Deck 7: Enzyme Mechanisms
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/105
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Enzyme Mechanisms
1
Binding of glucose to hexokinase causes a conformational change in the enzyme.This is an example of the __________ model of enzyme catalysis.
A) substrate-induced
B) lock and key
C) induced-fit
D) glove and hand
A) substrate-induced
B) lock and key
C) induced-fit
D) glove and hand
C
2
Which of the following is true of the induced-fit model of enzyme catalysis but NOT of the lock and key model of enzyme catalysis?
A) It was proposed by Emil Fischer.
B) It involves weak interactions of a substrate with an enzyme.
C) It involves a conformational change of the enzyme.
D) It involves noncovalent interactions of the substrate with the enzyme.
A) It was proposed by Emil Fischer.
B) It involves weak interactions of a substrate with an enzyme.
C) It involves a conformational change of the enzyme.
D) It involves noncovalent interactions of the substrate with the enzyme.
C
3
Which of the following is a way that an enzyme can increase the rate of a reaction inside a cell?
A) increasing the temperature of the cell
B) increasing the pressure inside the cell
C) increasing the substrate concentration inside the cell
D) orienting substrates appropriately for the reaction to occur
A) increasing the temperature of the cell
B) increasing the pressure inside the cell
C) increasing the substrate concentration inside the cell
D) orienting substrates appropriately for the reaction to occur
D
4
A mutation of Lys229 in aldolase leads to a loss of enzyme activity.This is most likely because the
A) active site can no longer exclude water.
B) active site can no longer include water.
C) enzyme can no longer hold the intermediate in the correct orientation for catalysis.
D) product will remain bound to the enzyme active site.
A) active site can no longer exclude water.
B) active site can no longer include water.
C) enzyme can no longer hold the intermediate in the correct orientation for catalysis.
D) product will remain bound to the enzyme active site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which answer correctly pairs the enzyme class with the type of reaction catalyzed?
A) lyase; formation of two products by hydrolyzing a substrate
B) transferase; transfer of H or O atoms
C) isomerase; intramolecular rearrangements
D) oxidoreductase; transfer of groups within molecules
A) lyase; formation of two products by hydrolyzing a substrate
B) transferase; transfer of H or O atoms
C) isomerase; intramolecular rearrangements
D) oxidoreductase; transfer of groups within molecules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An enzyme can increase the rate of a reaction inside a cell by __________ the energy of the __________.
A) lowering; transition state
B) increasing; product
C) lowering; substrate
D) increasing; transition state
A) lowering; transition state
B) increasing; product
C) lowering; substrate
D) increasing; transition state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the rate enhancement as a result of the presence of an enzyme if the uncatalyzed rate of the reaction is 1.2 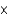 102 mmol/sec and the catalyzed rate is 2.4
102 mmol/sec and the catalyzed rate is 2.4 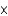
104 mmol/sec?
A) 0.005
B) 200
C) 2.88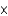
106
D) 2
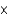 102 mmol/sec and the catalyzed rate is 2.4
102 mmol/sec and the catalyzed rate is 2.4 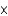
104 mmol/sec?
A) 0.005
B) 200
C) 2.88
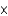
106
D) 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Nitrite reductase contains two histidine amino acids that coordinate a Cu2+ ion.When the ion is present in the enzyme,the ion is a __________ and the enzyme is a __________.
A) cofactor; apoenzyme
B) cofactor; holoenzyme
C) coenzyme; apoenzyme
D) coenzyme; holoenzyme
A) cofactor; apoenzyme
B) cofactor; holoenzyme
C) coenzyme; apoenzyme
D) coenzyme; holoenzyme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is a prosthetic group?
A) Mg2+
B) NADH
C) Zn2+
D) heme
A) Mg2+
B) NADH
C) Zn2+
D) heme

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The dihydrolipoyl transacetylase enzyme contains a lipoyl group.The lipoyl group is a(n)
A) ion.
B) apoenzyme.
C) prosthetic group.
D) holo group.
A) ion.
B) apoenzyme.
C) prosthetic group.
D) holo group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Enzymes usually bind substrates with __________ affinity and __________ specificity.
A) high; high.
B) high; low
C) low; low
D) low; high
A) high; high.
B) high; low
C) low; low
D) low; high

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is true of a coenzyme but NOT true of a prosthetic group?
A) It contains an organic component.
B) It is loosely associated with the enzyme.
C) It is necessary for enzyme function.
D) It is present in a holoenzyme but not an apoenzyme.
A) It contains an organic component.
B) It is loosely associated with the enzyme.
C) It is necessary for enzyme function.
D) It is present in a holoenzyme but not an apoenzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Enzyme active sites
A) are nonspecific.
B) are a pocket or cleft.
C) always exclude water.
D) can only bind a single substrate at a time.
A) are nonspecific.
B) are a pocket or cleft.
C) always exclude water.
D) can only bind a single substrate at a time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
An enzyme that requires the coenzyme nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide belongs to which enzyme class?
A) transferases
B) isomerases
C) ligases
D) oxidoreductases
A) transferases
B) isomerases
C) ligases
D) oxidoreductases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The transition state of a reaction is
A) higher in free energy than the product.
B) lower in free energy than the ground state of the substrate.
C) easily isolated.
D) equal to the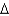
G‡ of the uncatalyzed reaction minus the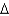
G‡ of the catalyzed reaction.
A) higher in free energy than the product.
B) lower in free energy than the ground state of the substrate.
C) easily isolated.
D) equal to the
G‡ of the uncatalyzed reaction minus the
G‡ of the catalyzed reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Consider the reaction coordinate diagram shown below.X is __________; Y is __________. 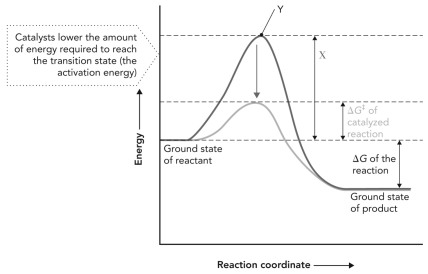
A) transition state; activation energy
B) G‡ of catalyzed reaction; transition state
G‡ of catalyzed reaction; transition state
C) activation energy of catalyzed reaction; transition state
D)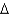 G‡ of uncatalyzed reaction; transition state
G‡ of uncatalyzed reaction; transition state

A) transition state; activation energy
B)
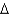 G‡ of catalyzed reaction; transition state
G‡ of catalyzed reaction; transition stateC) activation energy of catalyzed reaction; transition state
D)
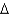 G‡ of uncatalyzed reaction; transition state
G‡ of uncatalyzed reaction; transition state
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Below is a ribbon diagram of an enzyme.Four regions of the enzyme are indicated.Which is most likely the active site? 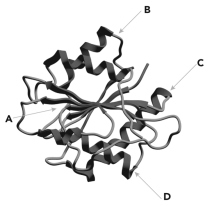
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is a holoenzyme?
A) pyruvate kinase with a bound K+
B) alcohol dehydrogenase
C) nitrite reductase
D) hexokinase
A) pyruvate kinase with a bound K+
B) alcohol dehydrogenase
C) nitrite reductase
D) hexokinase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Hexokinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate.Hexokinase belongs to which enzyme class?
A) transferase
B) ligase
C) oxidoreductase
D) hydrolase
A) transferase
B) ligase
C) oxidoreductase
D) hydrolase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A reaction coordinate diagram comparing an uncatalyzed reaction with an enzyme-catalyzed reaction can directly illustrate that the enzyme __________,but will not directly illustrate that the enzyme __________.
A) orients the substrates appropriately for the reaction to occur; provides an alternative path for product formation
B) provides an alternative path for product formation; stabilizes the transition state
C) stabilizes the transition state; orients the substrates appropriately for the reaction to occur
D) stabilizes the transition state; provides an alternative path for product formation
A) orients the substrates appropriately for the reaction to occur; provides an alternative path for product formation
B) provides an alternative path for product formation; stabilizes the transition state
C) stabilizes the transition state; orients the substrates appropriately for the reaction to occur
D) stabilizes the transition state; provides an alternative path for product formation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Reaction coordinate diagrams clearly show that the energy of an enzyme bound to a transition state is higher than the energies of the E + S,E + P,and ES that occur along the same reaction coordinate.The energy of an enzyme bound to a transition state analog would lie __________ in the diagram.
A) above the E + S but below the transition state
B) below the E + S
C) above the transition state
D) above E + S but below ES
A) above the E + S but below the transition state
B) below the E + S
C) above the transition state
D) above E + S but below ES

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Enzymes from four different species catalyze the same reaction.Based on the reaction coordinate diagrams below,which species contains an enzyme that experiences more bonding interactions with the transition state of the reaction? 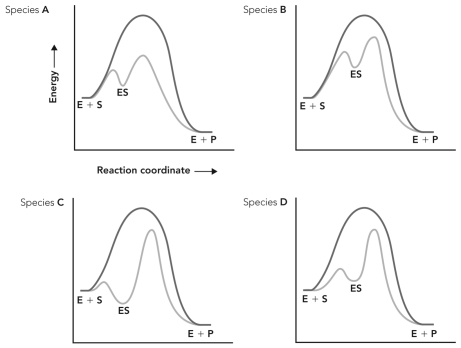
A) species A
B) species B
C) species C
D) species D

A) species A
B) species B
C) species C
D) species D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which type of reaction does not change the molecular formula of the product compared with that of the substrate?
A) condensation
B) reduction
C) hydrolysis
D) isomerization
A) condensation
B) reduction
C) hydrolysis
D) isomerization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The regulation of a biomolecule through the addition or removal of a molecular tag involves __________ reactions.
A) coenzyme-dependent redox
B) reversible covalent modification
C) metabolite transformation
D) isomerization
A) coenzyme-dependent redox
B) reversible covalent modification
C) metabolite transformation
D) isomerization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
All of the following are common catalytic reaction mechanisms in enzyme active sites EXCEPT __________ catalysis.
A) acid-base
B) covalent
C) metal ion
D) van der Waals
A) acid-base
B) covalent
C) metal ion
D) van der Waals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Refer to the reaction coordinate diagram below.The change in the activation energy of the reaction because of the presence of an enzyme is illustrated by the energy of __________ minus the energy of __________. 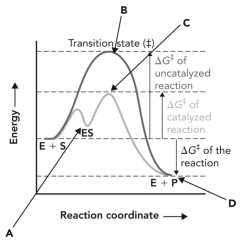
A) B; A
B) B; C
C) B; D
D) C; D

A) B; A
B) B; C
C) B; D
D) C; D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If an enzyme carries out acid-base catalysis,which of the following amino acids could act as general acid?
A) phenylalanine
B) glycine
C) histidine
D) alanine
A) phenylalanine
B) glycine
C) histidine
D) alanine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate is an example of which type of reaction?
A) hydrolysis
B) dehydration
C) isomerization
D) condensation
A) hydrolysis
B) dehydration
C) isomerization
D) condensation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Both the substrate and the tetrahedral intermediate,when associated with chymotrypsin,
A) contain an oxyanion.
B) interact with the oxyanion hole.
C) undergo a nucleophilic attack.
D) hydrogen bond to Asp102.
A) contain an oxyanion.
B) interact with the oxyanion hole.
C) undergo a nucleophilic attack.
D) hydrogen bond to Asp102.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which pair correctly matches the coenzymes most often used to mediate the described redox reactions?
A) NAD+/NADH; redox at C-O bonds
B) NADP+/NADPH; redox at C-C bonds
C) FAD/FADH2; redox at C-O bonds
D) FMN/FMNH2; redox at C-O bonds
A) NAD+/NADH; redox at C-O bonds
B) NADP+/NADPH; redox at C-C bonds
C) FAD/FADH2; redox at C-O bonds
D) FMN/FMNH2; redox at C-O bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When a nucleophile present in the enzyme attacks an electrophilic substrate to form an enzyme-substrate intermediate,this is an example of __________ catalysis.
A) covalent
B) acid-base
C) metal ion
D) hydrophobic
A) covalent
B) acid-base
C) metal ion
D) hydrophobic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The catalytic triad of chymotrypsin is composed of His57,Ser195,and
A) Gly193.
B) Glu103.
C) Asp120.
D) Asp102.
A) Gly193.
B) Glu103.
C) Asp120.
D) Asp102.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Many medicinal drugs are transition state analogs.They are good drugs because they can interact with the target enzyme active site and are
A) higher in energy than the transition state.
B) identical in structure to the transition state.
C) stable.
D) polar.
A) higher in energy than the transition state.
B) identical in structure to the transition state.
C) stable.
D) polar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In a reversible covalent modification reaction involving the phosphorylation of a target protein,which of the following amino acids is LEAST likely to be modified with a phosphate group?
A) Ser
B) Phe
C) Tyr
D) Thr
A) Ser
B) Phe
C) Tyr
D) Thr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Refer to the reaction coordinate diagram below.At what point is there a maximum number of interactions between the enzyme and the compound that it is binding? 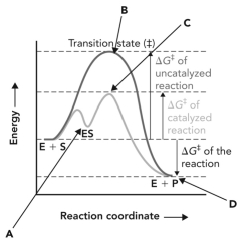
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The side chains of the amino acids that make up the catalytic triad of chymotrypsin contain all EXCEPT
A) a hydroxyl group.
B) a carboxylic acid.
C) an aromatic group.
D) an imidazole.
A) a hydroxyl group.
B) a carboxylic acid.
C) an aromatic group.
D) an imidazole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is true of the tetrahedral intermediate in the chymotrypsin mechanism?
A) It is lower in free energy than the substrate.
B) It is partially positively charged.
C) All bonds are the same length.
D) It contains an oxyanion.
A) It is lower in free energy than the substrate.
B) It is partially positively charged.
C) All bonds are the same length.
D) It contains an oxyanion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which amino acid acts as a general acid and a general base in the mechanism of chymotrypsin?
A) Ser195
B) His57
C) Gly193
D) Asp102
A) Ser195
B) His57
C) Gly193
D) Asp102

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The conversion of L-proline to D-proline is shown below.Which of the following characteristics would most likely be found in a transition state analog that inhibits an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction? 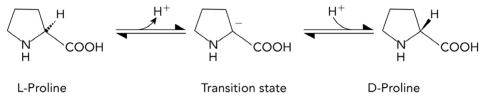
A) planar
B) positively charged at the -carbon
C) tetrahedral geometry at the -carbon
D) double bonds within the ring

A) planar
B) positively charged at the -carbon
C) tetrahedral geometry at the -carbon
D) double bonds within the ring

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The three general categories of enzyme-mediated reactions,which are determined on the basis of the work they accomplish,include all EXCEPT
A) coenzyme-dependent redox reactions.
B) reversible covalent modification.
C) hydrophobic collapse reactions.
D) metabolite transformation reactions.
A) coenzyme-dependent redox reactions.
B) reversible covalent modification.
C) hydrophobic collapse reactions.
D) metabolite transformation reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The hemithioacetal intermediate formed during the action of HMG-CoA reductase is stabilized by
A) Lys267.
B) Asp283.
C) His381.
D) Glu83.
A) Lys267.
B) Asp283.
C) His381.
D) Glu83.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The y-axis of a Lineweaver-Burk plot is
A) v0.
B) 1 / vo.
C) Km / vmax.
D) 1 / [S].
A) v0.
B) 1 / vo.
C) Km / vmax.
D) 1 / [S].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the rate constant for a reaction is determined to be equal to v / [Q][R],the reaction is the conversion of
A) Q to R.
B) R to Q.
C) R plus Q to a product.
D) It is impossible to determine the reaction given the information provided.
A) Q to R.
B) R to Q.
C) R plus Q to a product.
D) It is impossible to determine the reaction given the information provided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
For a reaction of S ![<strong>For a reaction of S P,the rate constant of the reaction is equal to</strong> A) k. B) k. C) 1 / v. D) [S] / v.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab7f_dc1d_b445_1d1f3f983f5c_TB6697_11_TB6697_11.jpg) P,the rate constant of the reaction is equal to
P,the rate constant of the reaction is equal to
A) k.
B)![<strong>For a reaction of S P,the rate constant of the reaction is equal to</strong> A) k. B) k. C) 1 / v. D) [S] / v.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab7f_dc1e_b445_d919326e1489_TB6697_11_TB6697_11.jpg) k.
k.
C) 1 / v.
D) [S] / v.
![<strong>For a reaction of S P,the rate constant of the reaction is equal to</strong> A) k. B) k. C) 1 / v. D) [S] / v.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab7f_dc1d_b445_1d1f3f983f5c_TB6697_11_TB6697_11.jpg) P,the rate constant of the reaction is equal to
P,the rate constant of the reaction is equal toA) k.
B)
![<strong>For a reaction of S P,the rate constant of the reaction is equal to</strong> A) k. B) k. C) 1 / v. D) [S] / v.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab7f_dc1e_b445_d919326e1489_TB6697_11_TB6697_11.jpg) k.
k.C) 1 / v.
D) [S] / v.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
For a reaction of Q + R ![<strong>For a reaction of Q + R P,the rate constant</strong> A) is equal to [Q][R] / [P]. B) has units of s<sup>-1</sup>. C) is a second-order rate constant. D) is equal to [P] / [Q][R].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab7f_dc1f_b445_c7e191ba2caf_TB6697_11_TB6697_11.jpg) P,the rate constant
P,the rate constant
A) is equal to [Q][R] / [P].
B) has units of s-1.
C) is a second-order rate constant.
D) is equal to [P] / [Q][R].
![<strong>For a reaction of Q + R P,the rate constant</strong> A) is equal to [Q][R] / [P]. B) has units of s<sup>-1</sup>. C) is a second-order rate constant. D) is equal to [P] / [Q][R].](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab7f_dc1f_b445_c7e191ba2caf_TB6697_11_TB6697_11.jpg) P,the rate constant
P,the rate constantA) is equal to [Q][R] / [P].
B) has units of s-1.
C) is a second-order rate constant.
D) is equal to [P] / [Q][R].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A mutation results in the change of Ser to Asp in the substrate binding pocket of chymotrypsin.Most likely,the mutant enzyme will
A) no longer catalyze the hydrolysis of a peptide bond because Asp cannot facilitate the nucleophilic attack.
B) no longer catalyze the hydrolysis of a peptide bond because Asp is unable to be deprotonated by His57.
C) preferentially hydrolyze substrates containing phenylalanine.
D) preferentially hydrolyze substrates containing lysine.
A) no longer catalyze the hydrolysis of a peptide bond because Asp cannot facilitate the nucleophilic attack.
B) no longer catalyze the hydrolysis of a peptide bond because Asp is unable to be deprotonated by His57.
C) preferentially hydrolyze substrates containing phenylalanine.
D) preferentially hydrolyze substrates containing lysine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the figure below,KM is indicated at 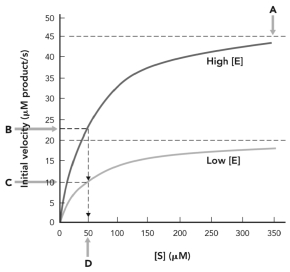
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The glutamate side chain in the active site of HMG-CoA reductase acts as a general base only after
A) the mevalonate binds to the active site.
B) the hydride from the second NADPH attacks the carbonyl center of the aldehyde.
C) a conformational change triggers the exchange of NADP+ for NADPH.
D) CoA is reduced to CoA-SH.
A) the mevalonate binds to the active site.
B) the hydride from the second NADPH attacks the carbonyl center of the aldehyde.
C) a conformational change triggers the exchange of NADP+ for NADPH.
D) CoA is reduced to CoA-SH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the steady-state condition assumed in Michaelis-Menten kinetics,__________ is relatively constant.
A) [ES]
B) [S]
C) v0
D) [ES] / [S]
A) [ES]
B) [S]
C) v0
D) [ES] / [S]

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is an assumption made when using Michaelis-Menten kinetics?
A) The conversion of E + P![<strong>Which of the following is an assumption made when using Michaelis-Menten kinetics?</strong> A) The conversion of E + P ES does not occur. B) k<sub>1</sub> > k<sub>2</sub> C) v<sub>0</sub> = v<sub>max</sub> at low [S] D) The conversion of EP E + P is rapid.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab80_0330_b445_69099cb54973_TB6697_11_TB6697_11.jpg)
ES does not occur.
B) k1 > k2
C) v0 = vmax at low [S]
D) The conversion of EP![<strong>Which of the following is an assumption made when using Michaelis-Menten kinetics?</strong> A) The conversion of E + P ES does not occur. B) k<sub>1</sub> > k<sub>2</sub> C) v<sub>0</sub> = v<sub>max</sub> at low [S] D) The conversion of EP E + P is rapid.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab80_0331_b445_29c217e545f1_TB6697_11_TB6697_11.jpg)
E + P is rapid.
A) The conversion of E + P
![<strong>Which of the following is an assumption made when using Michaelis-Menten kinetics?</strong> A) The conversion of E + P ES does not occur. B) k<sub>1</sub> > k<sub>2</sub> C) v<sub>0</sub> = v<sub>max</sub> at low [S] D) The conversion of EP E + P is rapid.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab80_0330_b445_69099cb54973_TB6697_11_TB6697_11.jpg)
ES does not occur.
B) k1 > k2
C) v0 = vmax at low [S]
D) The conversion of EP
![<strong>Which of the following is an assumption made when using Michaelis-Menten kinetics?</strong> A) The conversion of E + P ES does not occur. B) k<sub>1</sub> > k<sub>2</sub> C) v<sub>0</sub> = v<sub>max</sub> at low [S] D) The conversion of EP E + P is rapid.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab80_0331_b445_29c217e545f1_TB6697_11_TB6697_11.jpg)
E + P is rapid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The substrate binding pocket of __________ is best at accommodating substrates with small side chains.
A) elastase
B) chymotrypsin
C) enolase
D) trypsin
A) elastase
B) chymotrypsin
C) enolase
D) trypsin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The substrate binding pocket of __________ contains a(n)__________,which facilitates substrate specificity.
A) trypsin; Ser
B) chymotrypsin; Asp
C) trypsin; Asp
D) elastase; Gly
A) trypsin; Ser
B) chymotrypsin; Asp
C) trypsin; Asp
D) elastase; Gly

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following is NOT a function of the Mg2+ ions in the mechanism of enolase?
A) orientation of substrate in the active site
B) stabilizing the intermediate
C) making the proton at the C-2 position more acidic
D) electrophilic attack on the scissile bond
A) orientation of substrate in the active site
B) stabilizing the intermediate
C) making the proton at the C-2 position more acidic
D) electrophilic attack on the scissile bond

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Place the following HMG-CoA reductase steps in the correct order: A.Reduction of aldehyde
B)Breakdown of hemithioacetal
C)Reduction of thioester
D)Cofactor exchange
A) A, D, C, B
B) C, D, B, A
C) A, B, D, C
D) C, B, D, A
B)Breakdown of hemithioacetal
C)Reduction of thioester
D)Cofactor exchange
A) A, D, C, B
B) C, D, B, A
C) A, B, D, C
D) C, B, D, A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The initial velocity of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is followed at various substrate concentrations.At very high substrate concentrations it is observed that the initial velocity no longer increases as more substrate is added.The velocity under these conditions is known as
A) the ultimate velocity.
B) the maximum velocity.
C) v[S].
D) optimal velocity.
A) the ultimate velocity.
B) the maximum velocity.
C) v[S].
D) optimal velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
KM is equal to
A) k1 / (k-1 + k2).
B) (k-1 + k2) / k1.
C) 1/2 vmax.
D) vmax[S] / v0.
A) k1 / (k-1 + k2).
B) (k-1 + k2) / k1.
C) 1/2 vmax.
D) vmax[S] / v0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The mechanism of HMG-CoA reductase involves
A) two NADPH.
B) one NADPH.
C) two NADH.
D) one NADH.
A) two NADPH.
B) one NADPH.
C) two NADH.
D) one NADH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The role of Glu211 in the mechanism of enolase is to
A) facilitate the orientation of the phosphate group of the substrate.
B) act as a general base on the substrate.
C) act as a general acid on the intermediate.
D) make the proton at the C-2 position more acidic.
A) facilitate the orientation of the phosphate group of the substrate.
B) act as a general base on the substrate.
C) act as a general acid on the intermediate.
D) make the proton at the C-2 position more acidic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following functions as a general base in the mechanism of enolase?
A) Lys345
B) His57
C) Mg2+
D) Glu211
A) Lys345
B) His57
C) Mg2+
D) Glu211

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
On a plot of [product] versus time for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction,the v0 is equal to the
A) slope of the line / [S].
B) [P] at the lowest time point.
C) slope of the line.
D) y-intercept.
A) slope of the line / [S].
B) [P] at the lowest time point.
C) slope of the line.
D) y-intercept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A mixture of enzyme and inhibitor is run through a size-exclusion chromatography column.The activity of the enzyme is assessed before and after the chromatography.The enzyme has more activity after the chromatography step.Which of the following is true?
A) The enzyme was not eluted fully from the column.
B) The enzyme was denatured during chromatography.
C) The inhibitor is a reversible inhibitor.
D) The inhibitor is an irreversible inhibitor.
A) The enzyme was not eluted fully from the column.
B) The enzyme was denatured during chromatography.
C) The inhibitor is a reversible inhibitor.
D) The inhibitor is an irreversible inhibitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Below is a Lineweaver-Burk plot in which the axis labels have been removed.Interpret the plot to determine the vmax. 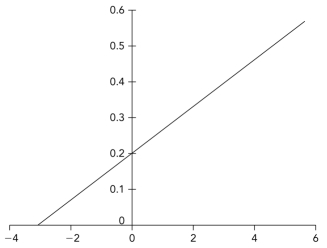
A) 0.2
B) 5
C) 3
D) 0.33

A) 0.2
B) 5
C) 3
D) 0.33

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Acetylcholinesterase is an important enzyme in the nervous system.Acetylcholinesterase activity is blocked by the nerve agent sarin gas,which forms a covalent bond with a Ser in the active site of the enzyme.Sarin gas is a(n)
A) allosteric effector.
B) competitive inhibitor.
C) reversible inhibitor.
D) irreversible inhibitor.
A) allosteric effector.
B) competitive inhibitor.
C) reversible inhibitor.
D) irreversible inhibitor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following statements are true?
A) ATCase is regulated by feedback inhibition.
B) CTP is an allosteric activator of ATCase.
C) ATP is an allosteric inhibitor of ATCase.
D) GTP is an allosteric inhibitor of ATCase.
A) ATCase is regulated by feedback inhibition.
B) CTP is an allosteric activator of ATCase.
C) ATP is an allosteric inhibitor of ATCase.
D) GTP is an allosteric inhibitor of ATCase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A kinase adds a phosphate group to a target enzyme,altering the catalytic efficiency of the enzyme.This is an example of
A) covalent modification.
B) proteolytic processing.
C) binding of regulatory molecules.
D) feedback inhibition.
A) covalent modification.
B) proteolytic processing.
C) binding of regulatory molecules.
D) feedback inhibition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following is NOT a primary mechanism that affects catalytic efficiency?
A) binding of regulatory molecules
B) covalent modification
C) proteolytic processing
D) cofactor degradation
A) binding of regulatory molecules
B) covalent modification
C) proteolytic processing
D) cofactor degradation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The Lineweaver-Burk plot shows data obtained for an enzyme in the absence and presence of a noncompetitive inhibitor.If the [I] is increased significantly in the experiment,the Vmaxapp would __________ and the Kmapp would __________. ![<strong>The Lineweaver-Burk plot shows data obtained for an enzyme in the absence and presence of a noncompetitive inhibitor.If the [I] is increased significantly in the experiment,the V<sub>maxapp</sub> would __________ and the K<sub>mapp</sub> would __________. </strong> A) decrease; decrease B) stay the same; decrease C) decrease; stay the same D) stay the same; stay the same](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab80_7865_b445_2f3c1ded9e91_TB6697_00_TB6697_00.jpg)
A) decrease; decrease
B) stay the same; decrease
C) decrease; stay the same
D) stay the same; stay the same
![<strong>The Lineweaver-Burk plot shows data obtained for an enzyme in the absence and presence of a noncompetitive inhibitor.If the [I] is increased significantly in the experiment,the V<sub>maxapp</sub> would __________ and the K<sub>mapp</sub> would __________. </strong> A) decrease; decrease B) stay the same; decrease C) decrease; stay the same D) stay the same; stay the same](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6697/11ea8d43_ab80_7865_b445_2f3c1ded9e91_TB6697_00_TB6697_00.jpg)
A) decrease; decrease
B) stay the same; decrease
C) decrease; stay the same
D) stay the same; stay the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A plot of 1 / v0 versus 1/[S] is called a __________ plot.Data in this plot have a slope equal to __________.
A) Lineweaver-Burk; Km/vmax
B) Lineweaver-Burk; -1/Km
C) Michaelis-Menten; Km/vmax
D) Michaelis-Menten; vmax
A) Lineweaver-Burk; Km/vmax
B) Lineweaver-Burk; -1/Km
C) Michaelis-Menten; Km/vmax
D) Michaelis-Menten; vmax

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the formation of an ESI complex,__________ inhibition can result.
A) mixed
B) competitive
C) covalent
D) anticompetitive
A) mixed
B) competitive
C) covalent
D) anticompetitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The Lineweaver-Burk plot shows data obtained for an enzyme in the absence and presence of a reversible inhibitor.Which type of inhibitor was used in the experiment? 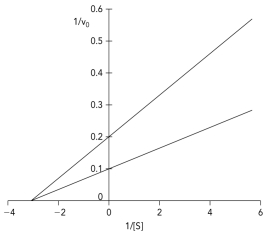
A) competitive
B) uncompetitive
C) mixed
D) noncompetitive

A) competitive
B) uncompetitive
C) mixed
D) noncompetitive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following pairs correctly matches the type of interaction observed between an inhibitor and an enzyme with the type of inhibition?
A) ionic; irreversible
B) covalent; irreversible
C) hydrogen bonding; reversible
D) hydrophobic; irreversible
A) ionic; irreversible
B) covalent; irreversible
C) hydrogen bonding; reversible
D) hydrophobic; irreversible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When compared with the T state of aspartate transcarbamoylase,the R state
A) has dissociated into two C3R3 complexes.
B) has greater separation of the catalytic subunits.
C) is bound to CTP.
D) has substrate bound in the ATP binding site.
A) has dissociated into two C3R3 complexes.
B) has greater separation of the catalytic subunits.
C) is bound to CTP.
D) has substrate bound in the ATP binding site.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
An enzyme undergoes a mutation that causes it to lose the ability to be regulated via phosphorylation.Which of the following mutations may lead to this loss of regulation? Assume that the overall structure is not altered by the mutation.
A) Ser
Thr
B) Thr
Ser
C) Tyr
Phe
D) Ser
Tyr
A) Ser

Thr
B) Thr

Ser
C) Tyr

Phe
D) Ser

Tyr

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which answer correctly classifies the compound with its relationship to aspartate transcarbamoylase?
A) ATP; allosteric inhibitor
B) ATP; allosteric activator
C) CTP; allosteric activator
D) CTP; substrate
A) ATP; allosteric inhibitor
B) ATP; allosteric activator
C) CTP; allosteric activator
D) CTP; substrate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The specificity constant is equal to
A) [Et][S] / v0.
B) Km / v0.
C) kcat / Km.
D) kcat / [Et].
A) [Et][S] / v0.
B) Km / v0.
C) kcat / Km.
D) kcat / [Et].

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A plot of vo versus [S] for aspartyl transcarbamoylase displays three sigmoidal lines.If the line in the middle represents the enzyme activity in the absence of any allosteric effectors,then the line to the __________ represents the enzyme in the __________ when bound to __________.
A) right; R state; CTP
B) right; T state; CTP
C) left; R state; GTP
D) left; T state; GTP
A) right; R state; CTP
B) right; T state; CTP
C) left; R state; GTP
D) left; T state; GTP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which type of interaction is more likely to be found between an enzyme and an irreversible inhibitor?
A) covalent bond
B) hydrogen bond
C) ionic interaction
D) van der Waals interaction
A) covalent bond
B) hydrogen bond
C) ionic interaction
D) van der Waals interaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
An inhibitor that binds only to the ES complex and not free enzyme is known as a(n)__________ inhibitor.
A) irreversible
B) competitive
C) uncompetitive
D) mixed
A) irreversible
B) competitive
C) uncompetitive
D) mixed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
An experiment is performed in which the kinetics of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction at different pHs is monitored.It is found that the Km does not change but that the kcat increases as the pH goes above 7.Which of the following is true?
A) A chemical group within the enzyme that has a pKa of around 7 is likely involved in the catalytic mechanism.
B) A chemical group with a pKa of around 7 must be deprotonated in order for substrate to bind.
C) A chemical group with a pKa of around 7 must be positively charged in order for the substrate to bind.
D) Protons are acting as positive heterotropic allosteric effectors of this enzyme.
A) A chemical group within the enzyme that has a pKa of around 7 is likely involved in the catalytic mechanism.
B) A chemical group with a pKa of around 7 must be deprotonated in order for substrate to bind.
C) A chemical group with a pKa of around 7 must be positively charged in order for the substrate to bind.
D) Protons are acting as positive heterotropic allosteric effectors of this enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A Lineweaver-Burk plot displays parallel lines for an enzyme in the absence and presence of increasing amounts of an inhibitor.The inhibitor in this experiment
A) binds both the free enzyme and the ES complex.
B) is competitive.
C) alters the Km but not the vmax.
D) is uncompetitive.
A) binds both the free enzyme and the ES complex.
B) is competitive.
C) alters the Km but not the vmax.
D) is uncompetitive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



