Deck 30: The International Financial System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/139
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 30: The International Financial System
1
China's exchange rate system from 1994 through 2005 is an example of
A) a floating exchange rate system.
B) a managed float exchange rate system.
C) a fixed exchange rate system.
D) a flexible exchange rate system.
E) the Bretton Woods System.
A) a floating exchange rate system.
B) a managed float exchange rate system.
C) a fixed exchange rate system.
D) a flexible exchange rate system.
E) the Bretton Woods System.
C
2
Under the Bretton Woods exchange rate system,set up in 1944,which of the following was true?
A) Americans could sell their dollars to the American government in exchange for gold.
B) Americans could sell their dollars to the American government in exchange for silver.
C) Americans could sell their dollars to foreign central banks in exchange for gold.
D) Foreign central banks could sell their dollars to the American government in exchange for gold.
A) Americans could sell their dollars to the American government in exchange for gold.
B) Americans could sell their dollars to the American government in exchange for silver.
C) Americans could sell their dollars to foreign central banks in exchange for gold.
D) Foreign central banks could sell their dollars to the American government in exchange for gold.
D
3
In the United States today,how much gold will the Federal Reserve give you in exchange for $1?
A) none
B) $1 worth of gold (based on the market price of an ounce of gold at the time you redeem the gold)
C) 1 ounce of gold
D) 1/35th of an ounce of gold
A) none
B) $1 worth of gold (based on the market price of an ounce of gold at the time you redeem the gold)
C) 1 ounce of gold
D) 1/35th of an ounce of gold
A
4
The gold standard is an example of
A) a floating exchange rate system.
B) a managed float exchange rate system.
C) a fixed exchange rate system.
D) a flexible exchange rate system.
E) the Bretton Woods System.
A) a floating exchange rate system.
B) a managed float exchange rate system.
C) a fixed exchange rate system.
D) a flexible exchange rate system.
E) the Bretton Woods System.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Airbus is a passenger aircraft manufacturer based in Europe,but like the rest of the global aerospace industry,conducts is business in U.S.dollars.Suppose Airbus sells an aircraft to Air France,and Air France pays Airbus in U.S.dollars.If the value of the U.S.dollar rises relative to the euro,Airbus's profits in Europe will ________ because it will receive ________ when it converts the dollars it earns from the sale into euros.
A) rise; more
B) rise; less
C) fall; more
D) fall; less
A) rise; more
B) rise; less
C) fall; more
D) fall; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The gold in Fort Knox backs all U.S.currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
During what period of time did the United States most consistently adhere to the gold standard?
A) from the nineteenth century until the 1930s
B) from the eighteenth century until the nineteenth century
C) from 1914 until 1929
D) from 1944 until 1980
A) from the nineteenth century until the 1930s
B) from the eighteenth century until the nineteenth century
C) from 1914 until 1929
D) from 1944 until 1980

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If a country's currency is determined only by the demand and supply for that country's currency,the country is said to have a
A) floating exchange rate.
B) fixed exchange rate.
C) gold standard.
D) managed float.
A) floating exchange rate.
B) fixed exchange rate.
C) gold standard.
D) managed float.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If currencies around the world are based on the gold standard,and Japan raises the amount of gold for which the yen will trade,then holding all else constant,
A) the yen will depreciate against the dollar.
B) the yen will appreciate against the dollar.
C) the value of the yen relative to the dollar will stay constant.
D) the value of U.S. exports to Japan in terms of the yen will increase.
A) the yen will depreciate against the dollar.
B) the yen will appreciate against the dollar.
C) the value of the yen relative to the dollar will stay constant.
D) the value of U.S. exports to Japan in terms of the yen will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The United States abandoned the Bretton Woods system of exchange rates in
A) the 1920s.
B) the 1940s.
C) the 1970s.
D) the 1990s.
A) the 1920s.
B) the 1940s.
C) the 1970s.
D) the 1990s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When the value of a currency is determined mostly by demand and supply,but with occasional government intervention,the exchange rate system is defined as
A) fixed.
B) floating.
C) managed float.
D) Bretton Woods.
A) fixed.
B) floating.
C) managed float.
D) Bretton Woods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In what year was the Bretton Woods system of currency exchange set up?
A) 1912
B) 1924
C) 1944
D) 1969
A) 1912
B) 1924
C) 1944
D) 1969

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Under the gold standard,to increase the money supply in the country,the government must
A) simply print more currency.
B) have enough gold to back up the increase in the money supply.
C) buy foreign currencies with dollars to increase foreign currency reserves.
D) increase the value of the country's currency on foreign exchange markets.
A) simply print more currency.
B) have enough gold to back up the increase in the money supply.
C) buy foreign currencies with dollars to increase foreign currency reserves.
D) increase the value of the country's currency on foreign exchange markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
You decide to work in Japan for the next 10 years,accumulate some savings,then move back to the United States and convert your savings from yen to dollars.At the time of your move,economists predict that consumers in the United States have reignited their love of Japanese products,especially hybrid cars,and expect that this strong preference for Japanese products will continue for the next decade.How should this influence your decision to work and save in Japan?
A) You should be discouraged as the growing U.S. preference for Japanese goods should increase the value of the yen to the dollar and decrease the value of your savings when converted to dollars.
B) You should be discouraged as the growing U.S. preference for Japanese goods should decrease the value of the yen to the dollar and decrease the value of your savings when converted to dollars.
C) You should be encouraged as the growing U.S. preference for Japanese goods should decrease the value of the yen to the dollar and raise the value of your savings when converted to dollars.
D) You should be encouraged as the growing U.S. preference for Japanese goods should increase the value of the yen to the dollar and raise the value of your savings when converted to dollars.
A) You should be discouraged as the growing U.S. preference for Japanese goods should increase the value of the yen to the dollar and decrease the value of your savings when converted to dollars.
B) You should be discouraged as the growing U.S. preference for Japanese goods should decrease the value of the yen to the dollar and decrease the value of your savings when converted to dollars.
C) You should be encouraged as the growing U.S. preference for Japanese goods should decrease the value of the yen to the dollar and raise the value of your savings when converted to dollars.
D) You should be encouraged as the growing U.S. preference for Japanese goods should increase the value of the yen to the dollar and raise the value of your savings when converted to dollars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The exchange rate system agreed to in 1944 in which the U.S.government agreed to buy or sell gold at a fixed price of $35 per ounce is referred to as
A) the gold standard.
B) the Bretton Woods System.
C) a floating currency standard.
D) a flexible exchange rate system.
A) the gold standard.
B) the Bretton Woods System.
C) a floating currency standard.
D) a flexible exchange rate system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Fluctuating exchange rates can alter a multinational firm's profits and losses.The U.S.corporation,Motorola,produces cell phones and sells cell phones in Mexico.If the dollar depreciates against the peso,then Motorola's revenues from these operations should ________ and its costs from these operations should ________.
A) rise; fall
B) rise; rise
C) fall; fall
D) fall; rise
A) rise; fall
B) rise; rise
C) fall; fall
D) fall; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose an economy's exchange rate system is the gold standard and vast tracks of gold are discovered,as is what happened in the United States in 1849.If the economy is at full employment,what should this discovery do?
A) It should raise the money supply but have no impact on the price level.
B) It should raise the money supply and cause inflation.
C) It should raise the money supply and cause disinflation.
D) It should lower the money supply and cause deflation.
E) it should not change the money supply.
A) It should raise the money supply but have no impact on the price level.
B) It should raise the money supply and cause inflation.
C) It should raise the money supply and cause disinflation.
D) It should lower the money supply and cause deflation.
E) it should not change the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The current exchange rate system in the United States is best described as a
A) silver standard.
B) managed float exchange rate system.
C) fixed exchange rate system.
D) gold standard.
A) silver standard.
B) managed float exchange rate system.
C) fixed exchange rate system.
D) gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Under which exchange rate system was a dollar redeemable for gold only if the dollar was presented by a foreign central bank?
A) the gold standard
B) a managed float exchange rate system
C) the Bretton Woods System
D) a fiat system
A) the gold standard
B) a managed float exchange rate system
C) the Bretton Woods System
D) a fiat system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Why did the United States abandon the gold standard in the 1930s?
A) The government wanted to rapidly expand the money supply in response to the Great Depression.
B) The government wanted to move away from a floating exchange rate system to a fixed exchange rate system.
C) The Treasury Department in the United States found it was cheaper to print paper money instead of gold coins.
D) New sources of gold were discovered, so the price of gold plummeted, dramatically reducing the value of the dollar.
A) The government wanted to rapidly expand the money supply in response to the Great Depression.
B) The government wanted to move away from a floating exchange rate system to a fixed exchange rate system.
C) The Treasury Department in the United States found it was cheaper to print paper money instead of gold coins.
D) New sources of gold were discovered, so the price of gold plummeted, dramatically reducing the value of the dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Expanding,contracting,and managing the money supply is easier for a central bank under the gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Purchasing power parity is the theory that,in the long run,exchange rates should be at a level such that equivalent amounts of any country's currency
A) will equalize nominal interest rates across countries.
B) are valued inversely relative to the size of its GDP.
C) should earn the same real rate of return.
D) allow one to buy the same amount of goods and services.
A) will equalize nominal interest rates across countries.
B) are valued inversely relative to the size of its GDP.
C) should earn the same real rate of return.
D) allow one to buy the same amount of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
You are a Canadian citizen who works in Toronto,Canada and owns a winter home in Phoenix,Arizona.When you spend the winters in Phoenix,an increase in the value of the Canadian dollar relative to the U.S.dollar should
A) help you as each Canadian dollar of your salary is now worth more U.S. dollars.
B) hurt you as each Canadian dollar of your salary is now worth less U.S. dollars.
C) hurt you as it is now more expensive to live in Phoenix since the Canadian dollar appreciation.
D) help you as it is now less expensive to live in Canada since the Canadian dollar appreciation.
A) help you as each Canadian dollar of your salary is now worth more U.S. dollars.
B) hurt you as each Canadian dollar of your salary is now worth less U.S. dollars.
C) hurt you as it is now more expensive to live in Phoenix since the Canadian dollar appreciation.
D) help you as it is now less expensive to live in Canada since the Canadian dollar appreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What factors are not important in determining exchange rate fluctuations in the long run?
A) relative price levels across countries
B) relative rates of productivity growth across countries
C) preferences for domestic and foreign goods across countries
D) speculating in currency markets
A) relative price levels across countries
B) relative rates of productivity growth across countries
C) preferences for domestic and foreign goods across countries
D) speculating in currency markets

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In 2011,a number of Canadians purchased homes in Arizona.Which of the following would not be a possible explanation for this?
A) The value of the Canadian dollar relative to the U.S. dollar increased during this time.
B) The U.S. dollar depreciated during this time.
C) The Canadian dollar appreciated during this time.
D) The U.S. dollar appreciated relative to the Canadian dollar during this time.
A) The value of the Canadian dollar relative to the U.S. dollar increased during this time.
B) The U.S. dollar depreciated during this time.
C) The Canadian dollar appreciated during this time.
D) The U.S. dollar appreciated relative to the Canadian dollar during this time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If two countries adhere to a gold standard,the exchange rate for their currencies is fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A Big Mac costs $4.00 in the United States and 9.00 reals in Brazil.If the exchange rate is 2 reals per dollar,purchasing power parity predicts that
A) the dollar will appreciate as the demand for dollars falls in the long run.
B) the dollar will appreciate as the supply of dollars falls in the long run.
C) the dollar will depreciate as the demand for dollars falls in the long run.
D) the dollar will depreciate as the supply of dollars rises in the long run.
A) the dollar will appreciate as the demand for dollars falls in the long run.
B) the dollar will appreciate as the supply of dollars falls in the long run.
C) the dollar will depreciate as the demand for dollars falls in the long run.
D) the dollar will depreciate as the supply of dollars rises in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An increase in the value of the U.S.dollar will
A) reduce Canadian demand for winter homes in Arizona.
B) increase Canadian demand for winter homes in Arizona.
C) reduce the cost of homes in Arizona for Canadian buyers.
D) increase the cost of homes in Arizona for American buyers.
A) reduce Canadian demand for winter homes in Arizona.
B) increase Canadian demand for winter homes in Arizona.
C) reduce the cost of homes in Arizona for Canadian buyers.
D) increase the cost of homes in Arizona for American buyers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The currency adopted by most countries in Western Europe is referred to as the
A) euro.
B) Eurodollar.
C) yen.
D) pound.
A) euro.
B) Eurodollar.
C) yen.
D) pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is most important in explaining exchange rate fluctuations in the short run?
A) relative price levels across countries
B) preferences for domestic and foreign goods
C) interest rates
D) relative rates of productivity growth across countries
A) relative price levels across countries
B) preferences for domestic and foreign goods
C) interest rates
D) relative rates of productivity growth across countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If one U.S.dollar could be exchanged for one Canadian dollar in 1970,and one U.S.dollar can now be exchanged for 1.13 Canadian dollars,which of the following is true?
A) The U.S. dollar lost value against the Canadian dollar.
B) The Canadian dollar lost value against the U.S. dollar.
C) The Canadian dollar gained value against the U.S. dollar.
D) Both A and C are true.
A) The U.S. dollar lost value against the Canadian dollar.
B) The Canadian dollar lost value against the U.S. dollar.
C) The Canadian dollar gained value against the U.S. dollar.
D) Both A and C are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
How were exchange rates determined under the gold standard? How did the Bretton Woods system differ from the gold standard?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the exchange rate between the U.S.dollar and the Indian rupee (rupees per dollar)is greater than the relative purchasing power between the two countries,which of the following would be true?
A) There are opportunities for profit by purchasing goods in India and then selling them in the United States.
B) Purchasing power parity predicts that the value of the dollar will rise as traders take advantage of arbitrage opportunities.
C) Purchasing power parity predicts that the dollar is undervalued as traders take advantage of arbitrage opportunities.
D) There are no arbitrage opportunities for which traders can take advantage.
A) There are opportunities for profit by purchasing goods in India and then selling them in the United States.
B) Purchasing power parity predicts that the value of the dollar will rise as traders take advantage of arbitrage opportunities.
C) Purchasing power parity predicts that the dollar is undervalued as traders take advantage of arbitrage opportunities.
D) There are no arbitrage opportunities for which traders can take advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A Big Mac costs $4.00 in the United States and 9.00 reals in Brazil.If the exchange rate is 2 reals per dollar,purchasing power parity predicts that
A) the dollar is undervalued.
B) the dollar is overvalued.
C) the real is undervalued.
D) both B and C are correct.
A) the dollar is undervalued.
B) the dollar is overvalued.
C) the real is undervalued.
D) both B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A Big Mac costs $4.00 in the United States and 9.00 reals in Brazil.If the exchange rate is 2 reals per dollar,what is the dollar cost of a Big Mac in Brazil?
A) $0.89
B) $2.25
C) $4.50
D) $8.00
A) $0.89
B) $2.25
C) $4.50
D) $8.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The current exchange rate system has which of the following characteristics?
A) The United States allows the dollar to float against other major currencies.
B) All developing countries allow their currencies to float against the dollar and other major currencies.
C) The countries of the European Union have adopted the gold standard.
D) Several developing countries in Asia have adopted the Bretton Woods system.
E) The current global foreign exchange system is a fixed system.
A) The United States allows the dollar to float against other major currencies.
B) All developing countries allow their currencies to float against the dollar and other major currencies.
C) The countries of the European Union have adopted the gold standard.
D) Several developing countries in Asia have adopted the Bretton Woods system.
E) The current global foreign exchange system is a fixed system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What are the three main exchange rate systems,and how do they operate?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
From the beginning of 1973 until October 2011,the value of the dollar has ________ relative to the Canadian dollar and ________ relative to the Japanese yen.
A) appreciated; appreciated
B) appreciated; depreciated
C) depreciated; appreciated
D) depreciated; depreciated
A) appreciated; appreciated
B) appreciated; depreciated
C) depreciated; appreciated
D) depreciated; depreciated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If the purchasing power of a dollar is greater than the purchasing power of the yen,purchasing power parity would predict that
A) in the short run, exchange rates will move to equalize the purchasing power of the dollar and the yen.
B) in the long run, exchange rates will move to equalize the purchasing power of the dollar and the yen.
C) in the long run, interest rates will move to equalize the purchasing power of the dollar and the yen.
D) in the short run, interest rates will move to equalize the purchasing power of the dollar and the yen.
A) in the short run, exchange rates will move to equalize the purchasing power of the dollar and the yen.
B) in the long run, exchange rates will move to equalize the purchasing power of the dollar and the yen.
C) in the long run, interest rates will move to equalize the purchasing power of the dollar and the yen.
D) in the short run, interest rates will move to equalize the purchasing power of the dollar and the yen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Managed float exchange systems were abandoned with the implementation of the gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If the GDP deflator in the United States is 114,and the GDP deflator in Ukraine is 142,which of the following exchange rates would the theory of purchasing power parity predict in the long run? (The Ukrainian currency is the hryvnia.)
A) 0.80 hryvnias per dollar
B) 1.25 hryvnias per dollar
C) 2.80 hryvnias per dollar
D) 28 hryvnias per dollar
A) 0.80 hryvnias per dollar
B) 1.25 hryvnias per dollar
C) 2.80 hryvnias per dollar
D) 28 hryvnias per dollar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
How will the exchange rate (foreign currency per dollar)respond to an increase in the relative rate of productivity growth in the United States in the long run?
A) Exchange rates will rise.
B) Exchange rates will fall.
C) Exchange rates will be unaffected by changes in the relative rate of productivity growth in the United States, both in the short run and in the long run.
D) The exchange rate will be affected in the short run, but not in the long run.
A) Exchange rates will rise.
B) Exchange rates will fall.
C) Exchange rates will be unaffected by changes in the relative rate of productivity growth in the United States, both in the short run and in the long run.
D) The exchange rate will be affected in the short run, but not in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If relative purchasing power between the United States and Argentina is 3.22 pesos per dollar,under which circumstances would we say that the dollar is "overvalued"?
A) if the actual exchange rate between the dollar and the Argentinean peso is 3.22 pesos per dollar
B) if the actual exchange rate between the dollar and the Argentinean peso is 4 pesos per dollar
C) if the actual exchange rate between the dollar and the Argentinean peso is 0.22 pesos per dollar
D) if the actual exchange rate between the dollar and the Argentinean peso is 3 pesos per dollar
A) if the actual exchange rate between the dollar and the Argentinean peso is 3.22 pesos per dollar
B) if the actual exchange rate between the dollar and the Argentinean peso is 4 pesos per dollar
C) if the actual exchange rate between the dollar and the Argentinean peso is 0.22 pesos per dollar
D) if the actual exchange rate between the dollar and the Argentinean peso is 3 pesos per dollar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the purchasing power of the dollar is greater than the purchasing power of the euro,purchasing power parity predicts that the exchange rate will
A) increase if the exchange rate is greater than 1 euro per dollar.
B) decrease if the exchange rate is less than 1 euro per dollar.
C) be equal to the relative purchasing power across the currencies in the long run.
D) not fluctuate and stay constant in the long run.
A) increase if the exchange rate is greater than 1 euro per dollar.
B) decrease if the exchange rate is less than 1 euro per dollar.
C) be equal to the relative purchasing power across the currencies in the long run.
D) not fluctuate and stay constant in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following explains why purchasing power parity does not completely explain long-run fluctuations in exchange rates?
A) Some goods and services produced in any country are not traded internationally.
B) Consumer preferences for goods and services across countries are very similar.
C) Most countries do not impose barriers to trade.
D) Most countries have free markets with little, if any, government regulation.
A) Some goods and services produced in any country are not traded internationally.
B) Consumer preferences for goods and services across countries are very similar.
C) Most countries do not impose barriers to trade.
D) Most countries have free markets with little, if any, government regulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The "Big Mac Theory of Exchange Rates" tests the accuracy of the purchasing power parity theory.In July 2011,the Economist reported that the average price of a Big Mac in the U.S.was $4.07.In Mexico,the average price of a Big Mac at that time was 32 pesos.What is the "implied exchange rate" between the peso and the dollar?
A) 1.30 pesos per dollar
B) 4.17 pesos per dollar
C) 7.86 pesos per dollar
D) 12.72 pesos per dollar
A) 1.30 pesos per dollar
B) 4.17 pesos per dollar
C) 7.86 pesos per dollar
D) 12.72 pesos per dollar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What explains the appreciation of the Japanese yen relative to the U.S.dollar from 1970 to the early 1990s?
A) Japanese productivity rose faster than U.S. productivity.
B) Japanese inflation rose faster than U.S. inflation.
C) U.S. consumers reduced their preferences for Japanese goods.
D) High tariffs and restrictive quotas in the United States caused the value of the dollar to decline.
A) Japanese productivity rose faster than U.S. productivity.
B) Japanese inflation rose faster than U.S. inflation.
C) U.S. consumers reduced their preferences for Japanese goods.
D) High tariffs and restrictive quotas in the United States caused the value of the dollar to decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Suppose the GDP deflator in the United States is 125 and the GDP deflator in Japan is 100.Also assume the United States has trade barriers on Japanese goods in the form of quotas.What does this imply about the exchange rate of yen per dollar under the theory of purchasing power parity in the long run?
A) The exchange rate of yen per dollar will be equal to 1.25.
B) The exchange rate of yen per dollar will be greater than 0.8.
C) The exchange rate of yen per dollar will be equal to 0.8.
D) The exchange rate of yen per dollar will be less than 0.8.
A) The exchange rate of yen per dollar will be equal to 1.25.
B) The exchange rate of yen per dollar will be greater than 0.8.
C) The exchange rate of yen per dollar will be equal to 0.8.
D) The exchange rate of yen per dollar will be less than 0.8.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the average productivity of American firms is rising more quickly than the average productivity of Indian firms,which of the following would you expect to see? (India's currency is the rupee.)
A) an increase in the value of the rupee relative to the dollar
B) a decrease in the prices of Indian products
C) a decrease in the quantity demanded of Indian products relative to American products
D) an increase in the quantity demanded of Indian products relative to American products
A) an increase in the value of the rupee relative to the dollar
B) a decrease in the prices of Indian products
C) a decrease in the quantity demanded of Indian products relative to American products
D) an increase in the quantity demanded of Indian products relative to American products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following would increase the value of the dollar in the long run?
A) an increase in inflation in the United States relative to other countries
B) an increase in the demand for American goods relative to goods from other countries
C) a decrease in U.S. tariffs on foreign goods
D) an increase in the supply of dollars on the foreign exchange market
A) an increase in inflation in the United States relative to other countries
B) an increase in the demand for American goods relative to goods from other countries
C) a decrease in U.S. tariffs on foreign goods
D) an increase in the supply of dollars on the foreign exchange market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Figure 30-1 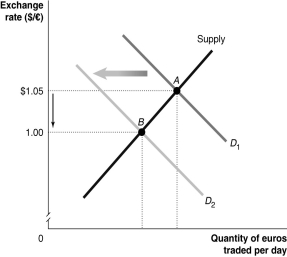
Refer to Figure 30-1.Which of the following would cause the change depicted in the figure above?
A) U.S. productivity rises relative to European productivity.
B) Europeans decrease their preferences for U.S. goods relative to European goods.
C) The European Union increases its quotas on French wine.
D) an increase in the price level of U.S. goods relative to European goods

Refer to Figure 30-1.Which of the following would cause the change depicted in the figure above?
A) U.S. productivity rises relative to European productivity.
B) Europeans decrease their preferences for U.S. goods relative to European goods.
C) The European Union increases its quotas on French wine.
D) an increase in the price level of U.S. goods relative to European goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
By 2011,how many European countries were members of the European Union?
A) 12
B) 15
C) 27
D) 57
A) 12
B) 15
C) 27
D) 57

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Countries that use the euro as their currency face similar concerns as countries did during the years of the gold standard in that each are (were)
A) unable to conduct monetary policy.
B) unable to conduct fiscal policy.
C) using currency which is backed by gold.
D) using a floating currency.
A) unable to conduct monetary policy.
B) unable to conduct fiscal policy.
C) using currency which is backed by gold.
D) using a floating currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
If the implied exchange rate between Big Mac prices in the United States and Poland is 2.13 zlotys per dollar,but the actual exchange rate between the United States and Poland is 3.16 zlotys per dollar,which of the following would you expect to see?
A) an appreciation of the dollar
B) an increase in the demand for zlotys
C) an increase in the demand for dollars
D) Both A and C are correct.
A) an appreciation of the dollar
B) an increase in the demand for zlotys
C) an increase in the demand for dollars
D) Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If,at the current exchange rate between the dollar and the Norwegian kroner of 5.78 kroner per dollar,the dollar is "overvalued," how do you expect demand and supply in the foreign exchange markets to respond?
A) The demand for the dollar will rise, while the supply of the kroner will fall.
B) The demand for the dollar will fall, while the supply of the kroner will rise.
C) The supply of the dollar will rise, while the demand for the kroner will fall.
D) The supply of the dollar will rise, while the demand for the kroner will rise.
A) The demand for the dollar will rise, while the supply of the kroner will fall.
B) The demand for the dollar will fall, while the supply of the kroner will rise.
C) The supply of the dollar will rise, while the demand for the kroner will fall.
D) The supply of the dollar will rise, while the demand for the kroner will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The central bank of the European Union is called the
A) Bundesbank.
B) Banco Europe.
C) Federal Reserve.
D) European Central Bank.
A) Bundesbank.
B) Banco Europe.
C) Federal Reserve.
D) European Central Bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If the GDP deflator in the United States is 114,and the GDP deflator in Ukraine is 142,which of the following changes would the theory of purchasing power parity predict? (The Ukrainian currency is the hryvnia.)
A) The demand for the dollar will rise since the dollar is undervalued.
B) The demand for the dollar will fall since the dollar is overvalued.
C) The supply of the dollar will fall since the dollar is undervalued.
D) No prediction regarding changes in the demand or supply of the dollar can be made without information on the exchange rate between the United States and Ukraine.
A) The demand for the dollar will rise since the dollar is undervalued.
B) The demand for the dollar will fall since the dollar is overvalued.
C) The supply of the dollar will fall since the dollar is undervalued.
D) No prediction regarding changes in the demand or supply of the dollar can be made without information on the exchange rate between the United States and Ukraine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If inflation in Russia is higher than it is in the United States,
A) the purchasing power of the ruble in buying Russian goods will rise relative to the dollar.
B) the value of the dollar will rise in the long run.
C) the value of the ruble will rise in the long run.
D) Both A and C are correct.
A) the purchasing power of the ruble in buying Russian goods will rise relative to the dollar.
B) the value of the dollar will rise in the long run.
C) the value of the ruble will rise in the long run.
D) Both A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Figure 30-2 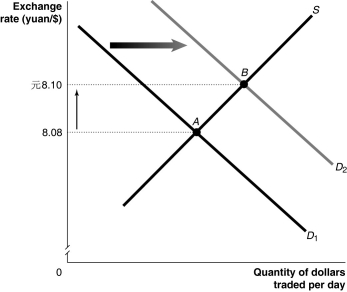
Refer to Figure 30-2.Which of the following would cause the change depicted in the figure above?
A) Lack of investment in infrastructure causes U.S. productivity to fall relative to Chinese productivity.
B) Tainted cat food from China causes U.S. consumers to decrease their preferences for Chinese goods relative to U.S. goods.
C) A new trade agreement with China results in the United States removing all tariffs on clothing imported from China.
D) An expansionary monetary policy causes an increase in the price level of U.S. goods relative to Chinese goods.

Refer to Figure 30-2.Which of the following would cause the change depicted in the figure above?
A) Lack of investment in infrastructure causes U.S. productivity to fall relative to Chinese productivity.
B) Tainted cat food from China causes U.S. consumers to decrease their preferences for Chinese goods relative to U.S. goods.
C) A new trade agreement with China results in the United States removing all tariffs on clothing imported from China.
D) An expansionary monetary policy causes an increase in the price level of U.S. goods relative to Chinese goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Because the value of the euro is determined by factors that affect the entire euro zone,during the recession of 2007-2009,individual countries using the euro
A) were unable to have their exchange rates depreciate.
B) were more insulated from unemployment increases than most countries.
C) experienced a greater increase in exports than did most countries.
D) were able to use expansionary monetary policy to lessen the impact of the recession.
A) were unable to have their exchange rates depreciate.
B) were more insulated from unemployment increases than most countries.
C) experienced a greater increase in exports than did most countries.
D) were able to use expansionary monetary policy to lessen the impact of the recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Figure 30-5 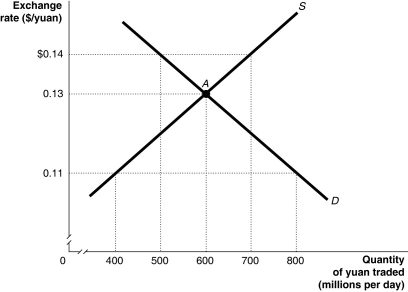
Refer to Figure 30-5.The Chinese government pegs the yuan to the dollar,at one of the specified exchange rates on the graph,such that it undervalues its currency.Using the figure above,this would generate a
A) a shortage of yuan equal to 400 million.
B) a shortage of yuan equal to 200 million.
C) a surplus of yuan equal to 200 million.
D) a surplus of yuan equal to 400 million.
E) a surplus of yuan equal to 300 million.

Refer to Figure 30-5.The Chinese government pegs the yuan to the dollar,at one of the specified exchange rates on the graph,such that it undervalues its currency.Using the figure above,this would generate a
A) a shortage of yuan equal to 400 million.
B) a shortage of yuan equal to 200 million.
C) a surplus of yuan equal to 200 million.
D) a surplus of yuan equal to 400 million.
E) a surplus of yuan equal to 300 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Members of the European Union decided to adopt a single currency by what year?
A) 2008
B) 2005
C) 1999
D) 1992
A) 2008
B) 2005
C) 1999
D) 1992

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
If a country's currency is "pegged" to the dollar,its exchange rate is
A) floating.
B) flexible.
C) fixed.
D) undervalued.
A) floating.
B) flexible.
C) fixed.
D) undervalued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Figure 30-5 
Refer to Figure 30-5.Suppose the pegged exchange rate is $0.11/yuan.Because of safety concerns and numerous product recalls,U.S.consumers lower their demand for Chinese products.Using the figure above,this would
A) increase the surplus of Chinese yuan.
B) decrease the surplus of Chinese yuan.
C) decrease the shortage of Chinese yuan.
D) increase the shortage of Chinese yuan.

Refer to Figure 30-5.Suppose the pegged exchange rate is $0.11/yuan.Because of safety concerns and numerous product recalls,U.S.consumers lower their demand for Chinese products.Using the figure above,this would
A) increase the surplus of Chinese yuan.
B) decrease the surplus of Chinese yuan.
C) decrease the shortage of Chinese yuan.
D) increase the shortage of Chinese yuan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Figure 30-3 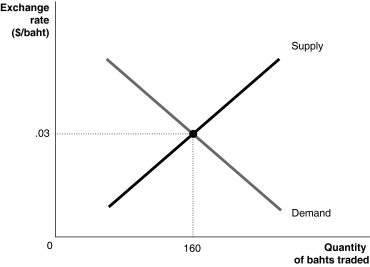
Refer to Figure 30-3.If the Thai government pegs its currency to the dollar at a value above $.03/baht,we would say the currency is
A) undervalued.
B) overvalued.
C) parity valued.
D) equilibrium valued.

Refer to Figure 30-3.If the Thai government pegs its currency to the dollar at a value above $.03/baht,we would say the currency is
A) undervalued.
B) overvalued.
C) parity valued.
D) equilibrium valued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is a drawback to having a common currency across countries,as in the European Union?
A) A common currency increases barriers to trade across countries, reducing opportunities for economic growth.
B) With a common currency, individual countries are no longer able to run independent monetary policies.
C) Having a common currency implies that the prices of goods across countries must always be the same, regardless of consumer preferences for goods across countries.
D) None of the above is a drawback to a common currency.
A) A common currency increases barriers to trade across countries, reducing opportunities for economic growth.
B) With a common currency, individual countries are no longer able to run independent monetary policies.
C) Having a common currency implies that the prices of goods across countries must always be the same, regardless of consumer preferences for goods across countries.
D) None of the above is a drawback to a common currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Figure 30-4 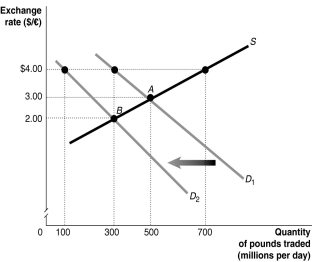
Refer to Figure 30-4.The equilibrium exchange rate is originally at A,$3/pound.Suppose the British government pegs its currency at $4/pound.Speculators expect that the value of the pound will drop and this shifts the demand curve for pounds to D2.If the government abandons the peg,the equilibrium exchange rate would be
A) $4/pound.
B) $3/pound.
C) $2/pound.
D) less than $2/pound.

Refer to Figure 30-4.The equilibrium exchange rate is originally at A,$3/pound.Suppose the British government pegs its currency at $4/pound.Speculators expect that the value of the pound will drop and this shifts the demand curve for pounds to D2.If the government abandons the peg,the equilibrium exchange rate would be
A) $4/pound.
B) $3/pound.
C) $2/pound.
D) less than $2/pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The currencies of Poland and Iceland (the zloty and the krona,respectively)declined in value relative to the euro following the financial crisis of 2008.This means that the
A) zloty and krona appreciated in value against the euro.
B) euro depreciated in value against the zloty and the krona.
C) zloty and krona depreciated in value against the euro.
D) zloty depreciated in value against the krona.
E) Both A and B are correct.
A) zloty and krona appreciated in value against the euro.
B) euro depreciated in value against the zloty and the krona.
C) zloty and krona depreciated in value against the euro.
D) zloty depreciated in value against the krona.
E) Both A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
You are made better off in which of the following situations?
A) you borrow 10,000 pesos, you earn income in dollars, the dollar depreciates against the peso, you must pay back the loan in pesos
B) you borrow $10,000, you earn income in pesos, the dollar depreciates against the peso, you must pay back the loan in dollars
C) you borrow $10,000, you earn income in pesos, the dollar appreciates against the peso, you must pay back the loan in dollars
D) you borrow 10,000 pesos, you earn income in pesos, the dollar depreciates against the peso, you must pay back the loan in pesos
A) you borrow 10,000 pesos, you earn income in dollars, the dollar depreciates against the peso, you must pay back the loan in pesos
B) you borrow $10,000, you earn income in pesos, the dollar depreciates against the peso, you must pay back the loan in dollars
C) you borrow $10,000, you earn income in pesos, the dollar appreciates against the peso, you must pay back the loan in dollars
D) you borrow 10,000 pesos, you earn income in pesos, the dollar depreciates against the peso, you must pay back the loan in pesos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a country sets a pegged exchange rate that is above the equilibrium exchange rate,how can the country maintain the peg?
A) by purchasing surplus domestic currency at the pegged rate
B) by selling surplus domestic currency at the pegged rate
C) by purchasing surplus domestic currency at the equilibrium exchange rate
D) by increasing the pegged exchange rate
A) by purchasing surplus domestic currency at the pegged rate
B) by selling surplus domestic currency at the pegged rate
C) by purchasing surplus domestic currency at the equilibrium exchange rate
D) by increasing the pegged exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is not an advantage to a country of choosing to fix its exchange rate against a major currency,rather than choosing a floating exchange rate?
A) Pegging allows the country more flexibility in conducting monetary policy.
B) Pegging helps avoid inflation in imported goods caused by currency depreciation for countries with significant levels of imports.
C) Pegging insures that interest payments stemming from foreign loans do not fluctuate with the value of the currency.
D) Pegging reduces the uncertainty caused by currency fluctuations and thereby simplifies business planning.
A) Pegging allows the country more flexibility in conducting monetary policy.
B) Pegging helps avoid inflation in imported goods caused by currency depreciation for countries with significant levels of imports.
C) Pegging insures that interest payments stemming from foreign loans do not fluctuate with the value of the currency.
D) Pegging reduces the uncertainty caused by currency fluctuations and thereby simplifies business planning.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Should European nations which are not currently using the euro choose to adopt the euro as their currency,these countries would risk giving up the ability to use ________ to stabilize their economies in the event of a recession.
A) expansionary fiscal policy
B) contractionary fiscal policy
C) expansionary monetary policy
D) contractionary monetary policy
A) expansionary fiscal policy
B) contractionary fiscal policy
C) expansionary monetary policy
D) contractionary monetary policy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A currency pegged at a value below the market equilibrium exchange rate is
A) overvalued.
B) undervalued.
C) achieving purchasing power parity.
D) None of the above are correct.
A) overvalued.
B) undervalued.
C) achieving purchasing power parity.
D) None of the above are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Figure 30-3 
Refer to Figure 30-3.Which of the following is not true?
A) U.S imports are cheaper at exchange rates greater than $.03/baht than at the equilibrium exchange rate.
B) The baht is overvalued at exchange rates greater than $.03/baht.
C) To achieve an exchange rate greater than $.03/baht, the Bank of Thailand must buy surplus dollars with bahts.
D) Thai exports to the United States are more expensive at exchange rates greater than $.03/baht than at the equilibrium exchange rate.

Refer to Figure 30-3.Which of the following is not true?
A) U.S imports are cheaper at exchange rates greater than $.03/baht than at the equilibrium exchange rate.
B) The baht is overvalued at exchange rates greater than $.03/baht.
C) To achieve an exchange rate greater than $.03/baht, the Bank of Thailand must buy surplus dollars with bahts.
D) Thai exports to the United States are more expensive at exchange rates greater than $.03/baht than at the equilibrium exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Figure 30-5 
Refer to Figure 30-5.Suppose the Chinese government decides to abandon pegging the yuan to the dollar at a rate which undervalues the yuan.Using the figure above,the equilibrium exchange rate would be ________ and Chinese exports to the United States would ________ in price.
A) $0.11/yuan; decrease
B) $0.11/yuan; increase
C) $0.14/yuan; increase
D) $0.13/yuan; increase
E) $0.13/yuan; decrease

Refer to Figure 30-5.Suppose the Chinese government decides to abandon pegging the yuan to the dollar at a rate which undervalues the yuan.Using the figure above,the equilibrium exchange rate would be ________ and Chinese exports to the United States would ________ in price.
A) $0.11/yuan; decrease
B) $0.11/yuan; increase
C) $0.14/yuan; increase
D) $0.13/yuan; increase
E) $0.13/yuan; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Figure 30-3 
Refer to Figure 30-3.At what level should the Thai government peg its currency to the dollar to make Thai exports cheaper to the United States?
A) greater than $.03/baht
B) less than $.03/baht
C) equal to $.03/baht
D) $1/baht

Refer to Figure 30-3.At what level should the Thai government peg its currency to the dollar to make Thai exports cheaper to the United States?
A) greater than $.03/baht
B) less than $.03/baht
C) equal to $.03/baht
D) $1/baht

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Figure 30-4 
Refer to Figure 30-4.The equilibrium exchange rate is at A,$3/pound.Suppose the British government pegs its currency at $4/pound.At the pegged exchange rate,
A) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 600 million.
B) there is a surplus of pounds equal to 400 million.
C) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 400 million.
D) there is a surplus of pounds equal to 600 million.
E) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 200 million.

Refer to Figure 30-4.The equilibrium exchange rate is at A,$3/pound.Suppose the British government pegs its currency at $4/pound.At the pegged exchange rate,
A) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 600 million.
B) there is a surplus of pounds equal to 400 million.
C) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 400 million.
D) there is a surplus of pounds equal to 600 million.
E) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 200 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
During the Chinese experience with pegging the yuan to the dollar,the yuan was undervalued.As a result,
A) there was a surplus of yuan on the market that the Chinese government had to purchase to maintain the peg, depleting China's reserves of dollars.
B) there was a surplus of dollars on the market that the Chinese government had to purchase to maintain the peg.
C) the prices of Chinese exports were higher than they would have been without the peg.
D) the equilibrium value of the yuan was below the pegged value of the yuan.
A) there was a surplus of yuan on the market that the Chinese government had to purchase to maintain the peg, depleting China's reserves of dollars.
B) there was a surplus of dollars on the market that the Chinese government had to purchase to maintain the peg.
C) the prices of Chinese exports were higher than they would have been without the peg.
D) the equilibrium value of the yuan was below the pegged value of the yuan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Pegging a country's exchange rate to the dollar can be advantageous if
A) the country does not trade much with the United States.
B) investors believe the dollar to be more stable than the domestic country's currency.
C) a country wishes to conduct independent monetary policy.
D) imports are not a significant fraction of the goods the country's consumers buy.
A) the country does not trade much with the United States.
B) investors believe the dollar to be more stable than the domestic country's currency.
C) a country wishes to conduct independent monetary policy.
D) imports are not a significant fraction of the goods the country's consumers buy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Figure 30-4 
Refer to Figure 30-4.The equilibrium exchange rate is at A,$3/pound.Suppose the British government pegs its currency at $4/pound.Speculators expect that the value of the pound will drop and this shifts the demand curve for pounds to D2.After the shift,
A) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 600 million.
B) there is a surplus of pounds equal to 400 million.
C) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 400 million.
D) there is a surplus of pounds equal to 600 million.
E) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 200 million.

Refer to Figure 30-4.The equilibrium exchange rate is at A,$3/pound.Suppose the British government pegs its currency at $4/pound.Speculators expect that the value of the pound will drop and this shifts the demand curve for pounds to D2.After the shift,
A) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 600 million.
B) there is a surplus of pounds equal to 400 million.
C) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 400 million.
D) there is a surplus of pounds equal to 600 million.
E) there is a shortage of pounds equal to 200 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 139 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



