Deck 16: Competing for Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/160
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Competing for Monopoly
1
A network good's:
A) consumption increases as income decreases.
B) value to one consumer increases the more that other consumers use the good.
C) allure derives from its low fixed costs and high marginal costs.
D) existence is made possible by the Internet.
A) consumption increases as income decreases.
B) value to one consumer increases the more that other consumers use the good.
C) allure derives from its low fixed costs and high marginal costs.
D) existence is made possible by the Internet.
value to one consumer increases the more that other consumers use the good.
2
Which statement about network goods is TRUE?
A) They are goods that are usually sold by large firms with a great deal of market power
B) They are goods that tend to have a large number of users or consumers.
C) They are goods whose value to one consumer increases the greater the total number of consumers.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) They are goods that are usually sold by large firms with a great deal of market power
B) They are goods that tend to have a large number of users or consumers.
C) They are goods whose value to one consumer increases the greater the total number of consumers.
D) All of the answers are correct.
All of the answers are correct.
3
Which one would NOT be considered a network good?
A) cell phones
B) quiet study rooms
C) e-mail programs
D) online player versus player games
A) cell phones
B) quiet study rooms
C) e-mail programs
D) online player versus player games
quiet study rooms
4
Which statement is TRUE regarding network goods?
A) Producers of network goods typically sell their product at a price below marginal cost.
B) Competition among companies producing network goods drives the price down to equal marginal cost.
C) Network goods typically sell at a price higher than marginal cost.
D) Marginal cost always equals average cost for network goods.
A) Producers of network goods typically sell their product at a price below marginal cost.
B) Competition among companies producing network goods drives the price down to equal marginal cost.
C) Network goods typically sell at a price higher than marginal cost.
D) Marginal cost always equals average cost for network goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Since its founding in 331 B.C.E., the city of Alexandria has been a center of trade for the Mediterranean countries, as well as the Middle Eastern countries. Part of this is due to geography, but it is also due to the network effect. What is the source of the network effect?
A) Ships want the best harbor available.
B) There is a lot of contestability for ports.
C) There are economies of scale due to a concentration of trade.
D) Merchants want to maximize trading opportunities.
A) Ships want the best harbor available.
B) There is a lot of contestability for ports.
C) There are economies of scale due to a concentration of trade.
D) Merchants want to maximize trading opportunities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A network good is a good whose value to one consumer:
A) increases the network of the consumer.
B) increases some, but decreases in value as other consumers use the good.
C) also creates the same value to other consumers as they use the good.
D) increases the more that other consumers use the good.
A) increases the network of the consumer.
B) increases some, but decreases in value as other consumers use the good.
C) also creates the same value to other consumers as they use the good.
D) increases the more that other consumers use the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which statement is NOT a feature of markets for network goods?
A) Network goods are usually sold by monopolies or oligopolies.
B) Standard wars are common in establishing network goods.
C) Competition in the market for network goods is "in the market" instead of "for the market."
D) When networks are important, the "best" product may not always win.
A) Network goods are usually sold by monopolies or oligopolies.
B) Standard wars are common in establishing network goods.
C) Competition in the market for network goods is "in the market" instead of "for the market."
D) When networks are important, the "best" product may not always win.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Network goods are usually sold by monopolies or oligopolies because:
A) the government doesn't enforce antitrust laws in network industries.
B) there is no benefit to using the product that other consumers use.
C) only the government is allowed to sell network goods.
D) consumers want to coordinate on the same standard.
A) the government doesn't enforce antitrust laws in network industries.
B) there is no benefit to using the product that other consumers use.
C) only the government is allowed to sell network goods.
D) consumers want to coordinate on the same standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which statement is NOT a feature of markets for network goods?
A) Only one network good in each industry can exist at one time.
B) When networks are important, the "best" product may not always win.
C) Competition in markets for network goods is "for the market" instead of "in the market."
D) Monopolies or oligopolies usually sell network goods.
A) Only one network good in each industry can exist at one time.
B) When networks are important, the "best" product may not always win.
C) Competition in markets for network goods is "for the market" instead of "in the market."
D) Monopolies or oligopolies usually sell network goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which statement is FALSE?
A) Network goods are usually sold by monopolies or oligopolies.
B) When networks are important the "best" products usually win.
C) Standard wars are common in establishing network goods.
D) Competition in network goods is for the market, not in the market.
A) Network goods are usually sold by monopolies or oligopolies.
B) When networks are important the "best" products usually win.
C) Standard wars are common in establishing network goods.
D) Competition in network goods is for the market, not in the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A network good is a good that people benefit ______ from as ______ people use it.
A) more; fewer
B) more; more
C) less; more
D) the most; no other
A) more; fewer
B) more; more
C) less; more
D) the most; no other

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Firms sometimes give away products for free in the hopes of:
A) selling other goods they produce at a higher price.
B) driving the competition out of business.
C) becoming the dominant standard.
D) creating a loyal customer base.
A) selling other goods they produce at a higher price.
B) driving the competition out of business.
C) becoming the dominant standard.
D) creating a loyal customer base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Multiple products can thrive in a network industry when:
A) the government decides to allow multiple products.
B) consumers don't care about coordination at all.
C) there are multiple niches to fill; each product can dominate one niche.
D) competitors all go after the same niche.
A) the government decides to allow multiple products.
B) consumers don't care about coordination at all.
C) there are multiple niches to fill; each product can dominate one niche.
D) competitors all go after the same niche.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which is the best example of a network good?
A) social media sites
B) laptop computers
C) automobiles
D) cable television
A) social media sites
B) laptop computers
C) automobiles
D) cable television

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Firms that produce goods that are the dominant standard goods in the market typically sell these goods at:
A) a loss.
B) a higher price than in a competitive market.
C) a lower price than in a competitive market.
D) marginal cost.
A) a loss.
B) a higher price than in a competitive market.
C) a lower price than in a competitive market.
D) marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which goods represent network goods?
A) Pepsi, toilet paper, headphones
B) calculator, oven, couch
C) Twitter, Microsoft Excel, Facebook
D) fireworks, lighthouse, swimming pool
A) Pepsi, toilet paper, headphones
B) calculator, oven, couch
C) Twitter, Microsoft Excel, Facebook
D) fireworks, lighthouse, swimming pool

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which is NOT a good example of a network good?
A) photo sharing Web sites
B) Internet dating sites
C) telephones
D) automobiles
A) photo sharing Web sites
B) Internet dating sites
C) telephones
D) automobiles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A network good is:
A) a broadcast show on radio or television.
B) a good that must be bought in large quantities in order to get discounted prices.
C) a good supplied by a large network of competitive firms.
D) a good whose value increases to consumers as more consumers use the good.
A) a broadcast show on radio or television.
B) a good that must be bought in large quantities in order to get discounted prices.
C) a good supplied by a large network of competitive firms.
D) a good whose value increases to consumers as more consumers use the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In 2011, Google introduced its social networking site, Google+. Even though Google+ is cleaner and more straightforward than its nearest competitor, Facebook, it still has trouble competing with Facebook because:
A) most people don't know about it.
B) Facebook has a monopoly on social networking.
C) everyone's already on Facebook.
D) the market is still contestable.
A) most people don't know about it.
B) Facebook has a monopoly on social networking.
C) everyone's already on Facebook.
D) the market is still contestable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which statement is TRUE?
A) Network goods are sold mostly in price-taker markets.
B) The network good is always the "best" good.
C) Monopolies may sell network goods.
D) All of these statements are true.
A) Network goods are sold mostly in price-taker markets.
B) The network good is always the "best" good.
C) Monopolies may sell network goods.
D) All of these statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which condition is required for a network good to succeed over a better good in the market?
A) The network good should have a minimal number of consumers so that customers are not competing for the same network.
B) The network good should have a much larger number of consumers or users than the better good.
C) The network good should be a free good.
D) All of these conditions are required.
A) The network good should have a minimal number of consumers so that customers are not competing for the same network.
B) The network good should have a much larger number of consumers or users than the better good.
C) The network good should be a free good.
D) All of these conditions are required.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Microsoft software is considered a network good because it is:
A) free to use.
B) the best product.
C) most likely to be compatible with other products and other readers, writers, and publishers.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) free to use.
B) the best product.
C) most likely to be compatible with other products and other readers, writers, and publishers.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Microsoft's market power stems from:
A) its control over a scarce resource.
B) economies of scale.
C) its product compatibility with a lot of other products.
D) being a government-created monopoly.
A) its control over a scarce resource.
B) economies of scale.
C) its product compatibility with a lot of other products.
D) being a government-created monopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Table: Homer, Marge Payoff Table
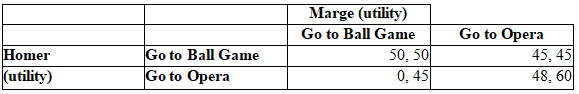
Refer to the table. The Nash equilibrium is (are):
A) (50, 50) and (48, 60).
B) (0, 45).
C) (45, 45).
D) (48, 60) and (45, 45).

Refer to the table. The Nash equilibrium is (are):
A) (50, 50) and (48, 60).
B) (0, 45).
C) (45, 45).
D) (48, 60) and (45, 45).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which BEST explains why monopolies or oligopolies tend to dominate the market for network goods?
I. Their products are the most likely to be compatible with other products.
II. They produce the "best" products in terms of quality and compatibility.
III. The power of coordination is so strong that monopolists and oligopolists can dominate the market even when they charge prices higher than their competitors.
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III
I. Their products are the most likely to be compatible with other products.
II. They produce the "best" products in terms of quality and compatibility.
III. The power of coordination is so strong that monopolists and oligopolists can dominate the market even when they charge prices higher than their competitors.
A) I only
B) I and II only
C) I and III only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Network goods are usually produced by:
A) competitive firms.
B) monopolies and oligopolies.
C) monopolistically competitive firms.
D) state and local governments.
A) competitive firms.
B) monopolies and oligopolies.
C) monopolistically competitive firms.
D) state and local governments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The most spoken language in the world is English with 1.8 billion speakers, but only 18% are native (by comparison, the next-most spoken language-standard Chinese-has 1.345 billion speakers and 63% are native). This relatively recent change has followed globalization. How does increased globalization explain why so many people choose to learn the same language as a second language?
A) Globalization creates an incentive for people to learn other cultures.
B) Globalization began a standards war of languages; English won.
C) Globalization made it cheaper to learn new languages thanks to gains from trade.
D) Globalization expands the network of English speakers.
A) Globalization creates an incentive for people to learn other cultures.
B) Globalization began a standards war of languages; English won.
C) Globalization made it cheaper to learn new languages thanks to gains from trade.
D) Globalization expands the network of English speakers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Internet dating services such as Match.com are in a market dominated by several large firms, making the market a(n:)
A) competitive market.
B) monopoly.
C) monopolistically competitive market.
D) oligopoly.
A) competitive market.
B) monopoly.
C) monopolistically competitive market.
D) oligopoly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Operating systems have network-good characteristics because of ______ issues.
A) complexity
B) simplicity
C) intangibility
D) compatibility
A) complexity
B) simplicity
C) intangibility
D) compatibility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The equilibrium in a market in which no participant has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally is called a:
A) market equilibrium.
B) Nash equilibrium.
C) coordinating equilibrium.
D) financial equilibrium.
A) market equilibrium.
B) Nash equilibrium.
C) coordinating equilibrium.
D) financial equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
When players are better off using the same strategy rather than different strategies, economists refer to this as:
I. Nash equilibrium.
II. coordination game.
III. dominant strategy.
IV. prisoner's dilemma.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II only
D) I, II, III, and IV
I. Nash equilibrium.
II. coordination game.
III. dominant strategy.
IV. prisoner's dilemma.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and II only
D) I, II, III, and IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When many people are involved and when they do not all agree about whether one good really is better than another, the best final equilibrium is usually determined by:
A) consumers.
B) the market.
C) the government.
D) historical accidents.
A) consumers.
B) the market.
C) the government.
D) historical accidents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Network goods are usually sold by:
A) monopolistically competitive firms or monopolies.
B) oligopolies or perfectly competitive firms.
C) perfectly competitive firms or monopolistically competitive firms.
D) monopolies or oligopolies.
A) monopolistically competitive firms or monopolies.
B) oligopolies or perfectly competitive firms.
C) perfectly competitive firms or monopolistically competitive firms.
D) monopolies or oligopolies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is meant by the concept of a Nash equilibrium?
A) It is an outcome where the player has played his or her dominant strategy.
B) It is an outcome where both players have the incentive to change their strategy.
C) It is the outcome where neither player wishes to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
D) It is the same as a dominant strategy outcome.
A) It is an outcome where the player has played his or her dominant strategy.
B) It is an outcome where both players have the incentive to change their strategy.
C) It is the outcome where neither player wishes to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
D) It is the same as a dominant strategy outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A Nash equilibrium:
A) means that no players have an incentive to change their strategy.
B) means that some players could be made better off by changing their strategy.
C) is suboptimal compared to Raj's equilibrium.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) means that no players have an incentive to change their strategy.
B) means that some players could be made better off by changing their strategy.
C) is suboptimal compared to Raj's equilibrium.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Table: Jim, Dan Payoff Table
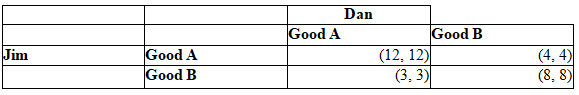
Refer to the table. Which of the following outcomes is NOT a Nash equilibrium?
I. (12, 12)
II. (4, 4)
III. (8, 8)
IV. (3, 3)
A) I and IV only
B) II and IV only
C) III only
D) I and III only

Refer to the table. Which of the following outcomes is NOT a Nash equilibrium?
I. (12, 12)
II. (4, 4)
III. (8, 8)
IV. (3, 3)
A) I and IV only
B) II and IV only
C) III only
D) I and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A Nash equilibrium in game theory is defined as a situation in which:
A) no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy even when other players change.
B) no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
C) any player has an incentive to change his or her strategy until he or she reaches the optimum.
D) any player has an incentive to change his or her strategy even when other players remain unchanged.
A) no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy even when other players change.
B) no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
C) any player has an incentive to change his or her strategy until he or she reaches the optimum.
D) any player has an incentive to change his or her strategy even when other players remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Competition in the case of network goods is:
A) "for the market."
B) "in the market."
C) "of the market."
D) "by the market."
A) "for the market."
B) "in the market."
C) "of the market."
D) "by the market."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which statement is TRUE?
A) The Nash equilibrium always maximizes social welfare.
B) Coordination games will always minimize total costs.
C) Coordination games always result in a Nash equilibrium outcome.
D) There is only one Nash equilibrium outcome for each coordination game.
A) The Nash equilibrium always maximizes social welfare.
B) Coordination games will always minimize total costs.
C) Coordination games always result in a Nash equilibrium outcome.
D) There is only one Nash equilibrium outcome for each coordination game.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the "market" for interpersonal greetings. In many Western countries, the expected form of greeting is a handshake. In many Eastern countries, the expected form of greeting is a bow. Both greetings "work" in the sense that they function as a form of acknowledging the other person, but bows are superior to handshakes because handshakes spread germs and bows don't. Why is it that handshakes persist in the West if bows are better?
A) No one wants to be the only one who bows when everyone else shakes hands.
B) People in the West are unaware that handshakes spread germs.
C) People in the West do not know how to bow, but do know how to shake hands.
D) Handshakes are not a Nash equilibrium.
A) No one wants to be the only one who bows when everyone else shakes hands.
B) People in the West are unaware that handshakes spread germs.
C) People in the West do not know how to bow, but do know how to shake hands.
D) Handshakes are not a Nash equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The term "accidents of history" describes:
A) actual equilibrium outcomes in a coordination game.
B) good equilibrium outcomes in a coordination game.
C) all equilibrium outcomes in a coordination game.
D) no equilibrium outcomes in a coordination game.
A) actual equilibrium outcomes in a coordination game.
B) good equilibrium outcomes in a coordination game.
C) all equilibrium outcomes in a coordination game.
D) no equilibrium outcomes in a coordination game.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The story of QWERTY is about:
A) how an inferior product can become the "locked-in" standard simply because it was first to market.
B) how network goods are noncontestable.
C) the absence of a Nash equilibrium when there are large fixed costs to entry.
D) the creation of monopoly power through the use of loyalty programs.
A) how an inferior product can become the "locked-in" standard simply because it was first to market.
B) how network goods are noncontestable.
C) the absence of a Nash equilibrium when there are large fixed costs to entry.
D) the creation of monopoly power through the use of loyalty programs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which is an example of a coordination game?
A) choosing a dress for a wedding while making sure no one is wearing the same thing
B) divvying up the parts of a group project so you don't have to do as much and everyone can work cohesively together
C) You're not sure where your study group is supposed to meet, but the library is the most likely place so you go there.
D) getting the roast beef at a restaurant-the same thing everyone else gets-because it is the best deal on the menu
A) choosing a dress for a wedding while making sure no one is wearing the same thing
B) divvying up the parts of a group project so you don't have to do as much and everyone can work cohesively together
C) You're not sure where your study group is supposed to meet, but the library is the most likely place so you go there.
D) getting the roast beef at a restaurant-the same thing everyone else gets-because it is the best deal on the menu

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Competition for the market rather than in the market:
A) is the reason why Friendster is no longer the leading social network.
B) explains why Microsoft Word is the leading word processing network.
C) means that Facebook may one day no longer be one of the leading social networks.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) is the reason why Friendster is no longer the leading social network.
B) explains why Microsoft Word is the leading word processing network.
C) means that Facebook may one day no longer be one of the leading social networks.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A Nash equilibrium is a situation:
A) that maximizes the collective gains to both players.
B) in which neither player in the game has an incentive to change strategies given the strategy of the other player.
C) in which one player could benefit from changing strategies given the strategy of the other player.
D) in which players play nondominant strategies.
A) that maximizes the collective gains to both players.
B) in which neither player in the game has an incentive to change strategies given the strategy of the other player.
C) in which one player could benefit from changing strategies given the strategy of the other player.
D) in which players play nondominant strategies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
For two players in a game, a Nash equilibrium is different from a dominant strategy in that:
A) the outcome in the Nash equilibrium may not be the best outcome for either of the players.
B) the Nash equilibrium always has unequal outcomes whereas the dominant strategy always has even outcomes.
C) there is always only one Nash equilibrium, but there may be more than one dominant strategy.
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) the outcome in the Nash equilibrium may not be the best outcome for either of the players.
B) the Nash equilibrium always has unequal outcomes whereas the dominant strategy always has even outcomes.
C) there is always only one Nash equilibrium, but there may be more than one dominant strategy.
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In a network good's market:
A) the output is usually split evenly among many different sellers.
B) the best product might not be the most popular product.
C) there is fierce competition "in the market."
D) the government is the low-cost leader.
A) the output is usually split evenly among many different sellers.
B) the best product might not be the most popular product.
C) there is fierce competition "in the market."
D) the government is the low-cost leader.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A Nash equilibrium is a situation in which:
A) the players are better off choosing the same strategy than if they choose different strategies.
B) all players select the worst outcome.
C) no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
D) one's costs are minimized.
A) the players are better off choosing the same strategy than if they choose different strategies.
B) all players select the worst outcome.
C) no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
D) one's costs are minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A ______ equilibrium is a situation in which no player in the game has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
A) Selten
B) Nash
C) local
D) game
A) Selten
B) Nash
C) local
D) game

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The story of John Nash was captured in the movie A Beautiful Mind. The movie attempts to explain the Nash equilibrium with one striking blond woman and several brunettes at a bar. In the scene, all the men prefer the blonde. But Nash realizes, "If we all go for the blonde, we block each other. Not a single one of us is going to get her. So then we go for her friends. But they will give us the cold shoulder because no one likes being second choice. But what if no one goes for the blonde? We don't get in each other's way, and we don't insult the other girls. That's the only way we win." The scene ends with all the guys dancing with the brunettes while the blonde sits alone. Why is this NOT a Nash equilibrium?
A) Any one man will be better off switching to the blonde.
B) Two men would be better off if they coordinated to the same woman.
C) There is a high switching cost to pursue the blonde.
D) Women will respect the men more if they compete for their affection.
A) Any one man will be better off switching to the blonde.
B) Two men would be better off if they coordinated to the same woman.
C) There is a high switching cost to pursue the blonde.
D) Women will respect the men more if they compete for their affection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which statement is TRUE regarding network goods?
A) Network goods are usually sold by monopolies or oligopolies.
B) Microsoft Word has always been the dominant word processing software
C) Microsoft Excel has always been the dominate spreadsheet software.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) Network goods are usually sold by monopolies or oligopolies.
B) Microsoft Word has always been the dominant word processing software
C) Microsoft Excel has always been the dominate spreadsheet software.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A coordination game is a situation in which:
A) the players are better off choosing the same strategy than if they choose different strategies, but there is also more than one strategy on which to potentially coordinate.
B) all players select the worst outcome.
C) no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
D) one's costs are minimized.
A) the players are better off choosing the same strategy than if they choose different strategies, but there is also more than one strategy on which to potentially coordinate.
B) all players select the worst outcome.
C) no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
D) one's costs are minimized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The market for network goods:
I. is dominated by a single monopolist.
II. is dominated by a series of monopolies.
III. ensures long-term profits for those companies that win the standard war.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III only
D) II and III only
I. is dominated by a single monopolist.
II. is dominated by a series of monopolies.
III. ensures long-term profits for those companies that win the standard war.
A) I only
B) II only
C) I and III only
D) II and III only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Firms that operate in contestable markets:
A) still price competitively since they face the threat of competition from new entrants.
B) are pure monopolies that set prices equal to consumers' highest willingness to pay.
C) earn zero economic profits.
D) face more competition when fixed costs are high.
A) still price competitively since they face the threat of competition from new entrants.
B) are pure monopolies that set prices equal to consumers' highest willingness to pay.
C) earn zero economic profits.
D) face more competition when fixed costs are high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
When the market for a network good is contestable,:
A) there is little competition.
B) many firms operate and compete for consumers in the industry.
C) it is hard for consumers to get locked into a "bad" outcome.
D) monopoly firms always charge prices well above their average costs.
A) there is little competition.
B) many firms operate and compete for consumers in the industry.
C) it is hard for consumers to get locked into a "bad" outcome.
D) monopoly firms always charge prices well above their average costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
QWERTY is used today because it is:
A) faster.
B) locked in.
C) simple.
D) superior in several dimensions.
A) faster.
B) locked in.
C) simple.
D) superior in several dimensions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
QWERTY is:
A) a keyboard layout.
B) a type of software.
C) an Internet browser.
D) a digital phone.
A) a keyboard layout.
B) a type of software.
C) an Internet browser.
D) a digital phone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the case of network goods, the best product may not win because of:
A) complexity issues.
B) simplicity issues.
C) lock-in.
D) intangibility.
A) complexity issues.
B) simplicity issues.
C) lock-in.
D) intangibility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What will determine the final equilibrium in a many-player coordination game?
A) The technically superior standard will always win.
B) Accidents of history will determine the final equilibrium.
C) People will rally behind the initial underdog.
D) No one will be able to make a decision until the government decides for them.
A) The technically superior standard will always win.
B) Accidents of history will determine the final equilibrium.
C) People will rally behind the initial underdog.
D) No one will be able to make a decision until the government decides for them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Suppose that some people drive on the left side of the road and some people drive on the right side of the road. Is this a Nash equilibrium?
A) Yes, because no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
B) Yes, because each person would prefer to unilaterally change strategies.
C) No, because no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
D) No, because each person would prefer to unilaterally change strategies.
A) Yes, because no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
B) Yes, because each person would prefer to unilaterally change strategies.
C) No, because no player has an incentive to change his or her strategy unilaterally.
D) No, because each person would prefer to unilaterally change strategies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A market is contestable if:
A) it is dominated by a single firm.
B) a competitor could credibly enter and take away business from the incumbent.
C) competitors allege that the dominant firm is an illegal monopoly.
D) prices are very high.
A) it is dominated by a single firm.
B) a competitor could credibly enter and take away business from the incumbent.
C) competitors allege that the dominant firm is an illegal monopoly.
D) prices are very high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which is NOT a good example of a contestable market?
A) low-cost airlines
B) electricity providers
C) a local Mexican restaurant
D) bottled water manufacturers
A) low-cost airlines
B) electricity providers
C) a local Mexican restaurant
D) bottled water manufacturers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Seventy-nine percent of U.S. households watched the series finale of M*A*S*H, on February 28, 1983. Although this television event was an experience made slightly more valuable because it was commonly shared, it is unlikely to be repeated on the same scale because of the expansion of cable television and the Internet. If M*A*S*H was a network good, based on the information provided, which of the following has the most explanatory power for why TV shows lose so much networking power?
A) Consumers were then willing to entertain competitive goods.
B) There are now few legal barriers to entry.
C) The incumbents lost their hard-to-replicate resource.
D) The benefits of the network became less than the benefit of watching something a person truly enjoyed.
A) Consumers were then willing to entertain competitive goods.
B) There are now few legal barriers to entry.
C) The incumbents lost their hard-to-replicate resource.
D) The benefits of the network became less than the benefit of watching something a person truly enjoyed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
How has the Internet made the market for videos more contestable?
A) Only professionals can create video content on the Internet.
B) It severely limits the amount of content available to consumers.
C) It creates new legal barriers to entry in the video distribution business.
D) It creates a much cheaper distribution channel than previously available.
A) Only professionals can create video content on the Internet.
B) It severely limits the amount of content available to consumers.
C) It creates new legal barriers to entry in the video distribution business.
D) It creates a much cheaper distribution channel than previously available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which statement is TRUE?
A) Network goods rarely ever face new competition.
B) Network goods are usually sold by monopolistically competitive firms.
C) Network goods might lose their dominance over time.
D) Companies producing network goods compete "in the market," not "for the market."
A) Network goods rarely ever face new competition.
B) Network goods are usually sold by monopolistically competitive firms.
C) Network goods might lose their dominance over time.
D) Companies producing network goods compete "in the market," not "for the market."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The port of Rhodes (of the famed Colossus of Rhodes) was a major trading hub during the Roman Republic, charging a small harbor tax on goods that passed through. When Rome fought Macedonia, Rhodes took a neutral stance much to Rome's chagrin. In response, Rome established a rival port on the nearby Isle of Delos and eliminated the harbor tax. Trade in Rhodes immediately fell by 85% and eventually the city-state disappeared forever. Why did Rome completely eliminate the tax instead of charging one just below what Rhodes charged?
A) to make consumers open to a new competitor
B) to remove a legal barrier to entry
C) to destroy Rhodes's excellent ports
D) to reduce the fixed cost of entry
A) to make consumers open to a new competitor
B) to remove a legal barrier to entry
C) to destroy Rhodes's excellent ports
D) to reduce the fixed cost of entry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Markets tend to be more easily monopolized when:
A) marginal costs are low.
B) average costs are high.
C) the good is a network good.
D) fixed costs are high.
A) marginal costs are low.
B) average costs are high.
C) the good is a network good.
D) fixed costs are high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
How do Facebook, Twitter, and Google+ compete "for the market"?
A) Many users will have accounts on all three services.
B) Everyone will use the service that has the most features.
C) The social networking market is not very competitive.
D) Users spend the most time on the same network where most of the people they know spend the most time.
A) Many users will have accounts on all three services.
B) Everyone will use the service that has the most features.
C) The social networking market is not very competitive.
D) Users spend the most time on the same network where most of the people they know spend the most time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Firms that operate in contestable markets:
A) still price competitively since they face the threat of competition from new entrants.
B) are pure monopolies that set price equal to consumers' highest willingness to pay.
C) earn zero economic profits.
D) face more competition when fixed costs are high.
A) still price competitively since they face the threat of competition from new entrants.
B) are pure monopolies that set price equal to consumers' highest willingness to pay.
C) earn zero economic profits.
D) face more competition when fixed costs are high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Contestable markets tend to arise when:
A) fixed costs are high.
B) the threat of new firms entering the market is low.
C) the incumbent firm does not control access to an important resource.
D) government regulations are in effect.
A) fixed costs are high.
B) the threat of new firms entering the market is low.
C) the incumbent firm does not control access to an important resource.
D) government regulations are in effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Companies that compete for the market and win:
A) stay on top forever.
B) are frequently displaced.
C) face no subsequent competition.
D) are free to raise prices as much as they want.
A) stay on top forever.
B) are frequently displaced.
C) face no subsequent competition.
D) are free to raise prices as much as they want.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which is NOT a good example of a contestable market?
A) low-cost airlines
B) electricity providers
C) a local Mexican restaurant
D) bottled-water manufacturers
A) low-cost airlines
B) electricity providers
C) a local Mexican restaurant
D) bottled-water manufacturers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Markets tend to be more easily monopolized when:
A) marginal costs are low.
B) average costs are high.
C) the good is a network good.
D) fixed costs are high.
A) marginal costs are low.
B) average costs are high.
C) the good is a network good.
D) fixed costs are high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which firm's market is the most contestable?
A) the only cable TV provider in town
B) the only sewer-and-water company in town
C) the only hospital in town
D) the only Chinese restaurant in town
A) the only cable TV provider in town
B) the only sewer-and-water company in town
C) the only hospital in town
D) the only Chinese restaurant in town

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Contestable markets tend to arise when:
A) fixed costs are high.
B) the threat of new firms entering the market is low.
C) the incumbent firm does not control access to an important resource.
D) government regulations are in effect.
A) fixed costs are high.
B) the threat of new firms entering the market is low.
C) the incumbent firm does not control access to an important resource.
D) government regulations are in effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Is electricity distribution a contestable market? Why or why not?
A) No, because there are high fixed costs of erecting power lines to every house.
B) No, because consumers feel loyal to their current power company.
C) Yes, because there are no legal barriers to entry.
D) Yes, because there are no fixed costs associated with distributing power.
A) No, because there are high fixed costs of erecting power lines to every house.
B) No, because consumers feel loyal to their current power company.
C) Yes, because there are no legal barriers to entry.
D) Yes, because there are no fixed costs associated with distributing power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The threat of new firms easily entering a market and taking customers away from an existing firm is characteristic of a:
A) contestable market.
B) nondominant market.
C) Nash market.
D) prisoner's dilemma.
A) contestable market.
B) nondominant market.
C) Nash market.
D) prisoner's dilemma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Facebook dominates as the premier social networking site with more than 500 million members. However, Google has recently released Google+, a social networking site that makes it easy to create circles of information just for your friends, parents, and professional life. The market for social networking is a(n):
A) interworked market.
B) contestable market.
C) intracompetitive market
D) separating-equilibrium market.
A) interworked market.
B) contestable market.
C) intracompetitive market
D) separating-equilibrium market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
When the market for a network good is contestable, then:
A) there is little competition.
B) many firms operate and compete for consumers in the industry.
C) it is hard for consumers to get locked into a bad outcome.
D) monopoly firms always charge prices well above their average costs.
A) there is little competition.
B) many firms operate and compete for consumers in the industry.
C) it is hard for consumers to get locked into a bad outcome.
D) monopoly firms always charge prices well above their average costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which is NOT a factor that increases the contestability of markets?
A) Fixed costs of market entry are low, relative to potential revenue.
B) The incumbent has no unique, hard-to-replicate resource.
C) Consumers are not open to the prospect of dealing with a new competitor.
D) There are few or no legal barriers to entry.
A) Fixed costs of market entry are low, relative to potential revenue.
B) The incumbent has no unique, hard-to-replicate resource.
C) Consumers are not open to the prospect of dealing with a new competitor.
D) There are few or no legal barriers to entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 160 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



