Deck 16: Money, banks, and the Federal Reserve System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/139
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Money, banks, and the Federal Reserve System
1
The policy aimed at managing interest rates to pursue macroeconomic objectives is called
A) fiscal policy.
B) interest rate policy.
C) monetary policy.
D) exchange rate policy.
A) fiscal policy.
B) interest rate policy.
C) monetary policy.
D) exchange rate policy.
monetary policy.
2
Inflation targeting is when the Reserve Bank of Australia uses monetary policy with the aim of keeping the inflation rate at an annual average of between 2 per cent and 3 per cent in the medium term.
True
3
According to the Reserve Bank of Australia,inflation targeting refers to monetary policy that aims to
A) achieve a particular annual rate of inflation on average over the business cycle.
B) achieve the same low rate of inflation every year.
C) control the money supply to achieve a target rate of inflation.
D) control the money supply to achieve a target rate of interest that will ensure a low rate of inflation.
A) achieve a particular annual rate of inflation on average over the business cycle.
B) achieve the same low rate of inflation every year.
C) control the money supply to achieve a target rate of inflation.
D) control the money supply to achieve a target rate of interest that will ensure a low rate of inflation.
achieve a particular annual rate of inflation on average over the business cycle.
4
If the interest rate increases,then
A) there will be an upward movement along the money demand curve.
B) there will be a downward movement along the money demand curve.
C) the money demand curve will shift to the right.
D) the money demand curve will shift to the left.
A) there will be an upward movement along the money demand curve.
B) there will be a downward movement along the money demand curve.
C) the money demand curve will shift to the right.
D) the money demand curve will shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
According to the Reserve Bank Act (1959),which of the following is not a goal of monetary policy?
A) Price stability
B) Economic growth
C) Maximising the value of the dollar relative to other currencies
D) Low rate of unemployment
A) Price stability
B) Economic growth
C) Maximising the value of the dollar relative to other currencies
D) Low rate of unemployment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The money demand curve has a
A) negative slope.
B) positive slope.
C) zero slope and is perfectly elastic.
D) positive slope for low levels of money demand and a negative slope for high levels of money demand.
A) negative slope.
B) positive slope.
C) zero slope and is perfectly elastic.
D) positive slope for low levels of money demand and a negative slope for high levels of money demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following are goals of monetary policy?
A) Maximising the value of the dollar relative to other currencies, economic growth, and high employment.
B) Price stability, maximising the value of the dollar relative to other currencies, and high employment.
C) Price stability, economic growth, and high employment.
D) Price stability, economic growth, and maximising the value of the dollar relative to other currencies.
A) Maximising the value of the dollar relative to other currencies, economic growth, and high employment.
B) Price stability, maximising the value of the dollar relative to other currencies, and high employment.
C) Price stability, economic growth, and high employment.
D) Price stability, economic growth, and maximising the value of the dollar relative to other currencies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Rising prices erode the value of money as a ________ and a ________.
A) unit of barter; unit of account
B) store of value; unit of liquidity
C) medium of exchange; store of value
D) store of value; unit of barter
A) unit of barter; unit of account
B) store of value; unit of liquidity
C) medium of exchange; store of value
D) store of value; unit of barter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What economic objectives are the Reserve Bank of Australia required to pursue in its conduct of monetary policy,and what relative importance is placed on these objectives?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The money demand curve is downward sloping because
A) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to financial assets.
B) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from financial assets to money.
C) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to shares.
D) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to bonds.
A) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to financial assets.
B) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from financial assets to money.
C) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to shares.
D) lower interest rates cause households and firms to switch from money to bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Reserve Bank of Australia targets a per annum inflation rate,on average over the business cycle,of between
A) 1 per cent and 2 per cent.
B) 2 per cent and 4 per cent.
C) 3 per cent and 4 per cent.
D) 2 per cent and 3 per cent.
A) 1 per cent and 2 per cent.
B) 2 per cent and 4 per cent.
C) 3 per cent and 4 per cent.
D) 2 per cent and 3 per cent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Give an example of a monetary policy target.Explain which monetary policy target the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)uses and why the RBA uses a policy target.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Board of the Reserve Bank of Australia has stated that it focuses on which of the following as its main goal of monetary policy?
A) Stability of financial markets
B) Low inflation
C) Economic growth
D) High labour force participation rate
A) Stability of financial markets
B) Low inflation
C) Economic growth
D) High labour force participation rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An increase in real GDP
A) increases the buying and selling of goods and services, and increases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
B) increases the buying and selling of goods and services, and decreases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
C) decreases the buying and selling of goods and services, and increases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
D) decreases the buying and selling of goods and services, and decreases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
A) increases the buying and selling of goods and services, and increases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
B) increases the buying and selling of goods and services, and decreases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
C) decreases the buying and selling of goods and services, and increases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.
D) decreases the buying and selling of goods and services, and decreases the demand for money as a medium of exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is inflation targeting?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is the main goal of monetary policy in Australia?
A) Lowering the rate of unemployment
B) Increasing the value of the Australian dollar relative to other currencies
C) Economic growth
D) Price stability
A) Lowering the rate of unemployment
B) Increasing the value of the Australian dollar relative to other currencies
C) Economic growth
D) Price stability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Money demand will increase if the price level ________ or if real GDP ________.
A) increases; decreases
B) decreases; decreases
C) increases; increases
D) decreases; increases
A) increases; decreases
B) decreases; decreases
C) increases; increases
D) decreases; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Maintaining a strong dollar in international currency markets is not one of the monetary policy goals of the Reserve Bank of Australia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The main goal of monetary policy in Australia is full employment of the labour force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The Reserve Bank of Australia's main monetary policy target is
A) the money supply.
B) the inflation rate.
C) real GDP.
D) the unemployment rate.
A) the money supply.
B) the inflation rate.
C) real GDP.
D) the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Open market operations occur when the Reserve Bank of Australia
A) purchases or sells corporate shares in the market to control interest rates.
B) controls the money supply.
C) makes loans to foreign banks.
D) purchases or sells short-dated financial instruments.
A) purchases or sells corporate shares in the market to control interest rates.
B) controls the money supply.
C) makes loans to foreign banks.
D) purchases or sells short-dated financial instruments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The money supply curve would be vertical if
A) banks and the RBA jointly determine the money supply.
B) the RBA is able to completely fix the money supply.
C) banks and households determine the money supply.
D) households and the RBA jointly determine the money supply.
A) banks and the RBA jointly determine the money supply.
B) the RBA is able to completely fix the money supply.
C) banks and households determine the money supply.
D) households and the RBA jointly determine the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following correctly describes what the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)used as monetary targets in the past?
A) The RBA used M3 as its main target after 1993.
B) The RBA focused on base money as a target after the deregulation of the financial system.
C) The RBA increased its reliance on interest rate targets in the early 1990s.
D) After 1996, the RBA focused on monetary targeting.
A) The RBA used M3 as its main target after 1993.
B) The RBA focused on base money as a target after the deregulation of the financial system.
C) The RBA increased its reliance on interest rate targets in the early 1990s.
D) After 1996, the RBA focused on monetary targeting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Accounts held with the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA)which are used by financial institutions to settle payments between each other and with the RBA are called
A) credit accounts.
B) real-time gross settlement accounts.
C) debit accounts.
D) exchange settlement accounts.
A) credit accounts.
B) real-time gross settlement accounts.
C) debit accounts.
D) exchange settlement accounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the 1970s and 1980s,which method of conducting monetary policy did the Reserve Bank of Australia use?
A) Interest rate targeting
B) Inflation targeting
C) Monetary targeting
D) Employment rate targeting
A) Interest rate targeting
B) Inflation targeting
C) Monetary targeting
D) Employment rate targeting

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The Reserve Bank of Australia uses open market operations
A) usually every day.
B) once a month when the Reserve Bank Board meets to discuss monetary policy.
C) only when it wants to increase or decrease the cash rate.
D) only when it is conducting monetary policy.
A) usually every day.
B) once a month when the Reserve Bank Board meets to discuss monetary policy.
C) only when it wants to increase or decrease the cash rate.
D) only when it is conducting monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A decrease in real GDP can
A) increase money demand and decrease the interest rate.
B) increase money demand and increase the interest rate.
C) decrease money demand and decrease the interest rate.
D) decrease money demand and increase the interest rate.
A) increase money demand and decrease the interest rate.
B) increase money demand and increase the interest rate.
C) decrease money demand and decrease the interest rate.
D) decrease money demand and increase the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The overnight cash rate is determined
A) administratively by the Reserve Bank of Australia.
B) by the supply of and demand for cash.
C) directly by household demand for funds.
D) directly by firm demand for funds.
A) administratively by the Reserve Bank of Australia.
B) by the supply of and demand for cash.
C) directly by household demand for funds.
D) directly by firm demand for funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The money market model is concerned with ________ and the loanable funds market model is concerned with ________.
A) short-term real interest rates; long-term nominal interest rates
B) short-term nominal interest rates; long-term nominal interest rates
C) short-term real interest rates; long-term real interest rates
D) short-term nominal interest rates; long-term real interest rates
A) short-term real interest rates; long-term nominal interest rates
B) short-term nominal interest rates; long-term nominal interest rates
C) short-term real interest rates; long-term real interest rates
D) short-term nominal interest rates; long-term real interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An increase in real GDP can
A) increase money demand and decrease the interest rate.
B) increase money demand and increase the interest rate.
C) decrease money demand and decrease the interest rate.
D) decrease money demand and increase the interest rate.
A) increase money demand and decrease the interest rate.
B) increase money demand and increase the interest rate.
C) decrease money demand and decrease the interest rate.
D) decrease money demand and increase the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Increases in the price level
A) increase the opportunity cost of holding money.
B) decrease the opportunity cost of holding money.
C) increase the quantity of money needed for buying and selling.
D) decrease the quantity of money needed for buying and selling.
A) increase the opportunity cost of holding money.
B) decrease the opportunity cost of holding money.
C) increase the quantity of money needed for buying and selling.
D) decrease the quantity of money needed for buying and selling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Figure 16.2 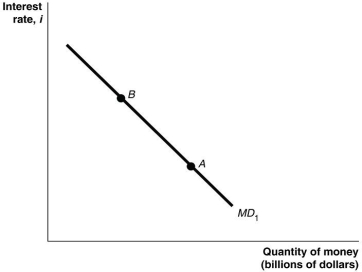
Refer to Figure 16.2.In this figure,a movement from point A to point B would be caused by
A) a decrease in real GDP.
B) an increase in the price level.
C) a decrease in the price level.
D) an increase in the interest rate.

Refer to Figure 16.2.In this figure,a movement from point A to point B would be caused by
A) a decrease in real GDP.
B) an increase in the price level.
C) a decrease in the price level.
D) an increase in the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 16.1 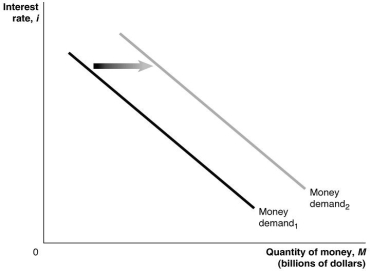
Refer to Figure 16.1.In this figure,the money demand curve would move from Money demand1 to Money demand2 if
A) real GDP decreased.
B) the price level increased.
C) the interest rate increased.
D) the Reserve Bank of Australia sold government securities.

Refer to Figure 16.1.In this figure,the money demand curve would move from Money demand1 to Money demand2 if
A) real GDP decreased.
B) the price level increased.
C) the interest rate increased.
D) the Reserve Bank of Australia sold government securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following does the Reserve Bank of Australia use as its main measure of monetary movements in Australia?
A) Credit
B) The cash rate
C) The money supply
D) The demand for money
A) Credit
B) The cash rate
C) The money supply
D) The demand for money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Reserve Bank of Australia can increase the cash rate by
A) borrowing from the banks using reverse repurchase agreements.
B) purchasing bonds and securities, which increases banks' reserves.
C) lending cash to banks using repurchase agreements.
D) purchasing bonds and securities, which decreases banks' reserves.
A) borrowing from the banks using reverse repurchase agreements.
B) purchasing bonds and securities, which increases banks' reserves.
C) lending cash to banks using repurchase agreements.
D) purchasing bonds and securities, which decreases banks' reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The Reserve Bank of Australia manages the supply of cash on a daily basis to
A) ensure that banks have sufficient cash to meet the demand for funds.
B) sterilise deficits and surpluses of cash in the financial system.
C) ensure that there are no large injections of cash into or withdrawals of cash out of the financial system.
D) ensure that the interest rate changes to create equilibrium in the money market.
A) ensure that banks have sufficient cash to meet the demand for funds.
B) sterilise deficits and surpluses of cash in the financial system.
C) ensure that there are no large injections of cash into or withdrawals of cash out of the financial system.
D) ensure that the interest rate changes to create equilibrium in the money market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Monetary policy targets the
A) long-term real rate of interest.
B) long-term nominal rate of interest.
C) short-term real rate of interest.
D) short-term nominal rate of interest.
A) long-term real rate of interest.
B) long-term nominal rate of interest.
C) short-term real rate of interest.
D) short-term nominal rate of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Under the current operation of monetary policy in Australia,the money supply is
A) perfectly inelastic at the current interest rate.
B) targeted by the use of open market operations.
C) fixed by the Reserve Bank of Australia.
D) perfectly elastic at the current interest rate.
A) perfectly inelastic at the current interest rate.
B) targeted by the use of open market operations.
C) fixed by the Reserve Bank of Australia.
D) perfectly elastic at the current interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If real GDP decreases
A) there will be an upward movement along the money demand curve.
B) there will be a downward movement along the money demand curve.
C) the money demand curve will shift to the right.
D) the money demand curve will shift to the left.
A) there will be an upward movement along the money demand curve.
B) there will be a downward movement along the money demand curve.
C) the money demand curve will shift to the right.
D) the money demand curve will shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The cash rate is the interest rate
A) the Reserve Bank of Australia charges commercial banks.
B) banks charge their largest customers.
C) banks charge each other for overnight loans.
D) on a government bond or security.
A) the Reserve Bank of Australia charges commercial banks.
B) banks charge their largest customers.
C) banks charge each other for overnight loans.
D) on a government bond or security.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The demand for loanable funds is determined by the willingness of ________ to borrow money to engage in new investment projects.
A) the government
B) households
C) banks
D) firms
A) the government
B) households
C) banks
D) firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
An increase in the real interest rate does which of the following?
A) Reduces the demand for loanable funds
B) Reduces saving
C) Reduces consumption spending
D) Increases the demand for loanable funds
A) Reduces the demand for loanable funds
B) Reduces saving
C) Reduces consumption spending
D) Increases the demand for loanable funds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
An increase in the real interest rate results in which of the following?
A) An increase in the demand for loanable funds.
B) A decrease in the demand for loanable funds.
C) An increase in the quantity of loanable funds supplied.
D) Both B and C will occur as a result of an increase in the real interest rate.
A) An increase in the demand for loanable funds.
B) A decrease in the demand for loanable funds.
C) An increase in the quantity of loanable funds supplied.
D) Both B and C will occur as a result of an increase in the real interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The demand for loanable funds has a ________ slope because,the lower the interest rate,the ________ number of investment projects are profitable,and the ________ the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
A) negative; greater; greater
B) negative; greater; lesser
C) negative; lesser; greater
D) positive; lesser; lesser
A) negative; greater; greater
B) negative; greater; lesser
C) negative; lesser; greater
D) positive; lesser; lesser

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A government budget surplus will shift the ________ curve for loanable funds to the ________ and the equilibrium real interest rate will ________.
A) supply; right; fall
B) supply; left; rise
C) demand; right; rise
D) demand; left; fall
A) supply; right; fall
B) supply; left; rise
C) demand; right; rise
D) demand; left; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the model of the market for loanable funds,which of the following will not shift the supply curve for loanable funds?
A) Expectations of high returns on investments.
B) A decrease in taxation on interest earned on savings accounts.
C) A government budget surplus.
D) A government budget deficit.
A) Expectations of high returns on investments.
B) A decrease in taxation on interest earned on savings accounts.
C) A government budget surplus.
D) A government budget deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Using the market for loanable funds,which of the following has the potential to raise the real interest rate?
A) An increase in the demand for loanable funds.
B) An increase in the quantity demanded of loanable funds.
C) An increase in the supply of loanable funds.
D) An increase in the quantity supplied of loanable funds.
A) An increase in the demand for loanable funds.
B) An increase in the quantity demanded of loanable funds.
C) An increase in the supply of loanable funds.
D) An increase in the quantity supplied of loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A government budget deficit will shift the ________ curve for loanable funds to the ________ and the equilibrium real interest rate will ________.
A) supply; right; fall
B) supply; left; rise
C) demand; right; rise
D) demand; left; fall
A) supply; right; fall
B) supply; left; rise
C) demand; right; rise
D) demand; left; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Equilibrium in the loanable funds market determines the
A) nominal interest rate.
B) current interest rate.
C) real interest rate.
D) expected interest rate.
A) nominal interest rate.
B) current interest rate.
C) real interest rate.
D) expected interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The supply of loanable funds has a ________ slope because,the greater the interest rate,the ________ the reward to savings,and the ________ the quantity of loanable funds supplied.
A) positive; lesser; lesser
B) positive; greater; lesser
C) negative; lesser; greater
D) positive; greater; greater
A) positive; lesser; lesser
B) positive; greater; lesser
C) negative; lesser; greater
D) positive; greater; greater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure 16.3 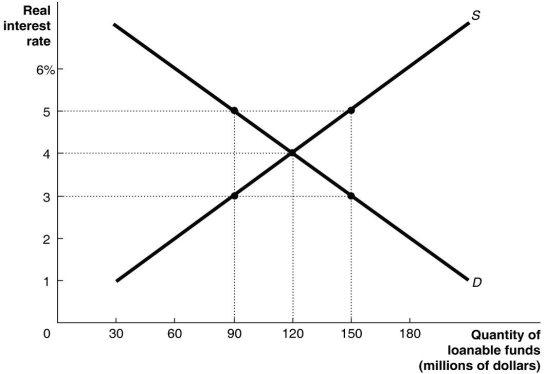
Refer to Figure 16.3.An increase in the supply of loanable funds could result in which of the following combinations of the real interest rate and quantity of loanable funds at a new equilibrium?
A) The real interest rate is 5 per cent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $150 million.
B) The real interest rate is 5 per cent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $90 million.
C) The real interest rate is 3 per cent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $150 million.
D) The real interest rate is 3 per cent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $90 million.

Refer to Figure 16.3.An increase in the supply of loanable funds could result in which of the following combinations of the real interest rate and quantity of loanable funds at a new equilibrium?
A) The real interest rate is 5 per cent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $150 million.
B) The real interest rate is 5 per cent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $90 million.
C) The real interest rate is 3 per cent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $150 million.
D) The real interest rate is 3 per cent, and the quantity of loanable funds is $90 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If firms are anticipating that the profitability of new investments will be lower in the future,then the ________ curve for loanable funds will shift to the ________.
A) supply; right
B) supply; left
C) demand; right
D) demand; left
A) supply; right
B) supply; left
C) demand; right
D) demand; left

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the model of the market for loanable funds,which of the following will not shift the demand curve for loanable funds?
A) Expectations of high returns on investments.
B) The effect of technological change on profitability.
C) Lower interest rates.
D) The expectation of a recession by businesses.
A) Expectations of high returns on investments.
B) The effect of technological change on profitability.
C) Lower interest rates.
D) The expectation of a recession by businesses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An increase in public saving has what impact on the market for loanable funds?
A) The supply of loanable funds increases.
B) The demand for loanable funds increases.
C) The supply of loanable funds decreases.
D) The demand for loanable funds decreases.
A) The supply of loanable funds increases.
B) The demand for loanable funds increases.
C) The supply of loanable funds decreases.
D) The demand for loanable funds decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If technological change increases the profitability of new investment for firms,then the ________ curve for loanable funds will shift to the ________ and the equilibrium real interest rate will ________.
A) supply; right; fall
B) supply; left; rise
C) demand; right; rise
D) demand; left; fall
A) supply; right; fall
B) supply; left; rise
C) demand; right; rise
D) demand; left; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A decrease in the real interest rate will
A) increase consumption and reduce investment.
B) increase saving and investment.
C) decrease investment and government spending.
D) increase consumption and investment.
A) increase consumption and reduce investment.
B) increase saving and investment.
C) decrease investment and government spending.
D) increase consumption and investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If you spend more of your income on consumption goods,which of the following will occur?
A) The production of investment goods will fall.
B) Economic growth will be stimulated.
C) Investments in education will rise.
D) For every dollar you spend on consumption, real GDP will fall by a dollar.
A) The production of investment goods will fall.
B) Economic growth will be stimulated.
C) Investments in education will rise.
D) For every dollar you spend on consumption, real GDP will fall by a dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Figure 16.3 
Refer to Figure 16.3.Beginning at equilibrium,if the government budget deficit rises,which of the following would you expect to see?
A) The quantity of loanable funds demanded by firms will rise above $120 million.
B) The quantity of loanable funds demanded by firms will fall below $120 million.
C) The budget deficit will have no impact on the quantity of loanable funds demanded by firms.
D) The interest rate will fall below 4 per cent.

Refer to Figure 16.3.Beginning at equilibrium,if the government budget deficit rises,which of the following would you expect to see?
A) The quantity of loanable funds demanded by firms will rise above $120 million.
B) The quantity of loanable funds demanded by firms will fall below $120 million.
C) The budget deficit will have no impact on the quantity of loanable funds demanded by firms.
D) The interest rate will fall below 4 per cent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Figure 16.3 
Refer to Figure 16.3.As a result of an increase in the government budget deficit,the ________ for loanable funds will ________,thereby ________ the equilibrium real interest rate and ________ the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds.
A) demand; rise; increasing; decreasing
B) supply; rise; decreasing; increasing
C) demand; fall; decreasing; decreasing
D) supply; fall; increasing; decreasing

Refer to Figure 16.3.As a result of an increase in the government budget deficit,the ________ for loanable funds will ________,thereby ________ the equilibrium real interest rate and ________ the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds.
A) demand; rise; increasing; decreasing
B) supply; rise; decreasing; increasing
C) demand; fall; decreasing; decreasing
D) supply; fall; increasing; decreasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Figure 16.3 
Refer to Figure 16.3.If the current real interest rate is 5 per cent,which of the following is true?
A) The loanable funds market is in equilibrium.
B) There is a surplus of loanable funds in the market.
C) There is a shortage of loanable funds in the market.
D) The quantity of loanable funds being demanded in the market is less than $90 million.

Refer to Figure 16.3.If the current real interest rate is 5 per cent,which of the following is true?
A) The loanable funds market is in equilibrium.
B) There is a surplus of loanable funds in the market.
C) There is a shortage of loanable funds in the market.
D) The quantity of loanable funds being demanded in the market is less than $90 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Rising nominal GDP will increase the demand for money and short-term interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What is the function of exchange settlement accounts?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Explain how a decrease in the tax rate on interest earned on savings would affect savings,investment,the interest rate,and economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The effect of monetary policy on long-term interest rates is usually
A) larger than its effect on short-term interest rates.
B) smaller than its effect on short-term interest rates.
C) immediate, as long-term rates are closely linked to the cash rate.
D) larger than its effect on short-term rates, but the effect occurs with a lag.
A) larger than its effect on short-term interest rates.
B) smaller than its effect on short-term interest rates.
C) immediate, as long-term rates are closely linked to the cash rate.
D) larger than its effect on short-term rates, but the effect occurs with a lag.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
For over a decade,monetary policy in Australia has been carried out mainly by using repurchase agreements rather than the outright purchase of government securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The Reserve Bank of Australia engages in open market operations only when it wants to change interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The Reserve Bank of Australia currently conducts monetary policy by controlling the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Describe how the Reserve Bank of Australia uses open market operations to change short-term and long-term interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Explain why the money demand curve is downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Explain and show graphically how a decrease in household saving affects the equilibrium interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A rise in the rate of interest on financial securities will lead to a movement downward along the money demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Empirical evidence shows that the impact of government budget deficits and surpluses on the equilibrium interest rate is quite large.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Explain why the demand for loanable funds curve has a negative slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
An increase in interest rates will usually,ceteris paribus,
A) increase investment spending.
B) decrease consumption spending.
C) increase government spending.
D) increase net exports.
A) increase investment spending.
B) decrease consumption spending.
C) increase government spending.
D) increase net exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Assume that the government reduces taxation on earnings from dividends on shares.Use the model of the loanable funds market to describe what will happen to savings,investment,economic growth,the real interest rate,and the quantity of loanable funds exchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
How does the Reserve Bank of Australia affect the supply of cash?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Explain how the Reserve Bank of Australia maintains its targeted cash rate on a daily basis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Economist Steve Landsburg has pointed out that Ebenezer Scrooge's change in behaviour from miser to spender might actually be detrimental to the economy because
A) Scrooge's miserly saving helped contribute to the production of investment goods rather than consumption goods.
B) Scrooge was happiest when he was saving money, and happiness is the key to economic growth.
C) saving has to be greater than consumption for the economy to grow.
D) Scrooge's consumption habits were more detrimental to the environment than were his earlier saving habits.
A) Scrooge's miserly saving helped contribute to the production of investment goods rather than consumption goods.
B) Scrooge was happiest when he was saving money, and happiness is the key to economic growth.
C) saving has to be greater than consumption for the economy to grow.
D) Scrooge's consumption habits were more detrimental to the environment than were his earlier saving habits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Government budget surpluses and deficits affect the supply of loanable funds,and therefore affect interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Explain and show graphically how a decrease in government spending,ceteris paribus,affects the equilibrium interest rate and equilibrium quantity of loanable funds in the market for loanable funds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



