost curve.
B)its marginal revenue curve.
C)identical to its market demand curve.
D)the same as the demand curve faced by a firm in perfect competition.
E)the same as its average cost curve.
A)its marginal cost curve.
B)its marginal revenue curve.
C)identical to its market demand curve.
D)the same as the demand curve faced by a firm in perfect competition.
E)the same as its average cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
According to the information provided in the table below, marginal revenue from the third unit of output is:
Table 9.1

A)$20.
B)$120.
C)$100.
D)$40.
E)$0.
Table 9.1

A)$20.
B)$120.
C)$100.
D)$40.
E)$0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Based on the information given in the table below, identify the range of output for which demand is unit elastic.

A)1 unit to 2 units
B)2 units to 3 units
C)3units to 4 units
D)4 units to 5 units
E)5 units to 6 units

A)1 unit to 2 units
B)2 units to 3 units
C)3units to 4 units
D)4 units to 5 units
E)5 units to 6 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of these is likely to be true of perfect competition but not of monopoly?
A)A firm can produce a good only if government licenses authorize it to produce the good.
B)A firm can sell a good in the market only if the government grants a patent to the firm.
C)A firm can earn economic profit in the long run.
D)A firm can shut down in the short run only if the price charged by it exceeds the average variable cost of production.
E)A firm can face competition from new entrants into the market in the long run.
A)A firm can produce a good only if government licenses authorize it to produce the good.
B)A firm can sell a good in the market only if the government grants a patent to the firm.
C)A firm can earn economic profit in the long run.
D)A firm can shut down in the short run only if the price charged by it exceeds the average variable cost of production.
E)A firm can face competition from new entrants into the market in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Patents stimulate investment:
A)by giving inventors an incentive to incur up-front costs of developing new products.
B)by giving tax breaks to inventors and researchers.
C)by guaranteeing an economic profit to a firm from the sale of a new product.
D)by lowering interest rates on loans taken for developing a new product.
E)by covering the total cost of research and development incurred by a start-up firm.
A)by giving inventors an incentive to incur up-front costs of developing new products.
B)by giving tax breaks to inventors and researchers.
C)by guaranteeing an economic profit to a firm from the sale of a new product.
D)by lowering interest rates on loans taken for developing a new product.
E)by covering the total cost of research and development incurred by a start-up firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
As a monopolist increases the quantity of output produced, _____.
A)both price and marginal revenue remain constant
B)price remains constant, but marginal revenue decreases
C)price decreases, but marginal revenue remains constant
D)both price and marginal revenue decrease, but price falls faster than marginal revenue
E)both price and marginal revenue decrease, but marginal revenue falls faster than price
A)both price and marginal revenue remain constant
B)price remains constant, but marginal revenue decreases
C)price decreases, but marginal revenue remains constant
D)both price and marginal revenue decrease, but price falls faster than marginal revenue
E)both price and marginal revenue decrease, but marginal revenue falls faster than price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is true of a patent?
A)It reduces a firm's incentive to develop new products.
B)It is issued in recognition of new works of art or literature.
C)It gives a firm a permanent exclusive right to produce a new good.
D)It gives a firm a temporary exclusive right to produce a new good.
E)It guarantees economic profits to a firm in the long run.
A)It reduces a firm's incentive to develop new products.
B)It is issued in recognition of new works of art or literature.
C)It gives a firm a permanent exclusive right to produce a new good.
D)It gives a firm a temporary exclusive right to produce a new good.
E)It guarantees economic profits to a firm in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
According to the information provided in the table below, marginal revenue from the sixth unit of output is:
Table 9.1

A)$10.
B)$60.
C)$100.
D)$40.
E)‒$40.
Table 9.1

A)$10.
B)$60.
C)$100.
D)$40.
E)‒$40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
$0.Given the information in the table below, the average revenue earned by the firm from four units of output is:

A)$12.
B)$3.
C)$4.
D)−$4.
E)$0.

A)$12.
B)$3.
C)$4.
D)−$4.
E)$0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following describes a monopolized market structure?
A)A market structure with a single buyer
B)Many firms with no control over price producing identical products with no differentiation
C)A few firms with some control over price producing similar products which are close substitutes
D)A few firms with no control over price producing highly differentiated products
E)A single firm producing a highly differentiated product and serving the entire market
A)A market structure with a single buyer
B)Many firms with no control over price producing identical products with no differentiation
C)A few firms with some control over price producing similar products which are close substitutes
D)A few firms with no control over price producing highly differentiated products
E)A single firm producing a highly differentiated product and serving the entire market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
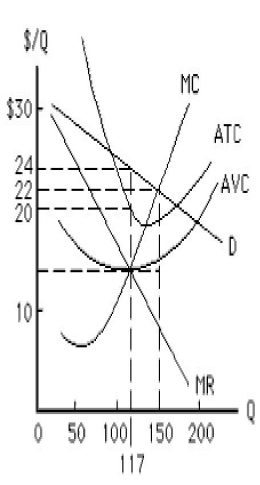
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopolist. The profit-maximizing output and price for the monopolist are:
Figure 9.1
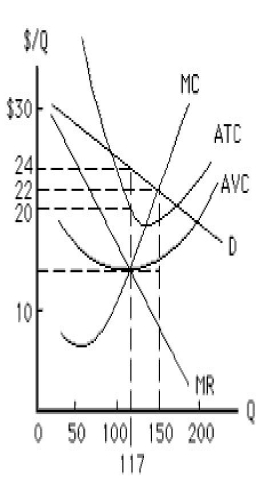
A)117 units and $14, respectively.
B)150 units and $22, respectively.
C)150 units and $14, respectively.
D)117 units and $22, respectively.
E)117 units and $24, respectively.
Figure 9.1

A)117 units and $14, respectively.
B)150 units and $22, respectively.
C)150 units and $14, respectively.
D)117 units and $22, respectively.
E)117 units and $24, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose a monopolist must choose between two points on its demand curve. It can either sell 100 units for $3 each or sell 140 units for $2 each. Which of the following is true?
A)The demand for the monopolist's product is price elastic for the given range of output.
B)The demand for the monopolist's product is unit elastic for the given range of output.
C)The demand for the monopolist's product is price inelastic for the given range of output.
D)The monopolist is facing a horizontal supply curve.
E)The monopolist is facing an upward-rising demand curve.
A)The demand for the monopolist's product is price elastic for the given range of output.
B)The demand for the monopolist's product is unit elastic for the given range of output.
C)The demand for the monopolist's product is price inelastic for the given range of output.
D)The monopolist is facing a horizontal supply curve.
E)The monopolist is facing an upward-rising demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
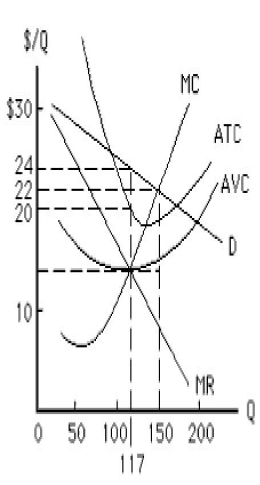
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopolist. The demand curve faced by the monopolist at the profit-maximizing output is:
Figure 9.1
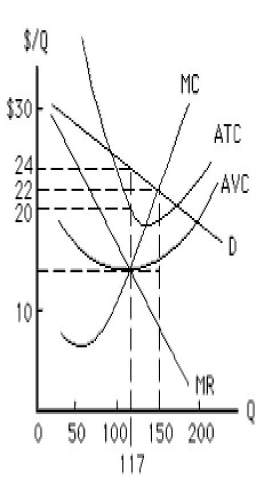
A)perfectly price elastic.
B)price elastic.
C)price inelastic.
D)unit price elastic.
E)perfectly price inelastic.
Figure 9.1

A)perfectly price elastic.
B)price elastic.
C)price inelastic.
D)unit price elastic.
E)perfectly price inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Suppose a single firm supplies all the ceramic windlasses in the U.S. The demand curve that the firm faces is:
A)elastic everywhere.
B)unit elastic everywhere.
C)inelastic only at the profit-maximizing output.
D)perfectly inelastic everywhere.
E)elastic only at the profit-maximizing output.
A)elastic everywhere.
B)unit elastic everywhere.
C)inelastic only at the profit-maximizing output.
D)perfectly inelastic everywhere.
E)elastic only at the profit-maximizing output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following can be concluded about a monopolist whose marginal revenue is zero for a particular output level?
A)The economic profit earned by the monopolist by producing that output level is zero.
B)Total revenue earned by the monopolist is maximum at that output level.
C)Total revenue earned by the monopolist increases at an increasing rate as output increases beyond that output level.
D)Total revenue earned by the monopolist increases at a decreasing rate as output increases beyond that output level.
E)Average revenue earned by the firm for that output level is less than marginal revenue for that output level.
A)The economic profit earned by the monopolist by producing that output level is zero.
B)Total revenue earned by the monopolist is maximum at that output level.
C)Total revenue earned by the monopolist increases at an increasing rate as output increases beyond that output level.
D)Total revenue earned by the monopolist increases at a decreasing rate as output increases beyond that output level.
E)Average revenue earned by the firm for that output level is less than marginal revenue for that output level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The figure below shows a non-discriminating monopolist. The total revenue earned by the monopolist at the profit-maximizing output is _____.
Figure 9.1
A)$2,574
B)$2,808
C)$2,100
D)$1,638
E)$3,300
Figure 9.1

A)$2,574
B)$2,808
C)$2,100
D)$1,638
E)$3,300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A monopolist must choose between two points on its demand curve. It can either sell 100 units for $3 each, or sell 150 units for $2 each. This implies that, for the given range of output, elasticity of demand for the monopolist's product is:
A)zero.
B)one.
C)more than one but less than two.
D)infinite.
E)between zero and one.
A)zero.
B)one.
C)more than one but less than two.
D)infinite.
E)between zero and one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
For a monopolist producing a level of output at which market demand is inelastic, _____.
A)short-run profit is maximum.
B)a decrease in price increases total revenue.
C)a decrease in price decreases total cost.
D)a decrease in price decreases total revenue.
E)an increase in output increases short-run economic profit.
A)short-run profit is maximum.
B)a decrease in price increases total revenue.
C)a decrease in price decreases total cost.
D)a decrease in price decreases total revenue.
E)an increase in output increases short-run economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The demand curve facing a non-discriminating monopolist:
A)is the same as its average revenue curve.
B)is perfectly price elastic.
C)is perfectly price inelastic.
D)lies above its average revenue curve.
E)lies below its marginal revenue curve.
A)is the same as its average revenue curve.
B)is perfectly price elastic.
C)is perfectly price inelastic.
D)lies above its average revenue curve.
E)lies below its marginal revenue curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves for a non-discriminating monopolist. The total cost incurred by the monopolist at the profit-maximizing output is _____.
Figure 9.1
A)$3,300
B)$3,400
C)$2,808
D)$2,340
E)$1,638
Figure 9.1

A)$3,300
B)$3,400
C)$2,808
D)$2,340
E)$1,638

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose the marginal revenue for a particular level of a monopolist's output is $40. This implies that:
A)total revenue is increasing for this output range.
B)total revenue is decreasing, but positive, for this output range.
C)total revenue is zero for this output range.
D)total revenue remains constant for this output range.
E)total revenue is negative for this output range.
A)total revenue is increasing for this output range.
B)total revenue is decreasing, but positive, for this output range.
C)total revenue is zero for this output range.
D)total revenue remains constant for this output range.
E)total revenue is negative for this output range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The loss-minimizing output for a non-discriminating monopolist represented on the table given below is _____.
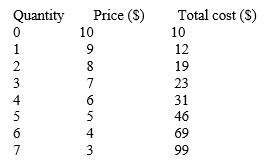
A)0 units
B)2 units
C)3 units
D)4 units
E)5 units
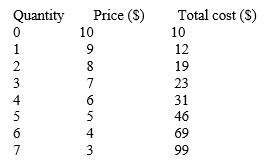
A)0 units
B)2 units
C)3 units
D)4 units
E)5 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The revenue-maximizing output for a non-discriminating monopolist represented in the table given below is _____.
Table 9.4
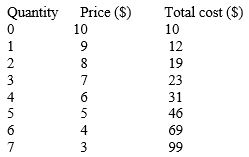
A)0 units
B)2 units
C)3 units
D)4 units
E)5 units
Table 9.4
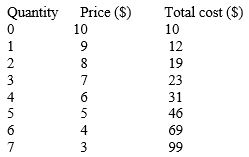
A)0 units
B)2 units
C)3 units
D)4 units
E)5 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A monopolist can either sell 100 units for $3 each or sell 160 units for $2 each. This implies that, for the given range of output, elasticity of demand for the monopolist's product is:
A)greater than one but not infinite.
B)one.
C)zero.
D)less than zero.
E)infinite.
A)greater than one but not infinite.
B)one.
C)zero.
D)less than zero.
E)infinite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is true for a monopolist?
A)Marginal revenue is maximized where demand is unit elastic.
B)Total revenue is maximized where demand is inelastic.
C)Marginal revenue is negative where demand is inelastic.
D)Total revenue is negative where demand is elastic.
E)Marginal revenue is lowest where demand is unit elastic.
A)Marginal revenue is maximized where demand is unit elastic.
B)Total revenue is maximized where demand is inelastic.
C)Marginal revenue is negative where demand is inelastic.
D)Total revenue is negative where demand is elastic.
E)Marginal revenue is lowest where demand is unit elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following equations describes the relationship between market price (P), average revenue (AR), and marginal revenue (MR) for a non-discriminating monopolist?
A)P = AR = MR
B)P > AR = MR
C)P = AR > MR
D)P > AR > MR
E)P = AR < MR
A)P = AR = MR
B)P > AR = MR
C)P = AR > MR
D)P > AR > MR
E)P = AR < MR

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves faced by a monopolist. At the profit-maximizing output level for the monopolist, _____.
Figure 9.1
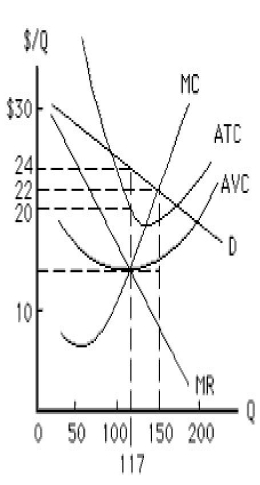
A)marginal revenue is zero
B)marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost
C)marginal cost is less than marginal revenue
D)marginal cost is equal to average total cost
E)price is equal to marginal cost
Figure 9.1

A)marginal revenue is zero
B)marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost
C)marginal cost is less than marginal revenue
D)marginal cost is equal to average total cost
E)price is equal to marginal cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A firm facing a downward-sloping demand curve sells 50 units of output at $10 each. Which of the following can be concluded about the firm's marginal revenue for this output level?
A)Marginal revenue is equal to $500.
B)Marginal revenue is more than $10.
C)Marginal revenue is equal to $10.
D)Marginal revenue is less than $10 but more than zero.
E)Marginal revenue is zero.
A)Marginal revenue is equal to $500.
B)Marginal revenue is more than $10.
C)Marginal revenue is equal to $10.
D)Marginal revenue is less than $10 but more than zero.
E)Marginal revenue is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Given the figure below, a non-discriminating, profit-maximizing monopolist will earn a profit of _____ per unit of output.
Figure 9.1
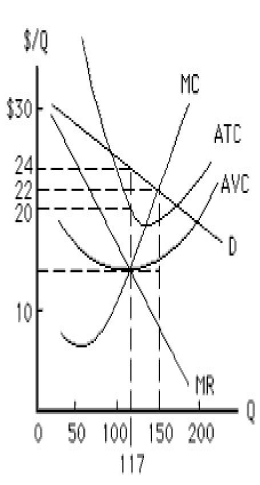
A)$10
B)$5
C)$4
D)$0
E)$15
Figure 9.1

A)$10
B)$5
C)$4
D)$0
E)$15

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A firm facing a downward-sloping demand curve sells 50 units of output at $10 each. The firm's average revenue is:
A)$500.
B)more than $10 but less than $500.
C)$10.
D)less than $10 but more than zero.
E)zero.
A)$500.
B)more than $10 but less than $500.
C)$10.
D)less than $10 but more than zero.
E)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Irving R. Associates is granted a patent for a new product for which there are no close substitutes. Which of the following conditions must be true at the profit-maximizing output produced by this firm?
A)Price is equal to marginal cost.
B)Average cost is less than marginal cost.
C)Marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
D)Marginal revenue is less than average variable cost.
E)Price is greater than average revenue.
A)Price is equal to marginal cost.
B)Average cost is less than marginal cost.
C)Marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
D)Marginal revenue is less than average variable cost.
E)Price is greater than average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The table below shows the price and output combinations at different output levels for a non price-discriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing price charged by this monopolist is _____.
Table 9.6
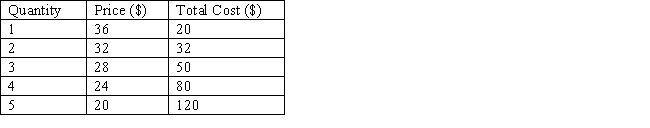
A)$36
B)$32
C)$28
D)$24
E)$20
Table 9.6

A)$36
B)$32
C)$28
D)$24
E)$20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A profit-maximizing monopolist never produces along the:
A)elastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is positive there.
B)elastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is negative there.
C)inelastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is negative there.
D)inelastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is positive there.
E)inelastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is zero there.
A)elastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is positive there.
B)elastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is negative there.
C)inelastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is negative there.
D)inelastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is positive there.
E)inelastic portion of the demand curve because marginal revenue is zero there.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The table below shows the price and output combinations at different output levels for a non price-discriminating monopolist. The total profit earned by this monopolist at the profit-maximizing output is _____.
Table 9.6
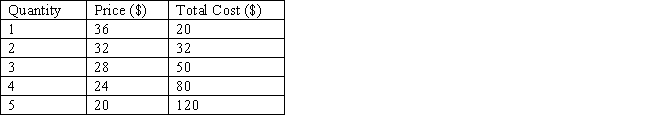
A)$16
B)−$20
C)$32
D)$34
E)-$16
Table 9.6

A)$16
B)−$20
C)$32
D)$34
E)-$16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A non-discriminating monopolist observes that marginal revenue is $23 and marginal cost is $30 at its present output level. In order to maximize profit it should:
A)raise price and lower output.
B)lower both price and output.
C)raise both price and output.
D)lower price and raise output.
E)lower output but leave price unchanged.
A)raise price and lower output.
B)lower both price and output.
C)raise both price and output.
D)lower price and raise output.
E)lower output but leave price unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves for a non-discriminating monopolist. The total cost incurred by the monopolist for producing the profit-maximizing output is:
Figure 9.2
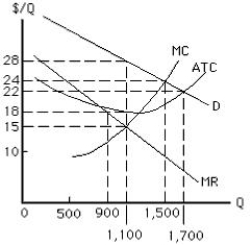
A)$16,500.
B)$24,200.
C)$16,200.
D)$19,800.
E)$30,800.
Figure 9.2

A)$16,500.
B)$24,200.
C)$16,200.
D)$19,800.
E)$30,800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A profit-maximizing monopolist supplies the quantity at which:
A)average revenue exceeds average cost by the greatest amount.
B)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the smallest amount.
C)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the greatest amount.
D)total revenue exceeds total cost by the greatest amount.
E)total revenue exceeds total cost by the smallest amount.
A)average revenue exceeds average cost by the greatest amount.
B)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the smallest amount.
C)marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the greatest amount.
D)total revenue exceeds total cost by the greatest amount.
E)total revenue exceeds total cost by the smallest amount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The profit-maximizing quantity for a monopolist that faces an upward-sloping marginal cost curve will:
A)occur at the minimum point of the marginal cost curve.
B)be less than the revenue-maximizing quantity.
C)be equal to the revenue-maximizing quantity.
D)occur along the unit elastic segment of the demand curve.
E)occur along the inelastic segment of the demand curve.
A)occur at the minimum point of the marginal cost curve.
B)be less than the revenue-maximizing quantity.
C)be equal to the revenue-maximizing quantity.
D)occur along the unit elastic segment of the demand curve.
E)occur along the inelastic segment of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following conditions is true at the profit-maximizing output for both a perfectly competitive firm and a monopoly?
A)Price equals marginal cost
B)Price is greater than marginal cost
C)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost
D)Marginal revenue is less than marginal cost
E)Marginal revenue is greater than average revenue
A)Price equals marginal cost
B)Price is greater than marginal cost
C)Marginal revenue equals marginal cost
D)Marginal revenue is less than marginal cost
E)Marginal revenue is greater than average revenue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves for a non-discriminating monopolist. The total revenue earned by the profit-maximizing monopolist at the profit-maximizing output is:
Figure 9.2
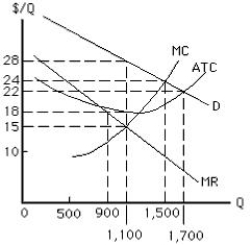
A)$16,200.
B)$36,000.
C)$39,600.
D)$30,800.
E)$31,000.
Figure 9.2

A)$16,200.
B)$36,000.
C)$39,600.
D)$30,800.
E)$31,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
For a monopolist that does not price discriminate, economic profit is maximized in the short run at a price of $140. Marginal revenue at that output level is:
A)equal to $140.
B)greater than $140.
C)less than $140.
D)less than marginal cost.
E)greater than average revenue.
A)equal to $140.
B)greater than $140.
C)less than $140.
D)less than marginal cost.
E)greater than average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is true of a monopolist in the short run?
A)It can charge whatever price it wants.
B)It charges more than what consumers are willing to pay.
C)It is constrained by marginal cost in setting price.
D)It is constrained by consumer demand in setting price.
E)It always earns an economic profit.
A)It can charge whatever price it wants.
B)It charges more than what consumers are willing to pay.
C)It is constrained by marginal cost in setting price.
D)It is constrained by consumer demand in setting price.
E)It always earns an economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following does a monopoly control that a perfectly competitive firm does not control?
A)Total production
B)Production technology
C)Price
D)Input usage
E)Plant size
A)Total production
B)Production technology
C)Price
D)Input usage
E)Plant size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A non-price discriminating monopolist's demand curve:
A)is horizontal at the market price.
B)lies to the right of its marginal revenue curve.
C)is the same as its marginal cost curve.
D)indicates that the firm must raise price to sell additional units.
E)lies above the marginal cost curve at all levels of output.
A)is horizontal at the market price.
B)lies to the right of its marginal revenue curve.
C)is the same as its marginal cost curve.
D)indicates that the firm must raise price to sell additional units.
E)lies above the marginal cost curve at all levels of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves for a non price-discriminating monopolist. At the profit-maximizing output, the non price-discriminating monopolist is earning a profit of _____.
Figure 9.2
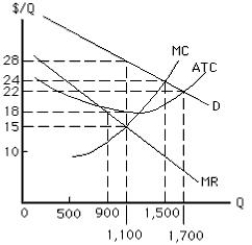
A)$6,200
B)$13,320
C)$11,000
D)$15,200
E)$0
Figure 9.2

A)$6,200
B)$13,320
C)$11,000
D)$15,200
E)$0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The table below shows the demand schedule faced by a monopolist and the total cost incurred by it in producing each output level. The maximum profit earned by the monopolist is _____.
Table 9.5
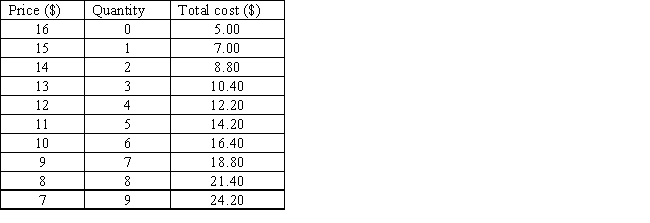
A)$5
B)$40.80
C)$43.60
D)$44.20
E)$42.60
Table 9.5

A)$5
B)$40.80
C)$43.60
D)$44.20
E)$42.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The figure below shows the cost and revenue curves for a non-discriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing output and price for a monopolist are:
Figure 9.2
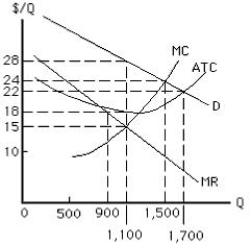
A)90 units and $18, respectively.
B)1,500 units and $24, respectively.
C)1,700 units and $22, respectively.
D)1,100 units and $28, respectively.
E)1,500 units and $22, respectively.
Figure 9.2

A)90 units and $18, respectively.
B)1,500 units and $24, respectively.
C)1,700 units and $22, respectively.
D)1,100 units and $28, respectively.
E)1,500 units and $22, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The table below shows the demand schedule faced by a monopolist and the total cost incurred by it in producing each output level. The profit-maximizing price for the monopolist is _____.
Table 9.5
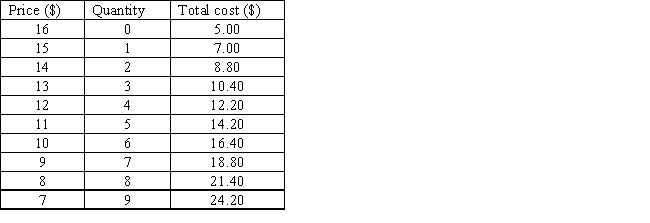
A)$14
B)$11
C)$10
D)$9
E)$8
Table 9.5

A)$14
B)$11
C)$10
D)$9
E)$8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The table below shows the price and output combinations at different output levels for a non price-discriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing output for this monopolist is _____.
Table 9.6
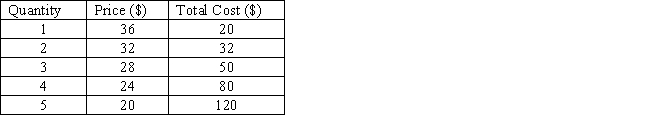
A)1 unit
B)2 units
C)3 units
D)4 units
E)5 units
Table 9.6

A)1 unit
B)2 units
C)3 units
D)4 units
E)5 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A monopolist is said to have market power because:
A)it faces an upward-sloping marginal cost curve.
B)it faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
C)it always earns positive profit both in the short run and the long run.
D)it charges a fixed price for its products.
E)it faces a high marginal cost of production.
A)it faces an upward-sloping marginal cost curve.
B)it faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
C)it always earns positive profit both in the short run and the long run.
D)it charges a fixed price for its products.
E)it faces a high marginal cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



