Deck 9: Population Ecology- the Wolf Watchers: Endangered Gray Wolves Return to the American West
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Population Ecology- the Wolf Watchers: Endangered Gray Wolves Return to the American West
1
____________ population growth produces an S curve when plotted over time.
A) Exponential
B) Biotic
C) Potential
D) Logistic
E) Resistance
A) Exponential
B) Biotic
C) Potential
D) Logistic
E) Resistance
Logistic
2
Individuals of a population that are spread out irregularly over their environment with no discernable pattern are referred to as living in a _____________ distribution.
A) random
B) clumped
C) uniform
D) irregular
E) none of the above
A) random
B) clumped
C) uniform
D) irregular
E) none of the above
random
3
The biotic potential of a population occurs when _____________.
A) the birth rate equals 100
B) the death rate equals 0
C) there are no environmental limits to survival or reproduction
D) choices A and B occur together
E) None of the above are correct.
A) the birth rate equals 100
B) the death rate equals 0
C) there are no environmental limits to survival or reproduction
D) choices A and B occur together
E) None of the above are correct.
there are no environmental limits to survival or reproduction
4
Which of the following are characteristics of a population?
A) all the same species
B) interaction between members
C) interbreeding
D) live in the same geographic area
E) all of the above
A) all the same species
B) interaction between members
C) interbreeding
D) live in the same geographic area
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Predators, competitors, and diseases are all examples of _____________.
A) limiting factors
B) density-independent factors
C) resistance factors
D) logistic factors
E) population growth factors
A) limiting factors
B) density-independent factors
C) resistance factors
D) logistic factors
E) population growth factors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Population density is best defined as _____________.
A) the location and spacing of individuals with their range
B) the number of individuals per unit area
C) individuals found in groups or patches with a habitat
D) individuals spread out irregularly over an environment and with no discernable pattern
E) none of the above
A) the location and spacing of individuals with their range
B) the number of individuals per unit area
C) individuals found in groups or patches with a habitat
D) individuals spread out irregularly over an environment and with no discernable pattern
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The term that describes a population growing at its biotic potential is ________________.
A) exponential growth
B) logistic growth
C) carrying capacity
D) birth rate < death rate
E) birth rate = death rate
A) exponential growth
B) logistic growth
C) carrying capacity
D) birth rate < death rate
E) birth rate = death rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following terms best describes the spacing density of humans in relation to the biosphere?
A) clumped distribution
B) random distribution
C) uniform distribution
D) r-adapted
E) none of the above
A) clumped distribution
B) random distribution
C) uniform distribution
D) r-adapted
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Why is it ultimately better for a population to have some resistance factors (i.e., factors that reduce a population's size)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Why might a minimum viable population not be an ecologically effective population?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A population at low density is more likely to _____________.
A) undergo high intraspecific competition
B) lose genetic variability
C) be randomly distributed
D) show rapid rates of disease spread
E) adapt to environmental changes
A) undergo high intraspecific competition
B) lose genetic variability
C) be randomly distributed
D) show rapid rates of disease spread
E) adapt to environmental changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is unlikely to be a factor in determining the minimum viable population for a specific population?
A) fire frequency
B) mating rituals
C) flocking
D) schooling behavior
E) foraging
A) fire frequency
B) mating rituals
C) flocking
D) schooling behavior
E) foraging

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Subtracting the death rate from the birth rate gives the _____________.
A) biotic potential
B) carrying capacity
C) logistic growth
D) population growth rate
E) exponential growth
A) biotic potential
B) carrying capacity
C) logistic growth
D) population growth rate
E) exponential growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Germany currently has a negative growth rate for people. Which of the following statements is true about this population?
A) birth rate > death rate
B) death rate > birth rate
C) birth rate = death rate
D) Choices A and C could be true.
E) None of the above is true.
A) birth rate > death rate
B) death rate > birth rate
C) birth rate = death rate
D) Choices A and C could be true.
E) None of the above is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Bighorn sheep were introduced to an island in the Gulf of California in 2010. Originally, 75 bighorns were introduced. When a census was taken in 2011, there were 100 bighorns found. What is the growth rate of the bighorns on the island?
A) 33%
B) 3%
C) 25%
D) 4%
E) 10%
A) 33%
B) 3%
C) 25%
D) 4%
E) 10%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which is the rarest form of population distribution naturally found in nature?
A) clumped distribution
B) uniform distribution
C) random distribution
D) irregular distribution
E) All types of distribution occur about equally.
A) clumped distribution
B) uniform distribution
C) random distribution
D) irregular distribution
E) All types of distribution occur about equally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is one negative effect of a low-density population?
A) competition for resources
B) quick spreading of disease
C) inbreeding
D) increased fighting
E) none of the above
A) competition for resources
B) quick spreading of disease
C) inbreeding
D) increased fighting
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The minimum viable population is _____________.
A) the smallest number of individuals that allows the population to survive long term
B) the smallest number of populations required to make up an ecosystem
C) the same number of individuals for each population
D) the smallest area required for a mating ritual
E) the smallest flock size that would protect against predators
A) the smallest number of individuals that allows the population to survive long term
B) the smallest number of populations required to make up an ecosystem
C) the same number of individuals for each population
D) the smallest area required for a mating ritual
E) the smallest flock size that would protect against predators

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following influences population size?
A) access to food
B) presence of predators
C) sufficient habitat
D) presence of pathogens
E) all of the above
A) access to food
B) presence of predators
C) sufficient habitat
D) presence of pathogens
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Why would a clumped distribution be an advantage for a bee-pollinated plant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which species' offspring are more likely to survive?
A) r-selected species
B) K-selected species
C) Both are likely to survive.
D) Neither is likely to survive.
A) r-selected species
B) K-selected species
C) Both are likely to survive.
D) Neither is likely to survive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Human populations have exceeded the natural carrying capacity of the Earth. Pick the factor(s) that allows us to increase the carrying capacity for humanity.
A) fossil fuel-based agriculture
B) advancements in healthcare
C) habitat destruction
D) biotechnology
E) all of the above
A) fossil fuel-based agriculture
B) advancements in healthcare
C) habitat destruction
D) biotechnology
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Lions in a savanna will increase in population as the total population of their prey species in the ecosystem increases. The number of lions present in the ecosystem is _____________.
A) a density-independent factor
B) a reproductive strategy
C) a density-dependent factor
D) the biotic potential
E) at carrying capacity
A) a density-independent factor
B) a reproductive strategy
C) a density-dependent factor
D) the biotic potential
E) at carrying capacity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of r-selected species?
A) long life
B) early maturity
C) rapid growth of an individual
D) many, small offspring
E) niche generalists
A) long life
B) early maturity
C) rapid growth of an individual
D) many, small offspring
E) niche generalists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Deer mice have a high biotic potential. Therefore, they have a _____________.
A) high birth rate and high death rate
B) high birth rate and low death rate
C) low birth rate and high death rate
D) low birth rate and low death rate
E) None of the above is correct.
A) high birth rate and high death rate
B) high birth rate and low death rate
C) low birth rate and high death rate
D) low birth rate and low death rate
E) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The number-one reason for the endangered status of many species is _____________.
A) disease
B) habitat destruction
C) storms and floods
D) volcanic activity
E) None of the above is correct.
A) disease
B) habitat destruction
C) storms and floods
D) volcanic activity
E) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All populations eventually reach a maximum number as they experience resistance factors. What is the name of the term describing this maximum size?
A) biotic potential
B) carrying capacity
C) growth rate
D) population density
E) population distribution
A) biotic potential
B) carrying capacity
C) growth rate
D) population density
E) population distribution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is a density-independent factor?
A) fire
B) avalanche
C) tornado
D) All of the above are density-independent factors.
E) All of the above are density-dependent factors.
A) fire
B) avalanche
C) tornado
D) All of the above are density-independent factors.
E) All of the above are density-dependent factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
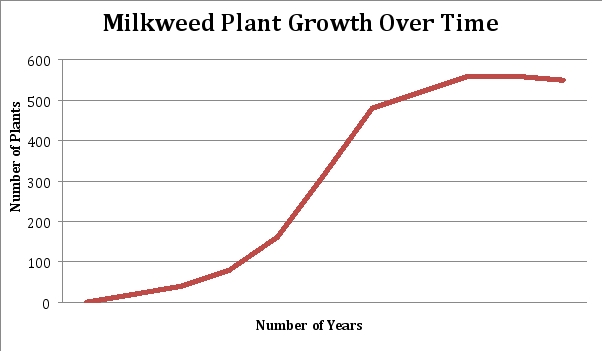
A farm field becomes abandoned and milkweed plants grow up in numbers over time. Based on the shape of the graph below, what kind of growth is this population experiencing? Where is the population in its growth, and what does this mean?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What are some biological characteristics of a species that determines their life-history strategy?
A) maturity rate
B) life span
C) level of fecundity
D) all the above
E) none of the above
A) maturity rate
B) life span
C) level of fecundity
D) all the above
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
________ population(s) is(are) more susceptible to the effects of predation.
A) A small
B) A large
C) Neither small nor large
D) Both small and large
E) A minimum viable
A) A small
B) A large
C) Neither small nor large
D) Both small and large
E) A minimum viable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Bacteria that can cause tooth decay undergo boom-and-bust cycles based on the availability of sugars in the mouth for growth. Which of the following is(are) a resistance factor(s) affecting the sugar's carrying capacity?
A) low-sugar food choices
B) brushing teeth
C) flossing teeth
D) dental care
E) all of the above
A) low-sugar food choices
B) brushing teeth
C) flossing teeth
D) dental care
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Early in the colonization of a new habitat, a population will show _____________, shifting to _____________ as the density of the population increases.
A) resistance; biotic potential
B) exponential growth; logistic growth
C) logistic growth; exponential growth
D) biotic potential; overshoot
E) None of the above is correct.
A) resistance; biotic potential
B) exponential growth; logistic growth
C) logistic growth; exponential growth
D) biotic potential; overshoot
E) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A predator is an example of a(n) _____________.
A) density-dependent factor
B) density-independent factor
C) commensalism
D) mutualism
E) herbivore
A) density-dependent factor
B) density-independent factor
C) commensalism
D) mutualism
E) herbivore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which species' population size is closer to its carrying capacity at any given time?
A) r-selected species
B) K-selected species
C) Both r-selected species and K-selected species would be able to survive
D) Neither r-selected species and K-selected species would survive
A) r-selected species
B) K-selected species
C) Both r-selected species and K-selected species would be able to survive
D) Neither r-selected species and K-selected species would survive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Several decades ago, around 24 rabbits were introduced into the wild of Australia, a country with no native rabbit population, mild winters, and large rabbit-friendly food supplies. Where do you think the rabbit population is today, and was it a big deal that only 24 rabbits were released?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What would happen to a large moose population if wolves were removed from the ecosystem? Explain your answer in terms of density-dependent or density-independent factors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which species would be better suited to survive an unexpected environmental change?
A) r-selected species
B) K-selected species
C) Both would be able to survive.
D) Neither would survive.
A) r-selected species
B) K-selected species
C) Both would be able to survive.
D) Neither would survive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following factors affecting the human population is not density dependent?
A) starvation
B) aggressive behavior
C) disease
D) forest fires
E) All of the factors listed above are density dependent.
A) starvation
B) aggressive behavior
C) disease
D) forest fires
E) All of the factors listed above are density dependent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Why is weather considered to be a density-independent factor?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How might the fact that a threatened prairie plant you are in charge of managing is an r-selected species influence the way you manage the population?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
During a typical predator-prey population cycle, the increase in the predator population is normally seen _____________ an increase in the prey population.
A) after
B) before
C) at the same time as
D) as not correlated with
E) as randomly changing with
A) after
B) before
C) at the same time as
D) as not correlated with
E) as randomly changing with

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When a wolf population goes from high to low as a result of a decrease in moose population, both the moose and wolves experience _____________.
A) boom-and-bust cycles
B) overshoot-and-crash cycles
C) natural population cycles
D) up-and-down cycles
E) None of the above is correct.
A) boom-and-bust cycles
B) overshoot-and-crash cycles
C) natural population cycles
D) up-and-down cycles
E) None of the above is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Habitat destruction, the number-one reason that species become endangered today, likely acts as which kind of regulator?
A) top-down regulation
B) bottom-up regulation
C) global warming
D) boom-and-bust regulation
E) keystone species pressure
A) top-down regulation
B) bottom-up regulation
C) global warming
D) boom-and-bust regulation
E) keystone species pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Fire can be an effective bottom-up regulator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Why is it difficult to determine whether a population's size is more affected by top-down or bottom-up regulation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Numerous towns and cities in the United States have a deer population problem due to the removal of predators. How would you explain that top-down regulation would help with the overpopulation problem? In addition, are there any bottom-up regulation strategies you would suggest to the townspeople?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Availability of water, food, and sunlight are all _________ regulators.
A) biotic
B) exponential
C) logarithmic
D) bottom-up
E) top-down
A) biotic
B) exponential
C) logarithmic
D) bottom-up
E) top-down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
How does maintaining the top-down regulation by wolves help in providing for diverse fish and amphibian communities in Yellowstone?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Fluctuations in populations that produce a very large population followed by a crash that lowers the population size drastically and is then repeated are called _____________.
A) exponential growth
B) log growth
C) boom-and-bust cycles
D) extirpation cycles
E) carrying capacity
A) exponential growth
B) log growth
C) boom-and-bust cycles
D) extirpation cycles
E) carrying capacity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which regulation is more likely to promote species diversity in the ecosystem?
A) top-down regulation
B) bottom-up regulation
C) global warming
D) boom-and-bust regulation
E) keystone species pressure
A) top-down regulation
B) bottom-up regulation
C) global warming
D) boom-and-bust regulation
E) keystone species pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
With global warming having increasing effects on the environment, which type of species (r or K) would you think would be better suited to survive such a global disturbance, and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If a population size is determined by food availability and not predation pressures, it is likely under which regulation type?
A) top-down regulation
B) bottom-up regulation
C) global warming
D) boom-and-bust regulation
E) keystone species pressure
A) top-down regulation
B) bottom-up regulation
C) global warming
D) boom-and-bust regulation
E) keystone species pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is an example of top-down regulation?
A) availability of sunlight
B) control of a prey population by a predator
C) large amounts of food
D) drought killing young willow trees
E) none of the above
A) availability of sunlight
B) control of a prey population by a predator
C) large amounts of food
D) drought killing young willow trees
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Draw a graph of population size over time for wolves and elk in Yellowstone National Park. (Hint: think about the predator-prey relationship between the two species.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The current interglacial period (global warming) has allowed humanity to expand in large numbers due to the increased capacity to grow food. Which characteristics of K-selected species will work against humanity if we have a sudden onset of the next ice age?
A) adaptation to stable environments
B) niche specialists
C) slower growth of individuals
D) late maturity
E) all of the above
A) adaptation to stable environments
B) niche specialists
C) slower growth of individuals
D) late maturity
E) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 56 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



