Deck 6: Series-Parallel Circuits
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/73
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Series-Parallel Circuits
1
A voltmeter, when connected across a component, can be viewed as being a resistor in series with that component.
False
2
Thevinizing a circuit creates an equivalent series circuit.
True
3
No problems could occur if a 10 V source and a 20 V source were connected in parallel.
False
4
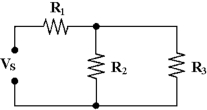
In Figure 6 -1, R2 is connected in .
A)series with R1
B)parallel with R3
C)parallel with R1
D)series with R3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5

R1 is in series with the series combination R2 and R3 in Figure 6 -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A loaded voltage divider is a series -parallel circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The superposition theorem applies only to electronic or electrical circuits with two or more sources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

In Figure 6 -1, R1 is connected in .
A)series with R3
B)series with R2
C)parallel with R3
D)parallel with R2
E)none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A series -parallel circuit consists of resistors in both series and parallel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10

R1 is in series with the parallel combination R2 and R3 in Figure 6 -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Two or more resistors connected in series form a circuit known as a voltage divider.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

R1 is in series with R3 in Figure 6 -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If two resistors are in parallel, they carry the same current.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A bridge circuit's resistances must all be of the same value to be in a balanced condition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Maximum power is achieved when the load resistance is approximately two times the source resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If two resistors are in parallel, they drop the same voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

R2 is in parallel with R3 in Figure 6 -1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18

If R3 opens in Figure 6 -1, VR1 .
A)remains the same
B)decreases to zero
C)decreases
D)increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The voltage across any open in a series -parallel circuit will be the source voltage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20

If Vs = 20 V, R1 = 10 kΩ, R2 = 50 kΩ and R3 = 15 kΩ in Figure 6 -1, PR2 equals .
A)8.63 mW
B)18.6 mW
C)2.30 mW
D)7.64 mW

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21

If R1 = 10 kΩ, R2 = 15 kΩ and R3 = 50 kΩ in Figure 6 -1, RT equals .
A)11.5 kΩ
B)10 kΩ
C)9.5 kΩ
D)21.5 kΩ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
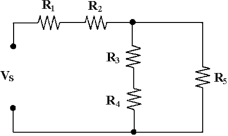
If every resistor in Figure 6 -2 equals 2.2 kΩ, what is the value of RT?
A)4.4 kΩ
B)5.5 kΩ
C)5.87 kΩ
D)2.2 kΩ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23

If R4 shorts in Figure 6 -2, VR5 .
A)remains the same
B)decreases
C)decreases to zero
D)increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
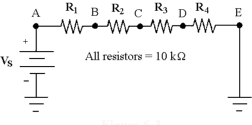
What is the resistance between points B and E in Figure 6 -3?
A)40 kΩ
B)10 kΩ
C)30 kΩ
D)20 kΩ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25

If Vs = 15 V and every resistor equals 2.2 kΩ in Figure 6 -2, what is the value of IR4?
A)2.55 mA
B)5.11 mA
C)0.42 mA
D)0.85 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

If Vs = 12 V in Figure 6 -3, what is the value of VEB if R3 shorts?
A)8 V
B)-3 V
C)-8 V
D)6 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27

In Figure 6 -2, R3 and R4 are connected in .
A)parallel with each other
B)series with R2
C)series with each other and in parallel with R5
D)series with R5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28

If all resistors equal 4.7 kΩ and Vs equals 20 V in Figure 6 -2, what is the value of IR3?
A)12.5 mA
B)1.06 mA
C)0.53 mA
D)11.99 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

If R1 shorts in Figure 6 -2, VR4 .
A)remains the same
B)equals VR2
C)decreases
D)increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30

If R2 opens in Figure 6 -2, VR3 .
A)decreases
B)causes the fuse to blow
C)remains the same
D)increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31

In Figure 6 -2, R3 and R4 are connected in .
A)parallel with R1 and R2
B)series with each other and R5
C)series with each other
D)series with each other and R1 and R2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32

If R1 = 50 kΩ, R2 = 10 kΩ, R3 = 10 kΩ, R4 = 50 kΩ and R5 = 10 kΩ in Figure 6 -2, what is the value of RT?
A)85.7 kΩ
B)8.57 kΩ
C)68.6 kΩ
D)130 kΩ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33

In Figure 6 -2 if R1 = 10 kΩ, R2 = 4.7 kΩ, R3 = 4.7 kΩ, R4 = 10 kΩ and R5 = 4.7 kΩ, RT = ?
A)6.1 kΩ
B)24.7 kΩ
C)18.3 kΩ
D)0 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34

If R3 shorts in Figure 6 -2, VR5 . Figure 6 -2
A)decreases
B)remains the same
C)increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

If Vs = 22 V in Figure 6 -3, what is the is the value of VDB?
A)-22 V
B)-11 V
C)11 V
D)5.5 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

If VR4 = 10 V in Figure 6 -3, what is the value of VAD?
A)30 V
B)10 V
C)40 V
D)20 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

If R1 = 4.7 kΩ, R2 = 3.3 kΩ, R3 = 1 kΩ and Vs = 50 V in Figure 6 -1, IT equals .
A)12.1 mA
B)75.7 mA
C)9.15 mA
D)8.8 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38

If Vs = 25 V, R1 = 10 kΩ, R2 = 15 kΩ and R3 = 50 kΩ in Figure 6 -1, IT equals .
A)1.58 mA
B)1.16 mA
C)2.5 mA
D)2.17 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

If all of the resistors in Figure 6 -2 are 4.7 kΩ, what is the value of RT?
A)4.7 kΩ
B)9.4 kΩ
C)12.5 kΩ
D)18.8 kΩ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

If R1 = 4.7 kΩ, R2 = 3.3 kΩ and R3 = 1 kΩ in Figure , the total resistance equals .
A)5700 Ω
B)660 Ω
C)5467 Ω
D)4125 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41

If the current is 1.2 mA in Figure 6 -3, what is the value of PT?
A)57.6 mW
B)5.76 mW
C)576 mW
D)0.576 mW

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The parallel combination of a 330 Ω resistor and a 470 Ω resistor is connected in series with the parallel combination of four 1 kΩ resistors. If a 100 V source is connected across the circuit, then which resistor carries the most current?
A)1 kΩ
B)470 Ω
C)330 Ω
A)1 kΩ
B)470 Ω
C)330 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If a voltage divider consists of two 10 kΩ resistors, which one of these load resistors will change the output voltage the most?
A)10 kΩ
B)1 MΩ
C)20 kΩ
D)100 kΩ
A)10 kΩ
B)1 MΩ
C)20 kΩ
D)100 kΩ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44

What is the resistance between points A and D in Figure 6 -3?
A)20 kΩ
B)10 kΩ
C)30 kΩ
D)40 kΩ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a two -source circuit, one source alone produces 10 mA through a branch. If the other source alone produces 8 mA in the opposite direction through the same branch, what is the total current through the branch?
A)18 mA
B)2 mA
C)10 mA
D)8 mA
A)18 mA
B)2 mA
C)10 mA
D)8 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In solving series -parallel circuits, the last and easiest to solve for is:
A)RT.
B)PT.
C)ET.
D)IT.
A)RT.
B)PT.
C)ET.
D)IT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Power in a series -parallel resistor circuit is dissipated as:
A)heat.
B)resistance change.
C)current flow.
D)voltage loss.
A)heat.
B)resistance change.
C)current flow.
D)voltage loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If four parallel 10 kΩ resistors are connected in series with a single 20 kΩ resistor and one of the parallel resistors opens, how does the voltage across the other parallel resistors change?
A)It remains the same.
B)It decreases.
C)It increases.
A)It remains the same.
B)It decreases.
C)It increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The parallel combination of a 330 Ω resistor and a 470 Ω resistor is connected in series with the parallel combination of four 1 kΩ resistors. If a 100 V source is connected across the circuit, then which resistor drops the most voltage?
A)330 Ω
B)470 Ω
C)1 kΩ
A)330 Ω
B)470 Ω
C)1 kΩ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50

If a fifth 10 kΩ resistor is connected in series in Figure 6 -3, how does VR4 change?
A)VR4 remains the same.
B)VR4 increases.
C)VR4 decreases.
D)VR4 increases to 10 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51

If VR3 = 17 V in Figure 6 -3, what is the value of P1?
A)17 mW
B)2.89 W
C)28.9 mW
D)1.7 mW

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In solving series -parallel circuits using Ohm's law, first solve for:
A)ET.
B)RT.
C)IT.
D)any of these, it doesn't matter.
A)ET.
B)RT.
C)IT.
D)any of these, it doesn't matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If four parallel 10 kΩ resistors are in series with a single 20 kΩ resistor and one of the parallel resistors shorts, the voltage across the other parallel resistors .
A)decreases
B)increases
C)remains the same
A)decreases
B)increases
C)remains the same

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54

If a 10 kΩ resistor is placed in parallel with R4 in Figure 6 -3, how will VR4 change?
A)VR4 will decrease.
B)VR4 will change to 4 volts.
C)VR4 will increase.
D)VR4 will remain the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55

If VR1 = 15 V in Figure 6 -3, what is the value of VBD?
A)-60 V
B)30 V
C)-30 V
D)60 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56

If Vs = 40 V and R3 opens in Figure 6 -3, what is the value of VR3?
A)40 V
B)20 V
C)0 V
D)30 V
E)10 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57

If Vs = 50 V in Figure 6 -3, what is the value of VCA?
A)-25 V
B)5 V
C)25 V
D)-5 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In solving series -parallel circuits using Ohm's law, first solve for:
A)the parallel current.
B)the series resistance.
C)the series current.
D)the parallel resistance.
A)the parallel current.
B)the series resistance.
C)the series current.
D)the parallel resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Two series 1 kΩ resistors are connected in parallel with a 2.2 kΩ resistor. If the voltage across one of the 1 kΩ resistors is 6 V, what is the voltage across the 2.2 kΩ resistor?
A)3 V
B)13.2 V
C)12 V
D)6 V
A)3 V
B)13.2 V
C)12 V
D)6 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60

If the current is 12 mA in Figure 6 -3, what is the value of VEB?
A)-360 V
B)240 V
C)360 V
D)-240 V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
One Ohm's law formula PT = P1 + P2 + etc. can be used to solve for total power in:
A)series -parallel circuits.
B)parallel circuits.
C)series circuits.
D)all of these.
A)series -parallel circuits.
B)parallel circuits.
C)series circuits.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Thevenin's theorem provides a method for:
A)designing complex series -parallel circuits.
B)simplifying complex series -parallel circuits.
C)building complex series -parallel circuits.
D)all of these.
A)designing complex series -parallel circuits.
B)simplifying complex series -parallel circuits.
C)building complex series -parallel circuits.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
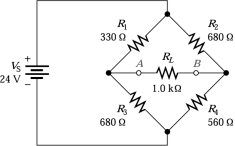
What approximate R1 resistor value would it take to balance this bridge circuit?
A)680 Ω
B)560 Ω
C)330 Ω
D)825 Ω

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the maximum power transfer theorem, maximum power is delivered to any load when the load resistance is:
A)less than one -half of the source resistance.
B)exactly equal to the source resistance.
C)larger than source resistance.
D)at least twice or more than the source resistance.
A)less than one -half of the source resistance.
B)exactly equal to the source resistance.
C)larger than source resistance.
D)at least twice or more than the source resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
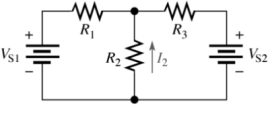
Determine the amount of current flow through R2 with the following component parameters. VS1 = 10 V, VS2 = 3 V, R1 = 2 k, R2 = 3 k, and R3 = 700
A)1.37mA
B)0 A
C)5.3 mA
D)1 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In the series portion of series -parallel circuits, the total resistance is:
A)equal to the largest resistance.
B)less than any one resistance.
C)greater than the largest resistance.
D)less than the largest resistance.
A)equal to the largest resistance.
B)less than any one resistance.
C)greater than the largest resistance.
D)less than the largest resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The difference between a balanced and an unbalanced Wheatstone bridge is measured by:
A)a galvanometer.
B)an ohmmeter.
C)an ammeter.
D)a voltmeter.
A)a galvanometer.
B)an ohmmeter.
C)an ammeter.
D)a voltmeter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The super position theorem provides a method for:
A)analyzing complex series -parallel circuits.
B)designing complex series -parallel circuits.
C)building complex series -parallel circuits.
D)all of these.
A)analyzing complex series -parallel circuits.
B)designing complex series -parallel circuits.
C)building complex series -parallel circuits.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the parallel portion of series -parallel circuits, the total resistance is:
A)less than the smallest resistance.
B)less than any one resistance.
C)equal to the smallest resistance.
D)greater than the largest resistance.
A)less than the smallest resistance.
B)less than any one resistance.
C)equal to the smallest resistance.
D)greater than the largest resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70

With circuit balanced there is:
A)Cannot be determined without detailed analysis.
B)no current through the load.
C)no current flow through the total circuit.
D)maximum current flow through the load.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71

If R1 is changed to 500 Ω, the Thevenin resistance and voltage would be:
A)595 and 807 mV.
B)595 and 3 V.
C)1 k and 807 mV.
D)1 k and 3 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72

If all of the resistors of this circuit are 5 kΩ and VS1 and VS2 are 10 V but opposing polarities, what would be the current flow through R2?
A)1.33 mA
B)13.33 mA
C)0 A
D)2.66 mA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The Wheatstone bridge circuit is widely used to measure:
A)precise resistances.
B)accurate currents.
C)exact voltages.
D)all of these.
A)precise resistances.
B)accurate currents.
C)exact voltages.
D)all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 73 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



