Deck 2: Physical Biochemistry: Energy Conversion,water,and Membranes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/99
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Physical Biochemistry: Energy Conversion,water,and Membranes
1
Which of the following best defines the first law of thermodynamics?
A) All spontaneous processes in the universe tend toward dispersal of energy.
B) Total amount of energy in the universe is a constant.
C) There is no entropy at zero Kelvin.
D) Entropy is a measure of disorder.
A) All spontaneous processes in the universe tend toward dispersal of energy.
B) Total amount of energy in the universe is a constant.
C) There is no entropy at zero Kelvin.
D) Entropy is a measure of disorder.
B
2
Energy conversion in a biological system operates under constant __________ and constant __________.
A) heat; pressure
B) work; heat
C) pressure; volume
D) volume; heat
A) heat; pressure
B) work; heat
C) pressure; volume
D) volume; heat
C
3
What chemical process is able to take place in the presence of solar energy?
A) anaerobic respiration
B) photosynthesis
C) hydrogenation
D) hydrolysis
A) anaerobic respiration
B) photosynthesis
C) hydrogenation
D) hydrolysis
B
4
For a reaction to be spontaneous,the change in the entropy of the universe must be
A) greater than zero.
B) less than zero.
C) equal to zero.
D) equal to 1.
A) greater than zero.
B) less than zero.
C) equal to zero.
D) equal to 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Given 80 grams of water,how many calories are required to raise the temperature  ?
?
A) 4.184 calories
B) 15.7 calories
C) 80 calories
D) Not enough information is given to calculate the answer.
 ?
?A) 4.184 calories
B) 15.7 calories
C) 80 calories
D) Not enough information is given to calculate the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the final molecule made from the oxidation of H2O by solar energy?
A) ozone
B) glucose
C) fructose
D) carbon dioxide
A) ozone
B) glucose
C) fructose
D) carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following best describes an open system?
A) Matter and energy are freely exchanged with the surroundings.
B) Energy is exchanged with the surroundings but matter is not.
C) Matter is exchanged with the surroundings but energy is not.
D) Neither matter nor energy is exchanged with the surroundings.
A) Matter and energy are freely exchanged with the surroundings.
B) Energy is exchanged with the surroundings but matter is not.
C) Matter is exchanged with the surroundings but energy is not.
D) Neither matter nor energy is exchanged with the surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Energy conversion in living systems is required for what three types of work?
A) osmotic work, chemical work, mechanical work
B) osmotic work, chemical work, potential work
C) kinetic work, chemical work, mechanical work
D) osmotic work, photosynthetic work, mechanical work
A) osmotic work, chemical work, mechanical work
B) osmotic work, chemical work, potential work
C) kinetic work, chemical work, mechanical work
D) osmotic work, photosynthetic work, mechanical work

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Given a biological system at 1 atm with 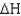 = 16 kJ/g,what is the internal energy of the system?
= 16 kJ/g,what is the internal energy of the system?
A) 15 kJ/g
B) 16 kJ/g
C) 14 kJ/g
D) Not enough information is given to calculate the answer.
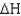 = 16 kJ/g,what is the internal energy of the system?
= 16 kJ/g,what is the internal energy of the system?A) 15 kJ/g
B) 16 kJ/g
C) 14 kJ/g
D) Not enough information is given to calculate the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The combustion of gasoline is considered exothermic because heat is
A) transferred from the surroundings to the system.
B) transferred from the system to the surroundings.
C) transferred to the universe.
D) not transferred.
A) transferred from the surroundings to the system.
B) transferred from the system to the surroundings.
C) transferred to the universe.
D) not transferred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Gibbs free energy can best be defined as the
A) difference between the enthalpy and entropy of a system at a given temperature.
B) difference between exothermic and endothermic energy of a system at a given temperature.
C) addition of enthalpy and entropy of a system at a given temperature.
D) difference between pressure and volume at a given temperature.
A) difference between the enthalpy and entropy of a system at a given temperature.
B) difference between exothermic and endothermic energy of a system at a given temperature.
C) addition of enthalpy and entropy of a system at a given temperature.
D) difference between pressure and volume at a given temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The difference between an oxidation reaction and a reduction reaction is that oxidation is the __________ and reduction is the __________.
A) loss of electrons; gain of electrons
B) gain of electrons; loss of electrons
C) loss of protons; gain of protons
D) gain of protons; loss of protons
A) loss of electrons; gain of electrons
B) gain of electrons; loss of electrons
C) loss of protons; gain of protons
D) gain of protons; loss of protons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The example of water freezing into ice shows
A) an increase in entropy of the system.
B) a decrease in entropy of the system.
C) no change in the entropy of the system.
D) a decrease in the entropy of the surroundings.
A) an increase in entropy of the system.
B) a decrease in entropy of the system.
C) no change in the entropy of the system.
D) a decrease in the entropy of the surroundings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following correctly describes the relationship between an ice cube melting on the table and the air surrounding it?
A) The ice cube is the system and the air is the surroundings.
B) The air is the system and the ice cube is the surroundings.
C) The ice cube is the system and only the air is the universe.
D) The air is the system and only the ice cube is the universe.
A) The ice cube is the system and the air is the surroundings.
B) The air is the system and the ice cube is the surroundings.
C) The ice cube is the system and only the air is the universe.
D) The air is the system and only the ice cube is the universe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is an example of a system?
A) the universe
B) the air
C) a test tube with reaction components
D) outer space
A) the universe
B) the air
C) a test tube with reaction components
D) outer space

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The change in entropy of a system is a function of a change in
A) temperature and pressure.
B) volume and pressure.
C) enthalpy and pressure.
D) enthalpy and temperature.
A) temperature and pressure.
B) volume and pressure.
C) enthalpy and pressure.
D) enthalpy and temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the figure below,which state of matter has the highest entropy? 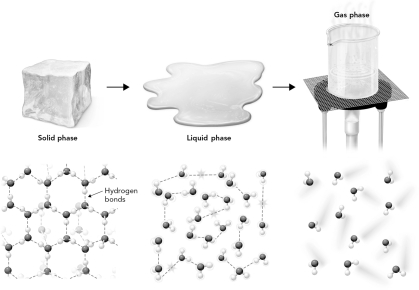
A) solid phase
B) liquid phase
C) gas phase
D) all are equal entropy.

A) solid phase
B) liquid phase
C) gas phase
D) all are equal entropy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The oxidation of glucose releases 15.7 kJ/g.Is this reaction spontaneous?
A) Yes, because it is exothermic.
B) No, because it is exothermic.
C) Yes, because it is endothermic.
D) The answer cannot be determined.
A) Yes, because it is exothermic.
B) No, because it is exothermic.
C) Yes, because it is endothermic.
D) The answer cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A hot pack on your arm is an example of what kind of system?
A) open
B) closed
C) isolated
D) surroundings
A) open
B) closed
C) isolated
D) surroundings

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For a given reaction with a 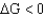 ,the reaction is
,the reaction is
A) favorable in the reverse direction.
B) favorable in the forward direction.
C) unfavorable in both directions.
D) favorable in both directions.
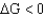 ,the reaction is
,the reaction isA) favorable in the reverse direction.
B) favorable in the forward direction.
C) unfavorable in both directions.
D) favorable in both directions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Hydrogen bonds in liquid water are formed between
A) two hydrogen atoms on the same molecule.
B) the oxygen of one molecule and the hydrogen of another.
C) protons and hydroxides.
D) two oxygen atoms on different molecules.
A) two hydrogen atoms on the same molecule.
B) the oxygen of one molecule and the hydrogen of another.
C) protons and hydroxides.
D) two oxygen atoms on different molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The standard free energy change is defined under what set of conditions?
A) 1 atm, 298 K, 1 M
B) 1 atm, 273 K, 1 M
C) 100 kPa, 273 K, 1 M
D) 100 kPa, 298 K, 1 M
A) 1 atm, 298 K, 1 M
B) 1 atm, 273 K, 1 M
C) 100 kPa, 273 K, 1 M
D) 100 kPa, 298 K, 1 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Given the energy charge equation below,if a biological system has an EC = 0.8,what is true about the concentrations of ATP,ADP,and AMP in the system? 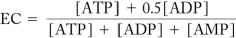
A) The concentrations are all equal.
B) There is more ADP in the system than ATP or AMP.
C) There is more ATP in the system than ADP or AMP.
D) There is more AMP in the system than ATP and ADP.
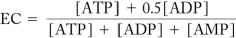
A) The concentrations are all equal.
B) There is more ADP in the system than ATP or AMP.
C) There is more ATP in the system than ADP or AMP.
D) There is more AMP in the system than ATP and ADP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the equilibrium constant (Keq)is greater than 1,which direction will the reaction proceed?
A) spontaneously to products
B) spontaneously to reactants
C) neither direction
D) Not enough information is given to determine the direction of reaction.
A) spontaneously to products
B) spontaneously to reactants
C) neither direction
D) Not enough information is given to determine the direction of reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In a hydrogen bond between a water molecule and another water molecule,
A) a hydrogen ion on the water molecule forms an ionic bond with the oxygen ion on the other water.
B) the hydrogen bond typically forms between the oxygen atom of the water and the hydrogen on the other water.
C) a hydrogen on the water molecule forms a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom on the other water.
D) the hydrogen atom forms an ionic bond with a carbon on the other water.
A) a hydrogen ion on the water molecule forms an ionic bond with the oxygen ion on the other water.
B) the hydrogen bond typically forms between the oxygen atom of the water and the hydrogen on the other water.
C) a hydrogen on the water molecule forms a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom on the other water.
D) the hydrogen atom forms an ionic bond with a carbon on the other water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the Gibbs free energy change value for a reaction is less than zero,this reaction is
A) exergonic.
B) endergonic.
C) exothermic.
D) endothermic.
A) exergonic.
B) endergonic.
C) exothermic.
D) endothermic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What chemical reaction causes ATP to be a high-energy molecule?
A) cleavage of phosphoanhydride bond
B) transfer of an adenylyl group to form a reactive intermediate
C) hydrolysis of phosphoryl group
D) oxidation of phosphoanhydride bond
A) cleavage of phosphoanhydride bond
B) transfer of an adenylyl group to form a reactive intermediate
C) hydrolysis of phosphoryl group
D) oxidation of phosphoanhydride bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If a reaction has a 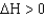 and a
and a 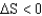
,then __________ and the reaction is __________ at all temperatures.
A)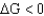 ; spontaneous
; spontaneous
B)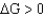 ; spontaneous
; spontaneous
C)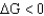 ; nonspontaneous
; nonspontaneous
D)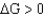 ; nonspontaneous
; nonspontaneous
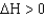 and a
and a 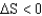
,then __________ and the reaction is __________ at all temperatures.
A)
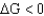 ; spontaneous
; spontaneousB)
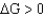 ; spontaneous
; spontaneousC)
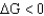 ; nonspontaneous
; nonspontaneousD)
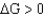 ; nonspontaneous
; nonspontaneous
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The interaction between an amino group and a carboxylate group is best characterized as
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) ionic interactions.
C) van der Waals interactions.
D) a covalent bond.
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) ionic interactions.
C) van der Waals interactions.
D) a covalent bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Under steady-state conditions in a mammalian cell,the adenine nucleotide concentrations are [ATP] = 3.3 mM,[ADP] = 1.2 mM,and [AMP] = 0.2 mM.What is the energy charge of this cell?
A) 0.83
B) 0.95
C) 0.72
D) 1.2
A) 0.83
B) 0.95
C) 0.72
D) 1.2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Organisms on Earth cannot easily exist at temperatures below  because at that temperature
because at that temperature
A) hydrogen bonds cannot exist.
B) water does not exist in a tetrahedron.
C) ice crystals form in the organism.
D) proton hopping cannot occur.
 because at that temperature
because at that temperatureA) hydrogen bonds cannot exist.
B) water does not exist in a tetrahedron.
C) ice crystals form in the organism.
D) proton hopping cannot occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The interaction between nonpolar molecules is best characterized as
A) a hydrogen bond.
B) ionic interactions.
C) van der Waals interactions.
D) a covalent bond.
A) a hydrogen bond.
B) ionic interactions.
C) van der Waals interactions.
D) a covalent bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The __________ system controls the interconversion among ATP,ADP,and AMP.
A) phosphorylate
B) adenylate
C) energy conversion
D) metabolism
A) phosphorylate
B) adenylate
C) energy conversion
D) metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Describe how an antifreeze protein functions.
A) Regularly spaced tyrosine residues prevent the ice crystals from growing.
B) Regularly spaced threonine resides prevent the ice crystals from growing.
C) Flickering clusters of hydrogen bonds prevent the ice crystals from growing.
D) The antifreeze protein prevents the water wires from forming.
A) Regularly spaced tyrosine residues prevent the ice crystals from growing.
B) Regularly spaced threonine resides prevent the ice crystals from growing.
C) Flickering clusters of hydrogen bonds prevent the ice crystals from growing.
D) The antifreeze protein prevents the water wires from forming.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A hydrogen bond can form between a hydrogen atom on a(n)
A) electronegative donor group and another electronegative atom.
B) cationic atom and another hydrogen.
C) nonpolar donor group and an electronegative atom.
D) ionic atom and another anion.
A) electronegative donor group and another electronegative atom.
B) cationic atom and another hydrogen.
C) nonpolar donor group and an electronegative atom.
D) ionic atom and another anion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If 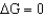 for a reaction,then this reaction
for a reaction,then this reaction
A) is favorable in the forward direction.
B) is favorable in the reverse direction.
C) is at equilibrium.
D) cannot occur.
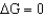 for a reaction,then this reaction
for a reaction,then this reactionA) is favorable in the forward direction.
B) is favorable in the reverse direction.
C) is at equilibrium.
D) cannot occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the equilibrium constant (Keq)is greater than 1,what is the value of 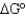 ?
?
A)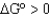
B)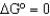
C)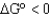
D)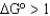
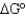 ?
?A)
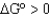
B)
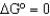
C)
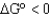
D)
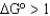

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The transfer of a phosphate from ATP to another molecule produces a(n)
A) low-energy intermediate.
B) highly reactive intermediate.
C) neutral energy intermediate.
D) It is not possible to transfer a phosphate to another molecule.
A) low-energy intermediate.
B) highly reactive intermediate.
C) neutral energy intermediate.
D) It is not possible to transfer a phosphate to another molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If a reaction has a 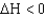 and
and 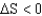
,under which conditions would the reaction be spontaneous in the forward direction?
A) low temperatures
B) high temperatures
C) high pressure
D) low pressure
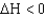 and
and 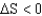
,under which conditions would the reaction be spontaneous in the forward direction?
A) low temperatures
B) high temperatures
C) high pressure
D) low pressure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Under what conditions could a biological reaction spontaneously proceed to reactants if the 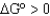 ?
?
A) Reactant concentrations are greater than product concentrations.
B) Product concentrations are greater than reactant concentrations.
C) Reactant concentrations are equal to product concentrations.
D) There are no conditions where this could happen.
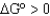 ?
?A) Reactant concentrations are greater than product concentrations.
B) Product concentrations are greater than reactant concentrations.
C) Reactant concentrations are equal to product concentrations.
D) There are no conditions where this could happen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following acids is the strongest given their Ka values?
A) HF (3.5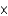
10-4)
B) HClO2 (1.1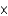
10-2)
C) HCN (4.9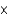
10-10)
D) HNO2 (4.6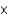
10-4)
A) HF (3.5
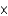
10-4)
B) HClO2 (1.1
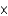
10-2)
C) HCN (4.9
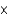
10-10)
D) HNO2 (4.6
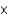
10-4)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Weak acids have a high pKa because the
A) HA concentration is high.
B) H+ concentration is high.
C) A-concentration is high.
D) HA concentration is low.
A) HA concentration is high.
B) H+ concentration is high.
C) A-concentration is high.
D) HA concentration is low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How do plants,fungi,and bacteria avoid the damaging effects of a hypotonic environment?
A) flexible cells walls
B) rigid cells walls
C) semipermeable cell walls
D) photosynthesis
A) flexible cells walls
B) rigid cells walls
C) semipermeable cell walls
D) photosynthesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the concentration of H+ in a solution of 0.05 M NaOH?
A) 5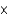 10-16 M
10-16 M
B) 2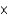 10-13 M
10-13 M
C) 5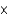 1012 M
1012 M
D) 140 M
A) 5
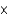 10-16 M
10-16 MB) 2
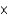 10-13 M
10-13 MC) 5
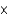 1012 M
1012 MD) 140 M

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is the Kw value for pure water at 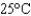 ?
?
A) 1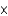
1014
B) 1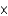
10-14
C) 7
D) 14
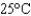 ?
?A) 1
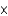
1014
B) 1
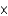
10-14
C) 7
D) 14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Calculate the pH of a solution that contains 3.9 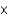 10-4M H+.
10-4M H+.
A) 4.59
B) 10.59
C) 3.41
D) 9.41
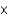 10-4M H+.
10-4M H+.A) 4.59
B) 10.59
C) 3.41
D) 9.41

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If an unknown solution has low pKa value,it can be said with certainty that it is
A) a weak acid.
B) a strong acid.
C) pure water.
D) a nonpolar solution.
A) a weak acid.
B) a strong acid.
C) pure water.
D) a nonpolar solution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
An organism in equilibrium with its environment is no longer alive because
A) homeostasis is required for life.
B) heterostasis is required for life.
C) an organism requires only exergonic reactions to be alive.
D) an organism requires only endergonic reactions to be alive.
A) homeostasis is required for life.
B) heterostasis is required for life.
C) an organism requires only exergonic reactions to be alive.
D) an organism requires only endergonic reactions to be alive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Red blood cells are placed into a solution of unknown solute concentration.After an hour they have all burst open.The best explanation is that the solution
A) had no solutes.
B) had a very high concentration of solutes.
C) had a very high concentration of solvent
D) was at equilibrium.
A) had no solutes.
B) had a very high concentration of solutes.
C) had a very high concentration of solvent
D) was at equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Limonene is a nonpolar molecule.The water molecules around it forms
A) hydrogen bonds with itself and entropy decreases.
B) ionic bonds with itself and the entropy decreases.
C) hydrogen bonds with limonene and the entropy increases.
D) covalent bonds with limonene and entropy increases.
A) hydrogen bonds with itself and entropy decreases.
B) ionic bonds with itself and the entropy decreases.
C) hydrogen bonds with limonene and the entropy increases.
D) covalent bonds with limonene and entropy increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the expected osmotic pressure around the cells for the plant with low turgor pressure shown below? 
A) hypotonic
B) hypertonic
C) isotonic
D) equilibrium

A) hypotonic
B) hypertonic
C) isotonic
D) equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Calculate the pH of a solution that contains 7.8 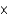 10-6 M OH-.
10-6 M OH-.
A) 1.28
B) 5.11
C) 12.72
D) 8.89
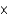 10-6 M OH-.
10-6 M OH-.A) 1.28
B) 5.11
C) 12.72
D) 8.89

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The effects of solutes on the colligative properties of a solution depend only on the
A) chemical properties of the solutes.
B) molecular mass of the solutes.
C) overall charge of the solute.
D) number of solute particles.
A) chemical properties of the solutes.
B) molecular mass of the solutes.
C) overall charge of the solute.
D) number of solute particles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Calculate the concentration of pH of a 0.023 M HCl solution.
A) 12.36
B) 3.68
C) 1.64
D) 2.30
A) 12.36
B) 3.68
C) 1.64
D) 2.30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is true?
A) A neutral solution contains [H2O] = [H+].
B) A neutral solution does not contain any H+ or OH-.
C) An acidic solution has [H+] > [OH-].
D) A basic solution does not contain H+.
A) A neutral solution contains [H2O] = [H+].
B) A neutral solution does not contain any H+ or OH-.
C) An acidic solution has [H+] > [OH-].
D) A basic solution does not contain H+.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Freezing point depression,boiling point elevation,and osmotic pressure are all what kind of properties?
A) intrinsic properties
B) colligative properties
C) state functions
D) hydrophobic effects
A) intrinsic properties
B) colligative properties
C) state functions
D) hydrophobic effects

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the concentration of OH- in a solution that contains 3.9 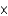 10-4 M H+?
10-4 M H+?
A) 2.6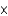 10-11 M
10-11 M
B) 3.9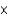 10-4
10-4
C) 2.7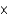 10-2 M
10-2 M
D) 1.0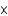 10-14 M
10-14 M
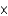 10-4 M H+?
10-4 M H+?A) 2.6
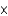 10-11 M
10-11 MB) 3.9
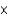 10-4
10-4 C) 2.7
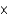 10-2 M
10-2 MD) 1.0
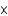 10-14 M
10-14 M
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Osmosis occurs when water diffuses through a
A) semipermeable membrane from high water to low water concentration.
B) nonpermeable membrane from high water to low water concentration.
C) semipermeable membrane from low water to high water concentration.
D) semipermeable membrane from high solute to low solute concentration.
A) semipermeable membrane from high water to low water concentration.
B) nonpermeable membrane from high water to low water concentration.
C) semipermeable membrane from low water to high water concentration.
D) semipermeable membrane from high solute to low solute concentration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Hydrophobic interactions between nonpolar molecules result from the
A) tendency to maximize water's interaction with nonpolar molecules.
B) strong attractions between nonpolar molecules.
C) water becoming more ordered around the nonpolar molecule.
D) water ionically bonding to the nonpolar molecule.
A) tendency to maximize water's interaction with nonpolar molecules.
B) strong attractions between nonpolar molecules.
C) water becoming more ordered around the nonpolar molecule.
D) water ionically bonding to the nonpolar molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
As a protein folds,what are the stabilizing forces that help keep the protein folded?
A) hydrophilic amino acids on the interior and hydrophobic amino acids on the exterior
B) increase in entropy in the surrounding water
C) favorable change in free energy
D) hydrophobic amino acids on the interior and hydrophilic amino acids on the exterior
A) hydrophilic amino acids on the interior and hydrophobic amino acids on the exterior
B) increase in entropy in the surrounding water
C) favorable change in free energy
D) hydrophobic amino acids on the interior and hydrophilic amino acids on the exterior

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A molecule with hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties is best described as
A) a zwitterion.
B) amphipathic.
C) polar.
D) nonpolar.
A) a zwitterion.
B) amphipathic.
C) polar.
D) nonpolar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A solution of which of the following would be a good buffer system?
A) HCl and NaOH
B) HCl and H2O
C) CH3COOH and NaCH3COO
D) NaOH and KOH
A) HCl and NaOH
B) HCl and H2O
C) CH3COOH and NaCH3COO
D) NaOH and KOH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Compare the reaction conditions for 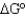 and
and 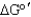
.
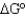 and
and 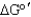
.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
You wish to prepare a solution with a pH of 5.44.If the pKa of the weak acid is 4.74,what ratio of weak base to weak acid should you use?
A) 0.70
B) 0.20
C) 1.4
D) 5.0
A) 0.70
B) 0.20
C) 1.4
D) 5.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The main function of the chloroplast is
A) protein biosynthesis.
B) to attach carbohydrates to lipids.
C) to convert light energy into chemical energy.
D) RNA synthesis.
A) protein biosynthesis.
B) to attach carbohydrates to lipids.
C) to convert light energy into chemical energy.
D) RNA synthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Differentiate between autotrophs and heterotrophs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Using the figure below,which of the following best describes the titration curve? 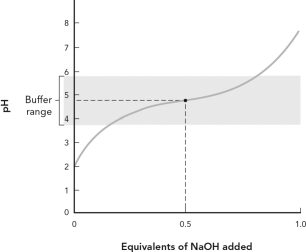
A) The equivalence point for the titration is pH = 7.
B) The midpoint of the titration is pH = 7.
C) The pKa for this weak acid is 4.76.
D) This is a titration of a weak base by NaOH.

A) The equivalence point for the titration is pH = 7.
B) The midpoint of the titration is pH = 7.
C) The pKa for this weak acid is 4.76.
D) This is a titration of a weak base by NaOH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Calculate the pH of a solution containing 0.105 M HA and 0.146 M A-.The Ka for the weak acid is 1.8 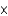 10-5.
10-5.
A) 4.88
B) 9.11
C) 4.74
D) 7.00
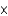 10-5.
10-5.A) 4.88
B) 9.11
C) 4.74
D) 7.00

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Compare the reaction conditions under which you measure Keq versus Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Calculate the 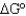 for the net reaction given the following two reactions:
for the net reaction given the following two reactions:
Reaction 1: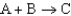
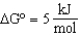
.
Reaction 2: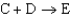
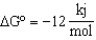 .
.
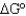 for the net reaction given the following two reactions:
for the net reaction given the following two reactions:Reaction 1:
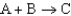
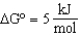
.
Reaction 2:
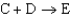
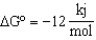 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The endomembrane system encompasses which part of the cell?
A) organelles
B) nucleus
C) cytoplasmic membrane structures
D) entire cell
A) organelles
B) nucleus
C) cytoplasmic membrane structures
D) entire cell

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The lateral mobility of lipids with membrane depends on temperature as well as other factors.What would be expected to happen to the lateral mobility if the temperature was decreased?
A) Mobility would be unaffected.
B) Mobility would increase.
C) Mobility would decrease.
D) The membrane would decompose.
A) Mobility would be unaffected.
B) Mobility would increase.
C) Mobility would decrease.
D) The membrane would decompose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The characteristic(s)of a phospholipid is/are that they
A) are overall nonpolar.
B) have a polar charged head group and nonpolar hydrocarbon tails.
C) have a nonpolar head group and polar hydrocarbon tails.
D) are overall polar.
A) are overall nonpolar.
B) have a polar charged head group and nonpolar hydrocarbon tails.
C) have a nonpolar head group and polar hydrocarbon tails.
D) are overall polar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The fluidity of a membrane depends on
A) the degree of saturation of the phospholipids.
B) the number of phospholipids in the membrane.
C) the size of the polar head group.
D) osmotic pressure.
A) the degree of saturation of the phospholipids.
B) the number of phospholipids in the membrane.
C) the size of the polar head group.
D) osmotic pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The endomembrane system is/are
A) an intracellular network of lipid bilayers.
B) energy converting organelles.
C) a membrane surrounding the cell.
D) nucleotide-containing membranes.
A) an intracellular network of lipid bilayers.
B) energy converting organelles.
C) a membrane surrounding the cell.
D) nucleotide-containing membranes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following are true about buffers?
A) An effective buffer is made from a strong acid and strong base.
B) A buffer is most resistant to changes in pH when [HA] = [A-].
C) A buffer is only resistant to changes in pH when acid is added.
D) The pH range of a buffering system is 0 to 14.
A) An effective buffer is made from a strong acid and strong base.
B) A buffer is most resistant to changes in pH when [HA] = [A-].
C) A buffer is only resistant to changes in pH when acid is added.
D) The pH range of a buffering system is 0 to 14.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Given a solution with pH > pKa,what are the relative concentrations of A- and HA?
A) [HA] > [A-]
B) [HA] < [A-]
C) [HA] = [A-]
D) [HA] = [A-] = 1
A) [HA] > [A-]
B) [HA] < [A-]
C) [HA] = [A-]
D) [HA] = [A-] = 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Calculate 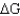
for a reaction given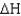
= 15.4 kJ/mole and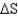
= 2.0 J/K at 298 K.Is this reaction spontaneous in the forward direction?
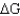
for a reaction given
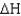
= 15.4 kJ/mole and
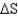
= 2.0 J/K at 298 K.Is this reaction spontaneous in the forward direction?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
How are polar molecules like glucose transported across a membrane?
A) There are holes in the membrane.
B) There are proteins that allow the transportation of polar molecules across the membrane.
C) Polar molecules cannot ever enter the cell.
D) Polar molecules diffuse across the hydrophobic barrier.
A) There are holes in the membrane.
B) There are proteins that allow the transportation of polar molecules across the membrane.
C) Polar molecules cannot ever enter the cell.
D) Polar molecules diffuse across the hydrophobic barrier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Justify the following sentence: The conversion of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen is a decrease of entropy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



