Deck 15: Regulation of Breathing
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Regulation of Breathing
1
Stimulation of the irritant receptors in the lung can result in which of the following?
1) Bronchoconstriction
2) Coughing
3) Narrowing of the glottis
A)1 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)1, 2, and 3
D)1 and 3 only
1) Bronchoconstriction
2) Coughing
3) Narrowing of the glottis
A)1 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)1, 2, and 3
D)1 and 3 only
C
2
Which of the following can cause laryngospasm and bradycardia through a vagovagal reflex?
1) Bronchoscopy
2) Endotracheal intubation
3) Tracheal suctioning
A)1 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)1, 2, and 3
D)1 and 2 only
1) Bronchoscopy
2) Endotracheal intubation
3) Tracheal suctioning
A)1 only
B)1 and 3 only
C)1, 2, and 3
D)1 and 2 only
C
3
Where are the inspiratory and expiratory centers in the brain found?
A) Broca's area
B) Neurons in the cerebellum
C) Pons
D) No such centers exist
A) Broca's area
B) Neurons in the cerebellum
C) Pons
D) No such centers exist
D
Explanation: Recent evidence shows that inspiratory and expiratory neurons are anatomically intermingled and do not necessarily inhibit one another. No clearly separate inspiratory and expiratory centers exist.
Explanation: Recent evidence shows that inspiratory and expiratory neurons are anatomically intermingled and do not necessarily inhibit one another. No clearly separate inspiratory and expiratory centers exist.
4
What receptors are known to cause an increase in ventilation when the patient's limbs are moved or cold water is splashed on the patient's face?
A) Irritant receptors
B) J receptors
C) Muscle spindles
D) Peripheral proprioceptors
A) Irritant receptors
B) J receptors
C) Muscle spindles
D) Peripheral proprioceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement(s) describe aspects of the Hering-Breuer reflex?
1) It affects the rate and depth of breathing during exercise.
2) It is only activated at large tidal volumes in normal adults.
3) Its impulses travel via the vagus nerve to the dorsal respiratory groups (DRGs).
4) Its receptors are located in the large and small airways.
A)1 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)2, 3, and 4 only
D)1, 2, 3, and 4
1) It affects the rate and depth of breathing during exercise.
2) It is only activated at large tidal volumes in normal adults.
3) Its impulses travel via the vagus nerve to the dorsal respiratory groups (DRGs).
4) Its receptors are located in the large and small airways.
A)1 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)2, 3, and 4 only
D)1, 2, 3, and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Sensory input to the dorsal respiratory neurons from the lungs, airways, and peripheral chemoreceptors is provided via which nerves?
1) Glossopharyngeal
2) Phrenic
3) Vagus
4) Trigeminal
A)1 and 2 only
B)1, 2, and 4 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)2 and 3 only
1) Glossopharyngeal
2) Phrenic
3) Vagus
4) Trigeminal
A)1 and 2 only
B)1, 2, and 4 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)2 and 3 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following control the inhibitory neurons that switch off the inspiratory ramp signal?
1) Apneustic center
2) Pneumotaxic center
3) Pulmonary stretch receptors
A)1, 2, and 3
B)1 and 2 only
C)3 only
D)2 and 3 only
1) Apneustic center
2) Pneumotaxic center
3) Pulmonary stretch receptors
A)1, 2, and 3
B)1 and 2 only
C)3 only
D)2 and 3 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The medulla oblongata contains which of the following areas?
1) Apneustic center
2) Dorsal respiratory group neurons (DRGs)
3) Pneumotaxic center
4) Ventral respiratory group neurons (VRGs)
A)1, 2, and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)3 only
D)1, 3, and 4 only
1) Apneustic center
2) Dorsal respiratory group neurons (DRGs)
3) Pneumotaxic center
4) Ventral respiratory group neurons (VRGs)
A)1, 2, and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)3 only
D)1, 3, and 4 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which receptors are primarily responsible for the initial increase in ventilation that occurs at the beginning of exercise?
A) Carotid chemoreceptors
B) Irritant receptors
C) J receptors
D) Proprioceptors
A) Carotid chemoreceptors
B) Irritant receptors
C) J receptors
D) Proprioceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What receptors cause a rapid shallow breathing pattern when stimulated by pulmonary disease?
A) Irritant receptors
B) J receptors
C) Muscle spindles
D) Peripheral proprioceptors
A) Irritant receptors
B) J receptors
C) Muscle spindles
D) Peripheral proprioceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What reflex is associated with the sensory stimulation of the pulmonary stretch receptors that stimulate a deeper breath upon inspiration?
A) Carotid
B) Head's paradoxical
C) Hering-Breuer
D) J receptor
A) Carotid
B) Head's paradoxical
C) Hering-Breuer
D) J receptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the effect when the deflation reflex is stimulated?
A) A strong inspiratory effort
B) Expiration is initiated
C) Cuts off all inspiratory signals
D) Stimulates the termination of expiration
A) A strong inspiratory effort
B) Expiration is initiated
C) Cuts off all inspiratory signals
D) Stimulates the termination of expiration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What stimulates the Hering-Breuer inflation reflex?
A) The DRG when it is time to end inspiratory efforts.
B) The stretch of receptors at high lung volumes.
C) The VRG when it is time for inspiration.
D) Very low lung volumes stimulate inspiration.
A) The DRG when it is time to end inspiratory efforts.
B) The stretch of receptors at high lung volumes.
C) The VRG when it is time for inspiration.
D) Very low lung volumes stimulate inspiration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The pneumotaxic center controls which of the following?
A) Response to changes in blood pH and PCO2
B) Rhythm of the full breathing cycle
C) When inspiration switches off (the inspiratory time)
D) When inspiration switches on (the expiratory time)
A) Response to changes in blood pH and PCO2
B) Rhythm of the full breathing cycle
C) When inspiration switches off (the inspiratory time)
D) When inspiration switches on (the expiratory time)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What receptors are associated with causing coughing, sneezing, and tachypnea when stimulated?
A) Irritant receptors
B) J receptors
C) Muscle spindles
D) Peripheral proprioceptors
A) Irritant receptors
B) J receptors
C) Muscle spindles
D) Peripheral proprioceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following can be stimulated by pulmonary J receptors?
1) Edema
2) Inflammatory processes
3) Pulmonary vascular congestion
A)1 and 3 only
B)1 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3
1) Edema
2) Inflammatory processes
3) Pulmonary vascular congestion
A)1 and 3 only
B)1 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
To which anatomic structures do the ventral respiratory centers send motor signals during inspiration?
1) Diaphragm
2) Larynx
3) Pharynx
4) Sternocleidomastoids
A)1, 2, and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)1 only
D)1, 2, and 4
1) Diaphragm
2) Larynx
3) Pharynx
4) Sternocleidomastoids
A)1, 2, and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)1 only
D)1, 2, and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What centers are located in the pons of the brainstem?
1) Apneustic center
2) Dorsal respiratory neurons
3) Pneumotaxic center
A)1, 2, and 3
B)2 and 3 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)1 and 2 only
1) Apneustic center
2) Dorsal respiratory neurons
3) Pneumotaxic center
A)1, 2, and 3
B)2 and 3 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)1 and 2 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Failure to switch off the brainstem inspiratory neurons can result in which of the following?
A) Apnea
B) Apneustic breathing
C) Biot's breathing
D) Cheyne-Stokes breathing
A) Apnea
B) Apneustic breathing
C) Biot's breathing
D) Cheyne-Stokes breathing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What negative responses can be elicited by suctioning a patient's airway?
1) Tachycardia
2) Coughing
3) Laryngospasm
4) Severe bronchospasm
A)1, 2, and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)2, 3, and 4 only
1) Tachycardia
2) Coughing
3) Laryngospasm
4) Severe bronchospasm
A)1, 2, and 3 only
B)2 and 4 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)2, 3, and 4 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the face of hyperoxia, what is the response of the peripheral chemoreceptors to hypercapnia?
A) There is a decreased drive to breathe.
B) There is an increased drive to breathe.
C) There is insufficient information.
D) There is virtually no response.
A) There is a decreased drive to breathe.
B) There is an increased drive to breathe.
C) There is insufficient information.
D) There is virtually no response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the face of chronically elevated levels of CO2, what happens to the response mediated by the central chemoreceptors?
A) It is accentuated or increased.
B) It is muted or decreased.
C) There is no change in the response.
D) There is no way to predict the body's response.
A) It is accentuated or increased.
B) It is muted or decreased.
C) There is no change in the response.
D) There is no way to predict the body's response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Why does it take approximately 24 hr for a full ventilatory response to develop to acute hypoxemia?
A) Initial cerebrospinal fluid alkalemia blunts the hypoxic ventilatory stimulus.
B) Peripheral chemoreceptors are slow to respond to decreased blood O2 levels.
C) Renal compensation for respiratory alkalosis increases chemoreceptor sensitivity.
D) A full ventilatory response is not possible until after the muscles become fatigued.
A) Initial cerebrospinal fluid alkalemia blunts the hypoxic ventilatory stimulus.
B) Peripheral chemoreceptors are slow to respond to decreased blood O2 levels.
C) Renal compensation for respiratory alkalosis increases chemoreceptor sensitivity.
D) A full ventilatory response is not possible until after the muscles become fatigued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following causes hypoxic stimulation of the carotid bodies?
1) Large decrease in arterial PO2
2) Large decrease in O2 content
3) CO poisoning
A)1 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)1, 2, and 3
D)1 and 3 only
1) Large decrease in arterial PO2
2) Large decrease in O2 content
3) CO poisoning
A)1 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)1, 2, and 3
D)1 and 3 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How should O2 therapy be administered to chronically hypercapnic patients?
A) Avoid giving any supplemental O2.
B) Give as much O2 as possible (60% to 100%).
C) Withhold O2 until the patient is intubated.
D) Give as much O2 as required to maintain adequate oxygenation.
A) Avoid giving any supplemental O2.
B) Give as much O2 as possible (60% to 100%).
C) Withhold O2 until the patient is intubated.
D) Give as much O2 as required to maintain adequate oxygenation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When given high concentrations of O2, a patient with chronic hypercapnia may develop a more serious respiratory acidosis. Which of the following might be contributing to the patient's increased PCO2?
1) Worsening ventilation-perfusion (VV/QQ) balance
2) Desensitization of the carotid bodies
3) Removal of the hypoxic stimulus
A)1 and 2 only
B)1 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3
1) Worsening ventilation-perfusion (VV/QQ) balance
2) Desensitization of the carotid bodies
3) Removal of the hypoxic stimulus
A)1 and 2 only
B)1 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Stimulation to increase ventilation does not occur until the PaO2 falls below what level?
A) 90 mm Hg
B) 80 mm Hg
C) 70 mm Hg
D) 60 mm Hg
A) 90 mm Hg
B) 80 mm Hg
C) 70 mm Hg
D) 60 mm Hg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is indirectly responsible for minute-to-minute control of breathing?
A) CO2 levels
B) HCO3-levels
C) Lactate levels
D) Oxygen (O2) levels
A) CO2 levels
B) HCO3-levels
C) Lactate levels
D) Oxygen (O2) levels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the response of a patient with chronic hypercapnia to a sudden acute rise in carbon dioxide?
A) In almost all of these patients, there will be no response.
B) The patient's drive to breathe will be increased.
C) This will further depress his or her respiratory centers.
D) This will induce apnea and sudden death.
A) In almost all of these patients, there will be no response.
B) The patient's drive to breathe will be increased.
C) This will further depress his or her respiratory centers.
D) This will induce apnea and sudden death.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following will occur during even strenuous exercise in a normal healthy individual?
A) Blood gases remain stable.
B) The arterial PCO2 rises.
C) The arterial pH falls.
D) The arterial PO2 falls.
A) Blood gases remain stable.
B) The arterial PCO2 rises.
C) The arterial pH falls.
D) The arterial PO2 falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In what manner would O2 therapy induce worsening 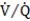 mismatch and thus a further elevation in CO2 in a chronically hypercapnic patient?
mismatch and thus a further elevation in CO2 in a chronically hypercapnic patient?
A) By improving blood flow to poorly ventilated alveoli
B) By decreasing blood flow to poorly ventilated alveoli
C) Causing bronchoconstriction, which worsens gas flow to lowareas
D) Causing bronchodilation, which improves gas flow to poorly ventilated alveoli
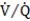 mismatch and thus a further elevation in CO2 in a chronically hypercapnic patient?
mismatch and thus a further elevation in CO2 in a chronically hypercapnic patient?A) By improving blood flow to poorly ventilated alveoli
B) By decreasing blood flow to poorly ventilated alveoli
C) Causing bronchoconstriction, which worsens gas flow to lowareas
D) Causing bronchodilation, which improves gas flow to poorly ventilated alveoli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What happens in chronic hypercapnia?
1) The central chemoreceptive response to CO2 is decreased.
2) The cerebrospinal fluid pH is restored to normal.
3) Responsiveness to increased CO2 is decreased.
A)1 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)2 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3
1) The central chemoreceptive response to CO2 is decreased.
2) The cerebrospinal fluid pH is restored to normal.
3) Responsiveness to increased CO2 is decreased.
A)1 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)2 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What group of nerve cells senses and responds to changes in the chemical composition of its fluid environment?
A) Chemoreceptors
B) Gamma-efferent system
C) Muscle spindle fibers
D) Proprioceptors
A) Chemoreceptors
B) Gamma-efferent system
C) Muscle spindle fibers
D) Proprioceptors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What has the primary responsibility for sensing and responding to changes in blood levels of CO2?
A) Apneustic centers
B) Central chemoreceptors
C) Peripheral chemoreceptors
D) Pneumotaxic center
A) Apneustic centers
B) Central chemoreceptors
C) Peripheral chemoreceptors
D) Pneumotaxic center

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which respond more rapidly to high levels of CO2?
A) Aortic chemoreceptors
B) Carotid chemoreceptors
C) Central chemoreceptors
D) Ventral respiratory centers
A) Aortic chemoreceptors
B) Carotid chemoreceptors
C) Central chemoreceptors
D) Ventral respiratory centers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Both anemia and carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning can cause severe hypoxia, yet neither condition results in a major stimulation of breathing. Why is this so?
A) The peripheral chemoreceptors do not respond to low O2 content.
B) Anemia and CO poisoning depresses the peripheral chemoreceptors.
C) Anemia and CO poisoning depresses the central chemoreceptors.
D) Anemia and CO cause stagnant hypoxia, not hypoxemia.
A) The peripheral chemoreceptors do not respond to low O2 content.
B) Anemia and CO poisoning depresses the peripheral chemoreceptors.
C) Anemia and CO poisoning depresses the central chemoreceptors.
D) Anemia and CO cause stagnant hypoxia, not hypoxemia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Coexisting arterial hypoxemia, acidemia, and high PaCO2 (i.e., asphyxia) will have what effect on the peripheral chemoreceptors?
A) There is a decreased drive to breathe.
B) There is a maximally increased drive to breathe.
C) There is insufficient information to make a determination.
D) There is virtually no response.
A) There is a decreased drive to breathe.
B) There is a maximally increased drive to breathe.
C) There is insufficient information to make a determination.
D) There is virtually no response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Adjustment of respiratory muscle contractions to accommodate varying loads is regulated by which of the following?
A) Medullary respiratory centers
B) Muscle spindle fiber feedback
C) Pontine apneustic center
D) Pontine pneumotaxic center
A) Medullary respiratory centers
B) Muscle spindle fiber feedback
C) Pontine apneustic center
D) Pontine pneumotaxic center

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following centers responds more strongly to high levels of CO2?
A) Aortic chemoreceptors
B) Carotid chemoreceptors
C) Central chemoreceptors
D) Ventral respiratory centers
A) Aortic chemoreceptors
B) Carotid chemoreceptors
C) Central chemoreceptors
D) Ventral respiratory centers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Where are the peripheral chemoreceptors located?
1) In the arch of the aorta
2) In the bifurcations of carotid arteries
3) On the ventrolateral surfaces of the medulla
A)1 and 2 only
B)2 only
C)2 and 3 only
D)1 and 3 only
1) In the arch of the aorta
2) In the bifurcations of carotid arteries
3) On the ventrolateral surfaces of the medulla
A)1 and 2 only
B)2 only
C)2 and 3 only
D)1 and 3 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Biot's respiration is most frequently observed in patients with which of the following?
A) Congestive heart failure
B) Increased intracranial pressure
C) Metabolic acidosis
D) Peripheral nerve disorders
A) Congestive heart failure
B) Increased intracranial pressure
C) Metabolic acidosis
D) Peripheral nerve disorders

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following are causes of central neurogenic hyperventilation?
1) Head trauma
2) Inadequate brain blood flow
3) Severe brain hypoxia
4) Hypothermia
A)2 and 3 only
B)1 and 4 only
C)2 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3 only
1) Head trauma
2) Inadequate brain blood flow
3) Severe brain hypoxia
4) Hypothermia
A)2 and 3 only
B)1 and 4 only
C)2 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A healthy 33-year-old woman relocates to an area approximately 8000 ft above sea level. On her first day, she begins to hyperventilate, but in 24 hr she shows signs of recovery. What is the probable cause of her condition?
A) Hypoxemia-mediated hyperventilation
B) Hypercapnia
C) Hyperoxia-mediated hyperventilation
D) Increased H+
A) Hypoxemia-mediated hyperventilation
B) Hypercapnia
C) Hyperoxia-mediated hyperventilation
D) Increased H+

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What does apneustic breathing indicate?
A) Damage to the cerebrum
B) Damage to the pons
C) Spinal cord transaction
D) Vagal nerve damage
A) Damage to the cerebrum
B) Damage to the pons
C) Spinal cord transaction
D) Vagal nerve damage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
You observe a patient's breathing pattern as very irregular, with periods of breathing interspersed with long periods of apnea. Which of the following terms would you use in charting this observation?
A) Apneustic breathing
B) Biot's respiration
C) Cheyne-Stokes breathing
D) Kussmaul's breathing
A) Apneustic breathing
B) Biot's respiration
C) Cheyne-Stokes breathing
D) Kussmaul's breathing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following can cause Cheyne-Stokes breathing?
1) Brain injuries
2) Congestive heart failure
3) Metabolic acidosis
A)1 and 2 only
B)2 and 3 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3
1) Brain injuries
2) Congestive heart failure
3) Metabolic acidosis
A)1 and 2 only
B)2 and 3 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
While observing a patient's breathing, you note that the depth and rate first increase, then decrease, followed by a period of apnea. Which of the following terms would you use in charting this observation?
A) Apneustic breathing
B) Biot's breathing
C) Cheyne-Stokes breathing
D) Paradoxical breathing
A) Apneustic breathing
B) Biot's breathing
C) Cheyne-Stokes breathing
D) Paradoxical breathing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Why does splashing cold water on the skin stimulate ventilation?
A) It decreases medullary inspiratory activity causing hyperpnea.
B) Hering-Breuer inflation reflex.
C) It increases medullary inspiratory activity causing hyperpnea.
D) J receptor.
A) It decreases medullary inspiratory activity causing hyperpnea.
B) Hering-Breuer inflation reflex.
C) It increases medullary inspiratory activity causing hyperpnea.
D) J receptor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A patient in the emergency room is displaying prolong inspiratory gasps interrupted by occasional expirations, what serious injury should be suspected on this patient?
1) Pneumotaxic center has been severed.
2) Vagus nerve has been severed.
3) Glossopharyngeal nerve has been severed.
A)2 and 3 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3
1) Pneumotaxic center has been severed.
2) Vagus nerve has been severed.
3) Glossopharyngeal nerve has been severed.
A)2 and 3 only
B)1 and 2 only
C)1 and 3 only
D)1, 2, and 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In patients with closed-head injuries, what may happen in the presence of hypercapnia?
A) High CO2 increases the risk of psychotic events.
B) High CO2 levels cause cerebral vasodilation and improved oxygenation.
C) Severe cerebral vasoconstriction results in anoxia and stroke.
D) Vasodilation causes increased intracranial pressure and possibly stops blood flow.
A) High CO2 increases the risk of psychotic events.
B) High CO2 levels cause cerebral vasodilation and improved oxygenation.
C) Severe cerebral vasoconstriction results in anoxia and stroke.
D) Vasodilation causes increased intracranial pressure and possibly stops blood flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



