Deck 3: Supply and Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/99
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Supply and Demand
1
Incorrect. The quantity supplied of a good is directly related to its price, ceteris paribus.
True
2
Ceteris paribus, an increase in the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity would be caused by an increase in supply
False
3
If the market for wheat is in equilibrium, the quantity of wheat demanded will equal the quantity of wheat supplied
True
4
Two goods are complements if an increase in the price of one causes an increase in the demand for the other good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Only sellers determine prices and output in competitive markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the price of pizza falls, the demand for pizza will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Ceteris paribus, if the price of lumber increases, we would expect an increase in the supply of lumber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Increasing government taxation or regulation of an industry generally increases the supply of goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When the price of steak falls, we would expect the quantity of steak demanded to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If the price of Good A increases and the demand for Good B increases as well, goods A and B are most likely complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If watermelons are normal goods, the demand for them will rise as consumer income rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If the demand for apples increases at the same time the supply of apples falls, the price of apples will tend to fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Ceteris paribus, when a demand curve shifts, both the equilibrium price and quantity traded will change in the same direction as a result

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In economics, a market does not primarily refer to a specific place, but rather to the process of buyers and sellers exchanging goods and services

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Incorrect. If the demand for a good increases when incomes rise and decreases when incomes fall, the good is called a normal good. See 3-2: Demand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Price reductions will usually result whenever the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at the current price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
According to the law of supply, other things equal, when the price of a good or service rises, the quantity supplied increases, but supply does not

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If input prices fall, the cost of production will also fall, causing the supply curve to shift to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to the law of demand, other things equal, when the price of a good or service falls, demand increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When both supply and demand shift in the same direction, the change in the equilibrium quantity traded will be in the same direction as the shifting curves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following would cause a rightward shift in the demand curve for oranges?
A)A freeze in Florida (a major orange producing state)
B)A new machine that allows orange growers to harvest oranges faster
C)A decrease in the price of apples
D)An announcement by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that oranges lower cholesterol
E)An increase in the price of oranges
A)A freeze in Florida (a major orange producing state)
B)A new machine that allows orange growers to harvest oranges faster
C)A decrease in the price of apples
D)An announcement by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) that oranges lower cholesterol
E)An increase in the price of oranges

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A decrease in the price of a good will:
A)increase the demand for the good
B)decrease the demand for the good.
C)increase quantity demanded of the good
D)decrease quantity demanded of the good.
E)decrease the slope of the demand curve.
A)increase the demand for the good
B)decrease the demand for the good.
C)increase quantity demanded of the good
D)decrease quantity demanded of the good.
E)decrease the slope of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The quantity demanded of a good is the amount that buyers:
A)are willing to buy.
B)are willing and able to buy.
C)are willing, able, and need to buy.
D)are able to buy.
E)need for their subsistence.
A)are willing to buy.
B)are willing and able to buy.
C)are willing, able, and need to buy.
D)are able to buy.
E)need for their subsistence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is true of a competitive market?
A)The rules of supply and demand do not apply to it.
B)Sellers have little market power.
C)The largest firm is the price maker.
D)Few sellers offer similar products.
E)Government plays an important role in a competitive market.
A)The rules of supply and demand do not apply to it.
B)Sellers have little market power.
C)The largest firm is the price maker.
D)Few sellers offer similar products.
E)Government plays an important role in a competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The law of demand states that, ceteris paribus, an increase in:
A)the price of a good causes its quantity demanded to increase.
B)the price of a good causes its quantity demanded to decrease.
C)the quantity demanded of a good causes its price to increase.
D)the quantity demanded of a good causes its price to decrease.
E)the quantity demanded of a good causes its supply to decrease.
A)the price of a good causes its quantity demanded to increase.
B)the price of a good causes its quantity demanded to decrease.
C)the quantity demanded of a good causes its price to increase.
D)the quantity demanded of a good causes its price to decrease.
E)the quantity demanded of a good causes its supply to decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The law of demand refers to the:
A)decrease in price that occurs as more units of a product are demanded.
B)increase in price that results from an increase in demand for a good in limited supply.
C)inverse relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded.
D)increase in the quantity of a good made available when its price increases.
E)direct relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded.
A)decrease in price that occurs as more units of a product are demanded.
B)increase in price that results from an increase in demand for a good in limited supply.
C)inverse relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded.
D)increase in the quantity of a good made available when its price increases.
E)direct relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is true of a competitive market?
A)In a competitive market, firms do not compete with each other.
B)In a competitive market, the firm that charges the minimum price earns the maximum revenue.
C)In a competitive market, the price of each unit of good is equal to the average variable cost.
D)In a competitive market, every seller charges a different price for its output.
E)In a competitive market, the price of each unit of the good is fixed.
A)In a competitive market, firms do not compete with each other.
B)In a competitive market, the firm that charges the minimum price earns the maximum revenue.
C)In a competitive market, the price of each unit of good is equal to the average variable cost.
D)In a competitive market, every seller charges a different price for its output.
E)In a competitive market, the price of each unit of the good is fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A decrease in quantity demanded:
A)is illustrated by a movement downward and to the right along a demand curve.
B)is illustrated by a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve.
C)shifts the demand curve to the left.
D)shifts the demand curve to the right.
E)increases the slope of the demand curve.
A)is illustrated by a movement downward and to the right along a demand curve.
B)is illustrated by a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve.
C)shifts the demand curve to the left.
D)shifts the demand curve to the right.
E)increases the slope of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An increase in quantity demanded:
A)is illustrated by a movement downward and to the right along a demand curve.
B)is illustrated by a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve.
C)is illustrated by a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve..
D)is illustrated by a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve
E)changes the slope of the demand curve.
A)is illustrated by a movement downward and to the right along a demand curve.
B)is illustrated by a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve.
C)is illustrated by a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve..
D)is illustrated by a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve
E)changes the slope of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is true of a competitive market?
A)The rules of supply and demand do not apply to it.
B)Buyers and sellers have substantial market power.
C)There is only one buyer in the market.
D)Many sellers offer identical products in a competitive market.
E)Government plays an important role in a competitive market.
A)The rules of supply and demand do not apply to it.
B)Buyers and sellers have substantial market power.
C)There is only one buyer in the market.
D)Many sellers offer identical products in a competitive market.
E)Government plays an important role in a competitive market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In economics, the demand for a good refers to the amount of the good that people:
A)would like to have if the good were free.
B)will buy at various prices.
C)need to achieve a minimum standard of living.
D)will buy at alternative income levels.
E)will receive from a welfare state.
A)would like to have if the good were free.
B)will buy at various prices.
C)need to achieve a minimum standard of living.
D)will buy at alternative income levels.
E)will receive from a welfare state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An increase in the price of a good will:
A)increase demand.
B)decrease demand.
C)increase the quantity demanded.
D)increase the slope of the demand curve.
E)increase the slope of the demand curve
A)increase demand.
B)decrease demand.
C)increase the quantity demanded.
D)increase the slope of the demand curve.
E)increase the slope of the demand curve

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 3-1 shows the shifts in the demand curve for a good. Using the graph and beginning on D1, a shift to D0 would indicate a(n):Figure 3-1 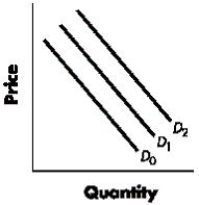
A)increase in demand.
B)decrease in demand.
C)increase in quantity demanded.
D)decrease in quantity demanded.
E)increase in the price of the good.

A)increase in demand.
B)decrease in demand.
C)increase in quantity demanded.
D)decrease in quantity demanded.
E)increase in the price of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A decrease in demand for a good could be caused by:
A)a decrease in the price of the good.
B)a decrease in the price of a complement of the good.
C)a technological advancement that decreases the cost of production of the good.
D)a decrease in the price of a substitute of the good.
E)an increase in the income of the consumers of the good.
A)a decrease in the price of the good.
B)a decrease in the price of a complement of the good.
C)a technological advancement that decreases the cost of production of the good.
D)a decrease in the price of a substitute of the good.
E)an increase in the income of the consumers of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When quantity demanded increases at every possible price, there is a(n):
A)leftward shift in the demand curve
B)rightward shift in the demand curve.
C)downward movement along the given demand curve.
D)upward movement along the given demand curve.
E)decrease in the slope of the given demand curve.
A)leftward shift in the demand curve
B)rightward shift in the demand curve.
C)downward movement along the given demand curve.
D)upward movement along the given demand curve.
E)decrease in the slope of the given demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Two goods are substitutes when a decrease in the price of one good:
A)decreases the demand for the other good.
B)decreases the quantity demanded of the other good.
C)increases the demand for the other good.
D)increases the quantity demanded of the other good.
E)increases the quantity supplied of the other good.
A)decreases the demand for the other good.
B)decreases the quantity demanded of the other good.
C)increases the demand for the other good.
D)increases the quantity demanded of the other good.
E)increases the quantity supplied of the other good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When quantity demanded decreases at every possible price, there is a(n):
A)leftward shift in the demand curve.
B)rightward shift in the demand curve.
C)a downward movement along the given demand curve.
D)upward movement along the given demand curve.
E)increase in the slope in the given demand curve.
A)leftward shift in the demand curve.
B)rightward shift in the demand curve.
C)a downward movement along the given demand curve.
D)upward movement along the given demand curve.
E)increase in the slope in the given demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Table 3-1 shows the demand schedules for gourmet ice cream of two individuals, Sven and Larry, and the rest of the market. At a price of $8, the quantity demanded in the market would be:Table 3-1 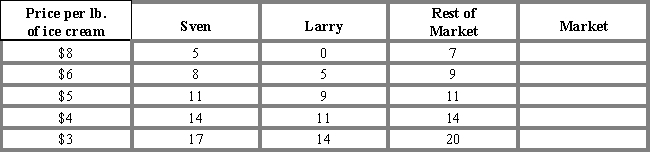
A)12.
B)22.
C)31.
D)39.
E)51.

A)12.
B)22.
C)31.
D)39.
E)51.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Table 3-1 shows the demand schedules for gourmet ice cream of two individuals, Sven and Larry, and the rest of the market. At $4, the quantity demanded in the market would be;Table 3-1 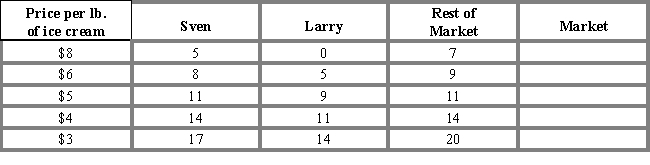
A)12.
B)22.
C)31
D)39.
E)51.

A)12.
B)22.
C)31
D)39.
E)51.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following would cause the demand curve for DVDs to shift to the right?
A)A decrease in the price of DVDs
B)A decrease in the price of DVD players
C)A decrease in the demand for watching movies in movie theaters
D)A decrease in the number of buyers in the market for DVDs
E)A decrease in the number of sellers in the market for DVDs
A)A decrease in the price of DVDs
B)A decrease in the price of DVD players
C)A decrease in the demand for watching movies in movie theaters
D)A decrease in the number of buyers in the market for DVDs
E)A decrease in the number of sellers in the market for DVDs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure 3-2 shows the shifts in the demand curve for a good. A change from Point A to Point E represents a(n):Figure 3-2 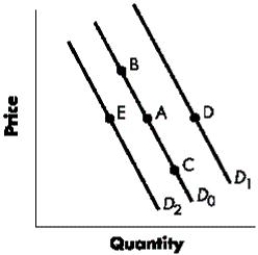
A)increase in demand.
B)decrease in demand
C)decrease in quantity demanded
D)increase in quantity demanded
E)increase in the price of the good.

A)increase in demand.
B)decrease in demand
C)decrease in quantity demanded
D)increase in quantity demanded
E)increase in the price of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 3-2 shows the shifts in the demand curve for a good. A change from Point A to Point C represents a(n):Figure 3-2 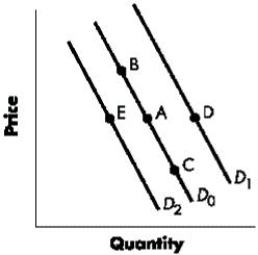
A)increase in demand.
B)decrease in demand.
C)decrease in quantity demanded.
D)increase in the price of the good.
E)increase in the price of the good

A)increase in demand.
B)decrease in demand.
C)decrease in quantity demanded.
D)increase in the price of the good.
E)increase in the price of the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is a difference between a change in quantity supplied and a change in supply?
A)A change in quantity supplied is caused by a change in a good's own, current price, while a change in supply is caused by a change in some other variable, such as input prices, prices of related goods, expectations, or taxes.
B)A change in quantity supplied is caused by a change in a good's own, current price, while a change in supply is caused by a change in some other variable, such as input prices, prices of related goods, expectations, or taxes
C)A change in quantity supplied is a change in the amount people want to sell, while a change in supply is a change in the amount they actually sell.
D)A change in supply and a change in the quantity supplied are the same thing.
E)A change in quantity supplied is illustrated by a shift in the supply curve, while a change in supply is illustrated by a movement along the given supply curve.
A)A change in quantity supplied is caused by a change in a good's own, current price, while a change in supply is caused by a change in some other variable, such as input prices, prices of related goods, expectations, or taxes.
B)A change in quantity supplied is caused by a change in a good's own, current price, while a change in supply is caused by a change in some other variable, such as input prices, prices of related goods, expectations, or taxes
C)A change in quantity supplied is a change in the amount people want to sell, while a change in supply is a change in the amount they actually sell.
D)A change in supply and a change in the quantity supplied are the same thing.
E)A change in quantity supplied is illustrated by a shift in the supply curve, while a change in supply is illustrated by a movement along the given supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Figure 3-3 shows shifts in the supply curve of a good. A change from Point A to Point B represents a(n):Figure 3-3 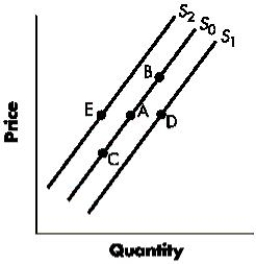
A)increase in the supply of the good.
B)decrease in the supply of the good
C)increase in the quantity supplied of the good.
D)decrease in the quantity supplied of the good.
E)decrease in the price of the good.

A)increase in the supply of the good.
B)decrease in the supply of the good
C)increase in the quantity supplied of the good.
D)decrease in the quantity supplied of the good.
E)decrease in the price of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A supply curve illustrates a(n) _____ relationship between _____ and _____.
A)direct; price; supply
B)direct; price; quantity demanded
C)direct; price; quantity supplied
D)inverse; price; quantity demanded
E)inverse; price; supply
A)direct; price; supply
B)direct; price; quantity demanded
C)direct; price; quantity supplied
D)inverse; price; quantity demanded
E)inverse; price; supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Table 3-2 shows a market of mid-sized autos. If these three firms represented the entire market, how many mid-sized autos would be supplied at a price of $30,000?Table 3-2 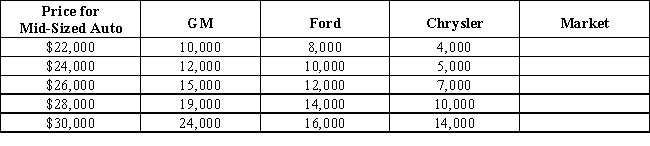
A)43,000
B)54,000
C)126,000
D)158,000
E)22,000

A)43,000
B)54,000
C)126,000
D)158,000
E)22,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Along the supply curve of a good, the:
A)supply of the good changes as its price changes.
B)quantity supplied of the good changes as its price changes.
C)supply of the good changes as technology changes.
D)quantity supplied of the good changes as technology changes.
E)quantity supplied of the good changes as income changes.
A)supply of the good changes as its price changes.
B)quantity supplied of the good changes as its price changes.
C)supply of the good changes as technology changes.
D)quantity supplied of the good changes as technology changes.
E)quantity supplied of the good changes as income changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A decrease in the number of sellers in the market for a good causes:
A)the supply curve of the good to shift to the left.
B)the supply curve of the good to shift to the right.
C)a movement up and to the right along a stationary supply curve of the good.
D)a movement downward and to the left along a stationary supply curve of the good.
E)a change in the slope of the supply curve of the good.
A)the supply curve of the good to shift to the left.
B)the supply curve of the good to shift to the right.
C)a movement up and to the right along a stationary supply curve of the good.
D)a movement downward and to the left along a stationary supply curve of the good.
E)a change in the slope of the supply curve of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure 3-2 shows the shifts in the demand curve for a good. A change from Point A to Point B represents a(n):Figure 3-2 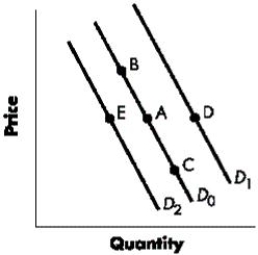
A)increase in demand.
B)decrease in demand.
C)decrease in quantity demanded.
D)increase in quantity demanded
E)decrease in the price of the good

A)increase in demand.
B)decrease in demand.
C)decrease in quantity demanded.
D)increase in quantity demanded
E)decrease in the price of the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Figure 3-3 shows shifts in the supply curve of a good. A change from Point A to Point E represents a(n):Figure 3-3 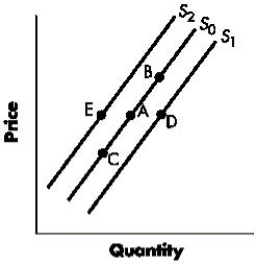
A)increase in supply
B)decrease in supply.
C)increase in quantity supplied.
D)decrease in quantity supplied
E)increase in the price of the good.

A)increase in supply
B)decrease in supply.
C)increase in quantity supplied.
D)decrease in quantity supplied
E)increase in the price of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The market supply schedule reflects the total quantity:
A)supplied at the market price.
B)supplied by all of the producers at the equilibrium price.
C)supplied at each price by all of the producers.
D)supplied by an individual firm at each price.
E)supplied by an individual firm at the equilibrium price.
A)supplied at the market price.
B)supplied by all of the producers at the equilibrium price.
C)supplied at each price by all of the producers.
D)supplied by an individual firm at each price.
E)supplied by an individual firm at the equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Figure 3-2 shows the shifts in the demand curve for a good. A change from Point A to Point D represents a(n):Figure 3-2 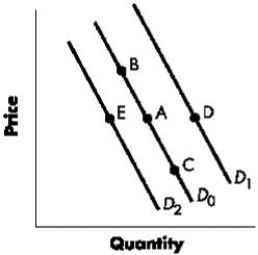
A)increase in demand
B)decrease in demand
C)decrease in quantity demanded.
D)increase in quantity demanded.
E)decrease in the price of the good

A)increase in demand
B)decrease in demand
C)decrease in quantity demanded.
D)increase in quantity demanded.
E)decrease in the price of the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 3-3 shows shifts in the supply curve of a good. A change from Point A to Point D represents a(n);Figure 3-3 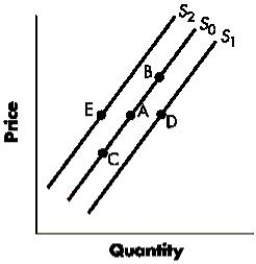
A)increase in the supply of the good.
B)decrease in the supply of the good
C)increase in the quantity supplied of the good
D)decrease in the quantity supplied of the good.
E)decrease in the price of the good

A)increase in the supply of the good.
B)decrease in the supply of the good
C)increase in the quantity supplied of the good
D)decrease in the quantity supplied of the good.
E)decrease in the price of the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is a difference between a change in quantity demanded and a change in demand?
A)A change in quantity demanded is caused by a change in a good's own current price, while a change in demand is caused by a change in some other variable, such as income, tastes, or expectations.
B)A change in demand is caused by a change in a good's own current price, while a change in quantity demanded is caused by a change in some other variable, such as income, tastes, or expectations.
C)A change in quantity demanded is a change in the amount people actually buy, while a change in demand is a change in the amount they want to buy.
D)A change in quantity demanded of a good is caused by a change in the availability of the good, while a change in demand is caused by a change in the price of the good.
E)A change in quantity demanded is illustrated by a shift in the demand curve, while a change in demand is illustrated by a movement along the given demand curve.
A)A change in quantity demanded is caused by a change in a good's own current price, while a change in demand is caused by a change in some other variable, such as income, tastes, or expectations.
B)A change in demand is caused by a change in a good's own current price, while a change in quantity demanded is caused by a change in some other variable, such as income, tastes, or expectations.
C)A change in quantity demanded is a change in the amount people actually buy, while a change in demand is a change in the amount they want to buy.
D)A change in quantity demanded of a good is caused by a change in the availability of the good, while a change in demand is caused by a change in the price of the good.
E)A change in quantity demanded is illustrated by a shift in the demand curve, while a change in demand is illustrated by a movement along the given demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A decrease in the price of a good will:
A)increase the supply of the good.
B)decrease the supply of the good
C)increase quantity supplied of the good.
D)decrease quantity supplied of the good.
E)increase the slope of the supply curve of the good.
A)increase the supply of the good.
B)decrease the supply of the good
C)increase quantity supplied of the good.
D)decrease quantity supplied of the good.
E)increase the slope of the supply curve of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Figure 3-3 shows shifts in the supply curve of a good. A change from Point A to Point C represents a(n):Figure 3-3 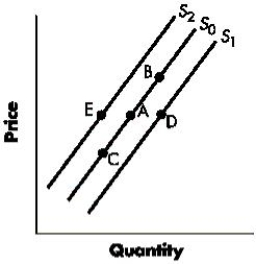
A)increase in the supply of the good.
B)decrease in the supply of the good.
C)increase in the quantity supplied of the good.
D)decrease in the quantity supplied of the good.
E)increase in the price of the good.

A)increase in the supply of the good.
B)decrease in the supply of the good.
C)increase in the quantity supplied of the good.
D)decrease in the quantity supplied of the good.
E)increase in the price of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Correct. In the given graph, a shift from D1 to D0 indicates a decrease in the demand for the good. See 3-2: DemandFigure 3-1 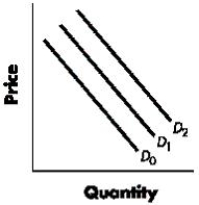
A)increase in demand.
B)increase in demand
C)increase in quantity demanded.
D)decrease in quantity demanded.
E)decrease in the price of the good.

A)increase in demand.
B)increase in demand
C)increase in quantity demanded.
D)decrease in quantity demanded.
E)decrease in the price of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
As a result of an increase in a product's price, the:
A)supply of the product increases.
B)supply of the product decreases.
C)quantity supplied of the product increases.
D)quantity supplied of the product decreases.
E)quantity demanded of the product increases.
A)supply of the product increases.
B)supply of the product decreases.
C)quantity supplied of the product increases.
D)quantity supplied of the product decreases.
E)quantity demanded of the product increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
According to the law of supply, ceteris paribus, the:
A)quantity supplied of a good will vary directly with the price of the good.
B)quantity supplied of a good will vary indirectly with the price of the good.
C)quantity supplied of a good will vary directly with consumers' income
D)quantity supplied of a good will vary indirectly with consumers' income.
E)quantity supplied of a good will vary indirectly with the size of the population.
A)quantity supplied of a good will vary directly with the price of the good.
B)quantity supplied of a good will vary indirectly with the price of the good.
C)quantity supplied of a good will vary directly with consumers' income
D)quantity supplied of a good will vary indirectly with consumers' income.
E)quantity supplied of a good will vary indirectly with the size of the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A movement along the supply curve of a good is caused by a change in:
A)the technology used in the production of the good.
B)the supplier's input prices.
C)expectations about future prices.
D)the price of the good.
E)the prices of the substitute of the good.
A)the technology used in the production of the good.
B)the supplier's input prices.
C)expectations about future prices.
D)the price of the good.
E)the prices of the substitute of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
At the equilibrium price, the quantity of the good that buyers are willing and able to buy:
A)is greater than the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
B)exactly equals the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
C)is less than the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
D)equals the maximum quantity that producers could produce.
E)equals the minimum quantity that producers need to produce.
A)is greater than the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
B)exactly equals the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
C)is less than the quantity that sellers are willing and able to sell.
D)equals the maximum quantity that producers could produce.
E)equals the minimum quantity that producers need to produce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When there is an excess quantity supplied of a product at the current price, then:
A)the market price must be below the equilibrium price.
B)the quantity demanded is greater than the equilibrium quantity.
C)the market price will tend to rise
D)the market price will tend to fall.
E)the quantity demanded will tend to fall.
A)the market price must be below the equilibrium price.
B)the quantity demanded is greater than the equilibrium quantity.
C)the market price will tend to rise
D)the market price will tend to fall.
E)the quantity demanded will tend to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The quantity sold of a daily newspaper will decline if;
A)newsprint becomes more expensive.
B)the printers' union makes wage concessions.
C)newspaper prices are reduced.
D)magazine prices rise.
E)magazine prices decline.
A)newsprint becomes more expensive.
B)the printers' union makes wage concessions.
C)newspaper prices are reduced.
D)magazine prices rise.
E)magazine prices decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A decrease in demand and an increase in supply are indicated by:
A)upward shifts in both curves.
B)downward shifts in both curves.
C)rightward shifts in both curves.
D)leftward shifts in both curves.
E)a downward shift in the demand curve, but an upward shift in the supply curve.
A)upward shifts in both curves.
B)downward shifts in both curves.
C)rightward shifts in both curves.
D)leftward shifts in both curves.
E)a downward shift in the demand curve, but an upward shift in the supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If a surplus exists in a market, then the actual price is:
A)above the equilibrium price and quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded.
B)above the equilibrium price and quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied.
C)below the equilibrium price and quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied.
D)below the equilibrium price and quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded.
E)equal to the equilibrium price and quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded.
A)above the equilibrium price and quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded.
B)above the equilibrium price and quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied.
C)below the equilibrium price and quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied.
D)below the equilibrium price and quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded.
E)equal to the equilibrium price and quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Table 3-3 shows the market demand and market supply schedules for large pepperoni pizzas. At a price of $10 per large pepperoni pizza, there is a _____ of _____ pizzas. 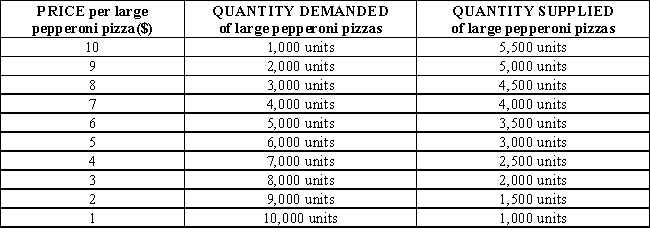
A)shortage; 4,500
B)surplus; 4,500
C)shortage; 6,500
D)surplus; 6,500
E)surplus; 3,000

A)shortage; 4,500
B)surplus; 4,500
C)shortage; 6,500
D)surplus; 6,500
E)surplus; 3,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In markets, prices move toward equilibrium because of:
A)the actions of buyers and sellers.
B)government regulations imposed on market participants.
C)decreased competition among sellers.
D)buyers' ability to affect market outcomes.
E)sellers' ability to affect market outcomes.
A)the actions of buyers and sellers.
B)government regulations imposed on market participants.
C)decreased competition among sellers.
D)buyers' ability to affect market outcomes.
E)sellers' ability to affect market outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A technological improvement that lowers production costs for Good A will:
A)shift the supply curve for A to the left.
B)shift the demand curve for A to the left.
C)shift the demand curve for A to the right.
D)shift the supply curve for A to the right.
E)decrease the quantity demanded of Good A.
A)shift the supply curve for A to the left.
B)shift the demand curve for A to the left.
C)shift the demand curve for A to the right.
D)shift the supply curve for A to the right.
E)decrease the quantity demanded of Good A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Figure 3-4 represents the market for butter. The equilibrium price of butter is: 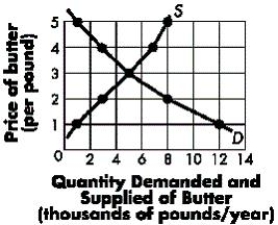
A)$5 per pound.
B)$3 per pound.
C)$2 per pound.
D)$1 per pound.
E)$4 per pound.

A)$5 per pound.
B)$3 per pound.
C)$2 per pound.
D)$1 per pound.
E)$4 per pound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What is the most likely effect of reducing costly regulations on the supply curve for a good?
A)The supply curve for the good will shift to the left.
B)The quantity supplied of the good will reduce.
C)The supply curve for the good will shift to the right
D)The supply curve for the good will not be affected.
E)The quantity supplied of the good will increase.
A)The supply curve for the good will shift to the left.
B)The quantity supplied of the good will reduce.
C)The supply curve for the good will shift to the right
D)The supply curve for the good will not be affected.
E)The quantity supplied of the good will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Table 3-3 shows the market demand and market supply schedules for large pepperoni pizzas. At a price of $4, there is a _____ of _____ pizzas. 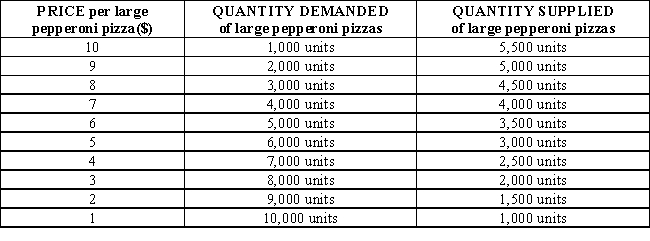
A)shortage; 4,500
B)surplus; 4,500
C)shortage; 6,500
D)surplus; 6,500
E)shortage; 3,000

A)shortage; 4,500
B)surplus; 4,500
C)shortage; 6,500
D)surplus; 6,500
E)shortage; 3,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A technological advancement in recycling made it possible to produce a greater quantity of paper from a given quantity of recyclednewspapers. Recycled paper is used to produce notebooks. According to the given scenario, which of the following statements will be true?
A)There will be a movement down along the supply curve of notebooks.
B)There will be a movement up along the supply curve of notebooks.
C)The supply curve for notebooks will shift to the left.
D)The supply curve for notebooks will shift to the right.
E)The supply curve for notebooks will become steeper.
A)There will be a movement down along the supply curve of notebooks.
B)There will be a movement up along the supply curve of notebooks.
C)The supply curve for notebooks will shift to the left.
D)The supply curve for notebooks will shift to the right.
E)The supply curve for notebooks will become steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Table 3-3 shows the market demand and market supply schedules for large pepperoni pizzas. In the given illustration, the equilibrium price per large pepperoni pizza is: 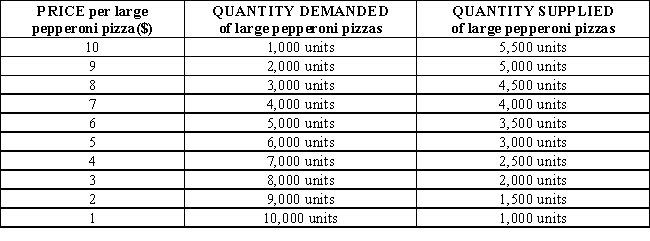
A)$9.
B)$8.
C)$7.
D)$6.
E)$5.

A)$9.
B)$8.
C)$7.
D)$6.
E)$5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If roses are currently selling for $30 per dozen but the equilibrium price of roses is $20 per dozen, then a:
A)shortage exists and the market price of roses is likely to increase.
B)shortage exists and the market price of roses is likely to decrease.
C)surplus exists and the market price of roses is likely to increase.
D)surplus exists and the market price of roses is likely to decrease.
E)decrease in the supply of roses in the market is likely to occur.
A)shortage exists and the market price of roses is likely to increase.
B)shortage exists and the market price of roses is likely to decrease.
C)surplus exists and the market price of roses is likely to increase.
D)surplus exists and the market price of roses is likely to decrease.
E)decrease in the supply of roses in the market is likely to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When there is an excess quantity demanded for a product at the current price, then:
A)the price will tend to fall
B)the price will tend to rise.
C)the price must be above the equilibrium price.
D)producers will reduce output and sales will fall.
E)the quantity demanded will tend to fall.
A)the price will tend to fall
B)the price will tend to rise.
C)the price must be above the equilibrium price.
D)producers will reduce output and sales will fall.
E)the quantity demanded will tend to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following would shift a supply curve for a good to the right?
A)An increase in taxes imposed on the production of the good
B)An increase in import restrictions on the good
C)an increase in import duties on the good
D)An increase in subsidies on the good
E)An increase in the price of the good
A)An increase in taxes imposed on the production of the good
B)An increase in import restrictions on the good
C)an increase in import duties on the good
D)An increase in subsidies on the good
E)An increase in the price of the good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The supply curve for a good will shift to the left if:
A)producers expect that the price of the good will soon be lower.
B)price decreases for a substitute for the good in production.
C)the input price for the good increases.
D)the number of suppliers of the good increases.
E)the price of the good decreases.
A)producers expect that the price of the good will soon be lower.
B)price decreases for a substitute for the good in production.
C)the input price for the good increases.
D)the number of suppliers of the good increases.
E)the price of the good decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is true of a market equilibrium?
A)At equilibrium, demand equals supply.
B)At equilibrium, quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
C)At equilibrium, market forces no longer apply.
D)At equilibrium, the "fairest" price for output is achieved.
E)At equilibrium, all the producers maximize their profits.
A)At equilibrium, demand equals supply.
B)At equilibrium, quantity demanded equals quantity supplied.
C)At equilibrium, market forces no longer apply.
D)At equilibrium, the "fairest" price for output is achieved.
E)At equilibrium, all the producers maximize their profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Table 3-4 shows the market demand and market supply schedules for music downloads. The equilibrium price of music downloads is: 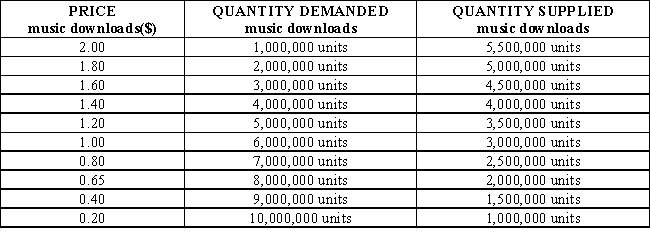
A)$0.80.
B)$1.00.
C)$1.20.
D)$1.40.
E)$1.60

A)$0.80.
B)$1.00.
C)$1.20.
D)$1.40.
E)$1.60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following would cause the quantity of wheat bread demanded to increase, but not the demand for wheat?
A)A reduction in the price of rye, used to produce rye bread
B)A new scientific study demonstrating that wheat bread reduces the risk of colon cancer
C)A decrease in the price of rye bread
D)An increase in the number of farmers growing wheat
E)A decrease in the number of farmers growing wheat
A)A reduction in the price of rye, used to produce rye bread
B)A new scientific study demonstrating that wheat bread reduces the risk of colon cancer
C)A decrease in the price of rye bread
D)An increase in the number of farmers growing wheat
E)A decrease in the number of farmers growing wheat

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



