Deck 15: Chemical Equilibrium
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/118
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Chemical Equilibrium
1
Dynamic equilibrium is established when the rate of the forward reaction goes to zero.
False
2
Since the equilibrium constant ( 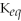
)is calculated using the numerical concentrations of reactants and products,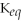
can never be a negative value.
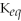
)is calculated using the numerical concentrations of reactants and products,
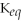
can never be a negative value.
True
3
The rate of a chemical reaction is inversely proportional to the temperature.
False
4
When dynamic equilibrium is achieved,the concentrations of reactants is equal to the concentrations of the products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The larger the equilibrium constant,the greater is the concentration of reactants relative to products at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
When dynamic equilibrium is achieved,the rates of the forward and backward reactions go to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The rate of a reaction increases with increasing concentrations of reactants because you have more collisions occurring in a given time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Reaction rates generally increase as a reaction proceeds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The rate of a chemical reaction is the amount of reactant that changes to product in a specific amount of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
As long as 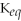
> 1,all reactants will eventually be consumed and leave us exclusively with product molecules.
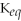
> 1,all reactants will eventually be consumed and leave us exclusively with product molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Equilibrium Constant, 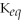
,is a way to quantify the relative concentrations of the reactants and products of a reaction at equilibrium.
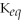
,is a way to quantify the relative concentrations of the reactants and products of a reaction at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The rate of a chemical reaction always remains the same from start to finish.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Collisions between reactant molecules do not always lead to the formation of product molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
It is not necessary to have a balanced equation before writing an equilibrium constant expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Equilibrium involves the ideas of sameness and constancy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Placing a [ ] around the formula of a chemical means that we are referring to the molar concentration of that chemical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A reversible reaction is one that can be stopped and then restarted as needed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A large equilibrium constant 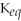
indicates that the forward reaction is largely favored.
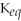
indicates that the forward reaction is largely favored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Living things are in equilibrium with their surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Dynamic equilibrium occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Adding heat to an exothermic reaction will cause the reaction to remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Decreasing the amount of carbon dioxide in the reaction below will cause the reaction to proceed to the right so that equilibrium will be restored. 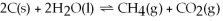
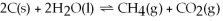

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Le Chatelier's principle states that when a chemical system at equilibrium is disturbed,the system shifts in a direction that minimizes the disturbance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A reaction that has 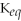
= 2.0 ×
will have high concentrations of products.
= 2.0 ×
will have high concentrations of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If you have a chamber of gases at equilibrium,compressing the gases to half the original volume would have the same effect as doubling the pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If 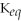
equals about ≈1,then neither direction is favored and significant amounts of both reactants and products are present at equilibrium.
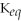
equals about ≈1,then neither direction is favored and significant amounts of both reactants and products are present at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In an exothermic reaction,you can consider the emitted heat as a reactant in this system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Decreasing the volume of the system below causes the reaction to shift towards the right. 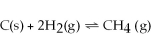
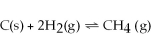

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The equilibrium expression for the reaction: 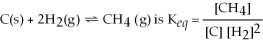
.
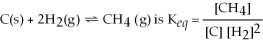
.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
For a given chemical equation,the coefficients for each substance become the exponents for each substance in the written equilibrium expression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Increasing the amount of carbon in the reaction below will cause the reaction to proceed to the left so that equilibrium will be restored. 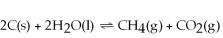
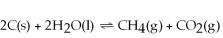

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The equilibrium expression for the reaction: 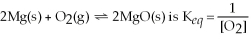
.
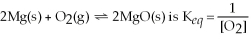
.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If 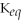
= 2 for the reaction X ⇌ Y,then the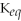
for Y ⇌ X will be 1/2 (or 0.5).
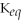
= 2 for the reaction X ⇌ Y,then the
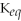
for Y ⇌ X will be 1/2 (or 0.5).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A reaction that has 
= 2.0 ×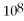
will have high concentrations of products.

= 2.0 ×
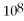
will have high concentrations of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Adding heat to an endothermic reaction causes the reaction to shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The equilibrium constant, 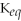
,for an equilibrium reaction will always be the same (at a given temperature)regardless of what the initial concentrations of reactants and products were.
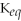
,for an equilibrium reaction will always be the same (at a given temperature)regardless of what the initial concentrations of reactants and products were.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Le Chatelier's principle states that a chemical system must have a shift in direction in order to force the system to reach equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The equilibrium expression for the reaction: 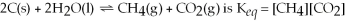
.
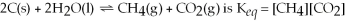
.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the equilibrium constant, 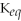
,for a reaction increases upon heating,the reaction must have been endothermic.
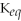
,for a reaction increases upon heating,the reaction must have been endothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Increasing the volume of the system below causes the reaction to shift towards the right. 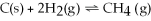

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is TRUE for a system that is in dynamic equilibrium?
A)The forward reaction goes to 100% completion.
B)The reaction rate of the forward reaction approaches zero.
C)The concentration of products is equal to the concentration of the reactants.
D)Both the forward and reverse reactions come to a halt.
E)none of the above
A)The forward reaction goes to 100% completion.
B)The reaction rate of the forward reaction approaches zero.
C)The concentration of products is equal to the concentration of the reactants.
D)Both the forward and reverse reactions come to a halt.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A compound with a very large 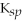
value is generally considered to be only partially soluble.
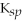
value is generally considered to be only partially soluble.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The chemical equation that would generate the equilibrium expression 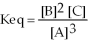
Is ________.(Assume all substances are gases in this reaction. )
A)C + 2B ⇌ 3A
B)3A ⇌ 2B + C
C)A ⇌ B + C
D)1/2 B + C ⇌ 1/3 A
E)none of the above
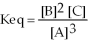
Is ________.(Assume all substances are gases in this reaction. )
A)C + 2B ⇌ 3A
B)3A ⇌ 2B + C
C)A ⇌ B + C
D)1/2 B + C ⇌ 1/3 A
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For the reaction aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD,the equilibrium expression is:
A)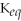
=
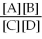
B)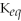
=
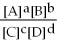
C)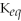
=
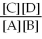
D)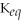
=
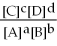
E)none of the above
A)
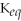
=
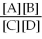
B)
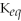
=
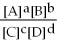
C)
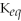
=
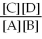
D)
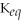
=
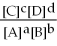
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A chemical equilibrium exists when:
A)reactants are completely changed to products.
B)there are equal amounts of reactants and products.
C)the rate at which reactants form products becomes zero.
D)the sum of reactant and product concentrations equals one mole.
E)the rate at which reactants form products is the same as the rate at which products form reactants.
A)reactants are completely changed to products.
B)there are equal amounts of reactants and products.
C)the rate at which reactants form products becomes zero.
D)the sum of reactant and product concentrations equals one mole.
E)the rate at which reactants form products is the same as the rate at which products form reactants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to the collision theory of chemical reactions:
A)high energy collisions result in few successful reactions as there isn't sufficient time for the products to react.
B)low energy collisions result in many successful reactions as there is sufficient time for the reactants to form products.
C)high energy collisions lead to the successful formation of products.
D)low energy collisions do not occur in the gas phase.
E)all of the above
A)high energy collisions result in few successful reactions as there isn't sufficient time for the products to react.
B)low energy collisions result in many successful reactions as there is sufficient time for the reactants to form products.
C)high energy collisions lead to the successful formation of products.
D)low energy collisions do not occur in the gas phase.
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Dissolving the compound PbCl2 into water can be represented as 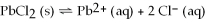
,so the equilibrium expression is Ksp =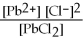
.
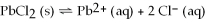
,so the equilibrium expression is Ksp =
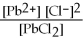
.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Why does the rate of the reaction decrease over time?
A)Exothermic reactions lose heat which cools the reaction which decreases reaction rate.
B)As the reaction proceeds,the concentration of the products results in fewer collisions.
C)As the reaction proceeds,a decrease in the concentration of reactants results in fewer successful collisions.
D)Not all molecules will react and some choose to stay in their present form.
E)none of the above
A)Exothermic reactions lose heat which cools the reaction which decreases reaction rate.
B)As the reaction proceeds,the concentration of the products results in fewer collisions.
C)As the reaction proceeds,a decrease in the concentration of reactants results in fewer successful collisions.
D)Not all molecules will react and some choose to stay in their present form.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Given N2 (g)+ 3 H2 (g)⇌ 2 NH3 (g),which scenario will allow you to eventually reach an equilibrium mixture involving these chemicals?
A)Place only N2 into a sealed vessel.
B)Place only H2 into a sealed vessel.
C)Place only NH3 into a sealed vessel.
D)All of the above scenarios.
E)none of the above
A)Place only N2 into a sealed vessel.
B)Place only H2 into a sealed vessel.
C)Place only NH3 into a sealed vessel.
D)All of the above scenarios.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
For the reaction 2A + B ⇌ 2C + 3D,the equilibrium expression is:
A)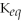
=
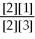
B)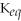
=
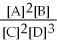
C)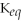
=
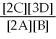
D)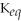
=
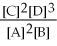
E)none of the above
A)
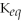
=
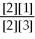
B)
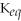
=
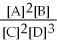
C)
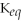
=
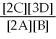
D)
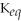
=
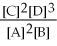
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following is TRUE about a chemical system in equilibrium?
A)No reaction takes place.
B)Temperature changes have no effect on reaction rate.
C)Addition of more reactants have no effect on reaction rate.
D)Reaction rate remains stable as long as temperature and pressure are stable.
E)none of the above
A)No reaction takes place.
B)Temperature changes have no effect on reaction rate.
C)Addition of more reactants have no effect on reaction rate.
D)Reaction rate remains stable as long as temperature and pressure are stable.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A description of life is:
A)Living things maintain and control their sameness.
B)Living things maintain and control their changelessness.
C)Living things maintain and control their equilibrium.
D)Living things maintain and control their disequilibrium.
E)none of the above
A)Living things maintain and control their sameness.
B)Living things maintain and control their changelessness.
C)Living things maintain and control their equilibrium.
D)Living things maintain and control their disequilibrium.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following changes will increase the reaction rate?
A)an increase in the concentration of the products
B)a decrease of the reaction temperature
C)allowing more time for the reaction
D)an increase in the concentration of reactants
E)all of the above
A)an increase in the concentration of the products
B)a decrease of the reaction temperature
C)allowing more time for the reaction
D)an increase in the concentration of reactants
E)all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose a wall divides a playground,and twenty balls lie on the ground on the east side,while forty balls lie on the west side.If a child on the east side of the wall always tosses a ball over the wall at the same time a child on the west side tosses a ball over the wall,then:
A)equilibrium has been established.
B)all balls will eventually end up on one side.
C)equilibrium will be established once thirty balls are on each side.
D)this system can never reach equilibrium.
E)none of the above
A)equilibrium has been established.
B)all balls will eventually end up on one side.
C)equilibrium will be established once thirty balls are on each side.
D)this system can never reach equilibrium.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If an equilibrium reaction shifts to the right when the system is cooled,this indicates that the reaction is endothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Iron(II)carbonate ( 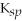
= 3.07 × 10-11)is more soluble than calcium fluoride (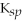
= 1.46 × 10-10).
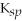
= 3.07 × 10-11)is more soluble than calcium fluoride (
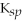
= 1.46 × 10-10).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following changes will increase reaction rate?
1.An increase in the concentration of reactants
2.An increase in temperature
3.Higher-energy collisions between reacting molecules
A)1 and 2 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)2 and 3 only
D)All of 1,2,and 3
E)Neither 1,2,or 3
1.An increase in the concentration of reactants
2.An increase in temperature
3.Higher-energy collisions between reacting molecules
A)1 and 2 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)2 and 3 only
D)All of 1,2,and 3
E)Neither 1,2,or 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A compound with a relatively small 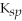
value indicates that the compound is only partially soluble.
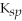
value indicates that the compound is only partially soluble.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A system is said to be in dynamic equilibrium when:
A)there is no longer any net change in the concentrations of products or reactants.
B)the forward and reverse reactions come to a halt.
C)the sum of the concentrations of the reactants is equal to the sum of the concentrations of the products.
D)you have let the reaction proceed for approximately 30 minutes and can assume there will be no more changes.
E)none of the above
A)there is no longer any net change in the concentrations of products or reactants.
B)the forward and reverse reactions come to a halt.
C)the sum of the concentrations of the reactants is equal to the sum of the concentrations of the products.
D)you have let the reaction proceed for approximately 30 minutes and can assume there will be no more changes.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A catalyst speeds up a chemical reaction as it is being consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
For the reaction 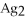
S(s)⇌ 2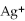
(aq)+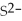
(aq),what happens to the equilibrium position if ammonium sulfate is added?
A)shifts to the left
B)shifts to the right
C)does nothing
D)doubles
E)halves
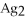
S(s)⇌ 2
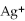
(aq)+
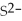
(aq),what happens to the equilibrium position if ammonium sulfate is added?
A)shifts to the left
B)shifts to the right
C)does nothing
D)doubles
E)halves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
For the reaction ![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_c24f_9ee3_639394dc18f1_TB6109_11.jpg)
S(s)⇌ 2![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_e960_9ee3_939e70755286_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)+![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_e961_9ee3_4d6e9ea5b594_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq),the equilibrium expression is:
A)![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_e962_9ee3_89621e0bdd86_TB6109_11.jpg)
=
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_e963_9ee3_ffdea58c35f5_TB6109_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_1074_9ee3_f34a920766a7_TB6109_11.jpg)
=
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_1075_9ee3_9bf21e067df5_TB6109_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_1076_9ee3_2f20888e2bcc_TB6109_11.jpg)
= [
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_1077_9ee3_c54e8f944b26_TB6109_11.jpg)
]2[
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_1078_9ee3_a58002757dcf_TB6109_11.jpg)
]
D)![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_3789_9ee3_731476620997_TB6109_11.jpg)
= [
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_378a_9ee3_e5a6e26b352c_TB6109_11.jpg)
S]
E)none of the above
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_c24f_9ee3_639394dc18f1_TB6109_11.jpg)
S(s)⇌ 2
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_e960_9ee3_939e70755286_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)+
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_e961_9ee3_4d6e9ea5b594_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq),the equilibrium expression is:
A)
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_e962_9ee3_89621e0bdd86_TB6109_11.jpg)
=
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_e963_9ee3_ffdea58c35f5_TB6109_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_1074_9ee3_f34a920766a7_TB6109_11.jpg)
=
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_1075_9ee3_9bf21e067df5_TB6109_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_1076_9ee3_2f20888e2bcc_TB6109_11.jpg)
= [
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_1077_9ee3_c54e8f944b26_TB6109_11.jpg)
]2[
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_1078_9ee3_a58002757dcf_TB6109_11.jpg)
]
D)
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_3789_9ee3_731476620997_TB6109_11.jpg)
= [
![<strong>For the reaction S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = B) = C) = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ] D) = [ S] E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_378a_9ee3_e5a6e26b352c_TB6109_11.jpg)
S]
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
For the reaction 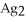
S(s)⇌ 2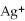
(aq)+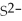
(aq),what happens to the equilibrium position if aqueous ammonium sulfide is added?
A)shifts to the left
B)shifts to the right
C)does nothing
D)doubles
E)halves
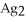
S(s)⇌ 2
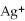
(aq)+
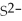
(aq),what happens to the equilibrium position if aqueous ammonium sulfide is added?
A)shifts to the left
B)shifts to the right
C)does nothing
D)doubles
E)halves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What must be TRUE for a reaction possessing a large equilibrium constant?
A)The reaction rate is fast.
B)The reaction rate is slow.
C)The forward reaction is favored.
D)The reverse reaction is favored.
E)none of the above
A)The reaction rate is fast.
B)The reaction rate is slow.
C)The forward reaction is favored.
D)The reverse reaction is favored.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
For the reaction 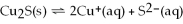
,the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: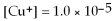
M,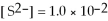
M.The equilibrium constant is:
A)1.0 ×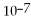
.
B)1.0 ×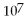
.
C)1.0 ×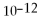
.
D)1.0 ×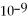
.
E)none of the above
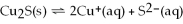
,the equilibrium concentrations are as follows:
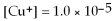
M,
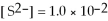
M.The equilibrium constant is:
A)1.0 ×
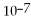
.
B)1.0 ×
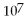
.
C)1.0 ×
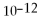
.
D)1.0 ×
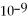
.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Le Chatelier's Principle states that:
A)a disturbing force must be applied to a system in order for it to reach equilibrium.
B)when a system at equilibrium is disturbed,a new equilibrium constant is established.
C)when a chemical system at equilibrium is disturbed,the system shifts in order to minimize the effect.
D)when a chemical system is at equilibrium it is no longer possible to alter the system.
E)none of the above
A)a disturbing force must be applied to a system in order for it to reach equilibrium.
B)when a system at equilibrium is disturbed,a new equilibrium constant is established.
C)when a chemical system at equilibrium is disturbed,the system shifts in order to minimize the effect.
D)when a chemical system is at equilibrium it is no longer possible to alter the system.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
For the reaction 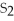
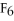
⇌ 2S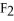
+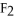
,the equilibrium expression is:
A)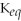
=
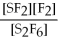
B)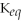
=
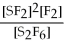
C)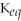
=
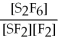
D)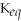
=
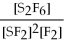
E)none of the above
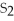
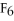
⇌ 2S
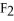
+
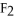
,the equilibrium expression is:
A)
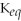
=
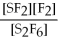
B)
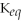
=
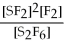
C)
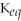
=
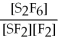
D)
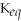
=
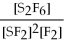
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
For the reaction 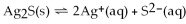
,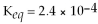
And the equilibrium concentration of silver ion is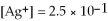
M.What is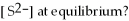
A)0.0038
B)9.6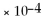
C)2.6 ×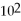
D)1.0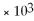
E)none of the above
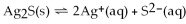
,
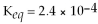
And the equilibrium concentration of silver ion is
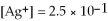
M.What is
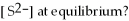
A)0.0038
B)9.6
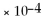
C)2.6 ×
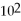
D)1.0
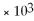
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
For the reaction 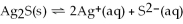
,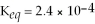
,and the equilibrium concentration of sulfide ion is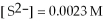
.What is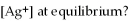
A)0.052 M
B)0.32 M
C)0.015 M
D)0.10 M
E)none of the above
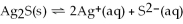
,
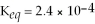
,and the equilibrium concentration of sulfide ion is
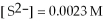
.What is
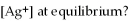
A)0.052 M
B)0.32 M
C)0.015 M
D)0.10 M
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
For the reaction ![<strong>For the reaction [ ] = 0.12 M, .The equilibrium constant is:</strong> A)0.44 B)0.15 C)2.3 D)6.7 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_5e9c_9ee3_2348bb41900f_TB6109_11.jpg)
[![<strong>For the reaction [ ] = 0.12 M, .The equilibrium constant is:</strong> A)0.44 B)0.15 C)2.3 D)6.7 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_5e9d_9ee3_03c2977591db_TB6109_11.jpg)
![<strong>For the reaction [ ] = 0.12 M, .The equilibrium constant is:</strong> A)0.44 B)0.15 C)2.3 D)6.7 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_5e9e_9ee3_3db756a37323_TB6109_11.jpg)
] = 0.12 M,![<strong>For the reaction [ ] = 0.12 M, .The equilibrium constant is:</strong> A)0.44 B)0.15 C)2.3 D)6.7 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_85af_9ee3_2da5953ffd7f_TB6109_11.jpg)
![<strong>For the reaction [ ] = 0.12 M, .The equilibrium constant is:</strong> A)0.44 B)0.15 C)2.3 D)6.7 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_85b0_9ee3_852a6f858016_TB6109_11.jpg)
.The equilibrium constant is:
A)0.44
B)0.15
C)2.3
D)6.7
E)none of the above
![<strong>For the reaction [ ] = 0.12 M, .The equilibrium constant is:</strong> A)0.44 B)0.15 C)2.3 D)6.7 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_5e9c_9ee3_2348bb41900f_TB6109_11.jpg)
[
![<strong>For the reaction [ ] = 0.12 M, .The equilibrium constant is:</strong> A)0.44 B)0.15 C)2.3 D)6.7 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_5e9d_9ee3_03c2977591db_TB6109_11.jpg)
![<strong>For the reaction [ ] = 0.12 M, .The equilibrium constant is:</strong> A)0.44 B)0.15 C)2.3 D)6.7 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_5e9e_9ee3_3db756a37323_TB6109_11.jpg)
] = 0.12 M,
![<strong>For the reaction [ ] = 0.12 M, .The equilibrium constant is:</strong> A)0.44 B)0.15 C)2.3 D)6.7 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_85af_9ee3_2da5953ffd7f_TB6109_11.jpg)
![<strong>For the reaction [ ] = 0.12 M, .The equilibrium constant is:</strong> A)0.44 B)0.15 C)2.3 D)6.7 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_85b0_9ee3_852a6f858016_TB6109_11.jpg)
.The equilibrium constant is:
A)0.44
B)0.15
C)2.3
D)6.7
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
For the reaction 2 A ⇌ B,the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: [A] = 0.056 M and [B] = 0.12 M.Calculate the equilibrium constant ( ![<strong>For the reaction 2 A ⇌ B,the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: [A] = 0.056 M and [B] = 0.12 M.Calculate the equilibrium constant ( )for the reaction.</strong> A)2.6 × 10<sup>-2</sup> B)0.26 C)2.1 D)38 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_378b_9ee3_85828bbd24a6_TB6109_11.jpg)
)for the reaction.
A)2.6 × 10-2
B)0.26
C)2.1
D)38
E)none of the above
![<strong>For the reaction 2 A ⇌ B,the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: [A] = 0.056 M and [B] = 0.12 M.Calculate the equilibrium constant ( )for the reaction.</strong> A)2.6 × 10<sup>-2</sup> B)0.26 C)2.1 D)38 E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd9_378b_9ee3_85828bbd24a6_TB6109_11.jpg)
)for the reaction.
A)2.6 × 10-2
B)0.26
C)2.1
D)38
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is TRUE of a system for which 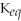
<< 1?
A)It will take a long time to reach equilibrium.
B)It will take a short time to reach equilibrium.
C)The equilibrium favors the reverse reaction.
D)The equilibrium favors the forward reaction.
E)none of the above
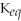
<< 1?
A)It will take a long time to reach equilibrium.
B)It will take a short time to reach equilibrium.
C)The equilibrium favors the reverse reaction.
D)The equilibrium favors the forward reaction.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following is TRUE of a system for which 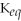
>> 1?
A)It will take a short time to reach equilibrium.
B)It will take a long time to reach equilibrium.
C)The equilibrium favors the reverse reaction.
D)The equilibrium favors the forward reaction.
E)none of the above
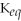
>> 1?
A)It will take a short time to reach equilibrium.
B)It will take a long time to reach equilibrium.
C)The equilibrium favors the reverse reaction.
D)The equilibrium favors the forward reaction.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
When writing the expression for an equilibrium constant,which type of substance IS included?
A)solids
B)pure liquids
C)gases
D)all of the above
E)none of these
A)solids
B)pure liquids
C)gases
D)all of the above
E)none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
For the reaction 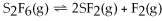
,the equilibrium concentrations are as follows: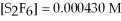
,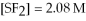
,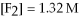
.The equilibrium constant is:
A)7.53 ×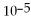
B)1.19 ×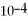
C)8.43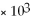
D)1.33 ×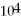
E)none of the above
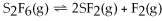
,the equilibrium concentrations are as follows:
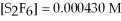
,
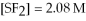
,
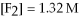
.The equilibrium constant is:
A)7.53 ×
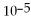
B)1.19 ×
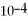
C)8.43
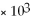
D)1.33 ×
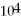
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
For the reaction 2 H2O (l)⇌ 2H2 (g)+ O2 (g),the equilibrium expression is:
A)![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_7429_9ee3_338ec8c7a73c_TB6109_11.jpg)
= [H2O]2
B)![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_9b3a_9ee3_2b1d81638c94_TB6109_11.jpg)
= [H2]2 [O2]
C)![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_9b3b_9ee3_8f2ee7a1b118_TB6109_11.jpg)
=
![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_9b3c_9ee3_854203f6412a_TB6109_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_9b3d_9ee3_67fdbc466c4b_TB6109_11.jpg)
=
![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_c24e_9ee3_f964743296fd_TB6109_11.jpg)
E)none of the above
A)
![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_7429_9ee3_338ec8c7a73c_TB6109_11.jpg)
= [H2O]2
B)
![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_9b3a_9ee3_2b1d81638c94_TB6109_11.jpg)
= [H2]2 [O2]
C)
![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_9b3b_9ee3_8f2ee7a1b118_TB6109_11.jpg)
=
![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_9b3c_9ee3_854203f6412a_TB6109_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_9b3d_9ee3_67fdbc466c4b_TB6109_11.jpg)
=
![<strong>For the reaction 2 H<sub>2</sub>O (l)⇌ 2H<sub>2</sub> (g)+ O<sub>2</sub> (g),the equilibrium expression is:</strong> A) = [H<sub>2</sub>O]<sup>2</sup> B) = [H<sub>2</sub>]<sup>2</sup> [O<sub>2</sub>] C) = D) = E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_c24e_9ee3_f964743296fd_TB6109_11.jpg)
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which equilibrium constant represents a reaction that favors the formation of the products to the greatest extent?
A)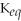
= 100
B)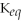
= 1.0 ×
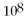
C)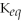
= 1.0 ×
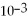
D)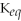
= 1.0 ×
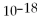
E)not enough information
A)
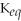
= 100
B)
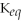
= 1.0 ×
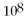
C)
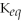
= 1.0 ×
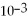
D)
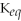
= 1.0 ×
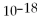
E)not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
For the reaction LiOH (s)⇌ Li+ (aq)+ OH- (aq), ![<strong>For the reaction LiOH (s)⇌ Li<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup> (aq), = 4.6 × ,and the equilibrium concentration for hydroxide ion is [OH<sup>-</sup>] = 0.042 M.What is [Li<sup>+</sup>] at equilibrium?</strong> A)0.11 M B)0.0046 M C)0.042 M D)An answer cannot be determined without [LiOH] value. E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbda_9730_9ee3_05cd50d1aeb3_TB6109_11.jpg)
= 4.6 ×![<strong>For the reaction LiOH (s)⇌ Li<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup> (aq), = 4.6 × ,and the equilibrium concentration for hydroxide ion is [OH<sup>-</sup>] = 0.042 M.What is [Li<sup>+</sup>] at equilibrium?</strong> A)0.11 M B)0.0046 M C)0.042 M D)An answer cannot be determined without [LiOH] value. E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbda_9731_9ee3_37e542a46599_TB6109_11.jpg)
,and the equilibrium concentration for hydroxide ion is [OH-] = 0.042 M.What is [Li+] at equilibrium?
A)0.11 M
B)0.0046 M
C)0.042 M
D)An answer cannot be determined without [LiOH] value.
E)none of the above
![<strong>For the reaction LiOH (s)⇌ Li<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup> (aq), = 4.6 × ,and the equilibrium concentration for hydroxide ion is [OH<sup>-</sup>] = 0.042 M.What is [Li<sup>+</sup>] at equilibrium?</strong> A)0.11 M B)0.0046 M C)0.042 M D)An answer cannot be determined without [LiOH] value. E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbda_9730_9ee3_05cd50d1aeb3_TB6109_11.jpg)
= 4.6 ×
![<strong>For the reaction LiOH (s)⇌ Li<sup>+</sup> (aq)+ OH<sup>-</sup> (aq), = 4.6 × ,and the equilibrium concentration for hydroxide ion is [OH<sup>-</sup>] = 0.042 M.What is [Li<sup>+</sup>] at equilibrium?</strong> A)0.11 M B)0.0046 M C)0.042 M D)An answer cannot be determined without [LiOH] value. E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbda_9731_9ee3_37e542a46599_TB6109_11.jpg)
,and the equilibrium concentration for hydroxide ion is [OH-] = 0.042 M.What is [Li+] at equilibrium?
A)0.11 M
B)0.0046 M
C)0.042 M
D)An answer cannot be determined without [LiOH] value.
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which equilibrium constant represents a reaction that favors the reactants to the greatest extent?
A)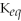
= 100
B)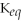
= 1.0 ×
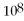
C)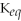
= 1.0 ×
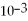
D)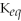
= 1.0 ×
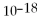
E)not enough information
A)
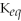
= 100
B)
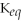
= 1.0 ×
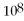
C)
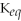
= 1.0 ×
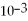
D)
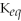
= 1.0 ×
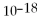
E)not enough information

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Identify the equation for which ![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_d7d9_9ee3_a3a2293a84ef_TB6109_11.jpg)
= [![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_d7da_9ee3_2195af608487_TB6109_11.jpg)
]2[![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_d7db_9ee3_55dfa72fd1f9_TB6109_11.jpg)
].
A)![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_d7dc_9ee3_692eafaaa47a_TB6109_11.jpg)
S(s)⇌
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_feed_9ee3_770325e83c95_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)+ 2
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_feee_9ee3_6d45eae6a011_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)
B)CuS(s)⇌![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_feef_9ee3_1bc49d9de5c6_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)+
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_fef0_9ee3_63ed147bbf9a_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)
C)![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_2601_9ee3_d73269c44357_TB6109_11.jpg)
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_2602_9ee3_0f6ee4a7bc37_TB6109_11.jpg)
S(s)⇌
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_2603_9ee3_e7689c27200f_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)+
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_2604_9ee3_716152ae4e2f_TB6109_11.jpg)
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_2605_9ee3_6f030e9cede3_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)
D)![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_4d16_9ee3_ef90cef5a7de_TB6109_11.jpg)
S(s)⇌ 2
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_4d17_9ee3_51093a9c2bcc_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)+
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_4d18_9ee3_4d47969f01af_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)
E)none of the above
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_d7d9_9ee3_a3a2293a84ef_TB6109_11.jpg)
= [
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_d7da_9ee3_2195af608487_TB6109_11.jpg)
]2[
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_d7db_9ee3_55dfa72fd1f9_TB6109_11.jpg)
].
A)
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_d7dc_9ee3_692eafaaa47a_TB6109_11.jpg)
S(s)⇌
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_feed_9ee3_770325e83c95_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)+ 2
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_feee_9ee3_6d45eae6a011_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)
B)CuS(s)⇌
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_feef_9ee3_1bc49d9de5c6_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)+
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd7_fef0_9ee3_63ed147bbf9a_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)
C)
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_2601_9ee3_d73269c44357_TB6109_11.jpg)
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_2602_9ee3_0f6ee4a7bc37_TB6109_11.jpg)
S(s)⇌
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_2603_9ee3_e7689c27200f_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)+
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_2604_9ee3_716152ae4e2f_TB6109_11.jpg)
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_2605_9ee3_6f030e9cede3_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)
D)
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_4d16_9ee3_ef90cef5a7de_TB6109_11.jpg)
S(s)⇌ 2
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_4d17_9ee3_51093a9c2bcc_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)+
![<strong>Identify the equation for which = [ ]<sup>2</sup>[ ].</strong> A) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ 2 (aq) B)CuS(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) C) S(s)⇌ (aq)+ (aq) D) S(s)⇌ 2 (aq)+ (aq) E)none of the above](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6109/11ea8a6b_bbd8_4d18_9ee3_4d47969f01af_TB6109_11.jpg)
(aq)
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 118 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



