Deck 27: The Reproductive System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/131
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 27: The Reproductive System
1
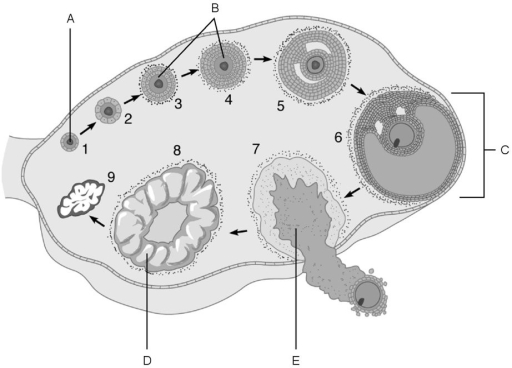 Figure 27.3
Figure 27.3Using Figure 27.3, match the following:
A) E
B) A
C) C
D) D
E) B
Vesicular (Graafian)follicle.
C
2
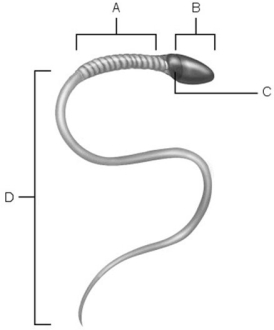 Figure 27.2
Figure 27.2Using Figure 27.2, match the following:
A) C
B) B
C) A
D) D
Area of compacted DNA.
A
3
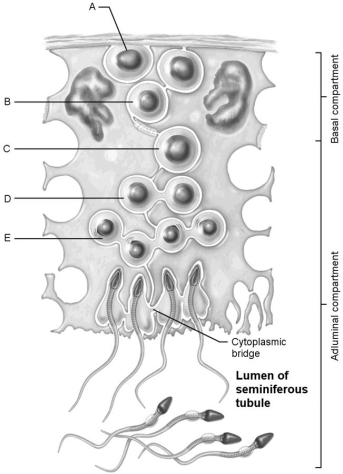
Figure 27.1
Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
A) A
B) C
C) D
D) E
E) B
First cells with n number of chromosomes.
C
4
 Figure 27.3
Figure 27.3Using Figure 27.3, match the following:
A) E
B) A
C) C
D) D
E) B
Primary follicles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
 Figure 27.3
Figure 27.3Using Figure 27.3, match the following:
A) E
B) A
C) C
D) D
E) B
Corpus luteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 Figure 27.2
Figure 27.2Using Figure 27.2, match the following:
A) C
B) B
C) A
D) D
Flagellum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7

Figure 27.1
Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
A) A
B) C
C) D
D) E
E) B
Early spermatids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Match the following:
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
Produces cells for growth and tissue repair.
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
Produces cells for growth and tissue repair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

Figure 27.1
Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
A) A
B) C
C) D
D) E
E) B
Type B spermatogonia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
 Figure 27.3
Figure 27.3Using Figure 27.3, match the following:
A) E
B) A
C) C
D) D
E) B
Primordial follicle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
 Figure 27.2
Figure 27.2Using Figure 27.2, match the following:
A) C
B) B
C) A
D) D
Location of nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
 Figure 27.2
Figure 27.2Using Figure 27.2, match the following:
A) C
B) B
C) A
D) D
Midpiece.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
 Figure 27.3
Figure 27.3Using Figure 27.3, match the following:
A) E
B) A
C) C
D) D
E) B
Mature follicle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
 Figure 27.3
Figure 27.3Using Figure 27.3, match the following:
A) E
B) A
C) C
D) D
E) B
The stage called ovulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Match the following:
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
Produces haploid cells.
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
Produces haploid cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Match the following:
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
One division consisting of prophase,metaphase,anaphase,and telophase.
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
One division consisting of prophase,metaphase,anaphase,and telophase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
 Figure 27.2
Figure 27.2Using Figure 27.2, match the following:
A) C
B) B
C) A
D) D
Location of mitochondria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18

Figure 27.1
Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
A) A
B) C
C) D
D) E
E) B
Stem cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
 Figure 27.2
Figure 27.2Using Figure 27.2, match the following:
A) C
B) B
C) A
D) D
Acrosome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

Figure 27.1
Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
A) A
B) C
C) D
D) E
E) B
Primary spermatocyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Match the following:
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
Forms tetrads.
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
Forms tetrads.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Match the following:
A) Gonorrhea
B) Syphilis
C) Chlamydia
D) Genital warts
E) Genital herpes
Organism responsible for up to half of the diagnosed cases of pelvic inflammatory disease.
A) Gonorrhea
B) Syphilis
C) Chlamydia
D) Genital warts
E) Genital herpes
Organism responsible for up to half of the diagnosed cases of pelvic inflammatory disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The prostate atrophies as a man ages,and it usually causes no health problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Match the following:
A) Gonorrhea
B) Syphilis
C) Chlamydia
D) Genital warts
E) Genital herpes
Human herpes virus type 2.
A) Gonorrhea
B) Syphilis
C) Chlamydia
D) Genital warts
E) Genital herpes
Human herpes virus type 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Match the following:
A) Gonorrhea
B) Syphilis
C) Chlamydia
D) Genital warts
E) Genital herpes
Urethritis in males.
A) Gonorrhea
B) Syphilis
C) Chlamydia
D) Genital warts
E) Genital herpes
Urethritis in males.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When a couple is having difficulty conceiving a child,it is necessary to investigate the sperm of the male.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Sexually transmitted infections are the most important cause of reproductive disorders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The adenohypophyseal hormone that triggers ovulation is estrogen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Ovarian follicles contain mature eggs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
It is necessary for the testes to be kept below body temperature for abundant,viable sperm formation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Match the following:
A) Gonorrhea
B) Syphilis
C) Chlamydia
D) Genital warts
E) Genital herpes
Treponema pallidum.
A) Gonorrhea
B) Syphilis
C) Chlamydia
D) Genital warts
E) Genital herpes
Treponema pallidum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The amount of testosterone and sperm produced by the testes is dependent on the influence of FSH alone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Match the following:
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
Occurs in two stages.
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
Occurs in two stages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A human egg or sperm contains 23 pairs of chromosomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The smaller cell produced by oogenesis meiosis I,called the first polar body,is essentially a packet of discarded nuclear material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Match the following:
A) Gonorrhea
B) Syphilis
C) Chlamydia
D) Genital warts
E) Genital herpes
Human papillomavirus.
A) Gonorrhea
B) Syphilis
C) Chlamydia
D) Genital warts
E) Genital herpes
Human papillomavirus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When it is cold,the scrotum is pulled away from the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The Pap smear is a test to detect cancerous changes in cells of the cervix.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The testis is divided into seminiferous tubules which contain the lobules that produce sperm and the ejaculatory duct that allows the sperm to be ejected from the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Match the following:
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
Produces four daughter cells.
A) Meiosis
B) Meiosis
C) Mitosis
D) Mitosis
Produces four daughter cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The corpus luteum secretes progesterone only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The first sign of puberty in females is budding breasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Sperm are ejaculated from the corpora cavernosa of the penis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements is true of metaphase I of meiosis I?
A) Joined homologous pair uniformly line up on the equatorial spindle with chromosome one at the top and chromosome 23 on the bottom.
B) Tetrads align randomly on the spindle equator with all the maternal homologs on one side and all the paternal homologs on the opposite side.
C) Homologous pairs align randomly on the spindle equator with a mix of paternal and maternal homologs destined for each of the daughter cells.
D) The sister chromatids line up randomly on the spindle equator with some maternal and paternal chromatids on both sides of the equator.
A) Joined homologous pair uniformly line up on the equatorial spindle with chromosome one at the top and chromosome 23 on the bottom.
B) Tetrads align randomly on the spindle equator with all the maternal homologs on one side and all the paternal homologs on the opposite side.
C) Homologous pairs align randomly on the spindle equator with a mix of paternal and maternal homologs destined for each of the daughter cells.
D) The sister chromatids line up randomly on the spindle equator with some maternal and paternal chromatids on both sides of the equator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Extremely stressful physical activity in young females can result in excessive bone mass due to large amounts of estrogen production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Ovulation occurs near the end of the ovarian cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Sperm from the male parent determines the sex of the child.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
All of the following things occur during meiosis I with the exception of one thing.Select the statement below that does not occur during meiosis I.
A) A single diploid (2n) cell has become two haploid (n) cells.
B) Portions of maternal chromosomes crossover with equivalent portions of paternal chromosomes.
C) The sister chromatids are separated from each other.
D) The homologous chromosomes are separated from each other.
A) A single diploid (2n) cell has become two haploid (n) cells.
B) Portions of maternal chromosomes crossover with equivalent portions of paternal chromosomes.
C) The sister chromatids are separated from each other.
D) The homologous chromosomes are separated from each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Select the statement which is false.
A) Meiosis II is essential the same process as mitosis except the starting cells are haploid (n).
B) Further genetic variation typically does not occur after meiosis I.
C) Crossing over is a source of genetic variability seen in meiosis while independent assortment is a source of genetic variability seen in mitosis.
D) Meiosis II is essential the same process as mitosis except the genetic material will not replicate before division takes place.
A) Meiosis II is essential the same process as mitosis except the starting cells are haploid (n).
B) Further genetic variation typically does not occur after meiosis I.
C) Crossing over is a source of genetic variability seen in meiosis while independent assortment is a source of genetic variability seen in mitosis.
D) Meiosis II is essential the same process as mitosis except the genetic material will not replicate before division takes place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Select the statement below that is false.
A) Meiosis results in haploid cells while mitosis results in diploid cells.
B) A cell undergoing meiosis results in 4 cells while a cell undergoing mitosis results in two cells.
C) Meiosis occurs only in stem cells while mitosis can occur in any of the body's cells.
D) Meiosis occurs only after the onset of puberty and produces genetically unique cells while mitosis occurs throughout an entire life time and produces genetically identical cells.
A) Meiosis results in haploid cells while mitosis results in diploid cells.
B) A cell undergoing meiosis results in 4 cells while a cell undergoing mitosis results in two cells.
C) Meiosis occurs only in stem cells while mitosis can occur in any of the body's cells.
D) Meiosis occurs only after the onset of puberty and produces genetically unique cells while mitosis occurs throughout an entire life time and produces genetically identical cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The molecule that enhances the ability of testosterone to promote spermatogenesis is inhibin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The testes are innervated by the sympathetic division of the ANS only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The soft mucosal lining of the uterus is the endometrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Select the statement which is true regarding independent assortment.
A) Its effects are significant in meiosis and in mitosis.
B) It only occurs in meiosis II.
C) It is a significant source of genetic variation only during meiosis I.
D) It is a significant source of genetic variation that occurs in meiosis I and meiosis II.
A) Its effects are significant in meiosis and in mitosis.
B) It only occurs in meiosis II.
C) It is a significant source of genetic variation only during meiosis I.
D) It is a significant source of genetic variation that occurs in meiosis I and meiosis II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A scrotal muscle that contracts in response to cold environmental temperature is the cremaster.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The primary function of the testes is to produce testosterone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The zona pellucida is formed as the follicle becomes a secondary follicle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The stage in meiosis where chromosomal exchange takes place is telophase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Female orgasm is required for conception.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The secretions of the bulbourethral glands neutralize traces of acidic urine in the urethra and serve as a lubricant during sexual intercourse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
How do the testes respond to exposure to excessive body warmth?
A) They move away from the pelvic cavity.
B) Excessive warmth is actually beneficial in that it speeds up the maturation of sperm.
C) They move close to the pelvic cavity.
D) Excessive warmth has no effect on the testicles because of their location in the scrotum.
A) They move away from the pelvic cavity.
B) Excessive warmth is actually beneficial in that it speeds up the maturation of sperm.
C) They move close to the pelvic cavity.
D) Excessive warmth has no effect on the testicles because of their location in the scrotum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The ability of sperm cells to move along the ductus deferens is due to ________.
A) peristaltic contractions
B) enzymatic activity
C) hormonal action
D) gravity
A) peristaltic contractions
B) enzymatic activity
C) hormonal action
D) gravity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Human egg and sperm are similar in that ________.
A) about the same number of each is produced per month
B) they have the same degree of motility
C) they are about the same size
D) they have the same number of chromosomes
A) about the same number of each is produced per month
B) they have the same degree of motility
C) they are about the same size
D) they have the same number of chromosomes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The oral contraceptive pill,informally called "the pill" contains an estrogen and progesterone or a synthetic mimic of this hormone.The combination of these two hormones taken in the pill and circulating in the blood work because.
A) The hormones cause the woman's body to mimic the activities of a pregnancy and disrupt the ovarian cycle, preventing ovulation.
B) The hormones create an acid condition in the vagina that acts as a spermicide.
C) The hormones prevent the proliferative or secretory phase of the menstrual cycle and the embryo will have no place to implant.
D) The hormones cause a thickening of the mucus plug at the cervix that prevents sperm from penetrating the womb and reaching the ovulated egg.
A) The hormones cause the woman's body to mimic the activities of a pregnancy and disrupt the ovarian cycle, preventing ovulation.
B) The hormones create an acid condition in the vagina that acts as a spermicide.
C) The hormones prevent the proliferative or secretory phase of the menstrual cycle and the embryo will have no place to implant.
D) The hormones cause a thickening of the mucus plug at the cervix that prevents sperm from penetrating the womb and reaching the ovulated egg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The genetic determinate for male reproductive development is ________.
A) inhibition of estrogen
B) the SRY gene
C) presence of testosterone
D) lack of an X chromosome
A) inhibition of estrogen
B) the SRY gene
C) presence of testosterone
D) lack of an X chromosome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
All but one of the events described below occur during spermiogenesis.Select the event that does not occur during spermiogenesis.
A) The centrioles migrate to the posterior end of the developing sperm to form the microtubules that make up the flagellum.
B) Mitochondrial DNA is packaged into the nucleus to be delivered to the egg during fertilization.
C) Excessive cytoplasm will be shed to reduce unneeded mass of the maturing sperm.
D) Mitochondria form around the proximal end of the flagellum. They will provide the ATP to drive the motion of the flagellum.
A) The centrioles migrate to the posterior end of the developing sperm to form the microtubules that make up the flagellum.
B) Mitochondrial DNA is packaged into the nucleus to be delivered to the egg during fertilization.
C) Excessive cytoplasm will be shed to reduce unneeded mass of the maturing sperm.
D) Mitochondria form around the proximal end of the flagellum. They will provide the ATP to drive the motion of the flagellum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If gametes were diploid like somatic cells,how many chromosomes would the zygote contain?
A) Twice the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to double and normal development could not occur.
B) Half the diploid number with no change in development.
C) Triple the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to triple and normal development would not occur.
D) There is no relationship between gametes and somatic cells.
A) Twice the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to double and normal development could not occur.
B) Half the diploid number with no change in development.
C) Triple the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to triple and normal development would not occur.
D) There is no relationship between gametes and somatic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following glands are responsible for 70% of the synthesis of semen?
A) the prostate
B) the seminal vesicles
C) the pituitary
D) the bulbourethral glands
A) the prostate
B) the seminal vesicles
C) the pituitary
D) the bulbourethral glands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
During spermiogenesis ________.
A) the acrosome migrates towards the posterior end of the spermatid because its hydrolytic enzymes will be needed for digestion of the excessive cytoplasm around the flagella of the developing sperm
B) the acrosome migrates towards the anterior end of the spermatid because its hydrolytic enzymes will be needed for penetration when the sperm contacts the egg during fertilization
C) the acrosome migrates towards the anterior end of the spermatid because its pointy shape helps the sperm to move more efficiently
D) the acrosome migrates towards the posterior end of the spermatid because of its ability to propel the flagella moving the sperm through the female reproductive system towards the egg
A) the acrosome migrates towards the posterior end of the spermatid because its hydrolytic enzymes will be needed for digestion of the excessive cytoplasm around the flagella of the developing sperm
B) the acrosome migrates towards the anterior end of the spermatid because its hydrolytic enzymes will be needed for penetration when the sperm contacts the egg during fertilization
C) the acrosome migrates towards the anterior end of the spermatid because its pointy shape helps the sperm to move more efficiently
D) the acrosome migrates towards the posterior end of the spermatid because of its ability to propel the flagella moving the sperm through the female reproductive system towards the egg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The dartos and cremaster muscles are important to the integrity of the male reproductive system.Which of the following is true about the role they play?
A) They regulate the temperature of the testes.
B) They contract to allow ejaculation.
C) They contract to push sperm along the ductus deferens.
D) They are responsible for penile erection.
A) They regulate the temperature of the testes.
B) They contract to allow ejaculation.
C) They contract to push sperm along the ductus deferens.
D) They are responsible for penile erection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The structures that receive the ovulated oocyte,providing a site for fertilization,are called the ________.
A) infundibula
B) fallopian tubes
C) Graafian follicles
D) fimbriae
A) infundibula
B) fallopian tubes
C) Graafian follicles
D) fimbriae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
All but one of the following statements are true regarding the differences between early and late spermatids.Select the answer below that does not reflect a difference between early and late spermatids.
A) Early spermatids are round and have excessive cytoplasm.
B) Early spermatids have not undergone meiosis and are still diploid.
C) Early spermatids have not undergone spermiogenesis.
D) Early spermatids have not formed a flagella.
A) Early spermatids are round and have excessive cytoplasm.
B) Early spermatids have not undergone meiosis and are still diploid.
C) Early spermatids have not undergone spermiogenesis.
D) Early spermatids have not formed a flagella.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
All but one of the following statements describes the necessity of the blood testis barrier.Select the one statement that does not describe a necessity of the blood testis barrier.
A) Spermatogenesis produces new combinations of genes and chromosomes that results in unique antigens that the immune system may see as foreign.
B) Spermatocytes undergo meiosis only during puberty, well after the immune system has come to recognize "self" from "non-self" cells.
C) Sperm can only be produced at temperatures lower than body temperature. Inflammation in the testis could raise the temperature too high to produce sperm.
D) Foreign antigens produced by the newly formed sperm could initiate an autoimmune response against the developing sperm.
A) Spermatogenesis produces new combinations of genes and chromosomes that results in unique antigens that the immune system may see as foreign.
B) Spermatocytes undergo meiosis only during puberty, well after the immune system has come to recognize "self" from "non-self" cells.
C) Sperm can only be produced at temperatures lower than body temperature. Inflammation in the testis could raise the temperature too high to produce sperm.
D) Foreign antigens produced by the newly formed sperm could initiate an autoimmune response against the developing sperm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Effects of estrogen include ________.
A) growth of the larynx
B) deepening of the voice
C) growth of the breasts at puberty
D) increased oiliness of the skin
A) growth of the larynx
B) deepening of the voice
C) growth of the breasts at puberty
D) increased oiliness of the skin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
All but one of the following statements is true of uterine function.Select the statement that is not true of uterine function.
A) The endometrium has a functional layer that the embryo will implant into.
B) Its rhythmic, reverse peristalsis can propel sperm toward the egg.
C) The narrow portion of the uterus near the cervix is the most typical site of fertilization.
D) The myometrium contracts to expel the fetus during child birth.
A) The endometrium has a functional layer that the embryo will implant into.
B) Its rhythmic, reverse peristalsis can propel sperm toward the egg.
C) The narrow portion of the uterus near the cervix is the most typical site of fertilization.
D) The myometrium contracts to expel the fetus during child birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins?
A) LH
B) GnRH
C) testosterone
D) FSH
A) LH
B) GnRH
C) testosterone
D) FSH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The most important risk for testicular cancer in young males is ________.
A) sexually transmitted infections
B) a diet high in fat
C) smoking
D) failure of the testis to make their normal decent
A) sexually transmitted infections
B) a diet high in fat
C) smoking
D) failure of the testis to make their normal decent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Fertilization generally occurs in the ________.
A) uterus
B) fallopian tubes
C) vagina
D) ovary
A) uterus
B) fallopian tubes
C) vagina
D) ovary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In humans,separation of the cells at the two-cell state following fertilization may lead to the production of twins,which in this case would be ________.
A) genetically identical
B) fraternal
C) dizygotic
D) potentially of different sexes
A) genetically identical
B) fraternal
C) dizygotic
D) potentially of different sexes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
All but one of the following statements is true with regard to the blood testis barrier.Select the one statement that is false.
A) The barrier is made up of astrocytes that surround blood vessels in the testis.
B) The barrier marks the border between the basal compartment and the adluminal compartment.
C) The barrier separates the spermatocytes dividing by meiosis from exposing their unique antigens to the immune system.
D) Sustentocytes form the barrier with tight junctions.
A) The barrier is made up of astrocytes that surround blood vessels in the testis.
B) The barrier marks the border between the basal compartment and the adluminal compartment.
C) The barrier separates the spermatocytes dividing by meiosis from exposing their unique antigens to the immune system.
D) Sustentocytes form the barrier with tight junctions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 131 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



