Deck 13: Monopoly
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/233
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Monopoly
1
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay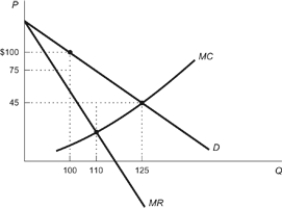
(Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay) Refer to the figure. What is the maximum price that the consumer is willing to pay for 100 units?
A) $100
B) $80
C) $75
D) $90
Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay

(Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay) Refer to the figure. What is the maximum price that the consumer is willing to pay for 100 units?
A) $100
B) $80
C) $75
D) $90
$100
2
In Chicago's Southside (and other places), auto mechanics (who work outside the formal sector, without a business license, advertising, or even a garage) will do work for gang members without charging them. In exchange, gang members chase away other mechanics who wish to operate in the area. These auto mechanics have monopoly power; what type of source does it come from?
A) barriers to entry
B) hard to duplicate inputs
C) innovation
D) economies of scale
A) barriers to entry
B) hard to duplicate inputs
C) innovation
D) economies of scale
barriers to entry
3
A profit-maximizing monopolist's total profit can be found by calculating:
A) MR - MC.
B) TR - TC.
C) AR - AC.
D) MC - MR.
A) MR - MC.
B) TR - TC.
C) AR - AC.
D) MC - MR.
TR - TC.
4
Which of the following is always TRUE for monopolies?
A) MR > D
B) P > MR
C) P > AC
D) TR < TC
A) MR > D
B) P > MR
C) P > AC
D) TR < TC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is TRUE for monopolists?
A) They charge a price below average cost, which guarantees above-normal profits.
B) Their marginal revenue increases with output.
C) They maximize profits by producing at the minimum of average costs.
D) They produce all units of output for which marginal revenue is greater than or equal to marginal cost.
A) They charge a price below average cost, which guarantees above-normal profits.
B) Their marginal revenue increases with output.
C) They maximize profits by producing at the minimum of average costs.
D) They produce all units of output for which marginal revenue is greater than or equal to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the demand curve for a firm is a straight line with negative slope, which of the following is the shortcut to finding the MR?
A) The demand curve starts below the marginal revenue curve and cuts the marginal revenue curve halfway down its length.
B) The marginal revenue curve starts at the same point as the demand curve and has twice the slope of the demand curve.
C) The marginal revenue curve is parallel to the demand curve with the same slope.
D) The marginal revenue curve starts at the same point as the demand curve and has a slope of 0.
A) The demand curve starts below the marginal revenue curve and cuts the marginal revenue curve halfway down its length.
B) The marginal revenue curve starts at the same point as the demand curve and has twice the slope of the demand curve.
C) The marginal revenue curve is parallel to the demand curve with the same slope.
D) The marginal revenue curve starts at the same point as the demand curve and has a slope of 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A monopoly is a firm:
A) that is exempt from patent protection.
B) that sets price above marginal cost without concern that other firms will enter the industry.
C) without market power.
D) that sets price higher than or equal to marginal cost.
A) that is exempt from patent protection.
B) that sets price above marginal cost without concern that other firms will enter the industry.
C) without market power.
D) that sets price higher than or equal to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) Market power is the ability to raise price and sell more units of a good.
B) Market power may result from government regulations or patent protection.
C) A monopoly is a firm without market power.
D) All of the answers are correct.
A) Market power is the ability to raise price and sell more units of a good.
B) Market power may result from government regulations or patent protection.
C) A monopoly is a firm without market power.
D) All of the answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When comparing a monopoly with a competitive industry, monopoly quantity:
A) and monopoly price will be lower than that of a competitive firm.
B) will be higher, and monopoly price will be lower, than that of a competitive firm.
C) will be lower, and monopoly price will be higher, than that of a competitive firm.
D) and monopoly price will be higher than that of a competitive firm.
A) and monopoly price will be lower than that of a competitive firm.
B) will be higher, and monopoly price will be lower, than that of a competitive firm.
C) will be lower, and monopoly price will be higher, than that of a competitive firm.
D) and monopoly price will be higher than that of a competitive firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is NOT a reason that monopolies arise?
A) patents
B) economies of scale
C) excess competition
D) control of natural resources
A) patents
B) economies of scale
C) excess competition
D) control of natural resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
For a monopolist, MR is always less than P because:
A) when a monopolist lowers the price to sell more units, it must lower the prices of all units sold.
B) MR is always less than P regardless of what type of firm we are discussing.
C) marginal revenue is always lower for the next unit sold.
D) when a monopolist needs to sell more units, it must lower marginal revenue in order to do so.
A) when a monopolist lowers the price to sell more units, it must lower the prices of all units sold.
B) MR is always less than P regardless of what type of firm we are discussing.
C) marginal revenue is always lower for the next unit sold.
D) when a monopolist needs to sell more units, it must lower marginal revenue in order to do so.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The power to raise price above marginal cost without fear that other firms will enter the market is:
A) market power.
B) firm power.
C) marginal power.
D) cost power.
A) market power.
B) firm power.
C) marginal power.
D) cost power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
GlaxoSmithKline prices Combivir, its AIDS drug:
A) at marginal cost.
B) at the same price as other firms do.
C) 25 times higher than the price of equivalent drugs in countries in which its patent is not recognized.
D) where supply intersects demand.
A) at marginal cost.
B) at the same price as other firms do.
C) 25 times higher than the price of equivalent drugs in countries in which its patent is not recognized.
D) where supply intersects demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the profit maximization condition for a monopolist?
A) MR > MC
B) MR = MC
C) AR = MC
D) AR = D
A) MR > MC
B) MR = MC
C) AR = MC
D) AR = D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay
(Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay) Refer to the figure. What is the profit that the monopolist is earning?
A) $10,000
B) $5,500
C) $4,500
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.
Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay

(Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay) Refer to the figure. What is the profit that the monopolist is earning?
A) $10,000
B) $5,500
C) $4,500
D) There is not enough information to answer the question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay
(Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay) Refer to the figure. What is the profit-maximizing quantity for this monopolist?
A) 125
B) 110
C) 100
D) 75
Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay

(Figure: Maximum Willingness to Pay) Refer to the figure. What is the profit-maximizing quantity for this monopolist?
A) 125
B) 110
C) 100
D) 75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
GlaxoSmithKline owns a government grant of temporary monopoly rights on the AIDS drug Combivir due to:
A) patents.
B) laws preventing entry of competitors.
C) economies of scale.
D) innovation.
A) patents.
B) laws preventing entry of competitors.
C) economies of scale.
D) innovation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When a pharmaceutical company discovers a new drug, patent law gives it market power by guaranteeing:
A) partial ownership of the right to sell the drug for an unlimited number of years.
B) partial ownership of the right to sell the drug for a limited number of years.
C) sole ownership of the right to sell the drug for a limited number of years.
D) sole ownership of the right to sell the drug for an unlimited number of years.
A) partial ownership of the right to sell the drug for an unlimited number of years.
B) partial ownership of the right to sell the drug for a limited number of years.
C) sole ownership of the right to sell the drug for a limited number of years.
D) sole ownership of the right to sell the drug for an unlimited number of years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements about monopoly power is correct?
A) Monopoly power is the power attained solely by dual firm monopolists.
B) Monopoly power is the power to raise prices above average cost without facing new entry of firms.
C) Monopoly power is only generated by governments.
D) Firms attaining monopoly power always set the price at the marginal cost.
A) Monopoly power is the power attained solely by dual firm monopolists.
B) Monopoly power is the power to raise prices above average cost without facing new entry of firms.
C) Monopoly power is only generated by governments.
D) Firms attaining monopoly power always set the price at the marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Figure: Monopolist Profits 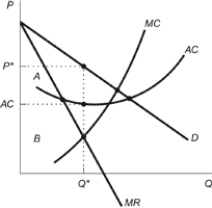 Refer to the figure. Which of the following answers correctly indicates the profit earned by this monopolist at the profit-maximizing quantity?
Refer to the figure. Which of the following answers correctly indicates the profit earned by this monopolist at the profit-maximizing quantity?
A) the area A + B
B) the area A - B
C) the area (A + B) - MC
D) area A
 Refer to the figure. Which of the following answers correctly indicates the profit earned by this monopolist at the profit-maximizing quantity?
Refer to the figure. Which of the following answers correctly indicates the profit earned by this monopolist at the profit-maximizing quantity?A) the area A + B
B) the area A - B
C) the area (A + B) - MC
D) area A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) maximizes profit by producing a quantity of 800 pills where marginal cost is $2 and average cost is $4. Consumers are willing to pay as much as $10 per pill when the quantity supplied is 800 pills. What is the maximum amount of profit that GSK can earn under these conditions?
A) $3,200
B) $4,800
C) $6,400
D) $8,000
A) $3,200
B) $4,800
C) $6,400
D) $8,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A firm with monopoly power is able to set a markup price that is:
A) lower than prices on similar goods sold by competitive firms.
B) the same as the prices on similar goods sold by competitive firms.
C) higher than prices on similar goods sold by competitive firms.
D) the maximum price all market participants will pay for similar goods.
A) lower than prices on similar goods sold by competitive firms.
B) the same as the prices on similar goods sold by competitive firms.
C) higher than prices on similar goods sold by competitive firms.
D) the maximum price all market participants will pay for similar goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Assuming the same cost structure, a competitive market produces ________ output at ________ prices than a monopoly market.
A) less; lower
B) more; lower
C) less; higher
D) more; higher
A) less; lower
B) more; lower
C) less; higher
D) more; higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Monopoly Profits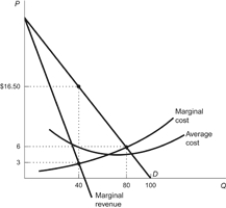
(Figure: Monopoly Profits) Refer to the figure. The monopolist earns a profit of:
A) $630.
B) $420.
C) $540.
D) $480.
Figure: Monopoly Profits

(Figure: Monopoly Profits) Refer to the figure. The monopolist earns a profit of:
A) $630.
B) $420.
C) $540.
D) $480.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
To maximize profit, the monopolist increases output:
A) until it is using full manufacturing capacity.
B) until marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue.
C) to the same amount it would produce if the firm was competitive, but maximizes price.
D) as long as the marginal revenue curve is higher than the demand curve.
A) until it is using full manufacturing capacity.
B) until marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue.
C) to the same amount it would produce if the firm was competitive, but maximizes price.
D) as long as the marginal revenue curve is higher than the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In a graph showing a straight-line market demand curve, the marginal revenue curve is:
A) a straight line that begins at the same point as the demand curve on the y-axis but with twice the slope.
B) a straight line that begins at the origin but with twice the slope of the demand curve.
C) the same straight line as the demand curve.
D) There is not enough information to complete the statement.
A) a straight line that begins at the same point as the demand curve on the y-axis but with twice the slope.
B) a straight line that begins at the origin but with twice the slope of the demand curve.
C) the same straight line as the demand curve.
D) There is not enough information to complete the statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
To maximize , a monopolist will produce the level of output where:
A) marginal revenue is equal to average cost.
B) average revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C) marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
D) average revenue is equal to average cost.
A) marginal revenue is equal to average cost.
B) average revenue is equal to marginal cost.
C) marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost.
D) average revenue is equal to average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Table: Monopolist
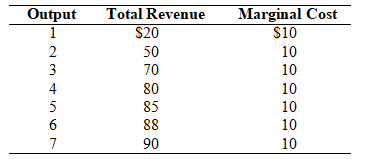
Refer to the table. What is the monopolist's profit-maximizing level of output?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

Refer to the table. What is the monopolist's profit-maximizing level of output?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a monopolist faces a straight-line negatively sloped demand curve, the price of the units it sells is always:
A) greater than the average revenue.
B) equal to marginal revenue.
C) greater than marginal revenue.
D) less than the average revenue.
A) greater than the average revenue.
B) equal to marginal revenue.
C) greater than marginal revenue.
D) less than the average revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The marginal revenue curve is a straight line beginning at the same point on the:
A) horizontal axis as the demand curve but with half of the slope.
B) vertical axis as the demand curve but with half of the slope.
C) horizontal axis as the demand curve but with twice the slope.
D) vertical axis as the demand curve but with twice the slope.
A) horizontal axis as the demand curve but with half of the slope.
B) vertical axis as the demand curve but with half of the slope.
C) horizontal axis as the demand curve but with twice the slope.
D) vertical axis as the demand curve but with twice the slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Monopoly Profits
(Figure: Monopoly Profits) Refer to the figure. What is the monopolist's optimal price and output level?
A) P = $3.00; Q = 40
B) P = $16.50; Q = 40
C) P = $6.00; Q = 40
D) P = $6.00; Q = 80
Figure: Monopoly Profits

(Figure: Monopoly Profits) Refer to the figure. What is the monopolist's optimal price and output level?
A) P = $3.00; Q = 40
B) P = $16.50; Q = 40
C) P = $6.00; Q = 40
D) P = $6.00; Q = 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Maximize Monopoly Profits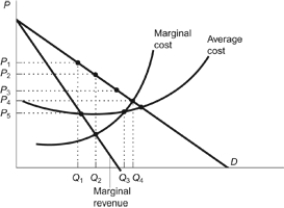
(Figure: Maximize Monopoly Profits) Refer to the figure. The monopolist will maximize its profit by producing at output equal to:
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q4.
Figure: Maximize Monopoly Profits

(Figure: Maximize Monopoly Profits) Refer to the figure. The monopolist will maximize its profit by producing at output equal to:
A) Q1.
B) Q2.
C) Q3.
D) Q4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose that a monopolist can sell five units of output at a price of $5 or six units of output at a price of $4. What is the marginal revenue of the sixth unit?
A) $24
B) $49
C) -$1
D) $4
A) $24
B) $49
C) -$1
D) $4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Monopoly power is best described as the ability to:
A) charge the profit-maximizing price.
B) produce the profit-maximizing output level.
C) earn economic profits without causing new firms to enter the market.
D) produce where marginal revenue intersects halfway between the origin and the demand curve.
A) charge the profit-maximizing price.
B) produce the profit-maximizing output level.
C) earn economic profits without causing new firms to enter the market.
D) produce where marginal revenue intersects halfway between the origin and the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which statement is TRUE?
A) If the monopolist's marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost, the monopolist can increase profit by selling more units at a lower price per unit.
B) If the monopolist's marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost, the monopolist can increase profit by selling fewer units at a higher price per unit.
C) When a monopolist produces where MR < MC it always earns a positive economic profit.
D) A monopolist is guaranteed monopoly profits by the government.
A) If the monopolist's marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost, the monopolist can increase profit by selling more units at a lower price per unit.
B) If the monopolist's marginal revenue is greater than its marginal cost, the monopolist can increase profit by selling fewer units at a higher price per unit.
C) When a monopolist produces where MR < MC it always earns a positive economic profit.
D) A monopolist is guaranteed monopoly profits by the government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the quantity demanded for a hand-carved pineapple is two at a price of $16, and the quantity demanded will increase to three if the seller lowers the price to $14, what is the seller's marginal revenue from selling 3 units of pineapple?
A) $8
B) $24
C) $10
D) $14
A) $8
B) $24
C) $10
D) $14

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A monopolist can sell 300 units of output for $29.00 per unit. Alternatively, it can sell 301 units of output for $28.25 per unit. The marginal revenue of the 301st unit of output is:
A) -$196.75.
B) -$0.75.
C) $196.75.
D) $28.25.
A) -$196.75.
B) -$0.75.
C) $196.75.
D) $28.25.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Typical evidence for the existence of market power would be market prices:
A) below production costs.
B) equal to production costs.
C) above production costs.
D) varying with market supply and demand conditions.
A) below production costs.
B) equal to production costs.
C) above production costs.
D) varying with market supply and demand conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Maximize Monopoly Profits
(Figure: Maximize Monopoly Profits) Refer to the figure. The monopolist will maximize its profit by charging a price equal to:
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P4.
Figure: Maximize Monopoly Profits

(Figure: Maximize Monopoly Profits) Refer to the figure. The monopolist will maximize its profit by charging a price equal to:
A) P1.
B) P2.
C) P3.
D) P4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When a monopolist decreases the price of its good, consumers:
A) buy the same amount of the good as before.
B) buy more.
C) buy less.
D) may buy more or less, depending on the price elasticity of demand.
A) buy the same amount of the good as before.
B) buy more.
C) buy less.
D) may buy more or less, depending on the price elasticity of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A firm with no competitors:
A) faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
B) faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
C) still faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D) has a perfectly elastic supply curve.
A) faces a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
B) faces a perfectly elastic demand curve.
C) still faces a downward-sloping demand curve.
D) has a perfectly elastic supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure: Monopolist 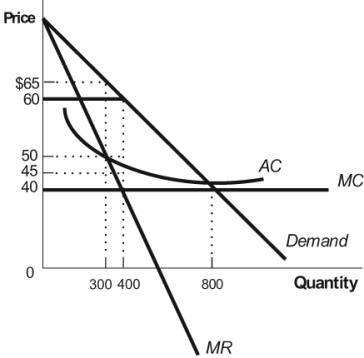 If this figure represents the demand and cost curves for a firm with market power, what price should the firm charge to maximize profits?
If this figure represents the demand and cost curves for a firm with market power, what price should the firm charge to maximize profits?
A) $40
B) $50
C) $60
D) $65
 If this figure represents the demand and cost curves for a firm with market power, what price should the firm charge to maximize profits?
If this figure represents the demand and cost curves for a firm with market power, what price should the firm charge to maximize profits?A) $40
B) $50
C) $60
D) $65

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Figure: Monopolist 4 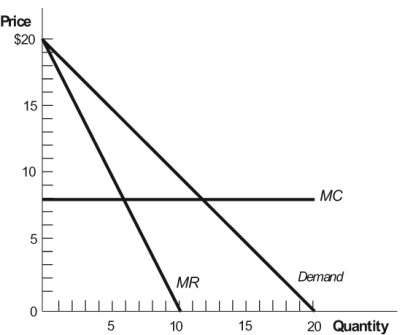 What is the profit-maximizing price and output level for the monopolist in this figure?
What is the profit-maximizing price and output level for the monopolist in this figure?
A) P = $8; Q = 6
B) P = $14; Q = 6
C) P = $8; Q = 12
D) P = $10; Q = 10
 What is the profit-maximizing price and output level for the monopolist in this figure?
What is the profit-maximizing price and output level for the monopolist in this figure?A) P = $8; Q = 6
B) P = $14; Q = 6
C) P = $8; Q = 12
D) P = $10; Q = 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A firm would prefer that its product demand curve is:
A) perfectly elastic.
B) elastic.
C) inelastic.
D) horizontal.
A) perfectly elastic.
B) elastic.
C) inelastic.
D) horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The more inelastic the demand curve for a product is, the:
A) higher is the monopolist's price markup.
B) smaller is the monopolist's price markup.
C) more responsive buyers are to a change in the price.
D) less chance monopolists will have to earn above-normal profits.
A) higher is the monopolist's price markup.
B) smaller is the monopolist's price markup.
C) more responsive buyers are to a change in the price.
D) less chance monopolists will have to earn above-normal profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The "You can't take it with you" effect potentially increases market power for pharmaceuticals if consumers who are dying of disease are also:
A) more inclined to spend their money on medicine than to save it.
B) more inclined to bequeath their money than spend it on medicine.
C) relatively sensitive to the price of life-saving pharmaceuticals.
D) relatively sensitive to how they spend money.
A) more inclined to spend their money on medicine than to save it.
B) more inclined to bequeath their money than spend it on medicine.
C) relatively sensitive to the price of life-saving pharmaceuticals.
D) relatively sensitive to how they spend money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) A monopolist's marginal cost is greater than its price.
B) The more inelastic the demand curve is, the greater is the monopolist's price markup.
C) The monopolist's profit is equal to P(Q - MR).
D) The position of the marginal revenue curve on the y-axis reflects consumer demand elasticity.
A) A monopolist's marginal cost is greater than its price.
B) The more inelastic the demand curve is, the greater is the monopolist's price markup.
C) The monopolist's profit is equal to P(Q - MR).
D) The position of the marginal revenue curve on the y-axis reflects consumer demand elasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Figure: Demand Curve 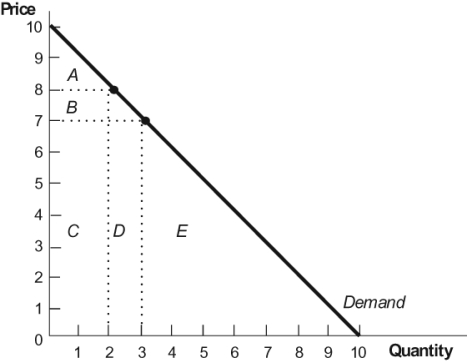 In this figure, the marginal revenue of the third unit is given by area:
In this figure, the marginal revenue of the third unit is given by area:
A) D.
B) C + D.
C) D - - B.
D) D + C + E.
 In this figure, the marginal revenue of the third unit is given by area:
In this figure, the marginal revenue of the third unit is given by area:A) D.
B) C + D.
C) D - - B.
D) D + C + E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Figure: Monopolist 2 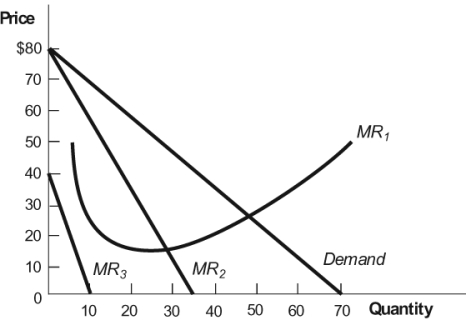 In this figure, the monopolist's marginal revenue curve is:
In this figure, the monopolist's marginal revenue curve is:
A) also the demand curve.
B) MR1.
C) MR2.
D) MR3.
 In this figure, the monopolist's marginal revenue curve is:
In this figure, the monopolist's marginal revenue curve is:A) also the demand curve.
B) MR1.
C) MR2.
D) MR3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Monopolist 3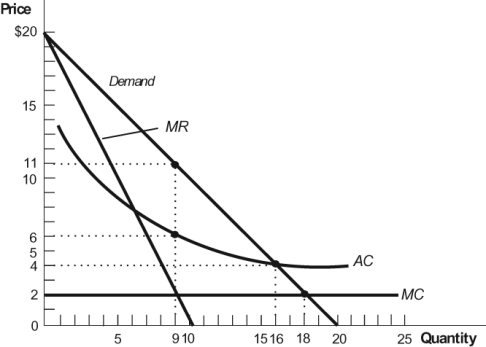
(Figure: Monopolist 3) In this figure, the monopolist's maximum profit is:
A) $99.
B) $45.
C) $36.
D) $54.
Figure: Monopolist 3

(Figure: Monopolist 3) In this figure, the monopolist's maximum profit is:
A) $99.
B) $45.
C) $36.
D) $54.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A firm can sell 1 unit at $9 or 2 units at $8 or 3 units at $7, and so on. What is the marginal revenue from the sale of the fifth unit?
A) $0
B) $1
C) $4
D) $5
A) $0
B) $1
C) $4
D) $5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Figure: Paint Market 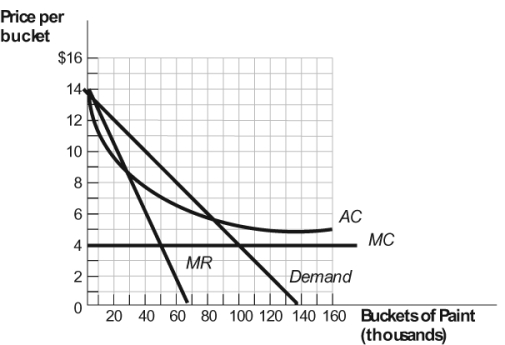 What is the profit or loss for this monopoly?
What is the profit or loss for this monopoly?
A) -$200,000
B) $10,000
C) $100,000
D) $250,000
 What is the profit or loss for this monopoly?
What is the profit or loss for this monopoly?A) -$200,000
B) $10,000
C) $100,000
D) $250,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following statements are TRUE?
I. Monopolists can raise prices as high as they want and still earn economic profits.
II. Even with no competitors, firms face a downward-sloping demand curve.
III. Just like competitive firms, monopolists maximize profits where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A) I and III only
B) II and III only
C) I and II only
D) I, II, and III
I. Monopolists can raise prices as high as they want and still earn economic profits.
II. Even with no competitors, firms face a downward-sloping demand curve.
III. Just like competitive firms, monopolists maximize profits where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
A) I and III only
B) II and III only
C) I and II only
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Figure: Monopoly Markup 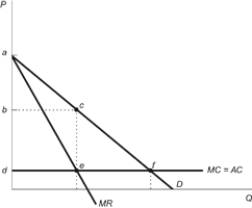 Refer to the figure. The monopolist's price markup is:
Refer to the figure. The monopolist's price markup is:
A) a - b.
B) b - d.
C) d.
D) a - d.
 Refer to the figure. The monopolist's price markup is:
Refer to the figure. The monopolist's price markup is:A) a - b.
B) b - d.
C) d.
D) a - d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A consumer is ________ likely to be sensitive to price if the purchase ________ covered by insurance.
A) more; is
B) less; is
C) less; is not
D) None of the answers is correct.
A) more; is
B) less; is
C) less; is not
D) None of the answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A monopoly is able to increase the markup of price over marginal cost:
A) when the demand is more price-elastic.
B) when the demand is less price-elastic.
C) when there is more marginal revenue per unit sold.
D) at will regardless of price-elasticity.
A) when the demand is more price-elastic.
B) when the demand is less price-elastic.
C) when there is more marginal revenue per unit sold.
D) at will regardless of price-elasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
For a linear demand curve, the marginal revenue curve has:
A) the same slope.
B) the reciprocal slope.
C) half the slope.
D) twice the slope.
A) the same slope.
B) the reciprocal slope.
C) half the slope.
D) twice the slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Monopolist 3
(Figure: Monopolist 3) In this figure, the profit-maximizing monopolist sells:
A) 9 units of output at $11 per unit.
B) 16 units of output at $4 per unit.
C) 9 units of output at $20 per unit.
D) 18 units of output at $2 per unit.
Figure: Monopolist 3

(Figure: Monopolist 3) In this figure, the profit-maximizing monopolist sells:
A) 9 units of output at $11 per unit.
B) 16 units of output at $4 per unit.
C) 9 units of output at $20 per unit.
D) 18 units of output at $2 per unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Graphically, a firm's marginal revenue curve is:
A) perfectly elastic and equal to their marginal cost curve.
B) downward-sloping and equal to the market demand curve.
C) downward-sloping, but with twice the slope of the market demand curve.
D) perfectly elastic but lies underneath the market demand curve.
A) perfectly elastic and equal to their marginal cost curve.
B) downward-sloping and equal to the market demand curve.
C) downward-sloping, but with twice the slope of the market demand curve.
D) perfectly elastic but lies underneath the market demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the monopolist's demand is given by P = 100 - Q, marginal revenue is given by:
A) MR = 100 - 2Q.
B) MR = 100 - Q.
C) MR = 100Q.
D) MR = 100Q - Q2.
A) MR = 100 - 2Q.
B) MR = 100 - Q.
C) MR = 100Q.
D) MR = 100Q - Q2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following effects would generally make demand curves more inelastic?
A) "You can't take it with you" effect
B) "Other people's money" effect
C) Both effects
D) Neither effect
A) "You can't take it with you" effect
B) "Other people's money" effect
C) Both effects
D) Neither effect

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A monopolist can raise its price further above marginal cost, the more ______ is the ______ for its product.
A) elastic; demand
B) inelastic; demand
C) elastic; supply
D) inelastic; supply
A) elastic; demand
B) inelastic; demand
C) elastic; supply
D) inelastic; supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure: Monopolist 5 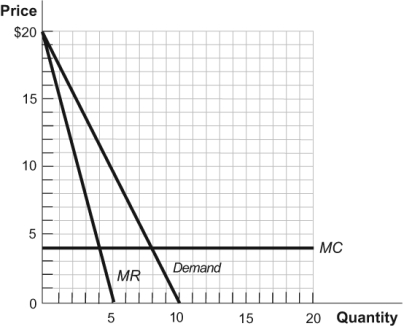
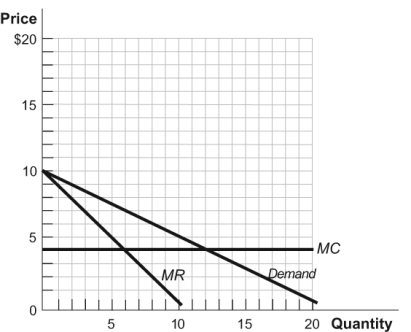
In these figures, the markup of price over marginal cost for the relatively inelastic demand is ______, and the markup of price over marginal cost for the relatively elastic demand is ______.
A) $10; $2
B) $15; $7.50
C) $7.50; $3
D) $5; $1


In these figures, the markup of price over marginal cost for the relatively inelastic demand is ______, and the markup of price over marginal cost for the relatively elastic demand is ______.
A) $10; $2
B) $15; $7.50
C) $7.50; $3
D) $5; $1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
With health insurance, medical treatments are often paid by someone other than the patient, which will make consumers with serious diseases relatively:
A) insensitive to the price of pharmaceuticals.
B) sensitive to the price of pharmaceuticals.
C) insensitive to the premium of health insurance.
D) sensitive to the premium of health insurance.
A) insensitive to the price of pharmaceuticals.
B) sensitive to the price of pharmaceuticals.
C) insensitive to the premium of health insurance.
D) sensitive to the premium of health insurance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If these were monopolistic markets, which one would clearly have a greater markup than a monopolized banana industry?
A) organic bananas
B) pencils
C) electric car
D) laptop computers
A) organic bananas
B) pencils
C) electric car
D) laptop computers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Under monopoly, the portion of the outgoing consumer surplus that is not transferred to the monopoly firm or still considered consumer surplus is:
A) known as deadweight loss.
B) proof that monopolies should not be allowed.
C) transferred to the government.
D) available to third parties who benefit from sales of the monopolist's output.
A) known as deadweight loss.
B) proof that monopolies should not be allowed.
C) transferred to the government.
D) available to third parties who benefit from sales of the monopolist's output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
When the demand curve for the profit-maximizing monopolist's product is relatively inelastic:
A) it cannot raise the price of the product above the marginal cost of the product.
B) raising the product's price will lower the total revenue for the product.
C) the product does not have good substitutes.
D) All of these choices are correct.
A) it cannot raise the price of the product above the marginal cost of the product.
B) raising the product's price will lower the total revenue for the product.
C) the product does not have good substitutes.
D) All of these choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When demand is inelastic, revenues increase and production costs decrease as the quantity produced declines, total profits will always increase with a higher price. Therefore, monopolists:
A) can't exist.
B) can't exist for industries in which demand is relatively inelastic.
C) can't maximize profits if they face a relatively inelastic demand.
D) will always raise their price until they get to an elastic portion of the demand curve.
A) can't exist.
B) can't exist for industries in which demand is relatively inelastic.
C) can't maximize profits if they face a relatively inelastic demand.
D) will always raise their price until they get to an elastic portion of the demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Other things being equal, the markup above marginal cost that a monopolist charges will be:
A) higher when there are more substitutes for the monopolist's product.
B) lower when there are more substitutes for the monopolist's product.
C) the same, no matter the number of substitutes for the monopolist's product.
D) zero if there are any substitutes for the monopolist's product.
A) higher when there are more substitutes for the monopolist's product.
B) lower when there are more substitutes for the monopolist's product.
C) the same, no matter the number of substitutes for the monopolist's product.
D) zero if there are any substitutes for the monopolist's product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
When a monopolist's demand curve is inelastic, raising the price:
A) increases total revenue and increases total cost.
B) decreases total revenue and increases total cost.
C) increases total revenue and decreases total cost.
D) decreases total revenue and decreases total cost.
A) increases total revenue and increases total cost.
B) decreases total revenue and increases total cost.
C) increases total revenue and decreases total cost.
D) decreases total revenue and decreases total cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A monopolist increased output by 100 units but cut prices by $20 to sell this additional output at $1,000 per unit. What is TRUE about marginal revenue?
A) MR totals $2,000.
B) MR totals $100,000.
C) MR totals -$2,000.
D) MR cannot be calculated with the information given.
A) MR totals $2,000.
B) MR totals $100,000.
C) MR totals -$2,000.
D) MR cannot be calculated with the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When a good has relatively few substitutes:
A) demand for the good is elastic.
B) monopolists will tend to increase their markup for the good.
C) monopolists will tend to decrease their markup for the good.
D) producers will be able to "steal" all of the consumer surplus from consumers.
A) demand for the good is elastic.
B) monopolists will tend to increase their markup for the good.
C) monopolists will tend to decrease their markup for the good.
D) producers will be able to "steal" all of the consumer surplus from consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The economic inefficiency of a monopolist can be measured by the:
A) excess profit generated by monopoly firms.
B) poor quality of service offered by monopoly firms.
C) number of consumers who are unable to purchase the product because of its high price.
D) deadweight loss involved relative to a competitive firm.
A) excess profit generated by monopoly firms.
B) poor quality of service offered by monopoly firms.
C) number of consumers who are unable to purchase the product because of its high price.
D) deadweight loss involved relative to a competitive firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Figure: Optimal Output 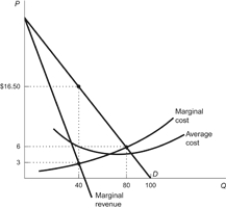 Refer to the figure. The competitive industry level of output is:
Refer to the figure. The competitive industry level of output is:
A) 40.
B) 65.
C) 80.
D) 100.
 Refer to the figure. The competitive industry level of output is:
Refer to the figure. The competitive industry level of output is:A) 40.
B) 65.
C) 80.
D) 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In which of the following product markets should we see a higher price markup?
A) one with lots of substitutes
B) one with few substitutes
C) one with a very elastic demand
D) one for a commodity good
A) one with lots of substitutes
B) one with few substitutes
C) one with a very elastic demand
D) one for a commodity good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Monopoly Markup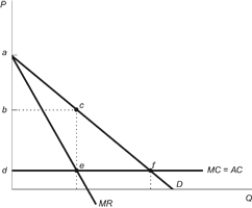
(Figure: Monopoly Markup) Refer to the figure. Consumer surplus under competition is represented by:
A) triangle abc.
B) triangle cef.
C) square bcde.
D) triangle adf.
Figure: Monopoly Markup

(Figure: Monopoly Markup) Refer to the figure. Consumer surplus under competition is represented by:
A) triangle abc.
B) triangle cef.
C) square bcde.
D) triangle adf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When demand is relatively elastic, monopolists will charge:
A) a higher markup.
B) a lower markup.
C) the same markup as when demand is relatively inelastic.
D) a price equal to marginal cost.
A) a higher markup.
B) a lower markup.
C) the same markup as when demand is relatively inelastic.
D) a price equal to marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Monopoly Markup
(Figure: Monopoly Markup) Refer to the figure. Consumer surplus under monopoly is represented by:
A) triangle abc.
B) triangle cef.
C) square bcde.
D) triangle adf.
Figure: Monopoly Markup

(Figure: Monopoly Markup) Refer to the figure. Consumer surplus under monopoly is represented by:
A) triangle abc.
B) triangle cef.
C) square bcde.
D) triangle adf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A monopolist sells in two different markets and charges the same price of $10 in both markets. In Market A, the demand curve is described by Qd = 50 - 2P. In Market B, the demand curve is described by Qd = 60 - P. If the monopolist lowers prices by $1 in the market with the more elastic demand and raises prices by $1 in the market with the more inelastic demand curve, by how much does its total revenue change?
A) -$27
B) $459
C) $767
D) $308
A) -$27
B) $459
C) $767
D) $308

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the following to answer questions:
Figure: Monopoly Markup
(Figure: Monopoly Markup) Refer to the figure. The deadweight loss attributable to monopoly is:
A) triangle abc.
B) triangle cef.
C) square bcde.
D) triangle adf.
Figure: Monopoly Markup

(Figure: Monopoly Markup) Refer to the figure. The deadweight loss attributable to monopoly is:
A) triangle abc.
B) triangle cef.
C) square bcde.
D) triangle adf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 233 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



