Deck 7: Managing Solid Waste- a Plastic Surf: Are the Oceans Teeming With Trash- Ecology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/61
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Managing Solid Waste- a Plastic Surf: Are the Oceans Teeming With Trash- Ecology
1
Matter cannot be created nor destroyed; it only changes form. This is the law of _________.
A) conservation of energy
B) waste management
C) conservation of matter
D) no returns
E) sustainability
A) conservation of energy
B) waste management
C) conservation of matter
D) no returns
E) sustainability
conservation of matter
2
Hazardous and nonhazardous wastes in developing countries often end up in open dumps. Which of the following is FALSE regarding open dumps?
A) Open dumps attract pests such as flies and rats.
B) Leachate from open dumps can contaminate groundwater.
C) Sanitary landfills and open dumps are essentially the same thing.
D) Open dumps are one of the cheapest ways to get rid of human trash.
E) All of the above are true.
A) Open dumps attract pests such as flies and rats.
B) Leachate from open dumps can contaminate groundwater.
C) Sanitary landfills and open dumps are essentially the same thing.
D) Open dumps are one of the cheapest ways to get rid of human trash.
E) All of the above are true.
Sanitary landfills and open dumps are essentially the same thing.
3
Sanitary landfills are commonly used in the United States to manage solid waste. Since decomposition in sanitary landfills relies upon anaerobic bacteria (those that live in oxygen-poor environments), a large amount of the greenhouse gas ______ is produced.
A) methane
B) carbon dioxide
C) oxygen
D) nitrogen
E) sulfur
A) methane
B) carbon dioxide
C) oxygen
D) nitrogen
E) sulfur
methane
4
Waste is _____________.
A) anything that humans do not deem valuable to survival
B) a human term used to describe things we throw away
C) any discarded item that can be naturally degraded in the environment
D) common in natural ecosystems
E) all of the above
A) anything that humans do not deem valuable to survival
B) a human term used to describe things we throw away
C) any discarded item that can be naturally degraded in the environment
D) common in natural ecosystems
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What are the characteristics of something that is nondegradable?
A) It does not degrade in normal atmospheric conditions.
B) It is mostly synthetic molecules.
C) It is chemically stable.
D) It cannot be broken down by naturally occurring enzymes.
E) All of the above choices are characteristics.
A) It does not degrade in normal atmospheric conditions.
B) It is mostly synthetic molecules.
C) It is chemically stable.
D) It cannot be broken down by naturally occurring enzymes.
E) All of the above choices are characteristics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Incineration of waste reduces its volume by 80-90%, which is good. What are problems associated with this practice?
A) the creation of air pollution
B) the creation of water pollution
C) the production of toxic solid waste
D) the cost of incinerators
E) All of the choices listed above are problems associated with incineration.
A) the creation of air pollution
B) the creation of water pollution
C) the production of toxic solid waste
D) the cost of incinerators
E) All of the choices listed above are problems associated with incineration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
One of the cheapest and most common methods of handling solid wastes in developing countries is _________.
A) sanitary landfills
B) incinerators
C) recycling
D) open dumps
E) composting
A) sanitary landfills
B) incinerators
C) recycling
D) open dumps
E) composting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Americans produce _______ amount of solid waste produced by most less-developed countries.
A) half the
B) the same
C) twice the
D) 10 times the
E) 100 times the
A) half the
B) the same
C) twice the
D) 10 times the
E) 100 times the

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

This picture shows people scavenging Cambodia's municipal garbage dump. What does their presence there imply about what has been thrown away?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why can't we permanently get rid of the waste we generate?
A) It is illegal to dump waste in the oceans.
B) Most states prohibit the burning of waste.
C) It would violate the law of conservation of matter.
D) Disposal costs are prohibitive.
E) None of the choices above fit the description.
A) It is illegal to dump waste in the oceans.
B) Most states prohibit the burning of waste.
C) It would violate the law of conservation of matter.
D) Disposal costs are prohibitive.
E) None of the choices above fit the description.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Incinerators reduce the volume of solid waste by about ______________.
A) 10-20%
B) 30-40%
C) 50-60%
D) 70-80%
E) 80-90%
A) 10-20%
B) 30-40%
C) 50-60%
D) 70-80%
E) 80-90%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the difference between degradable and biodegradable waste?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Even though a banana peel is biodegradable and is typically broken down at rapid rates, if you bury the peel deep within a landfill, it takes much longer to degrade. Why is this?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Currently, 54% of our waste is put into landfills. According to the EPA, which of the following shows available waste management techniques in order of most preferred to least preferred?
A) recycling/compost, incineration with energy capture, source reduction/reuse, landfilling
B) source reduction/reuse, recycling/composting, incineration with energy capture, landfilling
C) landfilling, recycling/composting, incineration with energy capture, source reduction/reuse
D) source reduction/reuse, incineration with energy capture, recycling/composting, incineration without energy capture
E) recycling/composting, source reduction/reuse, landfilling
A) recycling/compost, incineration with energy capture, source reduction/reuse, landfilling
B) source reduction/reuse, recycling/composting, incineration with energy capture, landfilling
C) landfilling, recycling/composting, incineration with energy capture, source reduction/reuse
D) source reduction/reuse, incineration with energy capture, recycling/composting, incineration without energy capture
E) recycling/composting, source reduction/reuse, landfilling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A manufacturer of potato chips claims that its packaging can be broken down by living organisms. This packaging is considered _____________.
A) industrial waste
B) nondegradable
C) biodegradable
D) All of the choices listed above fit the description.
E) None of the choices listed above fit the description.
A) industrial waste
B) nondegradable
C) biodegradable
D) All of the choices listed above fit the description.
E) None of the choices listed above fit the description.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the United States, 54% of all garbage is categorized as ___________ waste.
A) recycled paper
B) mining
C) municipal paper
D) agricultural and industrial
E) municipal metal
A) recycled paper
B) mining
C) municipal paper
D) agricultural and industrial
E) municipal metal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why is there no such thing as waste in natural, non-human ecosystems?
A) There is not enough consumption to produce waste.
B) The discarded matter of one organism becomes the resources for another.
C) All organisms reuse their own discarded matter.
D) There is one niche in every ecosystem that consumes all waste from the other members of the ecosystem.
E) Waste does exist in natural ecosystems; we just can't see it.
A) There is not enough consumption to produce waste.
B) The discarded matter of one organism becomes the resources for another.
C) All organisms reuse their own discarded matter.
D) There is one niche in every ecosystem that consumes all waste from the other members of the ecosystem.
E) Waste does exist in natural ecosystems; we just can't see it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In 2012 alone, each American produced about _____ of solid waste per day.
A) half a pound
B) 2.5 pounds
C) 3.2 pounds
D) 4.3 pounds
E) 10 pounds
A) half a pound
B) 2.5 pounds
C) 3.2 pounds
D) 4.3 pounds
E) 10 pounds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The majority of municipal solid waste produced in the United States ends up being __________.
A) recycled
B) composted
C) incinerated
D) landfilled
E) reused
A) recycled
B) composted
C) incinerated
D) landfilled
E) reused

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Everyday garbage or trash (solid waste) produced by individuals or small businesses is known as ____________.
A) municipal solid waste
B) industrial solid waste
C) hazardous waste
D) biodegradable
E) sanitary
A) municipal solid waste
B) industrial solid waste
C) hazardous waste
D) biodegradable
E) sanitary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What is hazardous waste, and why is it considered to be problematic? Discuss two ways the average person can reduce their contribution to the potential problems caused by hazardous waste.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When e-waste is improperly recycled, toxic metals can be released; this can include _________.
A) lead
B) mercury
C) chromium
D) all of the above
E) none of the above
A) lead
B) mercury
C) chromium
D) all of the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Infographic 7.1
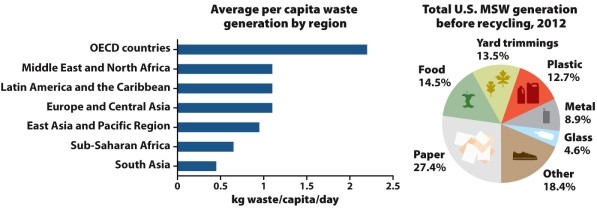
Refer to Infographic 7.1. The pie chart shows components of U.S. municipal solid waste. For each component, describe what can be done to avoid disposal at a sanitary landfill.

Refer to Infographic 7.1. The pie chart shows components of U.S. municipal solid waste. For each component, describe what can be done to avoid disposal at a sanitary landfill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Infographic 7.3.
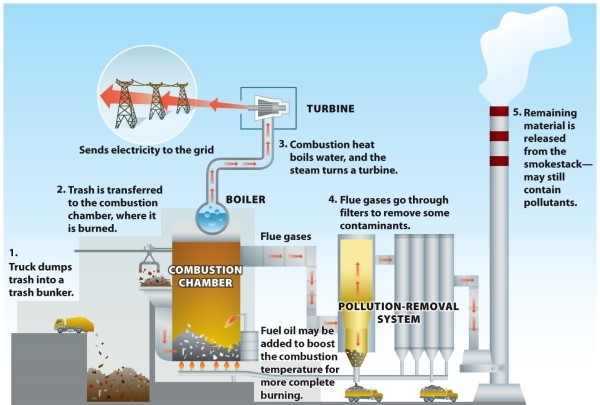
Refer to Infographic 7.3. Describe the pros and cons of a waste-to-energy incinerator.

Refer to Infographic 7.3. Describe the pros and cons of a waste-to-energy incinerator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is e-waste? Explain why recycling e-waste is a better idea than simply burying it in a hazardous waste landfill. What are the concerns with such recycling efforts?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Infographic 7.2.
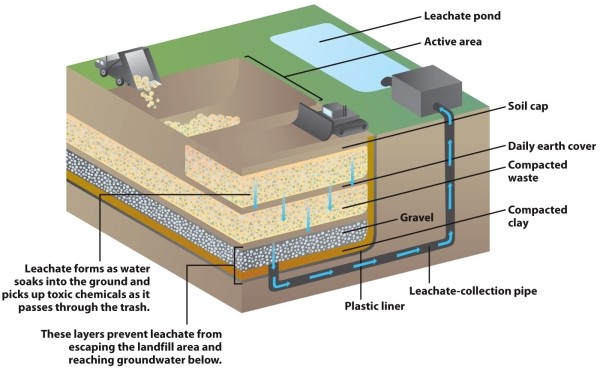
Refer to Infographic 7.2. From the diagram of a sanitary landfill, describe potential environmental issues associated with landfills and what steps are taken to protect the environment.

Refer to Infographic 7.2. From the diagram of a sanitary landfill, describe potential environmental issues associated with landfills and what steps are taken to protect the environment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
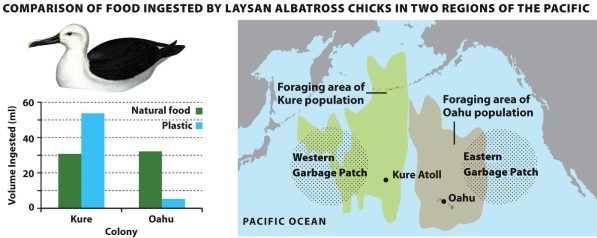
Refer to Infographic 7.4. Compare the foraging areas for the two populations of Laysan albatross chicks relative to the locations of the garbage patches. This comparison suggests that _________ birds likely eat more plastic because ___________.
A) the Oahu; they have a smaller foraging area
B) the Kure; a large portion of the Western Garbage Patch is in their foraging area
C) the Kure; they have a larger foraging area
D) the Oahu; their actual nesting site is closer to the Eastern Garbage Patch
E) neither the Kure nor the Oahu; they can both avoid foraging in the area of the garbage patches

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is the MOST appropriate way to handle hazardous waste?
A) Incinerate it, as burning eliminates all toxic waste.
B) Landfill it, as leachate contains the hazardous waste and prevents it from contaminating ground water.
C) Dump it in the ocean, as the volume of water dilutes the waste, essentially making it nonhazardous.
D) Send it to developing countries in Africa, as they have developed methods of extracting the valuable components of such waste without causing harm to the workers.
E) None of the above is an appropriate way to handle hazardous waste.
A) Incinerate it, as burning eliminates all toxic waste.
B) Landfill it, as leachate contains the hazardous waste and prevents it from contaminating ground water.
C) Dump it in the ocean, as the volume of water dilutes the waste, essentially making it nonhazardous.
D) Send it to developing countries in Africa, as they have developed methods of extracting the valuable components of such waste without causing harm to the workers.
E) None of the above is an appropriate way to handle hazardous waste.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Waste that is not disposed of correctly may end up in the oceans. How can we reduce the amount of waste that ends up in the oceans?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following waste and waste management techniques are best matched up so as to cause the least harm to ecosystems?
A) aluminum cans-incinerating
B) pesticides-dumping in waterways
C) paper waste-open dumps
D) yard waste-composting
E) e-waste-landfilling
A) aluminum cans-incinerating
B) pesticides-dumping in waterways
C) paper waste-open dumps
D) yard waste-composting
E) e-waste-landfilling

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is NOT a component of a newer sanitary landfill?
A) a leachate collection system
B) an incinerator
C) a plastic liner
D) compacted clay and waste
E) daily earth cover
A) a leachate collection system
B) an incinerator
C) a plastic liner
D) compacted clay and waste
E) daily earth cover

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
It has been shown that a bottle deposit, a center for returning and recycling bottles and cans, significantly reduces the amount of plastic or glass bottles and aluminum cans that end up in a landfill. Not all states have a bottle deposit. What would be the benefits of having a bottle deposit in all states?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Tiny bits of plastic gather in specific areas of the world's oceans where strong currents circle around areas with very weak, or even no, currents. These regions are called __________.
A) Bermuda triangles
B) gyres
C) pods
D) waterfills
E) neuston layers
A) Bermuda triangles
B) gyres
C) pods
D) waterfills
E) neuston layers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
__________ is harmful to humans; it is toxic, flammable, corrosive, explosive, and/or radioactive.
A) Biodegradable waste
B) Sanitary landfill waste
C) Municipal waste
D) Hazardous waste
E) Industrial waste
A) Biodegradable waste
B) Sanitary landfill waste
C) Municipal waste
D) Hazardous waste
E) Industrial waste

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Ecological concerns regarding plastics in oceans include which of the following?
A) Sea mammals can get tangled in discarded plastic items, such as fishing nets and six-pack rings.
B) Seabirds eat plastic, mistaking it for food, and may end up choking on the plastic.
C) Plastic absorbs fat-soluble pollutants such as PCBs and DDT; these are toxins known to bioaccumulate in the tissues of marine organisms and biomagnify up food chains.
D) Floating bits of plastic can serve as attachment points for fish eggs, barnacles, and many types of larval and juvenile organisms, and thus they could potentially transport harmful, invasive species to new locales.
E) All of the above are concerns regarding plastics in oceans.
A) Sea mammals can get tangled in discarded plastic items, such as fishing nets and six-pack rings.
B) Seabirds eat plastic, mistaking it for food, and may end up choking on the plastic.
C) Plastic absorbs fat-soluble pollutants such as PCBs and DDT; these are toxins known to bioaccumulate in the tissues of marine organisms and biomagnify up food chains.
D) Floating bits of plastic can serve as attachment points for fish eggs, barnacles, and many types of larval and juvenile organisms, and thus they could potentially transport harmful, invasive species to new locales.
E) All of the above are concerns regarding plastics in oceans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Aquatic ecosystems are considered particularly vulnerable to plastic waste. Describe four ways that plastic waste can affect aquatic species and ecosystems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Match the waste management method to its potential harm to ecosystems.
A) landfills-ground water contamination from leachate
B) incineration-production of methane, a greenhouse gas
C) ocean dumping-toxic ash as waste breaks down under sunlight
D) composting-thermal (heat) pollution in local waterways
E) recycling-release of hazardous waste due to combustion of recyclable material
A) landfills-ground water contamination from leachate
B) incineration-production of methane, a greenhouse gas
C) ocean dumping-toxic ash as waste breaks down under sunlight
D) composting-thermal (heat) pollution in local waterways
E) recycling-release of hazardous waste due to combustion of recyclable material

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What are the potential environmental consequences of disposing of waste via landfilling and incineration? What systems exist in each disposal method to try and prevent these potential problems?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is NOT considered hazardous waste?
A) pesticides
B) automotive oil
C) plastic bottles
D) e-waste
E) compact fluorescent light bulbs
A) pesticides
B) automotive oil
C) plastic bottles
D) e-waste
E) compact fluorescent light bulbs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Hazardous waste is __________.
A) any material that humans deem to be unwanted
B) everyday garbage or trash produced by individuals or small businesses
C) waste that is capable of being broken down by living organisms
D) waste that is incapable of being broken down under normal conditions
E) waste that is toxic, flammable, corrosive, explosive, or radioactive
A) any material that humans deem to be unwanted
B) everyday garbage or trash produced by individuals or small businesses
C) waste that is capable of being broken down by living organisms
D) waste that is incapable of being broken down under normal conditions
E) waste that is toxic, flammable, corrosive, explosive, or radioactive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A city is considering constructing a new industrial park to increase revenue and exports. They also want to make the park sustainable, so they should employ techniques used in __________.
A) industrial ecology
B) ecological downsizes
C) riparian restoration
D) landfill production
E) all of the above
A) industrial ecology
B) ecological downsizes
C) riparian restoration
D) landfill production
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What everyday changes can you make to reduce the amount of waste you produce?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Infographic 7.7.
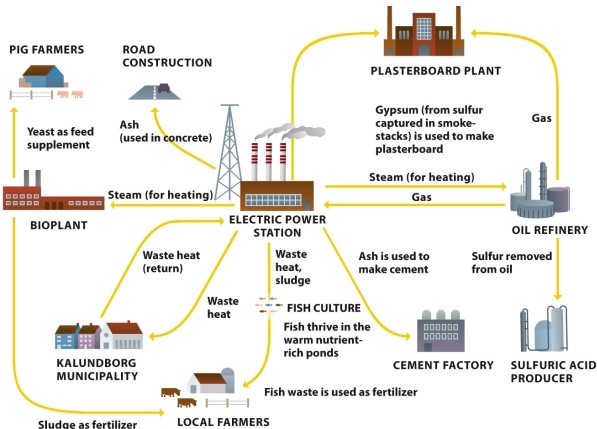
Refer to Infographic 7.7. Use the infographic to describe an eco-industrial park and the advantages of using such innovations.

Refer to Infographic 7.7. Use the infographic to describe an eco-industrial park and the advantages of using such innovations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following materials should NOT be added to a compost pile?
A) pet waste
B) livestock manure
C) paper
D) dead leaves
E) All of the above could be added to a compost pile.
A) pet waste
B) livestock manure
C) paper
D) dead leaves
E) All of the above could be added to a compost pile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Choosing to buy goods with minimal packaging is an example of ____.
A) refusing
B) reducing
C) reusing
D) recycling
E) de-manufacturing
A) refusing
B) reducing
C) reusing
D) recycling
E) de-manufacturing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consumers can decrease the amount of landfilled solid waste by ___________.
A) refusing to purchase products that contribute to solid waste generation
B) purchasing goods with minimal packaging
C) finding ways to reuse materials instead of purchasing new ones
D) actively recycling materials
E) All of the choices listed above will decrease the amount of landfilled solid waste.
A) refusing to purchase products that contribute to solid waste generation
B) purchasing goods with minimal packaging
C) finding ways to reuse materials instead of purchasing new ones
D) actively recycling materials
E) All of the choices listed above will decrease the amount of landfilled solid waste.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Infographic 7.8.

Refer to Infographic 7.8. What are the three required steps of recycling? Which step drives the entire process and is therefore most important?

Refer to Infographic 7.8. What are the three required steps of recycling? Which step drives the entire process and is therefore most important?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Disassembling equipment, machinery, and appliances into components which can be salvaged or reused is an example of ___________.
A) refusing
B) reducing
C) negative feedback
D) limited growth
E) de-manufacturing
A) refusing
B) reducing
C) negative feedback
D) limited growth
E) de-manufacturing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Declining to take a plastic bag for a few items purchased at a store is an example of ________.
A) refusing
B) reducing
C) reusing
D) recycling
E) de-manufacturing
A) refusing
B) reducing
C) reusing
D) recycling
E) de-manufacturing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Hazardous waste not only affects humans but also other living organisms in a variety of ecosystems when disposed of improperly. Explain how hazardous waste can affect different organisms and why it is important to reduce human use of these products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Composting kitchen and yard waste is an example of ____________.
A) refusing
B) reducing
C) reusing
D) recycling
E) de-manufacturing
A) refusing
B) reducing
C) reusing
D) recycling
E) de-manufacturing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Many states in the United States have "take back laws" which require manufacturers to take back some of their products (such as computers) after the consumer has finished with it. How does this encourage companies to rethink their product design?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Infographic 7.8.
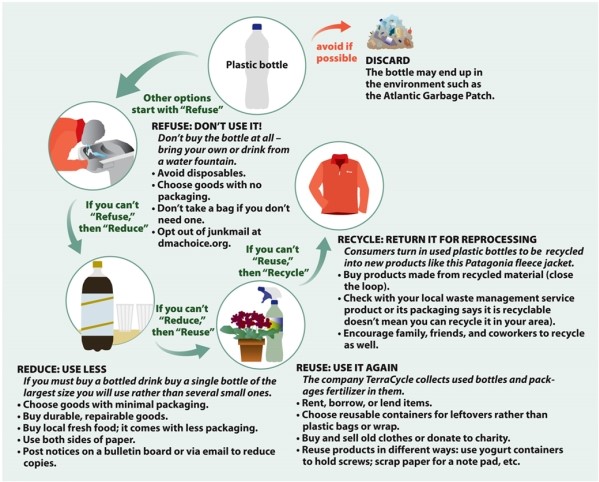
Refer to Infographic 7.8. What options do consumers have for disposing of their waste, and which options are the most environmentally friendly? Refer to the infographic to support your answer.

Refer to Infographic 7.8. What options do consumers have for disposing of their waste, and which options are the most environmentally friendly? Refer to the infographic to support your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
_______ is the process of allowing waste to biologically decompose in the presence of oxygen and water.
A) Bioaccumulation
B) Composting
C) Recycling
D) Eutrophication
E) Hypoxia
A) Bioaccumulation
B) Composting
C) Recycling
D) Eutrophication
E) Hypoxia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A soup company wants to reduce the waste associated with its soup packaging. Which option among the ones listed below would help it to accomplish this goal?
A) Make the soup out of organically grown vegetables.
B) Encourage consumers to burn the soup cans as a source of heat.
C) Package the soup in reusable glass containers.
D) Encourage the location of landfills in communities near the factory so that the surplus soup ingredients and packaging materials can be landfilled locally.
E) Package the soup in smaller cans.
A) Make the soup out of organically grown vegetables.
B) Encourage consumers to burn the soup cans as a source of heat.
C) Package the soup in reusable glass containers.
D) Encourage the location of landfills in communities near the factory so that the surplus soup ingredients and packaging materials can be landfilled locally.
E) Package the soup in smaller cans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
At the grocery store, you are faced with a dilemma. Which container of milk is the most eco-friendly (plastic, paperboard, or glass)? Discuss impacts and trade-offs for each type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is NOT a way to personally reduce your solid waste production?
A) filling a canteen instead of using plastic water bottles
B) buying goods with minimal packaging
C) composting kitchen and yard wastes
D) buying organic foods from developing countries
E) reusing plastic shopping bags for household chores
A) filling a canteen instead of using plastic water bottles
B) buying goods with minimal packaging
C) composting kitchen and yard wastes
D) buying organic foods from developing countries
E) reusing plastic shopping bags for household chores

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Often, humans use hazardous materials without even knowing that the products they are using are harmful. What are some products that qualify as household hazardous waste? What efforts do you think should be made to make people more aware of the products they are using and how they should be properly disposed of?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The four R's to help an individual limit waste production are _______________.
A) reclaim, rename, retake, and recycle
B) recycle, recycle, recycle, and recycle
C) ratify, rectify, remedy, and reframe
D) refuse, reduce, reuse, and recycle
E) revamp, retrofit, reduce, and regulation
A) reclaim, rename, retake, and recycle
B) recycle, recycle, recycle, and recycle
C) ratify, rectify, remedy, and reframe
D) refuse, reduce, reuse, and recycle
E) revamp, retrofit, reduce, and regulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
_________ require(s) manufacturers to take back some of their products after consumers are finished with them.
A) Cradle-to-cradle laws
B) Take back laws
C) De-manufacturing
D) Reuse laws
E) Reduction laws
A) Cradle-to-cradle laws
B) Take back laws
C) De-manufacturing
D) Reuse laws
E) Reduction laws

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 61 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



