Deck 9: International Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/195
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: International Trade
1
Consider the following statements:
I. Relative to a no-trade situation, if the United States exported wheat, the U.S. domestic wheat price would rise and domestic production of wheat would expand.
II. Relative to a no-trade situation, international trade causes the prices of all goods to rise.
A) I is true; II is false.
B) I is false; II is true.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Both I and II are false.
I. Relative to a no-trade situation, if the United States exported wheat, the U.S. domestic wheat price would rise and domestic production of wheat would expand.
II. Relative to a no-trade situation, international trade causes the prices of all goods to rise.
A) I is true; II is false.
B) I is false; II is true.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Both I and II are false.
I is true; II is false.
2
World supply of a good ______ domestic supply.
A) is less elastic than
B) is more elastic than
C) is equally elastic to
D) has indeterminate elasticity compared with
A) is less elastic than
B) is more elastic than
C) is equally elastic to
D) has indeterminate elasticity compared with
is more elastic than
3
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Trade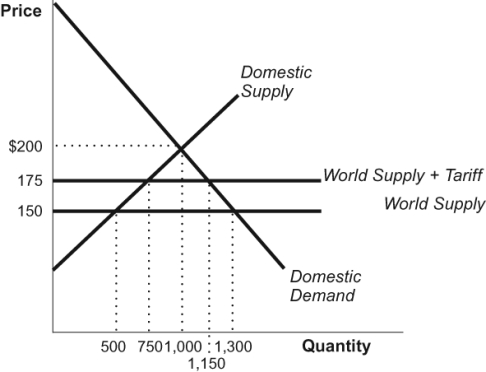
(Figure: Trade) Refer to the figure. If this figure represents the market for oil and the country imposes no tariffs on international trade, domestic consumption will be:
A) 500 units.
B) 1,000 units.
C) 1,150 units.
D) 1,300 units.
Figure: Trade

(Figure: Trade) Refer to the figure. If this figure represents the market for oil and the country imposes no tariffs on international trade, domestic consumption will be:
A) 500 units.
B) 1,000 units.
C) 1,150 units.
D) 1,300 units.
1,300 units.
4
If the world price of cotton is less than the price that would occur domestically without trade, then a country will:
A) decrease its demand for cotton, and increase its demand for cotton substitutes.
B) increase its demand for cotton, and decrease its demand for cotton substitutes.
C) import cotton.
D) export cotton.
A) decrease its demand for cotton, and increase its demand for cotton substitutes.
B) increase its demand for cotton, and decrease its demand for cotton substitutes.
C) import cotton.
D) export cotton.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade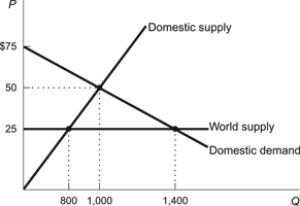
(Figure: Foreign Trade) Refer to the figure. What quantity would be traded in the absence of any international trade?
A) 600
B) 1,400
C) 1,000
D) 800
Figure: Foreign Trade

(Figure: Foreign Trade) Refer to the figure. What quantity would be traded in the absence of any international trade?
A) 600
B) 1,400
C) 1,000
D) 800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An increase in import trade tends to ______ domestic prices.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) hold constant
D) have an indeterminate effect on
A) increase
B) decrease
C) hold constant
D) have an indeterminate effect on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade
(Figure: Foreign Trade) Refer to the figure. What quantity would be imported?
A) 600
B) 1,400
C) 1,000
D) 800
Figure: Foreign Trade

(Figure: Foreign Trade) Refer to the figure. What quantity would be imported?
A) 600
B) 1,400
C) 1,000
D) 800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade
(Figure: Foreign Trade) Refer to the figure. What quantity would be produced domestically?
A) 600
B) 1,400
C) 1,000
D) 800
Figure: Foreign Trade

(Figure: Foreign Trade) Refer to the figure. What quantity would be produced domestically?
A) 600
B) 1,400
C) 1,000
D) 800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Trade
(Figure: Trade) Refer to the figure. With free international trade, the country in this figure will find that the good:
A) becomes cheaper for domestic consumers.
B) becomes more expensive for domestic consumers.
C) does not change in price.
D) may get cheaper or more expensive for domestic consumers but it is impossible to tell.
Figure: Trade

(Figure: Trade) Refer to the figure. With free international trade, the country in this figure will find that the good:
A) becomes cheaper for domestic consumers.
B) becomes more expensive for domestic consumers.
C) does not change in price.
D) may get cheaper or more expensive for domestic consumers but it is impossible to tell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When a country adopts free trade and becomes a net exporter of a good, that good:
A) becomes cheaper for domestic consumers.
B) becomes more expensive for domestic consumers.
C) does not change in price.
D) may get cheaper or more expensive for domestic consumers.
A) becomes cheaper for domestic consumers.
B) becomes more expensive for domestic consumers.
C) does not change in price.
D) may get cheaper or more expensive for domestic consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade
(Figure: Foreign Trade) Refer to the figure. What quantity would be traded in a free-trade environment?
A) 600
B) 1,400
C) 1,000
D) 800
Figure: Foreign Trade

(Figure: Foreign Trade) Refer to the figure. What quantity would be traded in a free-trade environment?
A) 600
B) 1,400
C) 1,000
D) 800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Table: Semiconductors
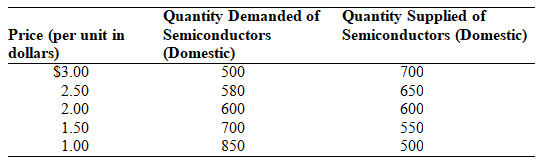
A) export 550 semiconductors.
B) export 150 semiconductors.
C) import 550 semiconductors.
D) import 150 semiconductors.

A) export 550 semiconductors.
B) export 150 semiconductors.
C) import 550 semiconductors.
D) import 150 semiconductors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Protectionism:
A) benefits domestic consumers and foreign producers.
B) places a tax on exports.
C) restricts trade through policies that favor domestic producers.
D) restricts the quantity of goods that can be exported.
A) benefits domestic consumers and foreign producers.
B) places a tax on exports.
C) restricts trade through policies that favor domestic producers.
D) restricts the quantity of goods that can be exported.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Trade
(Figure: Trade) Refer to the figure. If the world price for the good in this figure were higher than the domestic price, a move to free international trade means that the domestic economy would become:
A) a net importer of the good.
B) a net exporter of the good.
C) neither a net importer nor a net exporter of the good.
D) either a net importer or a net exporter of the good but it is impossible to say which.
Figure: Trade

(Figure: Trade) Refer to the figure. If the world price for the good in this figure were higher than the domestic price, a move to free international trade means that the domestic economy would become:
A) a net importer of the good.
B) a net exporter of the good.
C) neither a net importer nor a net exporter of the good.
D) either a net importer or a net exporter of the good but it is impossible to say which.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If Tyler and Alex are trading partners, do their gains from trade depend on whether Tyler and Alex live in the same country?
A) It is better if Tyler and Alex are both Americans.
B) It is better if one of them is American and one is not.
C) It is better if neither of them is American.
D) It doesn't matter in which country Tyler and Alex live.
A) It is better if Tyler and Alex are both Americans.
B) It is better if one of them is American and one is not.
C) It is better if neither of them is American.
D) It doesn't matter in which country Tyler and Alex live.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
International trade is similar to local trade because:
A) specialization does not occur in either case.
B) both are based on the concept of comparative advantage.
C) both are always efficient.
D) neither have political considerations.
A) specialization does not occur in either case.
B) both are based on the concept of comparative advantage.
C) both are always efficient.
D) neither have political considerations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following statements regarding trade is NOT true?
A) Trade increases productivity through specialization and production according to comparative advantage.
B) Trade raises the price of goods for both trading partners.
C) Trade increases productivity through specialization and the division of knowledge.
D) Trade makes people better off when preferences differ.
A) Trade increases productivity through specialization and production according to comparative advantage.
B) Trade raises the price of goods for both trading partners.
C) Trade increases productivity through specialization and the division of knowledge.
D) Trade makes people better off when preferences differ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The benefits of trade include:
I. greater productivity due to specialization.
II. higher output due to specialization according to comparative advantage.
III. increased welfare when preferences differ.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
I. greater productivity due to specialization.
II. higher output due to specialization according to comparative advantage.
III. increased welfare when preferences differ.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: International Trade 1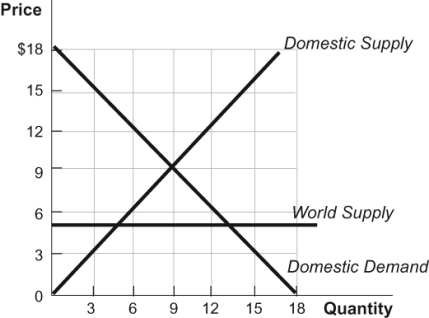
(Figure: International Trade 1) Refer to the figure. With the international trade in this figure, domestic consumption is ______ units, and ______ of those units are imported.
A) 9; 5
B) 13; 5
C) 13; 8
D) 20; 9
Figure: International Trade 1

(Figure: International Trade 1) Refer to the figure. With the international trade in this figure, domestic consumption is ______ units, and ______ of those units are imported.
A) 9; 5
B) 13; 5
C) 13; 8
D) 20; 9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: International Trade 1
(Figure: International Trade 1) Refer to the figure. According to the figure, which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) After international trade, price falls by $4 and consumption increases by 4 units.
B) After international trade, price falls by $4 and consumption decreases by 4 units.
C) After international trade, price rises by $4 and consumption increases by 8 units.
D) After international trade, price stays the same and consumption increases by 8 units.
Figure: International Trade 1

(Figure: International Trade 1) Refer to the figure. According to the figure, which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) After international trade, price falls by $4 and consumption increases by 4 units.
B) After international trade, price falls by $4 and consumption decreases by 4 units.
C) After international trade, price rises by $4 and consumption increases by 8 units.
D) After international trade, price stays the same and consumption increases by 8 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A tariff is a:
A) tax credit for domestic exports.
B) tax on imports.
C) temporary grant of monopoly rights.
D) renewable subsidy to the energy industry.
A) tax credit for domestic exports.
B) tax on imports.
C) temporary grant of monopoly rights.
D) renewable subsidy to the energy industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Import trade tends to ______ domestic quantity of a good exchanged.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) hold constant
D) have an indeterminate effect on
A) increase
B) decrease
C) hold constant
D) have an indeterminate effect on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff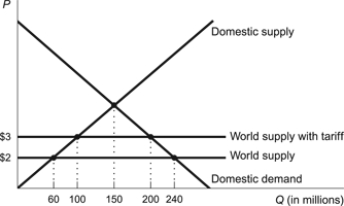
(Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff) Refer to the figure. A $1 tariff generates government revenue of:
A) $100 million.
B) $140 million.
C) $180 million.
D) $200 million.
Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff

(Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff) Refer to the figure. A $1 tariff generates government revenue of:
A) $100 million.
B) $140 million.
C) $180 million.
D) $200 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff
(Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff) Refer to the figure. A $1 tariff results in:
A) an increase in imports of 80 million units.
B) a decrease in imports of 80 million units.
C) an increase in imports of 100 million units.
D) a decrease in imports of 100 million units.
Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff

(Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff) Refer to the figure. A $1 tariff results in:
A) an increase in imports of 80 million units.
B) a decrease in imports of 80 million units.
C) an increase in imports of 100 million units.
D) a decrease in imports of 100 million units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Trade 2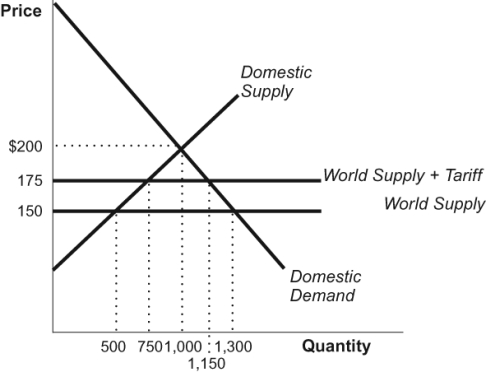
(Figure: Trade 2) Refer to the figure. In this figure representing the market for oil, what are the total revenues generated by the tariff?
A) $25,000
B) $20,000
C) $10,000
D) $5,000
Figure: Trade 2

(Figure: Trade 2) Refer to the figure. In this figure representing the market for oil, what are the total revenues generated by the tariff?
A) $25,000
B) $20,000
C) $10,000
D) $5,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The U.S. government restricting the quantity of sugar imports into the country is an example of a(n):
A) trade quota.
B) embargo.
C) trade settlement.
D) market hanger.
A) trade quota.
B) embargo.
C) trade settlement.
D) market hanger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Economic policies of protectionism include:
I. reduced trade barriers.
II. tariffs.
III. quotas.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
I. reduced trade barriers.
II. tariffs.
III. quotas.
A) I and II only
B) II and III only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is TRUE about the economic policy of "protectionism"?
A) It raises the prices of foreign goods in domestic markets.
B) It restricts competitive forces in domestic markets.
C) It can be achieved through quotas and tariffs.
D) All of the statements are correct.
A) It raises the prices of foreign goods in domestic markets.
B) It restricts competitive forces in domestic markets.
C) It can be achieved through quotas and tariffs.
D) All of the statements are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Imposing a restrictive quota on the import of sugar will likely:
A) increase the price of sugar and decrease the quantity consumed.
B) increase the price of sugar and increase the quantity consumed.
C) leave the price of sugar unchanged and decrease the quantity consumed.
D) leave the price of sugar unchanged and increase the quantity consumed.
A) increase the price of sugar and decrease the quantity consumed.
B) increase the price of sugar and increase the quantity consumed.
C) leave the price of sugar unchanged and decrease the quantity consumed.
D) leave the price of sugar unchanged and increase the quantity consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
According to the supply and demand framework in the text, an increase in import trade tends to ______ domestic production of a good.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) hold constant
D) have an indeterminate effect on
A) increase
B) decrease
C) hold constant
D) have an indeterminate effect on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A tariff is a:
A) tax on imports.
B) subsidy on exports.
C) restriction on the quantity of domestic goods consumed by foreigners.
D) restriction on the quantity of imports from foreign producers.
A) tax on imports.
B) subsidy on exports.
C) restriction on the quantity of domestic goods consumed by foreigners.
D) restriction on the quantity of imports from foreign producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A tariff is:
A) the restriction of trade through regulations on domestic producers.
B) a restriction on the quantity of goods that can be imported.
C) equal to exports minus imports.
D) a tax on imports.
A) the restriction of trade through regulations on domestic producers.
B) a restriction on the quantity of goods that can be imported.
C) equal to exports minus imports.
D) a tax on imports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following results from a tariff on imported goods?
I. domestic production increases
II. domestic consumption increases
III. government revenues increase
A) I and III only
B) II and III only
C) I and II only
D) I, II, and III
I. domestic production increases
II. domestic consumption increases
III. government revenues increase
A) I and III only
B) II and III only
C) I and II only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff
(Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff) Refer to the figure. A $1 tariff generates increased domestic production by:
A) $40 million units.
B) $90 million units.
C) $140 million units.
D) $180 million units.
Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff

(Figure: Foreign Trade with a Tariff) Refer to the figure. A $1 tariff generates increased domestic production by:
A) $40 million units.
B) $90 million units.
C) $140 million units.
D) $180 million units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A tariff on a good when the world price is lower than the domestic price leads to:
A) tariff revenues that will be lower than under free trade.
B) domestic imports that will be higher than under free trade.
C) lower domestic consumption of the good than under free trade.
D) lower domestic production of the good than under free trade.
A) tariff revenues that will be lower than under free trade.
B) domestic imports that will be higher than under free trade.
C) lower domestic consumption of the good than under free trade.
D) lower domestic production of the good than under free trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A trade quota is:
A) a restriction on the quantity of goods that can be imported.
B) a tax on imports.
C) a tax on exports.
D) the restriction of trade through regulations on domestic producers.
A) a restriction on the quantity of goods that can be imported.
B) a tax on imports.
C) a tax on exports.
D) the restriction of trade through regulations on domestic producers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Protectionism refers to government policies that:
A) restrict imports of foreign products.
B) give foreign producers tax credits in an effort to increase their exports.
C) stimulate trade between countries and increase domestic producers profit.
D) restrict the output of domestic producers to keep their prices high.
A) restrict imports of foreign products.
B) give foreign producers tax credits in an effort to increase their exports.
C) stimulate trade between countries and increase domestic producers profit.
D) restrict the output of domestic producers to keep their prices high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Shirts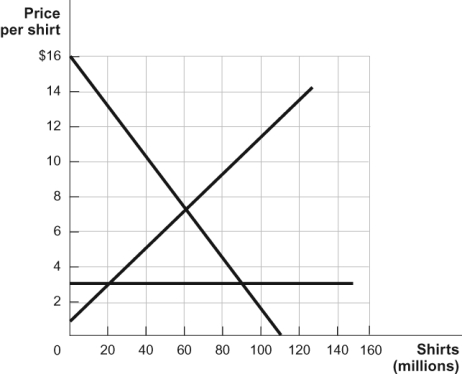
(Figure: Shirts) Refer to the figure. If a $5 tariff was levied on shirts, how much tax revenue would the government collect?
A) $0
B) $100 million
C) $200 million
D) $375 million
Figure: Shirts

(Figure: Shirts) Refer to the figure. If a $5 tariff was levied on shirts, how much tax revenue would the government collect?
A) $0
B) $100 million
C) $200 million
D) $375 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Trade 2
(Figure: Trade 2) Refer to the figure. In this figure representing the market for oil, by how much will domestic oil consumption increase or decrease following a tariff on imported oil?
A) increase by 250 units
B) increase by 300 units
C) decrease by 500 units
D) decrease by 150 units
Figure: Trade 2

(Figure: Trade 2) Refer to the figure. In this figure representing the market for oil, by how much will domestic oil consumption increase or decrease following a tariff on imported oil?
A) increase by 250 units
B) increase by 300 units
C) decrease by 500 units
D) decrease by 150 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Shirts
(Figure: Shirts) Refer to the figure. If a tariff raised the world price to $4 a shirt, how much deadweight loss would it create?
A) $5,000,000
B) $10,000,000
C) $120,000,000
D) $200,000,000
Figure: Shirts

(Figure: Shirts) Refer to the figure. If a tariff raised the world price to $4 a shirt, how much deadweight loss would it create?
A) $5,000,000
B) $10,000,000
C) $120,000,000
D) $200,000,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Bananas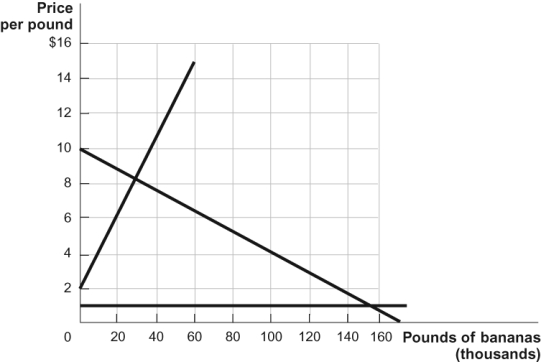
(Figure: Bananas) Refer to the figure. If there is a $3 tariff on bananas, domestic consumers buy ______ fewer bananas and domestic producers grow ______ additional bananas.
A) 50,000; 10,000
B) 75,000; 10,000
C) 50,000; 20,000
D) 75,000; 20,000
Figure: Bananas

(Figure: Bananas) Refer to the figure. If there is a $3 tariff on bananas, domestic consumers buy ______ fewer bananas and domestic producers grow ______ additional bananas.
A) 50,000; 10,000
B) 75,000; 10,000
C) 50,000; 20,000
D) 75,000; 20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Bananas
(Figure: Bananas) Refer to the figure. If there is a $3 tariff on bananas, approximately what percent of banana consumption comes from imports?
A) 8%
B) 10%
C) 90%
D) 93%
Figure: Bananas

(Figure: Bananas) Refer to the figure. If there is a $3 tariff on bananas, approximately what percent of banana consumption comes from imports?
A) 8%
B) 10%
C) 90%
D) 93%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: International Trade 2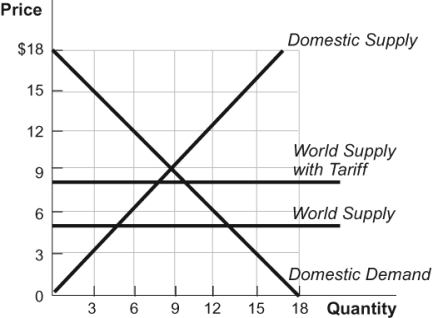
(Figure: International Trade 2) Refer to the figure. With the tariff in this figure, the domestic quantity demanded is ______, and the quantity supplied domestically is ______.
A) 10; 8
B) 8; 8
C) 10; 10
D) 9; 7
Figure: International Trade 2

(Figure: International Trade 2) Refer to the figure. With the tariff in this figure, the domestic quantity demanded is ______, and the quantity supplied domestically is ______.
A) 10; 8
B) 8; 8
C) 10; 10
D) 9; 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A tariff ______ the amount of output produced by domestic firms and ______ the amount of goods bought by domestic consumers.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Bananas
(Figure: Bananas) If there is a $3 tariff on bananas, what is the total tariff revenue?
A) $135,000
B) $180,000
C) $270,000
D) $360,000
Figure: Bananas

(Figure: Bananas) If there is a $3 tariff on bananas, what is the total tariff revenue?
A) $135,000
B) $180,000
C) $270,000
D) $360,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Shirts
(Figure: Shirts) Refer to the figure. If a tariff raised the world price to $4 a shirt, how much consumer surplus would be lost?
A) $5,000,000
B) $10,000,000
C) $85,000,000
D) $30,000,000
Figure: Shirts

(Figure: Shirts) Refer to the figure. If a tariff raised the world price to $4 a shirt, how much consumer surplus would be lost?
A) $5,000,000
B) $10,000,000
C) $85,000,000
D) $30,000,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade 2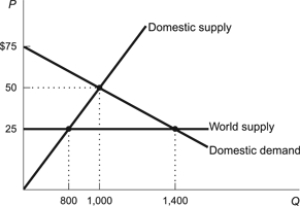
(Figure: Foreign Trade 2) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of wasted resources as a result of prohibiting trade in this market?
A) $30,000
B) $5,000
C) $2,500
D) $22,500
Figure: Foreign Trade 2

(Figure: Foreign Trade 2) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of wasted resources as a result of prohibiting trade in this market?
A) $30,000
B) $5,000
C) $2,500
D) $22,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade Market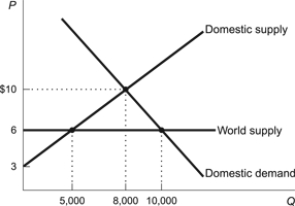
(Figure: Foreign Trade Market) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of wasted resources as a result of prohibiting trade in this market?
A) $10,000
B) $4,000
C) $7,500
D) $6,000
Figure: Foreign Trade Market

(Figure: Foreign Trade Market) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of wasted resources as a result of prohibiting trade in this market?
A) $10,000
B) $4,000
C) $7,500
D) $6,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What is the difference between a tariff and a trade quota?
A) A tariff is a tax on imported goods, and a trade quota is a quantity restriction on imported goods.
B) A tariff is a cash payment to domestic exporters, and a trade quota restricts the quantity of domestically produced goods foreigners can buy.
C) A tariff is a lump-sum tax on imported goods, and a trade quota is a sales tax on imported goods.
D) A tariff is a quantity trade restriction on imported goods, and a trade quota is a quantity tax on imported goods.
A) A tariff is a tax on imported goods, and a trade quota is a quantity restriction on imported goods.
B) A tariff is a cash payment to domestic exporters, and a trade quota restricts the quantity of domestically produced goods foreigners can buy.
C) A tariff is a lump-sum tax on imported goods, and a trade quota is a sales tax on imported goods.
D) A tariff is a quantity trade restriction on imported goods, and a trade quota is a quantity tax on imported goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Dividing the total tariff revenue in the trade diagram introduced in this chapter by the size of the tariff yields:
A) imports with free trade.
B) imports with tariff.
C) the size of increase in domestic production.
D) the size of decrease in domestic consumption.
A) imports with free trade.
B) imports with tariff.
C) the size of increase in domestic production.
D) the size of decrease in domestic consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Bananas
The diagram indicates the revenue distribution of a $299 30GB Apple iPod. Most of the "non-hardware costs" are product development (e.g., software and R&D), but also includes advertising and retail costs. If the key industry argument has merit, what does this diagram suggest about which industries are actually key?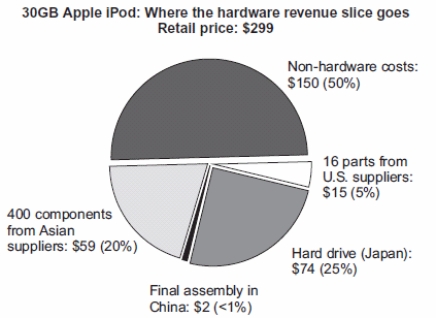
A) hard drives
B) electronic parts
C) advertising
D) product development
Figure: Bananas

The diagram indicates the revenue distribution of a $299 30GB Apple iPod. Most of the "non-hardware costs" are product development (e.g., software and R&D), but also includes advertising and retail costs. If the key industry argument has merit, what does this diagram suggest about which industries are actually key?

A) hard drives
B) electronic parts
C) advertising
D) product development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: International Trade 2
(Figure: International Trade 2) Refer to the figure. What is the size of the tariff in this figure?
A) $8
B) $3
C) $5
D) $1
Figure: International Trade 2

(Figure: International Trade 2) Refer to the figure. What is the size of the tariff in this figure?
A) $8
B) $3
C) $5
D) $1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade Market
(Figure: Foreign Trade Market) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of the deadweight loss created by the loss of foreign trade?
A) $10,000
B) $4,000
C) $36,000
D) $6,000
Figure: Foreign Trade Market

(Figure: Foreign Trade Market) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of the deadweight loss created by the loss of foreign trade?
A) $10,000
B) $4,000
C) $36,000
D) $6,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: International Trade 2
(Figure: International Trade 2) Refer to the figure. How much revenue does the tariff in this figure generate for the government?
A) $30
B) $24
C) $6
D) $54
Figure: International Trade 2

(Figure: International Trade 2) Refer to the figure. How much revenue does the tariff in this figure generate for the government?
A) $30
B) $24
C) $6
D) $54

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade 2
(Figure: Foreign Trade 2) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of the consumer surplus that consumers could gain if the trade restriction were removed?
A) $35,000
B) $22,500
C) $30,000
D) $25,000
Figure: Foreign Trade 2

(Figure: Foreign Trade 2) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of the consumer surplus that consumers could gain if the trade restriction were removed?
A) $35,000
B) $22,500
C) $30,000
D) $25,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The U.S. price of sugar is higher than the world price of sugar due primarily to a:
A) subsidy.
B) quota.
C) local content requirement.
D) tariff.
A) subsidy.
B) quota.
C) local content requirement.
D) tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A tariff ______ the world supply of a good.
A) reduces
B) increases
C) does not change
D) has no measurable effect on
A) reduces
B) increases
C) does not change
D) has no measurable effect on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: International Trade 2
(Figure: International Trade 2) Refer to the figure. At the tariff equilibrium in this figure, the quantity of imports is ______, which is ______ than at the free trade equilibrium.
A) 2; 10 units fewer
B) 2; 6 units fewer
C) 10; 2 units more
D) 10; 2 units fewer
Figure: International Trade 2

(Figure: International Trade 2) Refer to the figure. At the tariff equilibrium in this figure, the quantity of imports is ______, which is ______ than at the free trade equilibrium.
A) 2; 10 units fewer
B) 2; 6 units fewer
C) 10; 2 units more
D) 10; 2 units fewer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade 2
(Figure: Foreign Trade 2) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of the deadweight loss created as a result of prohibiting trade in this market?
A) $2,500
B) $10,000
C) $7,500
D) $5,000
Figure: Foreign Trade 2

(Figure: Foreign Trade 2) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of the deadweight loss created as a result of prohibiting trade in this market?
A) $2,500
B) $10,000
C) $7,500
D) $5,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade 2
(Figure: Foreign Trade 2) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of the producer surplus gained as a result of prohibiting trade in this market?
A) $15,000
B) $30,000
C) $12,500
D) $22,500
Figure: Foreign Trade 2

(Figure: Foreign Trade 2) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of the producer surplus gained as a result of prohibiting trade in this market?
A) $15,000
B) $30,000
C) $12,500
D) $22,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
I. If the United States bans the importation of bananas, consumer surplus will decrease.
II. If the United States bans the importation of bananas, producer surplus will decrease.
III. If the United States bans the importation of bananas, it will produce bananas at a cost exceeding their world purchase price.
A) I, II, and III
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) II and III only
I. If the United States bans the importation of bananas, consumer surplus will decrease.
II. If the United States bans the importation of bananas, producer surplus will decrease.
III. If the United States bans the importation of bananas, it will produce bananas at a cost exceeding their world purchase price.
A) I, II, and III
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: A Tariff on Imports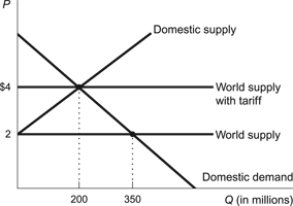
(Figure: A Tariff on Imports) Refer to the figure. Suppose the government intervenes with a $2 tariff; the total cost of the tariff to the citizens in that country is:
A) $350 million.
B) $400 million.
C) $550 million.
D) $700 million.
Figure: A Tariff on Imports

(Figure: A Tariff on Imports) Refer to the figure. Suppose the government intervenes with a $2 tariff; the total cost of the tariff to the citizens in that country is:
A) $350 million.
B) $400 million.
C) $550 million.
D) $700 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Costs of Tariffs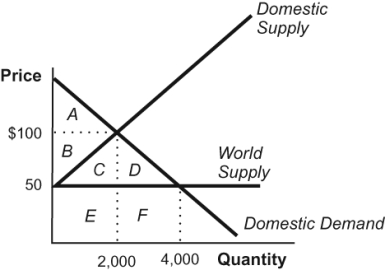
(Figure: Costs of Tariffs) Refer to the figure. In the figure representing the market for leather, domestic suppliers are the high-cost producers of leather. However, import restrictions push domestic prices up to $100. Which area represents the value of wasted resources?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Figure: Costs of Tariffs

(Figure: Costs of Tariffs) Refer to the figure. In the figure representing the market for leather, domestic suppliers are the high-cost producers of leather. However, import restrictions push domestic prices up to $100. Which area represents the value of wasted resources?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: World Imports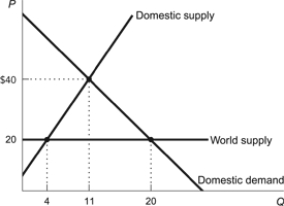
(Figure: World Imports) Refer to the figure. The solution for a country without trade restrictions is where the equilibrium price and quantity are ________, respectively.
A) $20 and 4
B) $40 and 11
C) $20 and 11
D) $20 and 20
Figure: World Imports

(Figure: World Imports) Refer to the figure. The solution for a country without trade restrictions is where the equilibrium price and quantity are ________, respectively.
A) $20 and 4
B) $40 and 11
C) $20 and 11
D) $20 and 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following decreases the volume of international trade?
A) increasing tariffs
B) decreasing quotas
C) lower transportation costs
D) stable monetary conditions
A) increasing tariffs
B) decreasing quotas
C) lower transportation costs
D) stable monetary conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
As a result of U.S. quotas on sugar imports, all of the following are true, EXCEPT:
A) the United States pays about twice the world price for sugar.
B) the gains to American producers are greater than the losses to American consumers.
C) foreign sugar producers-mostly in poor countries-suffer.
D) a small group of domestic sugar producers benefit.
A) the United States pays about twice the world price for sugar.
B) the gains to American producers are greater than the losses to American consumers.
C) foreign sugar producers-mostly in poor countries-suffer.
D) a small group of domestic sugar producers benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade Market
(Figure: Foreign Trade Market) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of the lost consumer surplus as a result of prohibiting trade in this market?
A) $26,000
B) $28,000
C) $32,000
D) $36,000
Figure: Foreign Trade Market

(Figure: Foreign Trade Market) Refer to the figure. What is the dollar value of the lost consumer surplus as a result of prohibiting trade in this market?
A) $26,000
B) $28,000
C) $32,000
D) $36,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
As a result of tariffs:
A) the opportunity cost of domestic production falls.
B) domestic producers waste resources producing goods for which they are not low-cost producers.
C) foreign producers gain additional profits at the expense of domestic consumers.
D) both domestic producers and consumers are protected from international competition.
A) the opportunity cost of domestic production falls.
B) domestic producers waste resources producing goods for which they are not low-cost producers.
C) foreign producers gain additional profits at the expense of domestic consumers.
D) both domestic producers and consumers are protected from international competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade Market
If quotas on sugar were eliminated in the United States, domestic production of sugar would fall. Why is this a benefit in economic terms for the United States?
I. Resources are freed up that could be used more efficiently elsewhere.
II. It is beneficial because it allows foreign producers of sugar to earn income and thus those countries are better off.
III. U.S. consumers are able to enjoy increased consumer surplus because of the lower prices of imported sugar.
A) I and II only
B) I and III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III
Figure: Foreign Trade Market

If quotas on sugar were eliminated in the United States, domestic production of sugar would fall. Why is this a benefit in economic terms for the United States?
I. Resources are freed up that could be used more efficiently elsewhere.
II. It is beneficial because it allows foreign producers of sugar to earn income and thus those countries are better off.
III. U.S. consumers are able to enjoy increased consumer surplus because of the lower prices of imported sugar.
A) I and II only
B) I and III only
C) II and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Without trade restrictions the price of tennis shoes is $30, and with trade restrictions the price of tennis shoes is $45. The difference in the two prices reflects:
A) per-unit profits.
B) the value of the extra resources for domestic production of an additional pair of tennis shoes.
C) the gain in consumer surplus from free trade.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) per-unit profits.
B) the value of the extra resources for domestic production of an additional pair of tennis shoes.
C) the gain in consumer surplus from free trade.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Costs of Tariffs
(Figure: Costs of Tariffs) Refer to the figure. In the figure representing the market for leather, what price would consumers pay for leather in the absence of a tariff or other import restrictions?
A) a price less than $50
B) $50
C) a price somewhere between $50 and $100
D) $100
Figure: Costs of Tariffs

(Figure: Costs of Tariffs) Refer to the figure. In the figure representing the market for leather, what price would consumers pay for leather in the absence of a tariff or other import restrictions?
A) a price less than $50
B) $50
C) a price somewhere between $50 and $100
D) $100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Foreign Trade Market
Which, if any, of the following conditions for efficient market functioning do tariffs and quotas violate?
I. demanders with the highest willingness to pay purchase the supply of goods
II. producers with the lowest costs produce and sell the supply of goods
III. the sum of consumer and producer surplus is maximized
A) I only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and III
D) III only
Figure: Foreign Trade Market

Which, if any, of the following conditions for efficient market functioning do tariffs and quotas violate?
I. demanders with the highest willingness to pay purchase the supply of goods
II. producers with the lowest costs produce and sell the supply of goods
III. the sum of consumer and producer surplus is maximized
A) I only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and III
D) III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: World Imports
(Figure: World Imports) Refer to the figure. The imposition of a $20 tariff would generate a value of lost gains from trade of:
A) $45.
B) $90.
C) $70.
D) $160.
Figure: World Imports

(Figure: World Imports) Refer to the figure. The imposition of a $20 tariff would generate a value of lost gains from trade of:
A) $45.
B) $90.
C) $70.
D) $160.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Costs of Tariffs
(Figure: Costs of Tariffs) Refer to the figure. From left to right, the first triangle, rectangle, and second triangle in the diagram for analyzing a tariff represent:
A) unexploited gains from trade due to decreased domestic consumption, wasted resources from increased domestic production, and tariff revenues, respectively.
B) tariff revenues, wasted resources from increased domestic production, and unexploited gains from trade due to decreased domestic consumption, respectively.
C) wasted resources from increased domestic production, unexploited gains from trade due to decreased domestic consumption, and tariff revenues, respectively.
D) wasted resources from increased domestic production, tariff revenues, and unexploited gains from trade due to decreased domestic consumption, respectively.
Figure: Costs of Tariffs

(Figure: Costs of Tariffs) Refer to the figure. From left to right, the first triangle, rectangle, and second triangle in the diagram for analyzing a tariff represent:
A) unexploited gains from trade due to decreased domestic consumption, wasted resources from increased domestic production, and tariff revenues, respectively.
B) tariff revenues, wasted resources from increased domestic production, and unexploited gains from trade due to decreased domestic consumption, respectively.
C) wasted resources from increased domestic production, unexploited gains from trade due to decreased domestic consumption, and tariff revenues, respectively.
D) wasted resources from increased domestic production, tariff revenues, and unexploited gains from trade due to decreased domestic consumption, respectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Suppose that a tariff increases domestic production of a good from 25 million units to 75 million units and raises the domestic price by $1.50. Assuming a linear domestic supply curve and a perfectly elastic world supply curve, what is the value of the resources wasted by increased domestic production?
A) $37.5 million
B) $50 million
C) $75 million
D) $150 million
A) $37.5 million
B) $50 million
C) $75 million
D) $150 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: A Tariff on Imports
(Figure: A Tariff on Imports) Refer to the figure. Suppose the government intervenes with a $2 tariff; the total value of deadweight loss as a result of the tariff is:
A) $150 million.
B) $200 million.
C) $400 million.
D) $550 million.
Figure: A Tariff on Imports

(Figure: A Tariff on Imports) Refer to the figure. Suppose the government intervenes with a $2 tariff; the total value of deadweight loss as a result of the tariff is:
A) $150 million.
B) $200 million.
C) $400 million.
D) $550 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: World Imports
(Figure: World Imports) Refer to the figure. An imposition of extreme trade restrictions that eliminated all trade in that market, would generate wasted resources of:
A) $70.
B) $530.
C) $90.
D) $160.
Figure: World Imports

(Figure: World Imports) Refer to the figure. An imposition of extreme trade restrictions that eliminated all trade in that market, would generate wasted resources of:
A) $70.
B) $530.
C) $90.
D) $160.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Costs of Tariffs
(Figure: Costs of Tariffs) Refer to the figure. In the figure representing the market for leather, domestic suppliers are the high-cost producers of leather. However, import restrictions push the domestic price up to $100. Which area represents the deadweight loss that results?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Figure: Costs of Tariffs

(Figure: Costs of Tariffs) Refer to the figure. In the figure representing the market for leather, domestic suppliers are the high-cost producers of leather. However, import restrictions push the domestic price up to $100. Which area represents the deadweight loss that results?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Economists consider tariffs to be:
A) necessary.
B) beneficial to domestic consumers.
C) harmful to domestic producers.
D) obstacles that reduce gains from trade.
A) necessary.
B) beneficial to domestic consumers.
C) harmful to domestic producers.
D) obstacles that reduce gains from trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
One of the costs of protectionism is:
A) increases in total national output.
B) a reduction in the variety of goods in domestic markets.
C) greater competition.
D) lower opportunity costs of domestic production.
A) increases in total national output.
B) a reduction in the variety of goods in domestic markets.
C) greater competition.
D) lower opportunity costs of domestic production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 195 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



