Deck 9: Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/351
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Firms in Perfectly Competitive Markets
1
Which of the following is true for a firm with a downward-sloping demand curve for its product?
A) Price, average revenue and marginal revenue are all equal.
B) Price, average revenue and marginal revenue are all different.
C) Price equals average revenue, but is greater than marginal revenue.
D) Price equals average revenue, but is less than marginal revenue.
A) Price, average revenue and marginal revenue are all equal.
B) Price, average revenue and marginal revenue are all different.
C) Price equals average revenue, but is greater than marginal revenue.
D) Price equals average revenue, but is less than marginal revenue.
Price equals average revenue, but is greater than marginal revenue.
2
A major difference between monopolistic competition and perfect competition is
A) the number of sellers in the market.
B) the degree by which the market demand curve slopes downwards.
C) that products are not standardised in monopolistic competition, unlike in perfect competition.
D) the barriers to entry in the two markets.
A) the number of sellers in the market.
B) the degree by which the market demand curve slopes downwards.
C) that products are not standardised in monopolistic competition, unlike in perfect competition.
D) the barriers to entry in the two markets.
that products are not standardised in monopolistic competition, unlike in perfect competition.
3
A monopolistically competitive firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve because
A) it is able to control price and quantity demanded.
B) there are few substitutes for its product.
C) of product differentiation.
D) its market decisions are affected by the decisions of its rivals.
A) it is able to control price and quantity demanded.
B) there are few substitutes for its product.
C) of product differentiation.
D) its market decisions are affected by the decisions of its rivals.
of product differentiation.
4
If the demand curve for a firm is downward sloping,its marginal revenue curve
A) will lie above the demand curve.
B) will lie below the demand curve.
C) is the same as the demand curve.
D) is horizontal.
A) will lie above the demand curve.
B) will lie below the demand curve.
C) is the same as the demand curve.
D) is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The reason that the coffeehouse market is monopolistically competitive rather than perfectly competitive is because
A) barriers to entry are very low.
B) there are many firms in the market.
C) products are differentiated.
D) entry into the market is blocked.
A) barriers to entry are very low.
B) there are many firms in the market.
C) products are differentiated.
D) entry into the market is blocked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A monopolistically competitive firm will
A) charge the same price as its competitors do.
B) always produce at the minimum efficient scale of production.
C) have some control over its price because its product is differentiated.
D) produce an output level that is productively and allocatively efficient.
A) charge the same price as its competitors do.
B) always produce at the minimum efficient scale of production.
C) have some control over its price because its product is differentiated.
D) produce an output level that is productively and allocatively efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The key characteristics of a monopolistically competitive market structure include
A) few sellers.
B) sellers selling similar but differentiated products.
C) high barriers to entry.
D) sellers acting to maximise revenue.
A) few sellers.
B) sellers selling similar but differentiated products.
C) high barriers to entry.
D) sellers acting to maximise revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is true of a typical firm in a monopolistically competitive industry?
A) Product differentiation allows a successful firm to emerge as a market leader in the industry.
B) All firms have identical cost structures.
C) The more successful firms have an incentive to merge in order to exert greater market power.
D) Each firm acts independently.
A) Product differentiation allows a successful firm to emerge as a market leader in the industry.
B) All firms have identical cost structures.
C) The more successful firms have an incentive to merge in order to exert greater market power.
D) Each firm acts independently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Table 9-1
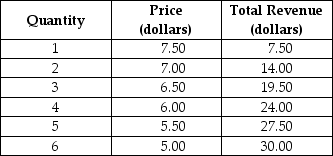
Refer to Table 9-1.What is the marginal revenue of the 3rd unit?
A) $6.50
B) $5.50
C) $1.83
D) $0.50

Refer to Table 9-1.What is the marginal revenue of the 3rd unit?
A) $6.50
B) $5.50
C) $1.83
D) $0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In monopolistic competition there is/are
A) many sellers who each face a downward-sloping demand curve.
B) a few sellers who each face a downward-sloping demand curve.
C) only one seller who faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D) many sellers who each face a perfectly elastic demand curve.
A) many sellers who each face a downward-sloping demand curve.
B) a few sellers who each face a downward-sloping demand curve.
C) only one seller who faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D) many sellers who each face a perfectly elastic demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following characteristics is not common to monopolistic competition and perfect competition?
A) Firms act to maximise profit.
B) Entry barriers into the industry are low.
C) The market demand curve is downward sloping.
D) Firms take market prices as given.
A) Firms act to maximise profit.
B) Entry barriers into the industry are low.
C) The market demand curve is downward sloping.
D) Firms take market prices as given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a monopolistically competitive firm cuts its price to increase its sales,it experiences a gain in revenue due to the
A) substitution effect.
B) income effect.
C) price effect.
D) output effect.
A) substitution effect.
B) income effect.
C) price effect.
D) output effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following characteristics is common to monopolistic competition and perfect competition?
A) Firms produce identical products.
B) Entry barriers into the industry are low.
C) Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D) Firms take market prices as given.
A) Firms produce identical products.
B) Entry barriers into the industry are low.
C) Each firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D) Firms take market prices as given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When a monopolistically competitive firm cuts its price to increase its sales,it experiences a loss in revenue due to the
A) substitution effect.
B) income effect.
C) price effect.
D) output effect.
A) substitution effect.
B) income effect.
C) price effect.
D) output effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is not an example of a monopolistically competitive market?
A) Automobile producers
B) Supermarkets
C) Video stores
D) Makers of women's clothing
A) Automobile producers
B) Supermarkets
C) Video stores
D) Makers of women's clothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
For a monopolistically competitive firm,marginal revenue
A) equals the price.
B) is greater than the price.
C) is less than the price.
D) and price are unrelated.
A) equals the price.
B) is greater than the price.
C) is less than the price.
D) and price are unrelated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The key characteristics of a monopolistically competitive market structure include
A) many small (relative to the total market) sellers acting independently.
B) all sellers sell a homogeneous product.
C) barriers to entry are strong.
D) sellers have no incentive to advertise their products.
A) many small (relative to the total market) sellers acting independently.
B) all sellers sell a homogeneous product.
C) barriers to entry are strong.
D) sellers have no incentive to advertise their products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Table 9-1

Refer to Table 9-1.The table shows
A) an elastic segment of the demand curve.
B) an inelastic segment of the demand curve.
C) a demand curve with an elastic segment from $7.50 to $6.50 followed by an inelastic segment.
D) a demand curve with an inelastic segment from $7.50 to $6.50 followed by an elastic segment.

Refer to Table 9-1.The table shows
A) an elastic segment of the demand curve.
B) an inelastic segment of the demand curve.
C) a demand curve with an elastic segment from $7.50 to $6.50 followed by an inelastic segment.
D) a demand curve with an inelastic segment from $7.50 to $6.50 followed by an elastic segment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
One reason why the coffeehouse market is competitive is that
A) demand for specialty coffee is very high.
B) it is trendy and therefore is likely to have a customer following.
C) barriers to entry are low.
D) consumption takes place in public.
A) demand for specialty coffee is very high.
B) it is trendy and therefore is likely to have a customer following.
C) barriers to entry are low.
D) consumption takes place in public.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If a firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve,
A) the demand for its product must be inelastic.
B) it can control both price and quantity sold.
C) it must reduce its price to sell more units.
D) it will always make a profit.
A) the demand for its product must be inelastic.
B) it can control both price and quantity sold.
C) it must reduce its price to sell more units.
D) it will always make a profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When a monopolistically competitive firm lowers its price,one good thing happens to the firm.What is this 'one good thing' called?
A) The output effect
B) The price effect
C) The income effect
D) The substitution effect
A) The output effect
B) The price effect
C) The income effect
D) The substitution effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
For the monopolistically competitive firm
A) price (P) = marginal revenue (MR) = average revenue (AR).
B) P = MR > AR.
C) P = AR > MR.
D) P > MR = AR.
A) price (P) = marginal revenue (MR) = average revenue (AR).
B) P = MR > AR.
C) P = AR > MR.
D) P > MR = AR.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Figure 9-3 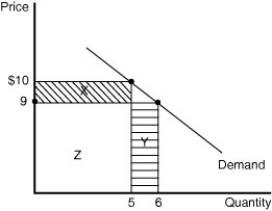
Refer to Figure 9-3.The marginal revenue from one additional unit sold is the sum of the gain in revenue from selling the additional unit and the loss in revenue from having to charge a lower price to sell the additional unit.Based on the diagram in the figure,
A) X represents the gain (price effect) and Y the loss (output effect).
B) X + Z represents the loss (output effect) and Y the gain (price effect).
C) Y represents the gain (output effect) and X the loss (price effect).
D) X represents the loss (price effect) and Y + Z the gain (output effect).

Refer to Figure 9-3.The marginal revenue from one additional unit sold is the sum of the gain in revenue from selling the additional unit and the loss in revenue from having to charge a lower price to sell the additional unit.Based on the diagram in the figure,
A) X represents the gain (price effect) and Y the loss (output effect).
B) X + Z represents the loss (output effect) and Y the gain (price effect).
C) Y represents the gain (output effect) and X the loss (price effect).
D) X represents the loss (price effect) and Y + Z the gain (output effect).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Table 9-1

Refer to Table 9-1.What portion of the marginal revenue of the 4th unit is due to the output effect and what portion is due to the price effect?
A) Output effect = $24.00; price effect = $19.50
B) Output effect = $6.50; price effect = $2.00
C) Output effect = -$0.50; price effect = $5.00
D) Output effect = $6.00; price effect = -$1.50

Refer to Table 9-1.What portion of the marginal revenue of the 4th unit is due to the output effect and what portion is due to the price effect?
A) Output effect = $24.00; price effect = $19.50
B) Output effect = $6.50; price effect = $2.00
C) Output effect = -$0.50; price effect = $5.00
D) Output effect = $6.00; price effect = -$1.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Because the monopolistically competitive firm faces a ________ demand curve for its product,it ________ the price of its output.
A) downward-sloping; cannot influence
B) horizontal; can influence
C) horizontal; cannot influence
D) downward-sloping; can influence
A) downward-sloping; cannot influence
B) horizontal; can influence
C) horizontal; cannot influence
D) downward-sloping; can influence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When a monopolistically competitive firm lowers it price,one bad thing happens to the firm.What is this 'one bad thing' called?
A) The output effect
B) The income effect
C) The substitution effect
D) The price effect
A) The output effect
B) The income effect
C) The substitution effect
D) The price effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following describes a difference between the marginal revenue and demand curves of a perfectly competitive firm and a monopolistically competitive firm?
A) The perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue and demand curves are the same; the marginal revenue curve of a monopolistically competitive firm lies above its demand curve.
B) The perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue and demand curves are the same; the marginal revenue curve of a monopolistically competitive firm lies below its demand curve.
C) The monopolistically competitive firm's marginal revenue and demand curves are the same; the marginal revenue curve of a perfectly competitive firm lies below its demand curve.
D) The marginal revenue curve of a monopolistically competitive firm lies below its demand curve; the marginal revenue curve of a perfectly competitive firm lies above its demand curve.
A) The perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue and demand curves are the same; the marginal revenue curve of a monopolistically competitive firm lies above its demand curve.
B) The perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue and demand curves are the same; the marginal revenue curve of a monopolistically competitive firm lies below its demand curve.
C) The monopolistically competitive firm's marginal revenue and demand curves are the same; the marginal revenue curve of a perfectly competitive firm lies below its demand curve.
D) The marginal revenue curve of a monopolistically competitive firm lies below its demand curve; the marginal revenue curve of a perfectly competitive firm lies above its demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Figure 9-3 
Refer to Figure 9-3.What is the marginal revenue of the 6th unit of output?
A) $4
B) $5
C) $9
D) $54

Refer to Figure 9-3.What is the marginal revenue of the 6th unit of output?
A) $4
B) $5
C) $9
D) $54

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is not a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
A) Firms are price takers.
B) There are many buyers and sellers.
C) Barriers to entry are low.
D) Firms sell similar, but not identical, products.
A) Firms are price takers.
B) There are many buyers and sellers.
C) Barriers to entry are low.
D) Firms sell similar, but not identical, products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
When a firm faces a downward-sloping demand curve,marginal revenue
A) must exceed price because the price effect outweighs the output effect.
B) is less than price because a firm must lower its price to sell more.
C) equals price because the firm sells a standardised product.
D) must exceed price because the output effect outweighs the price effect.
A) must exceed price because the price effect outweighs the output effect.
B) is less than price because a firm must lower its price to sell more.
C) equals price because the firm sells a standardised product.
D) must exceed price because the output effect outweighs the price effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements is true about marginal revenue?
A) If marginal revenue is zero, it means that quantity demanded falls to zero when a firm changes its price.
B) If marginal revenue is negative, the additional revenue received from selling 1 more unit of the good is smaller than the revenue lost from receiving a lower price on all the units that could have been sold at the original price.
C) If marginal revenue is positive, the additional revenue received from selling 1 more unit of the good is smaller than the revenue lost from receiving a lower price on all the units that could have been sold at the original price.
D) Marginal revenue increases as price falls and quantity sold increases.
A) If marginal revenue is zero, it means that quantity demanded falls to zero when a firm changes its price.
B) If marginal revenue is negative, the additional revenue received from selling 1 more unit of the good is smaller than the revenue lost from receiving a lower price on all the units that could have been sold at the original price.
C) If marginal revenue is positive, the additional revenue received from selling 1 more unit of the good is smaller than the revenue lost from receiving a lower price on all the units that could have been sold at the original price.
D) Marginal revenue increases as price falls and quantity sold increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is not a characteristic of monopolistic competition?
A) There are many buyers and sellers.
B) There are low barriers to entry.
C) Average revenue is equal to price.
D) The products sold by all firms are identical.
A) There are many buyers and sellers.
B) There are low barriers to entry.
C) Average revenue is equal to price.
D) The products sold by all firms are identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Every firm that has the ability to affect the price of the good or service it sells will
A) have a perfectly elastic demand curve.
B) have a marginal revenue curve that lies below its demand curve.
C) earn a short-run profit but break even in the long run.
D) shut down in the short run.
A) have a perfectly elastic demand curve.
B) have a marginal revenue curve that lies below its demand curve.
C) earn a short-run profit but break even in the long run.
D) shut down in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a monopolistically competitive firm lowers its price and,as a result,its total revenue decreases,then
A) the output effect of the price change was less than the price effect.
B) the output effect of the price change was greater than the price effect.
C) the firm's demand curve must have decreased.
D) the substitution effect of the price change was greater than the income effect.
A) the output effect of the price change was less than the price effect.
B) the output effect of the price change was greater than the price effect.
C) the firm's demand curve must have decreased.
D) the substitution effect of the price change was greater than the income effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Table 9-1

Refer to Table 9-1.What portion of the marginal revenue of the 5th unit is due to the output effect and what portion is due to the price effect?
A) Output effect = $3.00; price effect = $0.50
B) Output effect = $1.50; price effect = $2.00
C) Output effect = $5.50; price effect = -$2.00
D) Output effect = $4.00; price effect = -$0.50

Refer to Table 9-1.What portion of the marginal revenue of the 5th unit is due to the output effect and what portion is due to the price effect?
A) Output effect = $3.00; price effect = $0.50
B) Output effect = $1.50; price effect = $2.00
C) Output effect = $5.50; price effect = -$2.00
D) Output effect = $4.00; price effect = -$0.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A monopolistically competitive market is described as one in which there are
A) a few firms producing an identical product.
B) a large number of firms selling similar, but not identical, products.
C) a few firms producing differentiated products.
D) one large firm and many small firms producing identical products.
A) a few firms producing an identical product.
B) a large number of firms selling similar, but not identical, products.
C) a few firms producing differentiated products.
D) one large firm and many small firms producing identical products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Monopolistic competition is a market structure in which
A) firms produce and sell products for which there are no close substitutes.
B) the demand curve for a typical firm is horizontal.
C) firms cannot influence the market price.
D) barriers to entry are low.
A) firms produce and sell products for which there are no close substitutes.
B) the demand curve for a typical firm is horizontal.
C) firms cannot influence the market price.
D) barriers to entry are low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The Jeans Store sells 7 pairs of jeans per day when it charges $100 per pair.It sells 8 pairs of jeans per day at a price of $90 per pair.The marginal revenue of the 8th pair of jeans is
A) $20.
B) $90.
C) $100.
D) $700.
A) $20.
B) $90.
C) $100.
D) $700.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The demand curve of a monopolistically competitive firm
A) is horizontal because the firm must cut its price to sell more.
B) is perfectly elastic.
C) is downward sloping because it sells an identical product.
D) is downward sloping because it must cut its price to sell more.
A) is horizontal because the firm must cut its price to sell more.
B) is perfectly elastic.
C) is downward sloping because it sells an identical product.
D) is downward sloping because it must cut its price to sell more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The marginal revenue of a monopolistically competitive firm
A) cannot be negative because the price the firm charges will always be greater than zero.
B) can be negative if the firm charges a high price.
C) can be negative if the firm charges a low price.
D) will equal average revenue.
A) cannot be negative because the price the firm charges will always be greater than zero.
B) can be negative if the firm charges a high price.
C) can be negative if the firm charges a low price.
D) will equal average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Monopolistically competitive firms face a perfectly elastic demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
For a downward-sloping demand curve,marginal revenue decreases as quantity sold increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Why are demand and marginal revenue represented by the same curve for a firm in a perfectly competitive market,but by separate curves for a firm in a monopolistically competitive market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the profit-maximising rule for a monopolistically competitive firm?
A) To produce a quantity that maximises market share.
B) To produce a quantity that maximises total revenue.
C) To produce a quantity such that marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) To produce a quantity such that price equals marginal cost.
A) To produce a quantity that maximises market share.
B) To produce a quantity that maximises total revenue.
C) To produce a quantity such that marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
D) To produce a quantity such that price equals marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In monopolistic competition,if a firm produces a highly desirable product relative to its competitors,the firm will be able to raise its price without losing any customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Complete the following table.
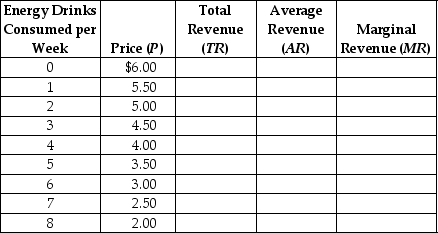


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Unlike a perfectly competitive firm,for a monopolistically competitive firm
A) price ≠ marginal cost for all output levels.
B) price ≠ marginal revenue for all output levels.
C) price ≠ average revenue for all output levels.
D) marginal revenue = marginal cost at the profit-maximising output.
A) price ≠ marginal cost for all output levels.
B) price ≠ marginal revenue for all output levels.
C) price ≠ average revenue for all output levels.
D) marginal revenue = marginal cost at the profit-maximising output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The marginal revenue of a monopolistically competitive firm will be positive at high prices and negative at low prices.
B) Because the demand curve for a monopolistically competitive firm is downward sloping, its marginal revenue will be negative.
C) The marginal revenue of a monopolistically competitive firm will always be positive.
D) The marginal revenue of a monopolistically competitive firm will be positive at low prices and negative at high prices.
A) The marginal revenue of a monopolistically competitive firm will be positive at high prices and negative at low prices.
B) Because the demand curve for a monopolistically competitive firm is downward sloping, its marginal revenue will be negative.
C) The marginal revenue of a monopolistically competitive firm will always be positive.
D) The marginal revenue of a monopolistically competitive firm will be positive at low prices and negative at high prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Firms in monopolistic competition compete by selling similar,but not identical,products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose a monopolistically competitive firm sells 25 units at a price of $10.Calculate its marginal revenue per unit of output if it sells 5 more units of output when it reduces its price to $9.
A) $270
B) $20
C) $4
D) $2.50
A) $270
B) $20
C) $4
D) $2.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A monopolistically competitive firm maximises profit where
A) price = marginal revenue.
B) price > marginal cost.
C) marginal revenue > average revenue.
D) total revenue > marginal cost.
A) price = marginal revenue.
B) price > marginal cost.
C) marginal revenue > average revenue.
D) total revenue > marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If marginal revenue is negative,then the revenue lost from receiving a lower price on all the units that could have been sold at the original price is smaller than the additional revenue from selling one more unit of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Table 9-2
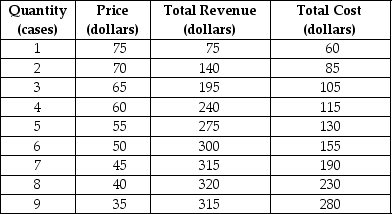 Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Refer to Table 9-2.What is the output (Q)that maximises profit,and what is the price (P)charged?
A) P = $55; Q = 5 cases
B) P = $50; Q = 6 cases
C) P = $45; Q = 7 cases
D) P = $40; Q = 8 cases
 Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.Refer to Table 9-2.What is the output (Q)that maximises profit,and what is the price (P)charged?
A) P = $55; Q = 5 cases
B) P = $50; Q = 6 cases
C) P = $45; Q = 7 cases
D) P = $40; Q = 8 cases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
One of the assumptions of monopolistic competition is that firms produce differentiated products.What does this assumption imply about the demand curve facing a representative firm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When a monopolistically competitive firm cuts its price to increase its sales,it experiences a loss in revenue due to the income effect and a gain in revenue due to the substitution effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Suppose that if a local McDonald's restaurant reduces the price of a Big Mac from $4.00 to $3.25,the number of Big Macs it sells per day will increase from 4 to 5.Explain the output effect and the price effect resulting from this change.Using a graph,illustrate both the loss in revenue from selling each of the first 4 Big Macs for $0.75 less and the additional revenue from selling 1 more Big Mac.What is the total change in revenue received which results from this price decrease?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
There are many cattle ranchers in the world,and there are also many McDonald's restaurants in the world.Why,then,does a McDonald's restaurant face a downward-sloping demand curve while a cattle rancher faces a horizontal demand curve?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What are the most important differences between perfectly competitive markets and monopolistically competitive markets?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Explain the differences between total revenue,average revenue,and marginal revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
New firms are able to enter monopolistically competitive markets because there are low barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Table 9-2
 Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Refer to Table 9-2.What is the marginal profit from producing and selling the 5th case?
A) $275
B) $145
C) $35
D) $20
 Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.Refer to Table 9-2.What is the marginal profit from producing and selling the 5th case?
A) $275
B) $145
C) $35
D) $20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Table 9-2
 Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Refer to Table 9-2.What is Eco Energy's profit?
A) $125
B) $140
C) $145
D) $150
 Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.Refer to Table 9-2.What is Eco Energy's profit?
A) $125
B) $140
C) $145
D) $150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure 9-4 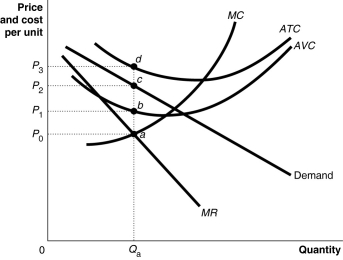 Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Refer to Figure 9-4.What is the area that represents the total revenue made by the firm?
A) 0P0aQa
B) 0P1bQa
C) 0P2cQa
D) 0P3dQa
 Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.Refer to Figure 9-4.What is the area that represents the total revenue made by the firm?
A) 0P0aQa
B) 0P1bQa
C) 0P2cQa
D) 0P3dQa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Figure 9-4  Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Refer to Figure 9-4.What is the area that represents the total variable cost of production?
A) 0P0aQa
B) 0P1bQa
C) P0abP1
D) P1bdP3
 Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.Refer to Figure 9-4.What is the area that represents the total variable cost of production?
A) 0P0aQa
B) 0P1bQa
C) P0abP1
D) P1bdP3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Both monopolistically competitive firms and perfectly competitive firms maximise profits
A) by producing where price equals average total cost.
B) by producing where marginal revenue equals average revenue.
C) by producing where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
D) by producing where price equals average variable cost.
A) by producing where price equals average total cost.
B) by producing where marginal revenue equals average revenue.
C) by producing where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
D) by producing where price equals average variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Table 9-3
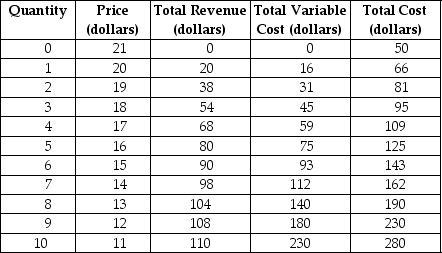 Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Refer to Table 9-3.If this firm continues to produce,what is likely to happen to the product's price in the long run?
A) It will fall.
B) It will increase
C) It will remain constant.
D) It cannot be determined without information on its long-run demand curve.
 Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.Refer to Table 9-3.If this firm continues to produce,what is likely to happen to the product's price in the long run?
A) It will fall.
B) It will increase
C) It will remain constant.
D) It cannot be determined without information on its long-run demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the short run,a profit-maximising firm's decision to produce should be guided by whether
A) it makes a profit.
B) its marginal profit is maximised.
C) its total revenue exceeds its fixed cost.
D) its total revenue covers its variable cost.
A) it makes a profit.
B) its marginal profit is maximised.
C) its total revenue exceeds its fixed cost.
D) its total revenue covers its variable cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Table 9-3
 Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Refer to Table 9-3.What is its average variable cost of production at its optimal output level?
A) $0 (because its optimal output = 0)
B) $15
C) $14.75
D) $29
 Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.Refer to Table 9-3.What is its average variable cost of production at its optimal output level?
A) $0 (because its optimal output = 0)
B) $15
C) $14.75
D) $29

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Figure 9-4  Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Refer to Figure 9-4.What is the area that represents the loss made by the firm?
A) The area P0adP3
B) The area P1bcP2
C) The area P0acP2
D) The area P2cdP3
 Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.Refer to Figure 9-4.What is the area that represents the loss made by the firm?
A) The area P0adP3
B) The area P1bcP2
C) The area P0acP2
D) The area P2cdP3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Figure 9-4  Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Refer to Figure 9-4.What is the area that represents the total fixed cost of production?
A) 0P1aQa
B) P0adP3
C) P1bdP3
D) That information cannot be determined from the graph.
 Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.Refer to Figure 9-4.What is the area that represents the total fixed cost of production?
A) 0P1aQa
B) P0adP3
C) P1bdP3
D) That information cannot be determined from the graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Figure 9-4  Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Refer to Figure 9-4.If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units,what is the price charged?
A) P0
B) P1
C) P2
D) P3
 Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.Refer to Figure 9-4.If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units,what is the price charged?
A) P0
B) P1
C) P2
D) P3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Suppose Jason owns a small pastry shop.Jason wants to maximise his profit,and thinking back to the university microeconomics class he took,he decides he needs to produce a quantity of pastries which will minimise his average total cost.Will Jason's strategy necessarily maximise profits for his pastry shop?
A) Yes; since Jason's pastry shop is in a perfectly competitive market, the only way to maximise profit is to produce the quantity where average total cost is minimised.
B) Not necessarily; this strategy will only maximise Jason's profit in the long run, but not in the short run.
C) No; in order to maximise profit, Jason would never want to produce the quantity where average total cost is minimised.
D) Not necessarily; depending on demand, Jason may maximise profit by producing a quantity other than that where average total cost is at a minimum.
A) Yes; since Jason's pastry shop is in a perfectly competitive market, the only way to maximise profit is to produce the quantity where average total cost is minimised.
B) Not necessarily; this strategy will only maximise Jason's profit in the long run, but not in the short run.
C) No; in order to maximise profit, Jason would never want to produce the quantity where average total cost is minimised.
D) Not necessarily; depending on demand, Jason may maximise profit by producing a quantity other than that where average total cost is at a minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Table 9-2
 Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Refer to Table 9-2.What is likely to happen to the product's price in the long run?
A) It will fall.
B) It will increase.
C) It will remain constant.
D) This cannot be determined without information on its long-run demand curve.
 Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.
Eco Energy is a monopolistically competitive producer of a sports beverage called Power On. Table 9-2 shows the firm's demand and cost schedules.Refer to Table 9-2.What is likely to happen to the product's price in the long run?
A) It will fall.
B) It will increase.
C) It will remain constant.
D) This cannot be determined without information on its long-run demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If price exceeds average variable cost but is less than average total cost,a firm
A) should further differentiate its product.
B) should stay in business for a while longer until its fixed costs expire.
C) is making some profit but less than maximum profit.
D) should shut down.
A) should further differentiate its product.
B) should stay in business for a while longer until its fixed costs expire.
C) is making some profit but less than maximum profit.
D) should shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Figure 9-5 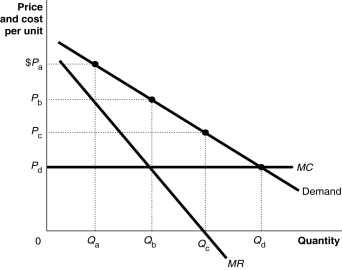
Refer to Figure 9-5.The chocolate store represented in the diagram is currently selling Qa units of chocolate at a price of Pa.Is this chocolate store maximising its profit and,if it is not,what would you recommend to the firm?
A) Yes, it is maximising its profit by charging the highest price possible.
B) No, it is not; since its marginal cost is constant, it should produce and sell as much chocolate as it can. It should sell Qd units at a price of Pd.
C) No, it is not; it should lower its price to Pc and sell Qc units.
D) No, it is not; it should lower its price to Pb and sell Qb units.

Refer to Figure 9-5.The chocolate store represented in the diagram is currently selling Qa units of chocolate at a price of Pa.Is this chocolate store maximising its profit and,if it is not,what would you recommend to the firm?
A) Yes, it is maximising its profit by charging the highest price possible.
B) No, it is not; since its marginal cost is constant, it should produce and sell as much chocolate as it can. It should sell Qd units at a price of Pd.
C) No, it is not; it should lower its price to Pc and sell Qc units.
D) No, it is not; it should lower its price to Pb and sell Qb units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figure 9-4  Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Refer to Figure 9-4.Should the firm represented in the diagram continue to stay in business despite its losses?
A) No, it should shut down.
B) Yes, its total revenue covers its variable cost.
C) No, it is not able to cover its fixed cost.
D) Yes, it should increase its revenue by raising its price.
 Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.
Figure 9-4 shows short-run cost and demand curves for a monopolistically competitive firm in the market for designer watches.Refer to Figure 9-4.Should the firm represented in the diagram continue to stay in business despite its losses?
A) No, it should shut down.
B) Yes, its total revenue covers its variable cost.
C) No, it is not able to cover its fixed cost.
D) Yes, it should increase its revenue by raising its price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Table 9-3
 Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Refer to Table 9-3.What is the best course of action for the firm in the short run?
A) It should shut down.
B) It should stay in business because it covers some of its fixed cost.
C) It should increase its sales by lowering its price.
D) It should not cut its price, but it should increase its sales by advertising.
 Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.Refer to Table 9-3.What is the best course of action for the firm in the short run?
A) It should shut down.
B) It should stay in business because it covers some of its fixed cost.
C) It should increase its sales by lowering its price.
D) It should not cut its price, but it should increase its sales by advertising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Assume price exceeds average variable cost over the relevant range of demand.If a monopolistically competitive firm is producing at an output where marginal revenue is $23 and marginal cost is $19,then to maximise profits the firm should
A) continue to produce the same quantity.
B) increase output.
C) decrease output.
D) shut down.
A) continue to produce the same quantity.
B) increase output.
C) decrease output.
D) shut down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Table 9-3
 Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Refer to Table 9-3.What are the profit-maximising/loss-minimising output level and price?
A) Q = 0 (firm should not produce)
B) Q = 3; P = $18
C) Q = 4; P = $17
D) Q = 5; P = $16
 Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.Refer to Table 9-3.What are the profit-maximising/loss-minimising output level and price?
A) Q = 0 (firm should not produce)
B) Q = 3; P = $18
C) Q = 4; P = $17
D) Q = 5; P = $16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Table 9-3
 Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Refer to Table 9-3.What is the amount of the firm's loss at its optimal output level?
A) $0
B) $41
C) $45
D) $50
 Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.
Table 9-3 shows the demand and cost schedules for a monopolistically competitive firm.Refer to Table 9-3.What is the amount of the firm's loss at its optimal output level?
A) $0
B) $41
C) $45
D) $50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 351 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



