Deck 13: Myocardial Infarction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/65
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Myocardial Infarction
1
In Figure 21,there is evidence of 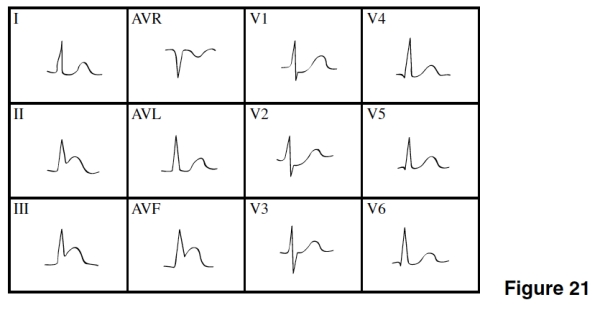
A)Anterior wall ischemia.
B)Anterior MI.
C)NSTEMI.
D)Inferior/posterior MI

A)Anterior wall ischemia.
B)Anterior MI.
C)NSTEMI.
D)Inferior/posterior MI
D
2
An acute inferior wall STEMI has ST elevation in leads
A)I,AVL,V5-6.
B)V1-4.
C)II,III,AVF.
D)V1-2.
A)I,AVL,V5-6.
B)V1-4.
C)II,III,AVF.
D)V1-2.
C
3
Mr.Johnson came to the hospital within the hour after his heart attack started.You would expect to see what indication of acute STEMI on his EKG?
A)ST segment elevation in the leads over the damaged area
B)ST segment depression in the leads over the damaged area
C)Significant Q waves in the leads over the damaged area
D)Tall,pointy P waves greater than 2.5 mms in lead II or V1
A)ST segment elevation in the leads over the damaged area
B)ST segment depression in the leads over the damaged area
C)Significant Q waves in the leads over the damaged area
D)Tall,pointy P waves greater than 2.5 mms in lead II or V1
A
4
An inferior MI is most often caused by occlusion of which coronary artery?
A)Right coronary artery
B)Left main
C)Circumflex
D)Left anterior descending
A)Right coronary artery
B)Left main
C)Circumflex
D)Left anterior descending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is indicative of myocardial injury?
A)ST elevation
B)ST depression
C)Significant Q wave
D)Inverted T wave
A)ST elevation
B)ST depression
C)Significant Q wave
D)Inverted T wave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is a reciprocal change seen in the area opposite an infarct?
A)ST elevation
B)ST depression
C)Tall,pointy T waves
D)Widened QRS complexes
A)ST elevation
B)ST depression
C)Tall,pointy T waves
D)Widened QRS complexes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A STEMI typically
A)Damages only the innermost layer of myocardium.
B)Does not cause the development of significant Q waves on the EKG.
C)Is dangerous because it can herald a subendocardial MI soon to come.
D)Is an MI that damages the full thickness of the myocardium in a certain area.
A)Damages only the innermost layer of myocardium.
B)Does not cause the development of significant Q waves on the EKG.
C)Is dangerous because it can herald a subendocardial MI soon to come.
D)Is an MI that damages the full thickness of the myocardium in a certain area.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a lateral wall MI,which coronary artery is occluded?
A)Right
B)Left anterior descending
C)Circumflex
D)Aorta
A)Right
B)Left anterior descending
C)Circumflex
D)Aorta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The ST segment depressions in leads II,III,and AVF in Figure 20 are 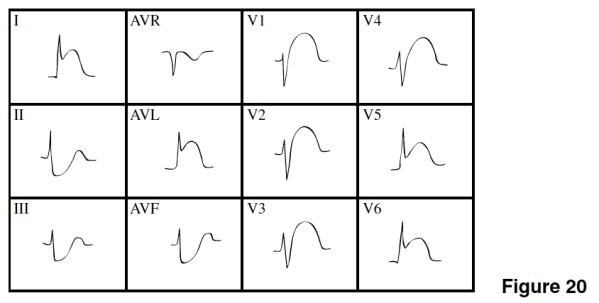
A)Indicative changes of the MI.
B)Reciprocal changes.
C)An indication of imminent extension of the MI.
D)Evidence of a new NSTEMI.

A)Indicative changes of the MI.
B)Reciprocal changes.
C)An indication of imminent extension of the MI.
D)Evidence of a new NSTEMI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The MI in Figure 20 is 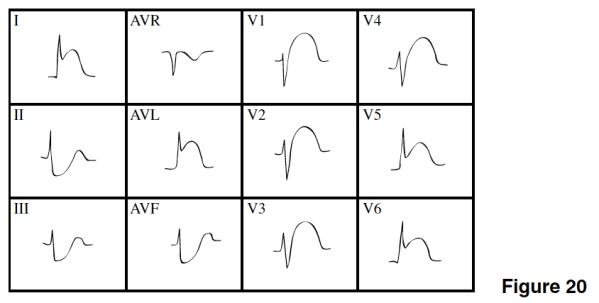
A)Extensive anterior (anterior-lateral).
B)Posterior.
C)Lateral.
D)Inferior.

A)Extensive anterior (anterior-lateral).
B)Posterior.
C)Lateral.
D)Inferior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If you were told that Figure 19's EKG was of a young black male,you would think of what cause of mild widespread ST elevation? 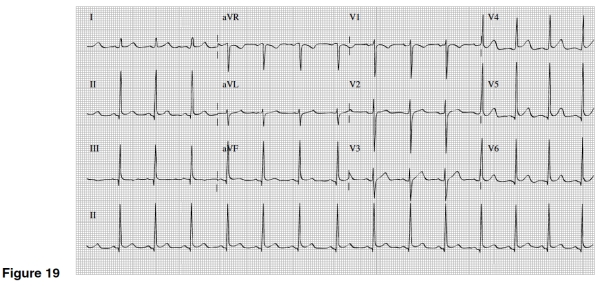
A)Pericarditis
B)Inferior MI
C)Early repolarization
D)Right ventricular infarction

A)Pericarditis
B)Inferior MI
C)Early repolarization
D)Right ventricular infarction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A posterior infarction is usually caused by occlusion of which coronary artery?
A)Left main
B)Circumflex
C)Left anterior descending
D)Right coronary artery
A)Left main
B)Circumflex
C)Left anterior descending
D)Right coronary artery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An anterior MI is caused by occlusion of which coronary artery?
A)Left anterior descending
B)Posterior descending
C)Right
D)Circumflex
A)Left anterior descending
B)Posterior descending
C)Right
D)Circumflex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The age of the MI in Figure 20 is 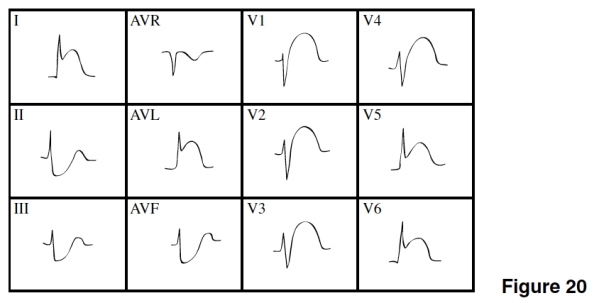
A)Acute.
B)Age indeterminate.
C)Old.
D)Impossible to tell.

A)Acute.
B)Age indeterminate.
C)Old.
D)Impossible to tell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Most MIs are caused by a
A)Blood clot in the pulmonary artery.
B)Coronary artery spasm.
C)Blood clot in a coronary artery.
D)Dysrhythmia.
A)Blood clot in the pulmonary artery.
B)Coronary artery spasm.
C)Blood clot in a coronary artery.
D)Dysrhythmia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
There is evidence of which of the following in Figure 19? 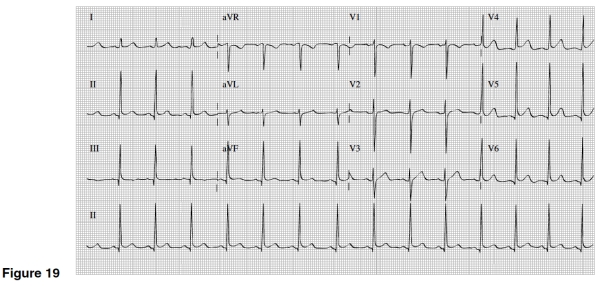
A)Slight ST segment elevation in multiple leads
B)Significant Q waves in II,III,and AVF
C)Inverted T waves in V1-6
D)Widespread ST depression and T wave inversions

A)Slight ST segment elevation in multiple leads
B)Significant Q waves in II,III,and AVF
C)Inverted T waves in V1-6
D)Widespread ST depression and T wave inversions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The _____ of an old STEMI typically remains on the EKG forever.
A)ST segment elevation
B)ST segment depression
C)Inverted T waves
D)Significant Q wave
A)ST segment elevation
B)ST segment depression
C)Inverted T waves
D)Significant Q wave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
ST segment elevation is indicative of
A)Myocardial necrosis.
B)Myocardial ischemia.
C)Myocardial injury.
D)Abnormal atrial depolarization.
A)Myocardial necrosis.
B)Myocardial ischemia.
C)Myocardial injury.
D)Abnormal atrial depolarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is indicative of myocardial necrosis?
A)ST elevation
B)ST depression
C)Significant Q wave
D)Inverted T wave
A)ST elevation
B)ST depression
C)Significant Q wave
D)Inverted T wave

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An inverted T wave is indicative of
A)Myocardial necrosis.
B)Myocardial ischemia.
C)Myocardial injury.
D)Abnormal ventricular depolarization.
A)Myocardial necrosis.
B)Myocardial ischemia.
C)Myocardial injury.
D)Abnormal ventricular depolarization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which kind of MI is best seen by looking at the EKG upside down from behind?
A)Inferior
B)Anteroseptal
C)Posterior
D)Lateral
A)Inferior
B)Anteroseptal
C)Posterior
D)Lateral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Mrs.Campho had a previous inferior MI about 20 years ago.What would you expect to see on her EKG that would be consistent with her old inferior MI?
A)ST elevation in II,III,and AVF
B)ST depression in II,III,and AVF
C)Significant Q wave in II,III,and AVF
D)Reciprocal ST depression in the anterior leads
A)ST elevation in II,III,and AVF
B)ST depression in II,III,and AVF
C)Significant Q wave in II,III,and AVF
D)Reciprocal ST depression in the anterior leads

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which kind of MI usually damages only the innermost layer of the myocardium?
A)NSTEMI
B)Transmural
C)Posterior
D)Anteroseptal
A)NSTEMI
B)Transmural
C)Posterior
D)Anteroseptal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The baseline for evaluating ST segments for elevation is the
A)PR interval.
B)PR segment.
C)QRS interval.
D)T wave.
A)PR interval.
B)PR segment.
C)QRS interval.
D)T wave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The order in which an MI progresses through "the three Is" is which of these?
A)Ischemia,injury,infarction
B)Ischemia,infarction,injury
C)Infarction,ischemia,injury
D)Injury,infarction,ischemia
A)Ischemia,injury,infarction
B)Ischemia,infarction,injury
C)Infarction,ischemia,injury
D)Injury,infarction,ischemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What color is an injured tissue?
A)Pale whitish
B)Black
C)Bluish
D)Bright red
A)Pale whitish
B)Black
C)Bluish
D)Bright red

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The normal R wave transition zone occurs around leads
A)II and III.
B)V1-2.
C)V3-4.
D)V5-6.
A)II and III.
B)V1-2.
C)V3-4.
D)V5-6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Subendocardial MI is an old term for
A)Inferior MI.
B)NSTEMI.
C)STEMI.
D)Transmural MI.
A)Inferior MI.
B)NSTEMI.
C)STEMI.
D)Transmural MI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Mr.Henry has ST segment elevations in II,III,and AVF along with reciprocal ST depression in I,AVL,and V1-4.Right-sided EKG shows ST elevation in V3-4R.His blood pressure is quite low.Mr.Henry is normally hypertensive.This description is consistent with
A)Pericarditis.
B)Early repolarization.
C)Inferior MI complicated by a right ventricular infarction.
D)Extensive anterior MI complicated by cardiogenic shock.
A)Pericarditis.
B)Early repolarization.
C)Inferior MI complicated by a right ventricular infarction.
D)Extensive anterior MI complicated by cardiogenic shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which leads look at the lateral wall of the left ventricle?
A)II,III,and AVF
B)I,II,and III
C)I,AVL,and V5-6
D)V1-2
A)II,III,and AVF
B)I,II,and III
C)I,AVL,and V5-6
D)V1-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Mac Jacob is a 21-year-old black man who complains of shortness of breath and comes to the ER.His cardiac enzymes are normal,but his EKG shows some slight ST segment elevations with a "fish-hook" at the end of the QRS complexes in V2-4.This is consistent with
A)Inferior MI.
B)Early repolarization.
C)Pericarditis.
D)Right ventricular infarction.
A)Inferior MI.
B)Early repolarization.
C)Pericarditis.
D)Right ventricular infarction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Indicative changes of a STEMI include which of the following?
A)ST segment elevation.
B)ST segment depression.
C)T wave flattening.
D)Fish-hook in V3.
A)ST segment elevation.
B)ST segment depression.
C)T wave flattening.
D)Fish-hook in V3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A significant Q wave
A)Is either 0.04 seconds wide or 1/3 to 1/4 the size of the R wave.
B)Is taller than the peak of the T wave.
C)Implies myocardial injury.
D)Is seen only in subendocardial MIs.
A)Is either 0.04 seconds wide or 1/3 to 1/4 the size of the R wave.
B)Is taller than the peak of the T wave.
C)Implies myocardial injury.
D)Is seen only in subendocardial MIs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the transition zone is between V1 and V2,the EKG is said to have
A)Malrotation.
B)Clockwise rotation.
C)Counterclockwise rotation.
D)Normal R wave progression.
A)Malrotation.
B)Clockwise rotation.
C)Counterclockwise rotation.
D)Normal R wave progression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is a reciprocal change?
A)ST elevation
B)T wave inversion
C)ST depression
D)Significant Q waves
A)ST elevation
B)T wave inversion
C)ST depression
D)Significant Q waves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The coronary artery that feeds blood to the damaged area of the heart in Figure 21 is the 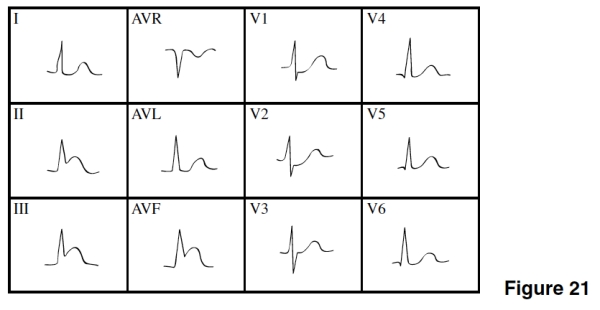
A)Right coronary artery.
B)Left anterior descending.
C)Circumflex.
D)Popliteal.

A)Right coronary artery.
B)Left anterior descending.
C)Circumflex.
D)Popliteal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An MI that has ST elevation is
A)Age indeterminate.
B)Acute.
C)Old.
D)Not an MI,just ischemia.
A)Age indeterminate.
B)Acute.
C)Old.
D)Not an MI,just ischemia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Occlusion is
A)Blockage.
B)An EKG finding seen in NSTEMIs.
C)An EKG finding consistent with ischemia.
D)The opening of a coronary artery.
A)Blockage.
B)An EKG finding seen in NSTEMIs.
C)An EKG finding consistent with ischemia.
D)The opening of a coronary artery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What kind of MI is indicated by significant Q waves in II,III,AVF,and V5-6?
A)Anterior-lateral
B)Inferior-posterior
C)Inferior-lateral
D)Anteroseptal
A)Anterior-lateral
B)Inferior-posterior
C)Inferior-lateral
D)Anteroseptal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
In which leads is a posterior MI evident?
A)I and II
B)V1-6
C)II,III,and AVR
D)V1-2
A)I and II
B)V1-6
C)II,III,and AVR
D)V1-2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Pericarditis is _____ of the pericardium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Leads V2-4 are inferior leads.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Hyperacute changes of an MI are those seen in the MI's earliest stages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Smiley-face ST elevation is concave and often seen in pericarditis.
Essay Questions
Essay Questions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The leads one looks at to find an inferior MI are _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Normal R wave transition is between V5 and V6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Ischemia is a reversible process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Early repolarization often has a unique EKG finding that makes recognition easier.What is that finding? _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
An age-indeterminate MI should have a significant Q wave along with T wave inversion,but the ST segment should be back to baseline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The normal T wave is tall and pointy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A coved ST segment is concave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An old inferior MI should show significant Q waves in II,III,and AVF even after several years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Ischemia causes myocardial tissue to turn black.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
ST elevation indicates ischemia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
An acute MI is indicated by ST segment depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Explain where the leads are placed for a right-sided EKG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
To detect right ventricular infarction,one must do a right-sided EKG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Counterclockwise rotation is indicated from R wave transition in V1-2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A right ventricular infarction is most often seen along with inferior MI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Name the three Is of infarction._____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Reciprocal ST depression is seen only when there is _____ in the indicative leads.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
An age-indeterminate MI is called a _____ by some authorities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A _____ MI is seen as a mirror image of an anterior MI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Inferior-lateral MI has indicative changes in leads _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Anterior MI has indicative changes in leads _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 65 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



