Deck 17: Externalities and the Environment
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/150
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Externalities and the Environment
1
Government allocation of pollution rights cannot be efficient if polluters cannot be easily identified and monitored.
True
2
Oil is an example of a renewable resource.
False
3
Coase argued that the free market should be able to solve an externality problem without assigning property rights.
False
4
An increase in the marginal cost of reducing greenhouse gas emissions will lead to lower air quality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
To achieve the socially optimal level of pollution, the biggest polluters should be targeted for the greatest reduction in pollution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When a system of pollution rights is in effect, polluters have no economic incentive to reduce the amount of pollution they generate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
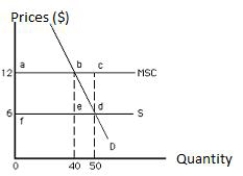
The following graph shows market equilibrium in the presence of an externality. The optimal air quality level is 50.
Figure 17.3
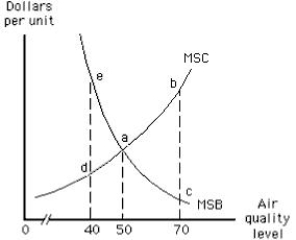
Figure 17.3


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Pollution occurs because property rights to some open-access resources are well defined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Most water pollution in the United States comes from manufacturing sites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Smokers and loud talkers help in generating positive externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The equilibrium price and quantity in a free market usually reflect private marginal costs and benefits, not social ones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Environmental problems result when social costs and benefits are different from private costs and benefits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Pollution occurs because property rights to exhaustible resources are well defined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Marginal social cost includes both the marginal private cost and the marginal external cost that production imposes on society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
It is in the long-run economic interest of the world to preserve rainforests, but it is not in the short-run economic interest of the inhabitants of the countries involved to do so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The optimal air quality is determined where the marginal social cost of improving air quality is equal to the marginal social benefit from cleaner air.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The Coase solution to the externality problem works only when bargaining costs are high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The marginal social benefit curve is downward sloping under variable technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Private property rights are easily assigned to open-access resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If the marginal social cost of producing a product exceeds the marginal social benefit, producers will produce less of it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An individual who listens to loud music late in the night is creating:
A)a positive externality.
B)a common-pool problem.
C)a negative externality.
D)a free-rider problem.
E)asymmetric information.
A)a positive externality.
B)a common-pool problem.
C)a negative externality.
D)a free-rider problem.
E)asymmetric information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Most of the Superfund expenditures have been used for court costs and legal fees.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An externality is:
A)a cost of a transaction that is borne by the government.
B)a benefit of a transaction that is enjoyed by the firms.
C)a cost or benefit that arises when market price changes.
D)any cost or benefit of a transaction that is not accounted for in the market price.
E)the revenue generated by a firm.
A)a cost of a transaction that is borne by the government.
B)a benefit of a transaction that is enjoyed by the firms.
C)a cost or benefit that arises when market price changes.
D)any cost or benefit of a transaction that is not accounted for in the market price.
E)the revenue generated by a firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is true of renewable resources?
A)Additional units of these resources can be purchased in the market.
B)Additional units of these resources are provided by the government.
C)Worn-out units cannot be repaired for further use.
D)They can be drawn on indefinitely if used conservatively.
E)They are available in finite amounts.
A)Additional units of these resources can be purchased in the market.
B)Additional units of these resources are provided by the government.
C)Worn-out units cannot be repaired for further use.
D)They can be drawn on indefinitely if used conservatively.
E)They are available in finite amounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Negative externalities of open resources arise because:
A)there are no enforceable property rights to open-access resources.
B)these are private goods and government enforces property rights.
C)consumers have to pay for each unit of production.
D)the government undertakes the distribution of these resources.
E)these are available in finite amounts.
A)there are no enforceable property rights to open-access resources.
B)these are private goods and government enforces property rights.
C)consumers have to pay for each unit of production.
D)the government undertakes the distribution of these resources.
E)these are available in finite amounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Governments often subsidize activities that generate positive externalities in order to get people to engage in more of them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In the absence of government intervention, the marginal social cost of pollution abatement would equal its marginal social benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Fishes in the ocean are:
A)exhaustible and also open-access resources.
B)renewable and also open-access resources.
C)private goods.
D)merit goods
E)renewable resources whenever property rights are well defined.
A)exhaustible and also open-access resources.
B)renewable and also open-access resources.
C)private goods.
D)merit goods
E)renewable resources whenever property rights are well defined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is a renewable resource?
A)Oil
B)Air
C)Coal
D)Iron ore
E)Uranium
A)Oil
B)Air
C)Coal
D)Iron ore
E)Uranium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A person can cause a negative externality by_______.
A)being immunized
B)having a loud conversation in the office
C)landscaping her lawn
D)paying taxes
E)attending school
A)being immunized
B)having a loud conversation in the office
C)landscaping her lawn
D)paying taxes
E)attending school

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The United States recycles a greater portion of its garbage than Japan does.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is a source of a positive externality?
A)A factory that pollutes a river
B)A person who litters the street
C)A car that emits carbon monoxide
D)A company that engages in research and development
E)A product that contributes to the greenhouse effect
A)A factory that pollutes a river
B)A person who litters the street
C)A car that emits carbon monoxide
D)A company that engages in research and development
E)A product that contributes to the greenhouse effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
_____ resources can be used indefinitely over time.
A)Open-access
B)Renewable
C)Cyclical
D)Recyclable
E)Exhaustible
A)Open-access
B)Renewable
C)Cyclical
D)Recyclable
E)Exhaustible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Private property rights are defined and enforced:
A)only in a capitalist economy.
B)only in a command economy.
C)by the largest firm in an economy.
D)by the market forces of demand and supply.
E)by government, by informal social actions, and by ethical norms.
A)only in a capitalist economy.
B)only in a command economy.
C)by the largest firm in an economy.
D)by the market forces of demand and supply.
E)by government, by informal social actions, and by ethical norms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When the consumption of a good or service imposes costs to society that are not reflected in the market price of the good, _____.
A)a negative externality arises
B)it implies that a renewable resource has been used in the production of the good
C)a positive externality arises
D)it implies that the good is a public good
E)it implies that a nonrenewable resource has been used in the production of the good
A)a negative externality arises
B)it implies that a renewable resource has been used in the production of the good
C)a positive externality arises
D)it implies that the good is a public good
E)it implies that a nonrenewable resource has been used in the production of the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A society is better off if the level of education exceeds the private equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is an example of a positive externality?
A)Water pollution.
B)John's roommate going on a diet
C)Second-hand smoke
D)A loud conversation in the workplace
E)The emission of harmful gases by a factory
A)Water pollution.
B)John's roommate going on a diet
C)Second-hand smoke
D)A loud conversation in the workplace
E)The emission of harmful gases by a factory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Markets tend to underproduce goods that generate positive externalities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A negative externality is likely to arise if:
A)the government sets up more schools.
B)a company introduces a research and development unit.
C)factories install devices to reduce the amount of chemicals released.
D)the government introduces a measles vaccine.
E)car owners refuse to pay for devices that reduce the emission of carbon monoxide.
A)the government sets up more schools.
B)a company introduces a research and development unit.
C)factories install devices to reduce the amount of chemicals released.
D)the government introduces a measles vaccine.
E)car owners refuse to pay for devices that reduce the emission of carbon monoxide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Pollution arises because:
A)the atmosphere is a nonrenewable resource.
B)the atmosphere is a renewable resource.
C)private property rights can be enforced on the atmosphere.
D)the atmosphere is an open-access resource.
E)the atmosphere is a private property.
A)the atmosphere is a nonrenewable resource.
B)the atmosphere is a renewable resource.
C)private property rights can be enforced on the atmosphere.
D)the atmosphere is an open-access resource.
E)the atmosphere is a private property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The following graph shows market equilibrium in the presence of externality in an economy. The equilibrium price and output (determined exclusively by private decisions) are _____.
Figure 17.2
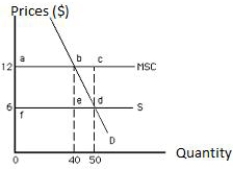
A)$6 and 50 units, respectively
B)$12 and 50 units, respectively
C)$12 and 40 units, respectively
D)$6 and 40 units, respectively
E)less than $6 and more than 50 units, respectively
Figure 17.2

A)$6 and 50 units, respectively
B)$12 and 50 units, respectively
C)$12 and 40 units, respectively
D)$6 and 40 units, respectively
E)less than $6 and more than 50 units, respectively

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Byproducts of production or consumption that impose costs on other consumers or firms are known as _______.
A)negative externalities
B)transaction costs
C)sunk costs
D)positive externalities
E)moral hazards
A)negative externalities
B)transaction costs
C)sunk costs
D)positive externalities
E)moral hazards

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The depletion of rainforests due to human activities like logging or cattle ranching is an example of:
A)a negative externality.
B)a positive externality.
C)adverse selection.
D)moral hazard.
E)arbitrage.
A)a negative externality.
B)a positive externality.
C)adverse selection.
D)moral hazard.
E)arbitrage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
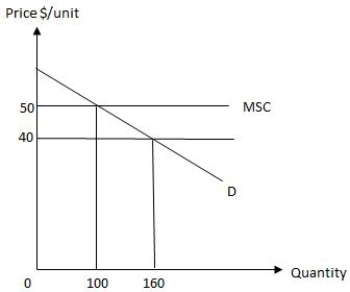
The following graph shows equilibrium in a market in the presence of an externality. If technology is fixed, the discrepancy between the market output and the efficient level of output is eliminated by______.
Figure 17.2
A)subsidizing production of the good by $10 per unit
B)taxing the firm producing the good $10 per unit
C)using a quota system to restrict production to 160 units.
D)subsidizing production of the good by $5 per unit
E)letting the private market operate freely
Figure 17.2

A)subsidizing production of the good by $10 per unit
B)taxing the firm producing the good $10 per unit
C)using a quota system to restrict production to 160 units.
D)subsidizing production of the good by $5 per unit
E)letting the private market operate freely

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The deforestation of rainforests due to human activities has increased because:
A)long-run economic considerations outweigh short-run considerations.
B)global economic considerations outweigh domestic considerations
C)private property rights can be enforced on rainforests.
D)the value of the jobs created by deforestation exceeds the cost to society.
E)there are no property rights on rainforests.
A)long-run economic considerations outweigh short-run considerations.
B)global economic considerations outweigh domestic considerations
C)private property rights can be enforced on rainforests.
D)the value of the jobs created by deforestation exceeds the cost to society.
E)there are no property rights on rainforests.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Fish in the sea can be harvested till:
A)the marginal benefit of catching more fish is less than the marginal cost.
B)the marginal benefit of catching more fish is greater than the marginal cost.
C)the marginal benefit of catching more fish becomes negative.
D)the marginal benefit of catching more fish becomes infinity.
E)the marginal benefit of catching more fish becomes zero.
A)the marginal benefit of catching more fish is less than the marginal cost.
B)the marginal benefit of catching more fish is greater than the marginal cost.
C)the marginal benefit of catching more fish becomes negative.
D)the marginal benefit of catching more fish becomes infinity.
E)the marginal benefit of catching more fish becomes zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
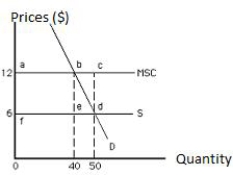
The following graph shows market equilibrium in the presence of an externality. The total social gain from producing the socially efficient output is:
Figure 17.2
A)$60.
B)$30.
C)$6.
D)$480.
E)$300.
Figure 17.2

A)$60.
B)$30.
C)$6.
D)$480.
E)$300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is true of open-access wildlife resources?
A)They are likely to be used efficiently.
B)They are not likely to be used at all.
C)It is unprofitable to use them.
D)They are likely to be used but unlikely to generate profit.
E)They are likely to be used until they become extinct.
A)They are likely to be used efficiently.
B)They are not likely to be used at all.
C)It is unprofitable to use them.
D)They are likely to be used but unlikely to generate profit.
E)They are likely to be used until they become extinct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Open-access resources tend to be ______.
A)conserved
B)taxed
C)overused
D)efficiently used
E)underutilized
A)conserved
B)taxed
C)overused
D)efficiently used
E)underutilized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
To solve the common-pool problem in fishing, governments can _____ or _____.
A)provide a subsidy; restrict production to the socially optimal level
B)impose a tax; restrict output
C)impose property rights ; prohibit resource use entirely
D)impose a depletion tax; make property rights flexible
E)provide a subsidy; shutdown all firms in this industry
A)provide a subsidy; restrict production to the socially optimal level
B)impose a tax; restrict output
C)impose property rights ; prohibit resource use entirely
D)impose a depletion tax; make property rights flexible
E)provide a subsidy; shutdown all firms in this industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The following graph shows equilibrium in a market in the presence of externality in an economy. The total social gain from producing the socially efficient output rather than the private equilibrium output is shown by the area ______.
Figure 17.2
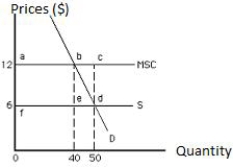
A)abdf
B)bed
C)bcd
D)acdf
E)bcde
Figure 17.2

A)abdf
B)bed
C)bcd
D)acdf
E)bcde

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is not an example of an open-access resource?
A)Deer in a forest
B)Fish in the ocean
C)Oil deposits
D)Wild flowers
E)Trees in a forest
A)Deer in a forest
B)Fish in the ocean
C)Oil deposits
D)Wild flowers
E)Trees in a forest

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The following graph shows market equilibrium in the presence of an externality in an economy. The socially efficient level of output is _____.
Figure 17.1
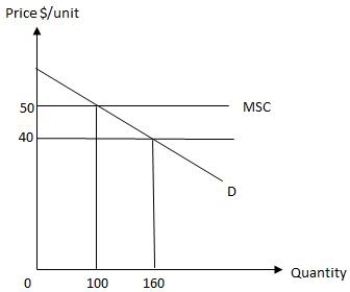
A)0 units
B)100 units
C)between 0 and 100 units
D)160 units
E)between 100 and 160 units
Figure 17.1

A)0 units
B)100 units
C)between 0 and 100 units
D)160 units
E)between 100 and 160 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose a city builds a new park that is advertised as being "open to the public" and the grass in the park is ruined by overuse within two months. This would be an example of _____.
A)adverse selection
B)moral hazard
C)the common-pool problem
D)a positive externality
E)arbitrage
A)adverse selection
B)moral hazard
C)the common-pool problem
D)a positive externality
E)arbitrage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The following graph shows market equilibrium in the presence of an externality in an economy. The equilibrium level of output for the firm is _____.
Figure 17.1
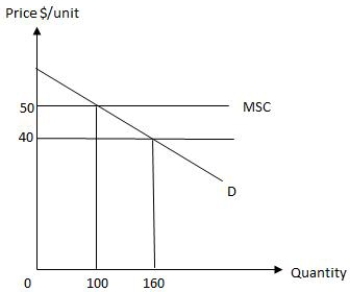
A)0 units
B)100 units
C)between 0 and 100 units
D)160 units
E)between 100 and 160 units
Figure 17.1

A)0 units
B)100 units
C)between 0 and 100 units
D)160 units
E)between 100 and 160 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The following graph shows equilibrium in a market in the presence of an externality. The amount by which the total social cost of producing the private equilibrium level of output exceeds the total social benefit is _____.
Figure 17.1
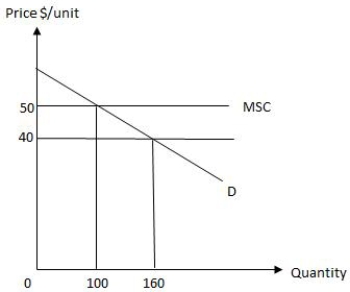
A)$3,000
B)$1,000
C)$5,000
D)$1,600
E)$1,400
Figure 17.1

A)$3,000
B)$1,000
C)$5,000
D)$1,600
E)$1,400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Open-access resources are owned by:
A)every individual in society.
B)large firms.
C)no one.
D)the government.
E)nonprofit agencies.
A)every individual in society.
B)large firms.
C)no one.
D)the government.
E)nonprofit agencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is an example of an open-access resource?
A)A city subway system
B)College education
C)The healthcare system in a city
D)Whales in the ocean
E)Pandas in a zoo
A)A city subway system
B)College education
C)The healthcare system in a city
D)Whales in the ocean
E)Pandas in a zoo

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The following graph shows market equilibrium in the presence of an externality. The socially efficient price and level of output are:
Figure 17.2
A)$6 and 50 units, respectively
B)$12 and 50 units, respectively
C)$12 and 40 units, respectively
D)$6 and 40 units, respectively
E)less than $6 and more than 50 units, respectively
Figure 17.2

A)$6 and 50 units, respectively
B)$12 and 50 units, respectively
C)$12 and 40 units, respectively
D)$6 and 40 units, respectively
E)less than $6 and more than 50 units, respectively

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The common-pool problem arises:
A)when goods are not rival in consumption.
B)in the presence of asymmetric information.
C)when property rights are well defined.
D)when exhaustible resources are overused.
E)when renewable resources are overused.
A)when goods are not rival in consumption.
B)in the presence of asymmetric information.
C)when property rights are well defined.
D)when exhaustible resources are overused.
E)when renewable resources are overused.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The marginal external cost is:
A)the additional cost imposed on society by producing an extra unit of a good.
B)the cost of producing an extra unit of damaged goods.
C)the additional cost of importing extra units of a good.
D)the total cost to society of producing a good.
E)the marginal cost divided by the marginal revenue.
A)the additional cost imposed on society by producing an extra unit of a good.
B)the cost of producing an extra unit of damaged goods.
C)the additional cost of importing extra units of a good.
D)the total cost to society of producing a good.
E)the marginal cost divided by the marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
At the market output and price for a good whose production causes pollution, _____.
A)the marginal social cost of production is negative
B)the marginal social cost of production exceeds the marginal social benefit of production
C)the marginal private cost of production equals the marginal private benefit of production
D)the marginal social benefit of production equals the marginal social cost of production
E)the marginal social benefit of production exceeds the marginal private cost of production
A)the marginal social cost of production is negative
B)the marginal social cost of production exceeds the marginal social benefit of production
C)the marginal private cost of production equals the marginal private benefit of production
D)the marginal social benefit of production equals the marginal social cost of production
E)the marginal social benefit of production exceeds the marginal private cost of production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The socially efficient level of output is determined where:
A)marginal social cost equals marginal social benefit.
B)marginal private cost equals marginal social benefit.
C)average social cost equals average private cost.
D)average private cost equals average social benefit.
E)total social cost equals total social benefit.
A)marginal social cost equals marginal social benefit.
B)marginal private cost equals marginal social benefit.
C)average social cost equals average private cost.
D)average private cost equals average social benefit.
E)total social cost equals total social benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A tannery discovers a technology that makes it cheaper to reduce the air pollution it generates. On a graph of the optimal level of air quality, the use of the new technology would be represented by:
A)a leftward shift of the marginal social cost curve.
B)a rightward shift of the marginal social cost curve.
C)movement to the right along the marginal social cost curve.
D)movement to the left along the marginal social cost curve.
E)a downward shift of the marginal social benefit curve.
A)a leftward shift of the marginal social cost curve.
B)a rightward shift of the marginal social cost curve.
C)movement to the right along the marginal social cost curve.
D)movement to the left along the marginal social cost curve.
E)a downward shift of the marginal social benefit curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In order to increase a society's total welfare, a production process that produces a negative externality should be _____.
A)taxed
B)encouraged to produce goods in excess of the socially optimum level
C)prohibited
D)subsidized if the good is produced for foreign markets
E)subsidized if the good is produced for the domestic market
A)taxed
B)encouraged to produce goods in excess of the socially optimum level
C)prohibited
D)subsidized if the good is produced for foreign markets
E)subsidized if the good is produced for the domestic market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose the production of electricity generates pollution. In this case, the optimal level of electricity is produced when the marginal social benefit from electricity production equals the _____.
A)marginal private cost of electricity production
B)marginal social cost of electricity production
C)marginal external cost of electricity production
D)marginal cost of labor used in electricity production
E)marginal cost of capital used in electricity production
A)marginal private cost of electricity production
B)marginal social cost of electricity production
C)marginal external cost of electricity production
D)marginal cost of labor used in electricity production
E)marginal cost of capital used in electricity production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If the marginal social benefit of consuming a product exceeds the marginal social cost, social welfare:
A)increases when output decreases.
B)decreases when output increases.
C)remains unchanged when output increases.
D)increases when output increases.
E)is at its maximum.
A)increases when output decreases.
B)decreases when output increases.
C)remains unchanged when output increases.
D)increases when output increases.
E)is at its maximum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In a free market, a firm's equilibrium output is determined:
A)where marginal social cost equals marginal social benefit.
B)where marginal private benefit equals marginal social benefit.
C)where marginal social cost equals marginal private cost.
D)where marginal private cost equals marginal private benefit.
E)by government.
A)where marginal social cost equals marginal social benefit.
B)where marginal private benefit equals marginal social benefit.
C)where marginal social cost equals marginal private cost.
D)where marginal private cost equals marginal private benefit.
E)by government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Imposition of tax on an open-access resource increases the marginal private cost of using the resource by _____.
A)zero
B)the amount of the tax
C)the marginal cost of the resource
D)the average private cost of using the resource
E)the average social cost of using the resource
A)zero
B)the amount of the tax
C)the marginal cost of the resource
D)the average private cost of using the resource
E)the average social cost of using the resource

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The marginal social benefit of good air:
A)declines as air quality improves.
B)rises as air quality improves.
C)remains constant as air quality improves.
D)initially falls but rises with higher improvement.
E)initially rises but becomes negative wither greater improvement.
A)declines as air quality improves.
B)rises as air quality improves.
C)remains constant as air quality improves.
D)initially falls but rises with higher improvement.
E)initially rises but becomes negative wither greater improvement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
To maximize social welfare in the presence of a negative externality, marginal __________ must equal marginal __________.
A)social cost; private cost
B)private cost; external cost
C)social cost; social benefit
D)private cost; social benefit
E)social cost; external cost
A)social cost; private cost
B)private cost; external cost
C)social cost; social benefit
D)private cost; social benefit
E)social cost; external cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Economists view pollution as an economic problem that arises because:
A)private enterprises always minimize the amount of pollution produced.
B)profitable firms rarely pollute.
C)the level of pollution declines as the economy grows.
D)firms that pollute do not pay the full social cost of producing their output.
E)pollution costs are borne by the consumer.
A)private enterprises always minimize the amount of pollution produced.
B)profitable firms rarely pollute.
C)the level of pollution declines as the economy grows.
D)firms that pollute do not pay the full social cost of producing their output.
E)pollution costs are borne by the consumer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
When using the economic efficiency approach to control air and water pollution, the government:
A)forces each firm to produce emissions in the most cost-efficient manner irrespective of its cost structure.
B)offers each firm the flexibility to reduce emissions in the most cost-effective manner, given its unique cost structure.
C)offers each firm the option of choosing between the cost-minimizing emission level and the profit-maximizing emission level.
D)provides each firm with fixed rules for reducing pollution.
E)offers each firm the option of using either total cost pricing or average cost pricing when determining the optimum emission level.
A)forces each firm to produce emissions in the most cost-efficient manner irrespective of its cost structure.
B)offers each firm the flexibility to reduce emissions in the most cost-effective manner, given its unique cost structure.
C)offers each firm the option of choosing between the cost-minimizing emission level and the profit-maximizing emission level.
D)provides each firm with fixed rules for reducing pollution.
E)offers each firm the option of using either total cost pricing or average cost pricing when determining the optimum emission level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Marginal social cost is equal to:
A)the total private cost of production.
B)marginal private cost.
C)marginal external cost.
D)marginal private cost plus marginal external cost.
E)marginal private cost divided by marginal external cost.
A)the total private cost of production.
B)marginal private cost.
C)marginal external cost.
D)marginal private cost plus marginal external cost.
E)marginal private cost divided by marginal external cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Society's total cost of producing a good:
A)includes only the private cost to a firm.
B)includes only the external cost.
C)includes all private and external costs.
D)includes the sunk cost and the total variable cost of a firm.
E)includes only the average variable cost of production.
A)includes only the private cost to a firm.
B)includes only the external cost.
C)includes all private and external costs.
D)includes the sunk cost and the total variable cost of a firm.
E)includes only the average variable cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the marginal social cost of producing a good exceeds the marginal private cost, then:
A)the quantity of the good being produced is too less.
B)the price charged for the good is too high.
C)the good produces a positive externality.
D)the good produces a negative externality.
E)social welfare is likely to increase by producing more of the good.
A)the quantity of the good being produced is too less.
B)the price charged for the good is too high.
C)the good produces a positive externality.
D)the good produces a negative externality.
E)social welfare is likely to increase by producing more of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The socially optimal level of output of a good that generates an externality occurs when:
A)the marginal private cost of production equal marginal private revenue.
B)the firm maximizes its profits.
C)the marginal private cost of production exceeds the marginal social cost of production.
D)the marginal social cost of production equals the marginal social benefit of production.
E)the marginal private cost of the good equals the marginal social benefit of the good.
A)the marginal private cost of production equal marginal private revenue.
B)the firm maximizes its profits.
C)the marginal private cost of production exceeds the marginal social cost of production.
D)the marginal social cost of production equals the marginal social benefit of production.
E)the marginal private cost of the good equals the marginal social benefit of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The optimal level of air pollution by a firm is:
A)the level at which the marginal private cost of improving air quality equals zero.
B)the level at which the marginal social cost of improving air quality equals the marginal social benefit.
C)the level at which the average social cost of improving air quality equals the average social benefit.
D)the level at which the total social cost of improving air quality equals the total social benefit.
E)the level at which the marginal social cost of improving air quality is minimized.
A)the level at which the marginal private cost of improving air quality equals zero.
B)the level at which the marginal social cost of improving air quality equals the marginal social benefit.
C)the level at which the average social cost of improving air quality equals the average social benefit.
D)the level at which the total social cost of improving air quality equals the total social benefit.
E)the level at which the marginal social cost of improving air quality is minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
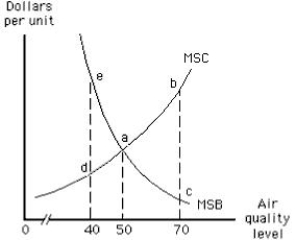
79
The following graph shows the market for pollution rights in an economy. The optimal level of air quality is ______.
Figure 17.3
A)0
B)40
C)50
D)70
E)greater than 70
Figure 17.3

A)0
B)40
C)50
D)70
E)greater than 70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
When using the traditional command-and-control approach to environmental regulation, the government attempts to:
A)set a minimum requirement and then allows the firm to determine the most efficient method for achieving this requirement.
B)determine the most efficient method for different industries.
C)make allowances for differences across industries and between firms.
D)set engineering standards that are applicable to all situations and do not recognize unique circumstances.
E)set a maximum requirement and then allows the individual firm the latitude of choosing the most efficient method.
A)set a minimum requirement and then allows the firm to determine the most efficient method for achieving this requirement.
B)determine the most efficient method for different industries.
C)make allowances for differences across industries and between firms.
D)set engineering standards that are applicable to all situations and do not recognize unique circumstances.
E)set a maximum requirement and then allows the individual firm the latitude of choosing the most efficient method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 150 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



