Deck 9: Rhythms Originating in the Av Junction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Rhythms Originating in the Av Junction
1
In which rhythm is decreased cardiac output most likely to be a concern?
A)Sinus rhythm
B)Accelerated junctional rhythm
C)Junctional bradycardia
D)Junctional rhythm
A)Sinus rhythm
B)Accelerated junctional rhythm
C)Junctional bradycardia
D)Junctional rhythm
C
2
The heart rate in Figure 8 is closest to 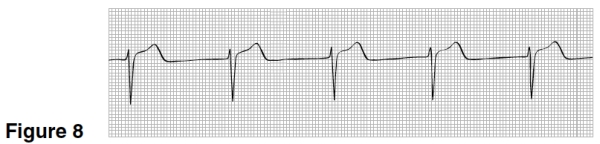
A)50.
B)75.
C)100.
D)125.

A)50.
B)75.
C)100.
D)125.
A
3
A junctional rhythm with a heart rate of 125 is called
A)Junctional bradycardia.
B)Junctional rhythm.
C)Accelerated junctional rhythm.
D)Junctional tachycardia.
A)Junctional bradycardia.
B)Junctional rhythm.
C)Accelerated junctional rhythm.
D)Junctional tachycardia.
D
4
Junctional tachycardia without visible P waves is best called
A)Sinus tachycardia.
B)SVT.
C)Atrial tachycardia.
D)PJCs.
A)Sinus tachycardia.
B)SVT.
C)Atrial tachycardia.
D)PJCs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which junctional rhythm has the same heart rate as sinus rhythm?
A)Junctional bradycardia
B)Junctional rhythm
C)Accelerated junctional rhythm
D)Junctional tachycardia
A)Junctional bradycardia
B)Junctional rhythm
C)Accelerated junctional rhythm
D)Junctional tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Junctional tachycardia has a heart rate of
A)40-60.
B)60-100.
C)Less than 40.
D)Greater than 100.
A)40-60.
B)60-100.
C)Less than 40.
D)Greater than 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Junctional tachycardia is associated with which medication toxicity?
A)Quinidine
B)Digitalis
C)Atropine
D)Oxygen
A)Quinidine
B)Digitalis
C)Atropine
D)Oxygen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In Figure 9,the P waves are 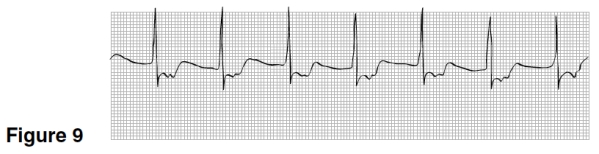
A)Upright,rounded,preceding the QRS.
B)Inverted preceding the QRS.
C)Not visible.
D)Inverted following the QRS.

A)Upright,rounded,preceding the QRS.
B)Inverted preceding the QRS.
C)Not visible.
D)Inverted following the QRS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The rhythm in Figure 9 originated 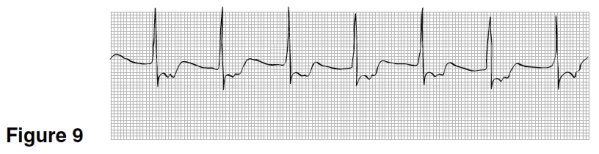
A)In the sinus node.
B)High up in the AV junction.
C)In the atrium.
D)Low down in the AV junction.

A)In the sinus node.
B)High up in the AV junction.
C)In the atrium.
D)Low down in the AV junction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In high junctional rhythms,the P wave is
A)Upright,rounded,preceding the QRS.
B)Inverted following the QRS.
C)Inverted preceding the QRS.
D)Hidden inside the QRS.
A)Upright,rounded,preceding the QRS.
B)Inverted following the QRS.
C)Inverted preceding the QRS.
D)Hidden inside the QRS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The AV node is located in the
A)Left atrium.
B)Right atrium.
C)Right ventricle.
D)Left ventricle.
A)Left atrium.
B)Right atrium.
C)Right ventricle.
D)Left ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Accelerated junctional rhythm has a heart rate of
A)Less than 40.
B)60-100.
C)40-100.
D)Greater than 100.
A)Less than 40.
B)60-100.
C)40-100.
D)Greater than 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In Figure 8,the rhythm is 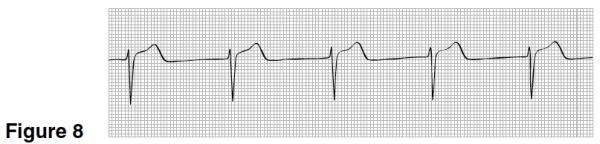
A)Sinus rhythm.
B)Junctional rhythm.
C)Atrial fibrillation.
D)Atrial tachycardia.

A)Sinus rhythm.
B)Junctional rhythm.
C)Atrial fibrillation.
D)Atrial tachycardia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The rhythm in Figure 9 is 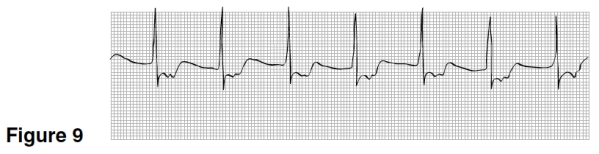
A)Sinus rhythm.
B)Accelerated juctional rhythm.
C)Atrial fibrillation.
D)Junctional bradycardia.

A)Sinus rhythm.
B)Accelerated juctional rhythm.
C)Atrial fibrillation.
D)Junctional bradycardia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A premature beat arising from the AV junction is called a
A)PAC.
B)Junctional escape beat.
C)PJC.
D)PVC.
A)PAC.
B)Junctional escape beat.
C)PJC.
D)PVC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Junctional bradycardia has a heart rate of
A)Less than 40.
B)60-100.
C)40-100.
D)Greater than 100.
A)Less than 40.
B)60-100.
C)40-100.
D)Greater than 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Treatment for occasional PJCs is to
A)Give atropine to speed the heart rate up.
B)Give digitalis to slow the heart rate down.
C)Shock the heart out of the rhythm.
D)Treat the cause.
A)Give atropine to speed the heart rate up.
B)Give digitalis to slow the heart rate down.
C)Shock the heart out of the rhythm.
D)Treat the cause.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Junctional rhythms originate in the
A)Sinoatrial junction.
B)Atrioventricular junction.
C)Sinoventricular junction.
D)Sinus node junction.
A)Sinoatrial junction.
B)Atrioventricular junction.
C)Sinoventricular junction.
D)Sinus node junction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
PJCs are a result of
A)Escape.
B)Usurpation.
C)Sinus node failure.
D)Atrial failure.
A)Escape.
B)Usurpation.
C)Sinus node failure.
D)Atrial failure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Treatment for the rhythm in Figure 8 could include ALL BUT 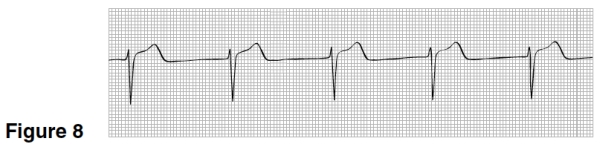
A)Atropine.
B)Oxygen.
C)Electrical shock to the heart.
D)No treatment.

A)Atropine.
B)Oxygen.
C)Electrical shock to the heart.
D)No treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
All junctional rhythms originate in the area around the AV node.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
"Retrograde" means forwards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which junctional rhythm WOULD NOT be treated with atropine?
A)Junctional bradycardia
B)Juctional rhythm
C)Accelerated junctional rhythm
D)Junctional tachycardia
A)Junctional bradycardia
B)Juctional rhythm
C)Accelerated junctional rhythm
D)Junctional tachycardia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Junctional rhythm has a heart rate the same as sinus bradycardia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Low junctional rhythms originate low down in the ventricle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Electrical shock is used to treat frequent PJCs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
"Antegrade" means backwards.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Junctional bradycardia must have a heart rate less than 20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Junctional tachycardia is usually a result of escape.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Junctional rhythms have retrograde conduction to the ventricles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Mid-junctional rhythms originate midway between the sinus node and the atria.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Junctional rhythm has no T waves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Conduction to the atria in junctional rhythms is said to be
A)Antegrade.
B)Retrograde.
C)Absent.
D)Silent.
A)Antegrade.
B)Retrograde.
C)Absent.
D)Silent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Junctional bradycardia is usually the result of usurpation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Junctional tachycardia has a heart rate greater than 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Treatment for junctional tachycardia might include withholding digitalis administration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In low junctional rhythms,the P wave is
A)Upright,rounded,preceding the QRS.
B)Inverted following the QRS.
C)Inverted preceding the QRS.
D)Hidden inside the QRS.
A)Upright,rounded,preceding the QRS.
B)Inverted following the QRS.
C)Inverted preceding the QRS.
D)Hidden inside the QRS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In mid-junctional rhythms,the P wave is
A)Upright,rounded,preceding the QRS.
B)Inverted following the QRS.
C)Inverted preceding the QRS.
D)Hidden inside the QRS.
A)Upright,rounded,preceding the QRS.
B)Inverted following the QRS.
C)Inverted preceding the QRS.
D)Hidden inside the QRS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
SVT and junctional tachycardia are similar in that
A)Both have inverted P waves.
B)Both can have hidden P waves.
C)Both have heart rates less than 40.
D)Both require electrical shock to the heart.
A)Both have inverted P waves.
B)Both can have hidden P waves.
C)Both have heart rates less than 40.
D)Both require electrical shock to the heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
All junctional rhythms are life-threatening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Junctional tachycardia has a heart rate _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Conduction to the atria is said to be _____ in junctional rhythms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
PJCs are _____beats from AV junction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
P waves hidden inside the QRS are a hallmark of junctional rhythms originating _____ in the AV junction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Junctional tachycardia is best called SVT if there are no _____ P waves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A P wave that is upside down is called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Junctional rhythm has a heart rate _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Atropine should be given for junctional bradycardia if the patient is _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



