Deck 10: Monopoly and Antitrust
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/253
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Monopoly and Antitrust
1
A firm's demand for labour curve is also called its
A) marginal revenue product of labour curve.
B) marginal factor cost of labour curve.
C) marginal valuation curve.
D) marginal benefit of labour curve.
A) marginal revenue product of labour curve.
B) marginal factor cost of labour curve.
C) marginal valuation curve.
D) marginal benefit of labour curve.
marginal revenue product of labour curve.
2
Figure 10-1 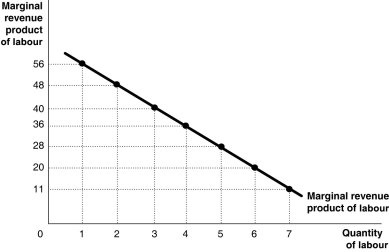 Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.
Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.
Refer to Figure 10-1.If Dale can sell her doilies at $2 each,what is the marginal product of the 5th worker?
A) $28
B) 28 doilies
C) 14 doilies
D) $56
 Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.
Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.Refer to Figure 10-1.If Dale can sell her doilies at $2 each,what is the marginal product of the 5th worker?
A) $28
B) 28 doilies
C) 14 doilies
D) $56
14 doilies
3
Figure 10-1  Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.
Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.
Refer to Figure 10-1.Suppose the market price of doilies rises to $3.What happens to the curve given in the diagram?
A) Nothing, because labour's productivity has not changed.
B) There will be a movement along the curve.
C) The curve shifts to the right.
D) We cannot answer the question without knowing if Dale would want to hire more workers.
 Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.
Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.Refer to Figure 10-1.Suppose the market price of doilies rises to $3.What happens to the curve given in the diagram?
A) Nothing, because labour's productivity has not changed.
B) There will be a movement along the curve.
C) The curve shifts to the right.
D) We cannot answer the question without knowing if Dale would want to hire more workers.
The curve shifts to the right.
4
A firm's primary interest when it hires an additional worker is
A) the cost of hiring the additional worker.
B) how the average output of the firm will be affected by this new worker.
C) the extra revenue the firm realises from hiring that worker.
D) whether or not the new worker gets along with the firm's existing workers.
A) the cost of hiring the additional worker.
B) how the average output of the firm will be affected by this new worker.
C) the extra revenue the firm realises from hiring that worker.
D) whether or not the new worker gets along with the firm's existing workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The firm's gain in profit from hiring another worker is
A) the marginal revenue product of the extra worker.
B) the difference between marginal revenue product and the wage of the worker.
C) the extra output of the extra worker.
D) the reduction in costs from hiring another worker.
A) the marginal revenue product of the extra worker.
B) the difference between marginal revenue product and the wage of the worker.
C) the extra output of the extra worker.
D) the reduction in costs from hiring another worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Table 10-1
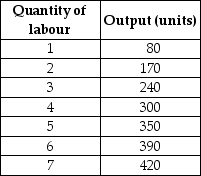
Refer to Table 10-1.Suppose the output price is $3.If the wage rate is $90,what is the profit-maximising quantity of labour that the firm should hire?
A) 7 units
B) 5 units
C) 4 units
D) 3 units

Refer to Table 10-1.Suppose the output price is $3.If the wage rate is $90,what is the profit-maximising quantity of labour that the firm should hire?
A) 7 units
B) 5 units
C) 4 units
D) 3 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Firms use information on labour's marginal revenue product to determine
A) how much to produce at each output price.
B) how many workers to hire at each wage rate.
C) how much marginal product to produce at each wage rate.
D) how much labour service to supply at each wage rate.
A) how much to produce at each output price.
B) how many workers to hire at each wage rate.
C) how much marginal product to produce at each wage rate.
D) how much labour service to supply at each wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The labour market is considered to be one of the more important markets in an economy because
A) most people typically earn the bulk of their income from wages and salaries.
B) most people are concerned that wages determined in the labour market are unfair.
C) the usual market forces do not hold in the labour market.
D) the labour market does not reach an equilibrium.
A) most people typically earn the bulk of their income from wages and salaries.
B) most people are concerned that wages determined in the labour market are unfair.
C) the usual market forces do not hold in the labour market.
D) the labour market does not reach an equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Suppose you have worked at a local sandwich shop for six months and now you plan to ask your manager for a raise.How can you convince your manager that you are worth more money than you are currently being paid?
A) By threatening to quit if he refuses to give you a raise.
B) By demonstrating to your manager the marginal revenue product your employment contributes to the sandwich shop.
C) By explaining to him how difficult it is for you to save enough money to go to university.
D) By convincing him that you are a dedicated worker and ready to take on more responsibilities at the shop.
A) By threatening to quit if he refuses to give you a raise.
B) By demonstrating to your manager the marginal revenue product your employment contributes to the sandwich shop.
C) By explaining to him how difficult it is for you to save enough money to go to university.
D) By convincing him that you are a dedicated worker and ready to take on more responsibilities at the shop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Table 10-1

Refer to Table 10-1.If the output price is $3,what is the marginal revenue product of the fifth unit of labour?
A) $1050
B) $360
C) $210
D) $150

Refer to Table 10-1.If the output price is $3,what is the marginal revenue product of the fifth unit of labour?
A) $1050
B) $360
C) $210
D) $150

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Marginal revenue product for a perfectly competitive seller is equal to
A) the output price multiplied by the total product of labour.
B) the output price multiplied by the number workers hired.
C) the change in total revenue that results from hiring another worker.
D) the marginal cost of production.
A) the output price multiplied by the total product of labour.
B) the output price multiplied by the number workers hired.
C) the change in total revenue that results from hiring another worker.
D) the marginal cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the difference between labour's marginal product and marginal revenue product?
A) The marginal product of labour is the increase in output as a result of hiring an additional worker, while the marginal revenue product of labour is the increase in profit as a result of hiring an additional worker.
B) The marginal revenue product of labour is the dollar value of hiring an additional worker, while the marginal product of labour is the increase in the firm's physical output as a result of hiring an additional worker.
C) The marginal product of labour is the additional labour's contribution to the firm's total output, while the marginal revenue product is the additional labour's contribution to the firm's total sales revenue.
D) Labour's marginal product is a measure of labour's productivity, while labour's marginal revenue product is a measure of labour's ability to sell the firm's products.
A) The marginal product of labour is the increase in output as a result of hiring an additional worker, while the marginal revenue product of labour is the increase in profit as a result of hiring an additional worker.
B) The marginal revenue product of labour is the dollar value of hiring an additional worker, while the marginal product of labour is the increase in the firm's physical output as a result of hiring an additional worker.
C) The marginal product of labour is the additional labour's contribution to the firm's total output, while the marginal revenue product is the additional labour's contribution to the firm's total sales revenue.
D) Labour's marginal product is a measure of labour's productivity, while labour's marginal revenue product is a measure of labour's ability to sell the firm's products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The demand for labour is described as a derived demand because
A) it is derived by workers seeking to earn income to fund the consumption of goods and services.
B) it is derived by producers seeking to make profits by starting new businesses.
C) it is derived from the demand for products that use labour in the production process.
D) it is derived from government institutions which rely on labour markets for the purpose of raising tax revenue.
A) it is derived by workers seeking to earn income to fund the consumption of goods and services.
B) it is derived by producers seeking to make profits by starting new businesses.
C) it is derived from the demand for products that use labour in the production process.
D) it is derived from government institutions which rely on labour markets for the purpose of raising tax revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Table 10-1

Refer to Table 10-1.Suppose the output price is $3.If the firm represented in the table is maximising its profit by hiring six workers,what is the wage rate?
A) $120
B) $65
C) $40
D) There is insufficient information to answer the question.

Refer to Table 10-1.Suppose the output price is $3.If the firm represented in the table is maximising its profit by hiring six workers,what is the wage rate?
A) $120
B) $65
C) $40
D) There is insufficient information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Demand in factor markets differs from demand in product markets in that
A) the demand for a factor of production is difficult to determine.
B) the demand for a factor of production is influenced by workers' productivity and by the producers' expected sales revenues, not by tastes and preferences of consumers.
C) demand for a factor of production is based on the tastes and preferences of firms.
D) demand for a factor of production is based on the tastes and preferences of resource owners.
A) the demand for a factor of production is difficult to determine.
B) the demand for a factor of production is influenced by workers' productivity and by the producers' expected sales revenues, not by tastes and preferences of consumers.
C) demand for a factor of production is based on the tastes and preferences of firms.
D) demand for a factor of production is based on the tastes and preferences of resource owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Table 10-1

Refer to Table 10-1.The marginal product of the fourth unit of labour is
A) 300.
B) 75.
C) 60.
D) 15.

Refer to Table 10-1.The marginal product of the fourth unit of labour is
A) 300.
B) 75.
C) 60.
D) 15.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Marginal revenue product of labour for a competitive seller is
A) the change in total product from hiring one more worker.
B) equal to the marginal product of labour multiplied by the output price.
C) the output price multiplied by the quantity sold.
D) the marginal revenue of the product multiplied by the output price.
A) the change in total product from hiring one more worker.
B) equal to the marginal product of labour multiplied by the output price.
C) the output price multiplied by the quantity sold.
D) the marginal revenue of the product multiplied by the output price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Figure 10-1  Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.
Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.
Refer to Figure 10-1.If the wage rate is $40,how many workers should Dale hire?
A) 6 labour units
B) 5 labour units
C) 4 labour units
D) 3 labour units
 Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.
Figure 10-1 shows the marginal revenue product for Dale's Hand-Sewn Doilies, a producer of linen doilies.Refer to Figure 10-1.If the wage rate is $40,how many workers should Dale hire?
A) 6 labour units
B) 5 labour units
C) 4 labour units
D) 3 labour units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A reason why a perfectly competitive firm's demand for labour curve slopes downward is that
A) each additional unit of labour hired is less efficient than previously hired units.
B) in the short run, as more labour is hired, labour's marginal product falls because of the law of diminishing returns.
C) the extra cost of hiring additional units of labour increases as a firm hires more units of labour.
D) the firm's demand curve for the product that uses labour is downward sloping.
A) each additional unit of labour hired is less efficient than previously hired units.
B) in the short run, as more labour is hired, labour's marginal product falls because of the law of diminishing returns.
C) the extra cost of hiring additional units of labour increases as a firm hires more units of labour.
D) the firm's demand curve for the product that uses labour is downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the difference between a firm's marginal revenue and its marginal revenue product?
A) Marginal revenue is the change in sales revenue from selling one more unit of output, while marginal revenue product is the profit earned from hiring one more worker.
B) Marginal revenue is the change in sales revenue from selling one more unit of output, while marginal revenue product is the change in total revenue from hiring one more worker.
C) Marginal revenue is the increase in revenue when a firm raises its output price, while marginal revenue product is the increase in marginal product when a firm hires an additional worker.
D) There is no difference between the two terms.
A) Marginal revenue is the change in sales revenue from selling one more unit of output, while marginal revenue product is the profit earned from hiring one more worker.
B) Marginal revenue is the change in sales revenue from selling one more unit of output, while marginal revenue product is the change in total revenue from hiring one more worker.
C) Marginal revenue is the increase in revenue when a firm raises its output price, while marginal revenue product is the increase in marginal product when a firm hires an additional worker.
D) There is no difference between the two terms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Table 10-2
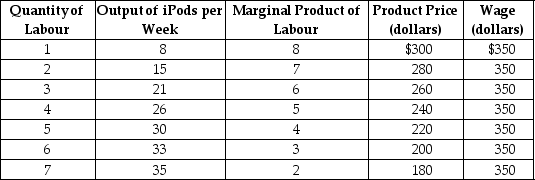
Refer to Table 10-2.The firm represented in the table
A) has market power in the factor market.
B) has market power in the output market.
C) has market power in both the factor and product market.
D) has no market power in the factor or product market.

Refer to Table 10-2.The firm represented in the table
A) has market power in the factor market.
B) has market power in the output market.
C) has market power in both the factor and product market.
D) has no market power in the factor or product market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Table 10-2

Refer to Table 10-2.What is the profit-maximising quantity of labour that the firm should hire?
A) 5 units
B) 4 units
C) 3 units
D) 2 units

Refer to Table 10-2.What is the profit-maximising quantity of labour that the firm should hire?
A) 5 units
B) 4 units
C) 3 units
D) 2 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose a competitive firm is paying a wage of $12 an hour and sells its product at $3 per unit.Assume that labour is the only input.If the last worker hired increases output by three units per hour,then to maximise profits the firm should
A) not change the number of workers it currently hires.
B) lay off some of its workers.
C) hire additional workers.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) not change the number of workers it currently hires.
B) lay off some of its workers.
C) hire additional workers.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following will not cause the labour demand curve to shift to the right?
A) An increase in the price of the firm's product.
B) A technological improvement that increases labour productivity.
C) An increase in human capital in the labour force.
D) An increase in the market wage rate.
A) An increase in the price of the firm's product.
B) A technological improvement that increases labour productivity.
C) An increase in human capital in the labour force.
D) An increase in the market wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An increase in a perfectly competitive firm's demand for labour could be caused by
A) a decrease in the market wage rate.
B) an increase in the market demand for the firm's product.
C) a decrease in the marginal product of workers.
D) an increase in the quantity of labour supplied.
A) a decrease in the market wage rate.
B) an increase in the market demand for the firm's product.
C) a decrease in the marginal product of workers.
D) an increase in the quantity of labour supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose a competitive firm pays a wage of $12 an hour and sells its product at $3 per unit.Assume that labour is the only input.If hiring another worker would increase output by five units per hour,then to maximise profits the firm should
A) not change the number of workers it currently hires.
B) lay off some of its workers.
C) hire the additional worker.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) not change the number of workers it currently hires.
B) lay off some of its workers.
C) hire the additional worker.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Table 10-2

Refer to Table 10-2.The marginal revenue product of labour from the third unit of labour is
A) $5460.
B) $1560.
C) $1260.
D) $780.

Refer to Table 10-2.The marginal revenue product of labour from the third unit of labour is
A) $5460.
B) $1560.
C) $1260.
D) $780.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The demand for labour is different from the demand for final goods and services because
A) the demand for labour is derived from the demand for the good or service the labour is used to produce.
B) it is a demand for people, not inanimate objects.
C) the demand for labour is more inelastic than the demand for the goods and services produced with this labour.
D) the law of demand does not apply to the demand for labour.
A) the demand for labour is derived from the demand for the good or service the labour is used to produce.
B) it is a demand for people, not inanimate objects.
C) the demand for labour is more inelastic than the demand for the goods and services produced with this labour.
D) the law of demand does not apply to the demand for labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is a factor market?
A) It is a market where financial instruments are traded.
B) It is a market where stocks and bonds are traded.
C) It is a market where producers buy consumption and capital goods.
D) It is a market where resources used to produce final goods are traded.
A) It is a market where financial instruments are traded.
B) It is a market where stocks and bonds are traded.
C) It is a market where producers buy consumption and capital goods.
D) It is a market where resources used to produce final goods are traded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Marginal revenue product can be calculated using the formula marginal product × output price
A) only if output price is constant.
B) only if the marginal product of labour is constant.
C) only if the both marginal product of labour and the output price are constant.
D) only if the firm has market power in the labour market.
A) only if output price is constant.
B) only if the marginal product of labour is constant.
C) only if the both marginal product of labour and the output price are constant.
D) only if the firm has market power in the labour market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If a worker can produce 20 units of output which can be sold for $4 per unit,what is the maximum wage that firm should pay to hire this worker?
A) $80
B) $80 minus the firm's profit mark-up
C) It depends on what the going wage rate is in the labour market.
D) There is insufficient information to answer the question.
A) $80
B) $80 minus the firm's profit mark-up
C) It depends on what the going wage rate is in the labour market.
D) There is insufficient information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Suppose a competitive firm is paying a wage of $12 an hour and sells its product at $3 per unit.Assume that labour is the only input.If hiring another worker would increase output by three units per hour,then to maximise profits the firm should
A) not change the number of workers it currently hires.
B) not hire an additional worker.
C) hire another worker.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) not change the number of workers it currently hires.
B) not hire an additional worker.
C) hire another worker.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
One difference between the labour market and markets for goods and services is
A) the demand in the labour market is inelastic; the demand for goods and services may be elastic or inelastic.
B) the supply of labour is perfectly inelastic because the quantity supplied is constant. The elasticity of supply for goods and services is different in different markets.
C) concepts of fairness arise more frequently in labour markets than in the markets for goods and services.
D) in the labour market, firms are suppliers while households are demanders.
A) the demand in the labour market is inelastic; the demand for goods and services may be elastic or inelastic.
B) the supply of labour is perfectly inelastic because the quantity supplied is constant. The elasticity of supply for goods and services is different in different markets.
C) concepts of fairness arise more frequently in labour markets than in the markets for goods and services.
D) in the labour market, firms are suppliers while households are demanders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The demand for labour depends primarily on the additional output produced as a result of hiring an additional worker and
A) the additional revenue received from selling the output produced as a result of hiring an additional worker.
B) the payment made to the worker for producing the additional output.
C) the elasticity of demand for the output produced by the worker.
D) the number of workers willing to produce the additional output.
A) the additional revenue received from selling the output produced as a result of hiring an additional worker.
B) the payment made to the worker for producing the additional output.
C) the elasticity of demand for the output produced by the worker.
D) the number of workers willing to produce the additional output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Let MP = marginal product,P = output price,and W = wage,then the equation that represents a situation where a competitive firm should lay off some workers to maximise profits is
A) P × MP = W.
B) P × MP > W.
C) P × MP < W.
D) MP × W = P.
A) P × MP = W.
B) P × MP > W.
C) P × MP < W.
D) MP × W = P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the legal sector in America,some practice areas have declined in recent years.For example,personal-injury and medical-malpractice cases have been undercut by state laws limiting class-action suits,out-of-state plaintiffs and payouts on damages,and securities class-action litigation has declined in part because of a buoyant stock market.How does this affect the market for lawyers?
A) The demand for lawyers shifts to the left.
B) The supply of lawyers shifts to the left.
C) The quantity of lawyers demanded decreases and this is represented by a movement along the demand curve.
D) Both the demand and supply curves decrease.
A) The demand for lawyers shifts to the left.
B) The supply of lawyers shifts to the left.
C) The quantity of lawyers demanded decreases and this is represented by a movement along the demand curve.
D) Both the demand and supply curves decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Table 10-2

Refer to Table 10-2.The marginal profit from hiring the second unit of labour is
A) $4200.
B) $1960.
C) $1800.
D) $1450.

Refer to Table 10-2.The marginal profit from hiring the second unit of labour is
A) $4200.
B) $1960.
C) $1800.
D) $1450.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A decrease in the wage rate causes
A) an increase in the quantity of labour demanded.
B) a rightward shift of the firm's labour demand curve.
C) a leftward shift of the firm's labour demand curve.
D) a decrease in labour's productivity.
A) an increase in the quantity of labour demanded.
B) a rightward shift of the firm's labour demand curve.
C) a leftward shift of the firm's labour demand curve.
D) a decrease in labour's productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An increase in the wage rate causes
A) a rightward shift of the firm's labour demand curve.
B) a leftward shift of the firm's labour demand curve.
C) a decrease in the quantity of labour demanded.
D) an increase in labour's marginal productivity.
A) a rightward shift of the firm's labour demand curve.
B) a leftward shift of the firm's labour demand curve.
C) a decrease in the quantity of labour demanded.
D) an increase in labour's marginal productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Let MP = marginal product,P = output price,and W = wage,then the equation that represents the condition where a competitive firm would hire another worker is
A) P × MP = W.
B) P × MP < W.
C) P × MP > W.
D) P × W > MP.
A) P × MP = W.
B) P × MP < W.
C) P × MP > W.
D) P × W > MP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The benefit to the firm from hiring one additional worker is called the
A) marginal revenue product of labour.
B) marginal revenue.
C) marginal profit.
D) total revenue.
A) marginal revenue product of labour.
B) marginal revenue.
C) marginal profit.
D) total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following describes a difference between the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour?
A) The marginal product of labour declines as each additional worker is hired because of the law of diminishing returns. The marginal revenue product of labour declines as each additional worker is hired because of diseconomies of scale.
B) The marginal product of labour declines as each additional worker is hired because of the law of diminishing returns. The marginal revenue product increases as each additional worker is hired because of increases in the productivity of labour.
C) The marginal product of labour is inelastic. The marginal revenue product of labour is elastic.
D) The marginal product of labour measures the change in output as additional workers are hired. The marginal revenue product measures the change in revenue as additional workers are hired.
A) The marginal product of labour declines as each additional worker is hired because of the law of diminishing returns. The marginal revenue product of labour declines as each additional worker is hired because of diseconomies of scale.
B) The marginal product of labour declines as each additional worker is hired because of the law of diminishing returns. The marginal revenue product increases as each additional worker is hired because of increases in the productivity of labour.
C) The marginal product of labour is inelastic. The marginal revenue product of labour is elastic.
D) The marginal product of labour measures the change in output as additional workers are hired. The marginal revenue product measures the change in revenue as additional workers are hired.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Table 10-3
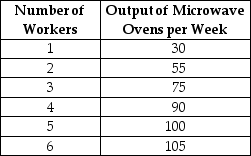 Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.
Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.
Refer to Table 10-3.What is the amount of profit added as a result of hiring the 4th worker?
A) $7200
B) $1200
C) $800
D) $400
 Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.
Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.Refer to Table 10-3.What is the amount of profit added as a result of hiring the 4th worker?
A) $7200
B) $1200
C) $800
D) $400

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The demand curve for labour is also
A) the demand curve for the output produced with labour since the demand for labour is a derived demand.
B) the marginal product of labour curve.
C) the marginal revenue product of labour curve.
D) the supply curve for the output labour is used to produce.
A) the demand curve for the output produced with labour since the demand for labour is a derived demand.
B) the marginal product of labour curve.
C) the marginal revenue product of labour curve.
D) the supply curve for the output labour is used to produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Figure 10-2 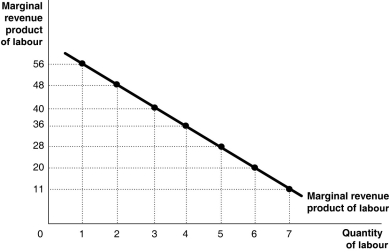 Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.
Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.
Refer to Figure 10-2.If Becca can sell her bracelets at $3 each,what is the marginal product of the 4th worker?
A) $36
B) 12 bracelets
C) 36 bracelets
D) $144
 Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.
Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.Refer to Figure 10-2.If Becca can sell her bracelets at $3 each,what is the marginal product of the 4th worker?
A) $36
B) 12 bracelets
C) 36 bracelets
D) $144

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
As more output is produced,the marginal product of labour declines
A) because of the law of diminishing returns.
B) if firms reduce the wage paid to labour.
C) if the firm's output supply curve is inelastic.
D) because the firm's marginal revenue declines.
A) because of the law of diminishing returns.
B) if firms reduce the wage paid to labour.
C) if the firm's output supply curve is inelastic.
D) because the firm's marginal revenue declines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A firm's demand curve for labour slopes downwards because
A) of the law of diminishing marginal returns.
B) firms supply less labour as the wage rate rises.
C) workers supply less labour services as the wage rate falls.
D) of rising marginal product.
A) of the law of diminishing marginal returns.
B) firms supply less labour as the wage rate rises.
C) workers supply less labour services as the wage rate falls.
D) of rising marginal product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An increase in the demand for orthodontic services leads to
A) an increase in the supply of orthodontists.
B) lower prices for orthodontic care.
C) an increase in the demand for orthodontists.
D) a rise in the rates of dental insurance.
A) an increase in the supply of orthodontists.
B) lower prices for orthodontic care.
C) an increase in the demand for orthodontists.
D) a rise in the rates of dental insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The term 'derived demand' refers to
A) the demand for financial products called derivatives.
B) the demand for a factor of production that is derived from the demand for the good the factor produces.
C) a firm's estimated demand curve derived from sales data.
D) a demand curve that derives from the availability of resources.
A) the demand for financial products called derivatives.
B) the demand for a factor of production that is derived from the demand for the good the factor produces.
C) a firm's estimated demand curve derived from sales data.
D) a demand curve that derives from the availability of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure 10-2  Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.
Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.
Refer to Figure 10-2.Suppose the market price of bracelets falls to $2.What happens to the curve given in the diagram?
A) Nothing, because labour's productivity has not changed.
B) There will be a movement along the curve.
C) The curve shifts to the left.
D) We cannot answer the question without knowing if Becca would want to hire more workers.
 Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.
Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.Refer to Figure 10-2.Suppose the market price of bracelets falls to $2.What happens to the curve given in the diagram?
A) Nothing, because labour's productivity has not changed.
B) There will be a movement along the curve.
C) The curve shifts to the left.
D) We cannot answer the question without knowing if Becca would want to hire more workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A firm should hire more workers to increase its profits if
A) the marginal product of labour is greater than the wage the firm will pay these workers.
B) the wage rate is less than the marginal revenue product of labour.
C) there is enough capital and other resources for the workers to use.
D) the demand for labour is elastic.
A) the marginal product of labour is greater than the wage the firm will pay these workers.
B) the wage rate is less than the marginal revenue product of labour.
C) there is enough capital and other resources for the workers to use.
D) the demand for labour is elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
For a firm that is a price taker in the market for labour,the marginal revenue product of labour equals the
A) marginal product of labour multiplied by the wage rate.
B) marginal product of labour multiplied by the product price.
C) marginal product of labour divided by the wage rate.
D) marginal product of labour multiplied by the marginal cost of production.
A) marginal product of labour multiplied by the wage rate.
B) marginal product of labour multiplied by the product price.
C) marginal product of labour divided by the wage rate.
D) marginal product of labour multiplied by the marginal cost of production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Holding the price of a firm's output constant,if the marginal product of labour increases
A) the marginal revenue product of labour decreases.
B) the marginal revenue product of labour also increases.
C) the marginal products of other inputs also increase.
D) the marginal revenue product of labour may increase or decrease.
A) the marginal revenue product of labour decreases.
B) the marginal revenue product of labour also increases.
C) the marginal products of other inputs also increase.
D) the marginal revenue product of labour may increase or decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The change in a firm's revenue as a result of hiring one more worker
A) is the definition of the marginal product of labour.
B) is equal to the firm's marginal cost.
C) is the definition of the marginal revenue product of labour.
D) will be negative if the demand for the firm's output is inelastic.
A) is the definition of the marginal product of labour.
B) is equal to the firm's marginal cost.
C) is the definition of the marginal revenue product of labour.
D) will be negative if the demand for the firm's output is inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Table 10-3
 Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.
Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.
Refer to Table 10-3.What is the amount of revenue added as a result of hiring the 4th worker?
A) $1200
B) $7200
C) 15 microwaves
D) 90 microwaves
 Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.
Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.Refer to Table 10-3.What is the amount of revenue added as a result of hiring the 4th worker?
A) $1200
B) $7200
C) 15 microwaves
D) 90 microwaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The marginal revenue product of labour is defined as
A) the change in the firm's revenue as a result of selling one more unit of output.
B) the change in the firm's output as a result of hiring one more worker.
C) the change in the firm's profit as a result of hiring one more worker.
D) the change in the firm's revenue as a result of hiring one more worker.
A) the change in the firm's revenue as a result of selling one more unit of output.
B) the change in the firm's output as a result of hiring one more worker.
C) the change in the firm's profit as a result of hiring one more worker.
D) the change in the firm's revenue as a result of hiring one more worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The marginal product of labour is
A) the payment made to workers for their contribution to the output they produce.
B) equal to the demand for labour.
C) the change in a firm's revenue as a result of hiring one more worker.
D) the additional output a firm produces as a result of hiring one more worker.
A) the payment made to workers for their contribution to the output they produce.
B) equal to the demand for labour.
C) the change in a firm's revenue as a result of hiring one more worker.
D) the additional output a firm produces as a result of hiring one more worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Table 10-3
 Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.
Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.
Refer to Table 10-3.What is Hotspur's profit-maximising quantity of labour?
A) 2 workers
B) 3 workers
C) 5 workers
D) 6 workers
 Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.
Hotspur Incorporated, a manufacturer of microwave ovens, is a price taker in its input and output markets. The firm hires labour at a constant wage rate of $800 per week and sells microwave ovens at a constant price of $80. Table 10-3 shows the relationship between the quantity of labour it hires and the quantity of microwave ovens it produces.Refer to Table 10-3.What is Hotspur's profit-maximising quantity of labour?
A) 2 workers
B) 3 workers
C) 5 workers
D) 6 workers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Marginal revenue product falls as more labour is hired because
A) the price of the product must fall for a perfectly competitive firm to sell more.
B) the wage rate rises as more workers work more hours.
C) the marginal product of labour is negative as additional units of labour are hired.
D) the marginal product of labour falls as a result of the law of diminishing returns.
A) the price of the product must fall for a perfectly competitive firm to sell more.
B) the wage rate rises as more workers work more hours.
C) the marginal product of labour is negative as additional units of labour are hired.
D) the marginal product of labour falls as a result of the law of diminishing returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Figure 10-2  Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.
Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.
Refer to Figure 10-2.If the wage rate is $20,how many workers should Becca hire?
A) 6
B) 5
C) 4
D) 3
 Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.
Figure 10-2 shows the marginal revenue product for Becca's Baubles, a producer of hand-beaded bracelets.Refer to Figure 10-2.If the wage rate is $20,how many workers should Becca hire?
A) 6
B) 5
C) 4
D) 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An increase in the price of grape juice causes an increase in the marginal revenue product of labour used to produce grape juice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Table 10-4
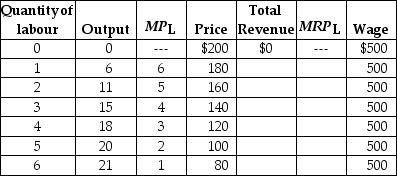 Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.
Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.
Refer to Table 10-4.What are the price and quantity of workers that result in the maximum amount of revenue Apple would earn from selling iPods?
A) $180; 1
B) $140; 2
C) $120; 2
D) $120; 4
 Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.
Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.Refer to Table 10-4.What are the price and quantity of workers that result in the maximum amount of revenue Apple would earn from selling iPods?
A) $180; 1
B) $140; 2
C) $120; 2
D) $120; 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An increase in the supply of capital,which is a complement to labour,will lead to
A) a decrease in the quantity of labour demanded.
B) an increase in the demand for labour.
C) a decrease in the demand for labour.
D) an increase in the quantity of labour demanded.
A) a decrease in the quantity of labour demanded.
B) an increase in the demand for labour.
C) a decrease in the demand for labour.
D) an increase in the quantity of labour demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The marginal product of labour curve is the demand curve for labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Suppose a competitive firm is paying a wage of $12 an hour.Assume that labour is the only input.If hiring another worker would increase output by four units per hour,then to maximise profits the firm should
A) not change the number of workers it currently hires.
B) hire the extra worker.
C) lay off some workers.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) not change the number of workers it currently hires.
B) hire the extra worker.
C) lay off some workers.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The demand for labour is a derived demand.Explain what is meant by the term 'derived demand.'

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What are the five most important variables that cause the market demand curve for labour to shift?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The market demand curve for labour
A) is determined by adding up the quantity of labour demanded by each firm at each wage, holding constant the other variables that affect the willingness of firms to hire workers.
B) is the same as the market demand curve for the product labour produces because it is a derived demand.
C) is determined by adding up the demand for labour by each firm at each wage, holding constant the other variables that affect the willingness of firms to hire workers.
D) is perfectly inelastic because there is a finite number of workers in the market for labour.
A) is determined by adding up the quantity of labour demanded by each firm at each wage, holding constant the other variables that affect the willingness of firms to hire workers.
B) is the same as the market demand curve for the product labour produces because it is a derived demand.
C) is determined by adding up the demand for labour by each firm at each wage, holding constant the other variables that affect the willingness of firms to hire workers.
D) is perfectly inelastic because there is a finite number of workers in the market for labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A profit-maximising firm should hire workers up to the point where labour's marginal revenue product equals the wage rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The marginal product of labour is the increase in output as a result of hiring an additional worker while the marginal revenue product of labour is the increase in profit as a result of hiring an additional worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Table 10-4
 Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.
Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.
Refer to Table 10-4.What are the price and quantity of workers that result in the maximum amount of profit Apple would earn from selling iPods?
A) $140; 2
B) $160; 2
C) $140; 3
D) $180; 1
 Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.
Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.Refer to Table 10-4.What are the price and quantity of workers that result in the maximum amount of profit Apple would earn from selling iPods?
A) $140; 2
B) $160; 2
C) $140; 3
D) $180; 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Technological advancements that increase labour's productivity shift the labour supply curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following factors will not cause the labour demand curve to shift?
A) Increases in human capital
B) Changes in technology
C) Change in the price of the product produced with labour
D) The wage rate
A) Increases in human capital
B) Changes in technology
C) Change in the price of the product produced with labour
D) The wage rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A decrease in the amount of human capital acquired by workers will lead to a decrease in the supply of labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is not held constant along a firm's demand curve for labour?
A) The quantity of other inputs used by the firm
B) The wage rate
C) Changes in technology
D) The price of the product produced by the firm
A) The quantity of other inputs used by the firm
B) The wage rate
C) Changes in technology
D) The price of the product produced by the firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
An increase in a perfectly competitive firm's demand for labour could be caused by
A) a decrease in the market wage rate.
B) an increase in the amount of human capital among the labour force.
C) an increase in the supply of labour.
D) a decrease in the market price of the product the firm produces.
A) a decrease in the market wage rate.
B) an increase in the amount of human capital among the labour force.
C) an increase in the supply of labour.
D) a decrease in the market price of the product the firm produces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Suppose a competitive firm is paying a wage of $12 an hour and sells its product at $3 per unit.Assume that labour is the only input.If the last worker hired produces four units of output per hour,then to maximise profits the firm should
A) not change the number of workers it currently hires.
B) lay off some workers.
C) hire another worker.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
A) not change the number of workers it currently hires.
B) lay off some workers.
C) hire another worker.
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Labour demand is considered a derived demand because producers do not demand labour for itself but only because labour is used to produce output that consumers desire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Table 10-4
 Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.
Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.
Refer to Table 10-4.What are the quantity of labour and marginal revenue product of labour that will maximise the profit Apple would earn from selling iPods?
A) 2; $160
B) 3; $340
C) 2; $680
D) 3; $140
 Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.
Table 10-4 lists data for the production of Apple iPods. Apple is assumed to be a price maker, so to increase its sales of iPods the firm must lower its price. MPL and MRPL refer to the marginal product of labour and the marginal revenue product of labour, respectively.Refer to Table 10-4.What are the quantity of labour and marginal revenue product of labour that will maximise the profit Apple would earn from selling iPods?
A) 2; $160
B) 3; $340
C) 2; $680
D) 3; $140

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An increase in the supply of capital,which is a substitute to labour,will lead to a decrease in the demand for labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 253 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



