Deck 8: Mental Health and Illness
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Match between columns
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/25
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Mental Health and Illness
1
Which of the following statements is a measurement of someone's depression level?
A)I drink with friends.
B)I feel depressed.
C)Life is not challenging.
D)I am very self-confidant.
A)I drink with friends.
B)I feel depressed.
C)Life is not challenging.
D)I am very self-confidant.
I am very self-confidant.
1
Match the term to its definition by filling in the letter before the term in the appropriate blank.
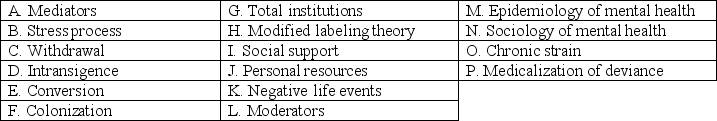 ____ The study of the social arrangements that affect mental illness and its consequences.
____ The study of the social arrangements that affect mental illness and its consequences.
____ Day-to-day role strains that may cause mental health problems over time by the accumulation of small amounts of stress.
____ Places where individuals are isolated from the rest of society.
____ A way of managing life in an institution involving the curtailing of interaction with others.
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by showing that their institution is a desirable place to live.
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by living up to the expectations of the staff and doctors.
____ The study of the distribution of mental health disorders and distress across social groups.
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by rebelling against the staff expectations.
____ Ways in which social problems-including mental health-have come under medical boundaries.
____ Part of the stress process that includes the personal and social resources that affect the direction or strength of the relationship between a stressor and mental health.
____ Part of the stress process referring to any event deemed unwanted or stressful to an individual.
____ Part of the stress process referring to elements of our self-concept that may be beneficial in managing events.
____ Access to friends and family available to help during stressful or difficult times.
____ A model that outlines the relationships among social statuses,stressful experiences (stressors),the resources people bring to deal with problems,and the outcomes (distress)they experience.
____ Part of the stress process referring to resources that act as mechanisms through which stressors relate to outcomes.
____ The consequence of accepting a label as mentally ill which ultimately produces pathological symptoms.
 ____ The study of the social arrangements that affect mental illness and its consequences.
____ The study of the social arrangements that affect mental illness and its consequences.____ Day-to-day role strains that may cause mental health problems over time by the accumulation of small amounts of stress.
____ Places where individuals are isolated from the rest of society.
____ A way of managing life in an institution involving the curtailing of interaction with others.
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by showing that their institution is a desirable place to live.
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by living up to the expectations of the staff and doctors.
____ The study of the distribution of mental health disorders and distress across social groups.
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by rebelling against the staff expectations.
____ Ways in which social problems-including mental health-have come under medical boundaries.
____ Part of the stress process that includes the personal and social resources that affect the direction or strength of the relationship between a stressor and mental health.
____ Part of the stress process referring to any event deemed unwanted or stressful to an individual.
____ Part of the stress process referring to elements of our self-concept that may be beneficial in managing events.
____ Access to friends and family available to help during stressful or difficult times.
____ A model that outlines the relationships among social statuses,stressful experiences (stressors),the resources people bring to deal with problems,and the outcomes (distress)they experience.
____ Part of the stress process referring to resources that act as mechanisms through which stressors relate to outcomes.
____ The consequence of accepting a label as mentally ill which ultimately produces pathological symptoms.
____ The study of the social arrangements that affect mental illness and its consequences.[Answer:N]
____ Day-to-day role strains that may cause mental health problems over time by the accumulation of small amounts of stress.[Answer:O]
____ Places where individuals are isolated from the rest of society.[Answer:G]
____ A way of managing life in an institution involving the curtailing of interaction with others.[Answer:C]
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by showing that their institution is a desirable place to live.[Answer:F]
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by living up to the expectations of the staff and doctors.[Answer:E]
____ The study of the distribution of mental health disorders and distress across social groups.[Answer:M]
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by rebelling against the staff expectations.[Answer:D]
____ Ways in which social problems-including mental health-have come under medical boundaries.[Answer:P]
____ Part of the stress process that includes the personal and social resources that affect the direction or strength of the relationship between a stressor and mental health.[Answer:L]
____ Part of the stress process referring to any event deemed unwanted or stressful to an individual.[Answer:K]
____ Part of the stress process referring to elements of our self-concept that may be beneficial in managing events.[Answer:J]
____ Access to friends and family available to help during stressful or difficult times.[Answer:I]
____ A model that outlines the relationships among social statuses,stressful experiences (stressors),the resources people bring to deal with problems,and the outcomes (distress)they experience.[Answer:B]
____ Part of the stress process referring to resources that act as mechanisms through which stressors relate to outcomes.[Answer:A]
____ The consequence of accepting a label as mentally ill which ultimately produces pathological symptoms.[Answer:H]
____ Day-to-day role strains that may cause mental health problems over time by the accumulation of small amounts of stress.[Answer:O]
____ Places where individuals are isolated from the rest of society.[Answer:G]
____ A way of managing life in an institution involving the curtailing of interaction with others.[Answer:C]
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by showing that their institution is a desirable place to live.[Answer:F]
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by living up to the expectations of the staff and doctors.[Answer:E]
____ The study of the distribution of mental health disorders and distress across social groups.[Answer:M]
____ A way in which patients manage institutionalization by rebelling against the staff expectations.[Answer:D]
____ Ways in which social problems-including mental health-have come under medical boundaries.[Answer:P]
____ Part of the stress process that includes the personal and social resources that affect the direction or strength of the relationship between a stressor and mental health.[Answer:L]
____ Part of the stress process referring to any event deemed unwanted or stressful to an individual.[Answer:K]
____ Part of the stress process referring to elements of our self-concept that may be beneficial in managing events.[Answer:J]
____ Access to friends and family available to help during stressful or difficult times.[Answer:I]
____ A model that outlines the relationships among social statuses,stressful experiences (stressors),the resources people bring to deal with problems,and the outcomes (distress)they experience.[Answer:B]
____ Part of the stress process referring to resources that act as mechanisms through which stressors relate to outcomes.[Answer:A]
____ The consequence of accepting a label as mentally ill which ultimately produces pathological symptoms.[Answer:H]
2
The loss of a job is represented in which component or components of the stress process?
A)stressors
B)outcomes
C)mediators and moderators
D)social and economic characteristics
A)stressors
B)outcomes
C)mediators and moderators
D)social and economic characteristics
stressors
3
Marital status fits into which component of the stress process?
A)stressors
B)outcomes
C)moderators
D)social and economic characteristics
A)stressors
B)outcomes
C)moderators
D)social and economic characteristics
social and economic characteristics
4
Jenna Howard found that those with more social and fiscal capital were able to do what?
A)access mental health services at higher rates
B)successfully "de-label" themselves as mentally ill
C)use less medication in the treatment of mental illness
D)avoid institutionalization
A)access mental health services at higher rates
B)successfully "de-label" themselves as mentally ill
C)use less medication in the treatment of mental illness
D)avoid institutionalization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
__________ suggests that even if mental illness is only partly socially constructed,the consequence of being labeled as such can produce pathological symptoms
A)Modified labeling theory
B)Stigma theory
C)Status characteristics theory
D)Structural theory
A)Modified labeling theory
B)Stigma theory
C)Status characteristics theory
D)Structural theory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Given the research on the epidemiology of mental health,which group is more likely than the others to report problems with drinking? with depression?
A)married people;singles
B)African Americans;Latinos
C)African Americans;whites
D)men;women
A)married people;singles
B)African Americans;Latinos
C)African Americans;whites
D)men;women

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Goffman's research on total institutions showed that many patients in insane asylums generally __________.
A)resist their roles as patients
B)focus on getting better
C)easily conform to their roles
D)always obey those in authority
A)resist their roles as patients
B)focus on getting better
C)easily conform to their roles
D)always obey those in authority

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How can minority status impact mental health ratings?
A)Minorities often have lower economic status,which is associated with more distress.
B)Minorities are less likely to have mental health problems.
C)Minorities have different social constructions of mental health problems than other groups.
D)Minorities are more likely to have genetic mental health problems.
A)Minorities often have lower economic status,which is associated with more distress.
B)Minorities are less likely to have mental health problems.
C)Minorities have different social constructions of mental health problems than other groups.
D)Minorities are more likely to have genetic mental health problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is a social support that may help reduce the effects of negative life events?
A)living in a poor neighborhood
B)having a happy marriage
C)effectively repressing emotions
D)living in a very urbanized environment
A)living in a poor neighborhood
B)having a happy marriage
C)effectively repressing emotions
D)living in a very urbanized environment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Of the following people,who is more likely to be diagnosed with an aggression disorder by a mental health professional than the others?
A)Walter,a white male showing aggressive behavior
B)Kaysha,a white female showing aggressive behavior
C)Thomas,a black male showing aggressive behavior
D)Anna,a black female showing aggressive behavior
A)Walter,a white male showing aggressive behavior
B)Kaysha,a white female showing aggressive behavior
C)Thomas,a black male showing aggressive behavior
D)Anna,a black female showing aggressive behavior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
How do scholars of group processes examine the concept of mental illness?
A)It is viewed as a status characteristic like race or gender.
B)It is viewed as a normal part of group interactions.
C)It is viewed as a major area of group research.
D)It is viewed as a way for individuals in groups to negotiate identity.
A)It is viewed as a status characteristic like race or gender.
B)It is viewed as a normal part of group interactions.
C)It is viewed as a major area of group research.
D)It is viewed as a way for individuals in groups to negotiate identity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What kind of stressors do college students typically report?
A)adjustment problems
B)deaths of loved ones
C)job losses
D)fears of professors
A)adjustment problems
B)deaths of loved ones
C)job losses
D)fears of professors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The stresses associated with living in urban areas come from __________,whereas the stresses associated with rural areas tend to be a result of __________.
A)lack of stimulation;ambient hazards
B)ambient hazards;lack of stimulation
C)urban malaise;rural malaise
D)negative life events;chronic stresses
A)lack of stimulation;ambient hazards
B)ambient hazards;lack of stimulation
C)urban malaise;rural malaise
D)negative life events;chronic stresses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Why was 1656 an important date in the history of mental illness,according to Michel Foucault?
A)It is the year that psychotropic drugs became widely available in Europe.
B)It is the year that the "hospital general" opened,marking the beginning of the great confinement of mentally ill people.
C)It is the first year in which psychoanalysis was used to treat mentally ill people.
D)It is the year that psychotropic drugs were introduced to the New World.
A)It is the year that psychotropic drugs became widely available in Europe.
B)It is the year that the "hospital general" opened,marking the beginning of the great confinement of mentally ill people.
C)It is the first year in which psychoanalysis was used to treat mentally ill people.
D)It is the year that psychotropic drugs were introduced to the New World.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following coping strategies emphasizes patients' attempts to rebel against asylum staff?
A)conversion
B)intransigence
C)withdrawal
D)colonization
A)conversion
B)intransigence
C)withdrawal
D)colonization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which sociologist is most associated with concept of stigma?
A)Erving Goffman
B)Georg Simmel
C)George Herbert Mead
D)Herbert Blumer
A)Erving Goffman
B)Georg Simmel
C)George Herbert Mead
D)Herbert Blumer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which social theorist applied role theory to understanding the sick?
A)Peter Conrad
B)Michel Foucault
C)Talcott Parsons
D)Herbert Blumer
A)Peter Conrad
B)Michel Foucault
C)Talcott Parsons
D)Herbert Blumer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following would be considered a total institution?
A)a college
B)a police station
C)a prison
D)a family household
A)a college
B)a police station
C)a prison
D)a family household

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Higher socioeconomic status is associated with __________ of mental disorder.
A)a lower incidence
B)a higher incidence
C)neither a lower nor a higher incidence
D)the absence
A)a lower incidence
B)a higher incidence
C)neither a lower nor a higher incidence
D)the absence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following forces are associated with putting aspects of social life,including mental illness,under the boundaries of medical professionals?
A)the power and authority of medical professionals
B)the seeking out psychotropic drugs by patients
C)the weakening of medical unions
D)the end of public mental institutions
A)the power and authority of medical professionals
B)the seeking out psychotropic drugs by patients
C)the weakening of medical unions
D)the end of public mental institutions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Match between columns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Studies have found that discrimination of any kind __________ levels of mental illness.
A)increases
B)decreases
C)fails to impact
D)eliminates
A)increases
B)decreases
C)fails to impact
D)eliminates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Read the vignette and answer the questions that follow.
Trudy was very excited about her first year of college.However,she was very nervous on the first day of class.Although she liked the class,she just could not find herself responding to questions and discussion in class.Initially,she joined a couple of clubs but never showed up to any of the meetings.She had planned to focus her time on studying but started to feel tired all of the time,though her sleep was not very restful.Her grades started slipping and she decided to go to the college health clinic to see what was wrong with her.
Using the stress process paradigm,what is the likely source of Trudy's malady?
A)a life event
B)chronic strains
C)mediators and moderators
D)social and economic characteristics
Trudy was very excited about her first year of college.However,she was very nervous on the first day of class.Although she liked the class,she just could not find herself responding to questions and discussion in class.Initially,she joined a couple of clubs but never showed up to any of the meetings.She had planned to focus her time on studying but started to feel tired all of the time,though her sleep was not very restful.Her grades started slipping and she decided to go to the college health clinic to see what was wrong with her.
Using the stress process paradigm,what is the likely source of Trudy's malady?
A)a life event
B)chronic strains
C)mediators and moderators
D)social and economic characteristics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Read the vignette and answer the questions that follow.
Trudy was very excited about her first year of college.However,she was very nervous on the first day of class.Although she liked the class,she just could not find herself responding to questions and discussion in class.Initially,she joined a couple of clubs but never showed up to any of the meetings.She had planned to focus her time on studying but started to feel tired all of the time,though her sleep was not very restful.Her grades started slipping and she decided to go to the college health clinic to see what was wrong with her.
Given the research and theory on the medicalization of deviance,how will the clinic likely treat Trudy's malady in today's world?
A)by providing reading materials to cope with freshman life
B)by trying some form of medication to treat depression
C)by giving her some ideas for ways to mediate her problems
D)by giving her some ideas for ways to moderate her problems
Trudy was very excited about her first year of college.However,she was very nervous on the first day of class.Although she liked the class,she just could not find herself responding to questions and discussion in class.Initially,she joined a couple of clubs but never showed up to any of the meetings.She had planned to focus her time on studying but started to feel tired all of the time,though her sleep was not very restful.Her grades started slipping and she decided to go to the college health clinic to see what was wrong with her.
Given the research and theory on the medicalization of deviance,how will the clinic likely treat Trudy's malady in today's world?
A)by providing reading materials to cope with freshman life
B)by trying some form of medication to treat depression
C)by giving her some ideas for ways to mediate her problems
D)by giving her some ideas for ways to moderate her problems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 25 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



