Deck 19: Money Supply and Money Demand
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/102
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Money Supply and Money Demand
1
If currency held by the public equals $100 billion,reserves held by banks equal $50 billion,and bank deposits equal $500 billion,then the monetary base equals:
A) $50 billion.
B) $100 billion.
C) $150 billion.
D) $600 billion.
A) $50 billion.
B) $100 billion.
C) $150 billion.
D) $600 billion.
$150 billion.
2
The banking system creates:
A) liquidity.
B) wealth.
C) reserves.
D) currency.
A) liquidity.
B) wealth.
C) reserves.
D) currency.
liquidity.
3
In a fractional-reserve banking system,banks create money when they:
A) accept deposits.
B) make loans.
C) hold reserves.
D) exchange currency for deposits.
A) accept deposits.
B) make loans.
C) hold reserves.
D) exchange currency for deposits.
make loans.
4
In a system with fractional-reserve banking:
A) all banks must hold reserves equal to a fraction of their loans.
B) no banks can make loans.
C) the banking system completely controls the size of the money supply.
D) all banks must hold reserves equal to a fraction of their deposits.
A) all banks must hold reserves equal to a fraction of their loans.
B) no banks can make loans.
C) the banking system completely controls the size of the money supply.
D) all banks must hold reserves equal to a fraction of their deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In a 100-percent-reserve banking system,if a customer deposits $100 of currency into a bank,then the money supply:
A) increases by $100.
B) decreases by $100.
C) increases by more than $100.
D) remains the same.
A) increases by $100.
B) decreases by $100.
C) increases by more than $100.
D) remains the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The monetary base consists of:
A) currency held by the public,plus reserves held by banks.
B) all outstanding currency,plus reserves held by banks.
C) all outstanding currency,plus demand deposits.
D) all bank reserves.
A) currency held by the public,plus reserves held by banks.
B) all outstanding currency,plus reserves held by banks.
C) all outstanding currency,plus demand deposits.
D) all bank reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Financial intermediation is the process of:
A) settling disputes between borrowers and lenders.
B) advising corporations on whether to expand using debt or equity.
C) transferring funds from savers to borrowers.
D) converting from a barter economy to a money economy.
A) settling disputes between borrowers and lenders.
B) advising corporations on whether to expand using debt or equity.
C) transferring funds from savers to borrowers.
D) converting from a barter economy to a money economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In a 100-percent banking system,chartered banks:
A) can increase the money supply.
B) can decrease the money supply.
C) can either increase or decrease the money supply.
D) cannot affect the money supply.
A) can increase the money supply.
B) can decrease the money supply.
C) can either increase or decrease the money supply.
D) cannot affect the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If the proceeds of all loans are deposited somewhere in the banking system and if rr denotes the reserve-deposit ratio,then the total money supply is:
A) reserves divided by rr.
B) 1/rr.
C) reserves times rr.
D) reserves divided by (1 - rr).
A) reserves divided by rr.
B) 1/rr.
C) reserves times rr.
D) reserves divided by (1 - rr).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Bank reserves equal:
A) gold kept in bank vaults.
B) gold kept at the central bank.
C) currency plus deposits.
D) deposits that banks have received but have not lent out.
A) gold kept in bank vaults.
B) gold kept at the central bank.
C) currency plus deposits.
D) deposits that banks have received but have not lent out.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In a system with 100-percent-reserve banking:
A) all banks must hold reserves equal to 100 percent of their loans.
B) no banks can make loans.
C) the banking system completely controls the size of the money supply.
D) no banks can accept deposits.
A) all banks must hold reserves equal to 100 percent of their loans.
B) no banks can make loans.
C) the banking system completely controls the size of the money supply.
D) no banks can accept deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The difference between the chartered banks and other financial intermediaries is that only banks have the legal authority to:
A) transfer funds from savers to borrowers.
B) pay interest on debt obligations.
C) manage portfolios of assets.
D) create assets that are part of the money supply (as usually measured).
A) transfer funds from savers to borrowers.
B) pay interest on debt obligations.
C) manage portfolios of assets.
D) create assets that are part of the money supply (as usually measured).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In Canada,the money supply is determined:
A) only by the Bank of Canada.
B) only by the behaviour of individuals who hold money and of banks in which money is held.
C) jointly by the Bank of Canada and by the behaviour of individuals who hold money and of banks in which money is held.
D) according to a constant-growth-rate rule.
A) only by the Bank of Canada.
B) only by the behaviour of individuals who hold money and of banks in which money is held.
C) jointly by the Bank of Canada and by the behaviour of individuals who hold money and of banks in which money is held.
D) according to a constant-growth-rate rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Liabilities of chartered banks include:
A) reserves.
B) currency in the hands of the public.
C) loans to customers.
D) deposits of the bank customers.
A) reserves.
B) currency in the hands of the public.
C) loans to customers.
D) deposits of the bank customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Assets of chartered banks include:
A) money market mutual funds.
B) currency in the hands of the public.
C) loans to customers.
D) deposits of bank customers.
A) money market mutual funds.
B) currency in the hands of the public.
C) loans to customers.
D) deposits of bank customers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Banks create money in:
A) a 100-percent-reserve banking system but not in a fractional-reserve banking system.
B) a fractional-reserve banking system but not in a 100-percent-reserve banking system.
C) both a 100-percent-reserve banking system and a fractional-reserve banking system.
D) neither a 100-percent-reserve banking system nor a fractional-reserve banking system.
A) a 100-percent-reserve banking system but not in a fractional-reserve banking system.
B) a fractional-reserve banking system but not in a 100-percent-reserve banking system.
C) both a 100-percent-reserve banking system and a fractional-reserve banking system.
D) neither a 100-percent-reserve banking system nor a fractional-reserve banking system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The basic definition of the money supply involves:
A) currency plus reserves.
B) currency plus the monetary base.
C) currency plus deposits.
D) the monetary base plus deposits.
A) currency plus reserves.
B) currency plus the monetary base.
C) currency plus deposits.
D) the monetary base plus deposits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The size of the monetary base is determined by:
A) the Bank of Canada.
B) the Bank of Canada and the chartered banks.
C) preferences of households about the form of money they wish to hold.
D) business policies of banks and the laws regulating banks.
A) the Bank of Canada.
B) the Bank of Canada and the chartered banks.
C) preferences of households about the form of money they wish to hold.
D) business policies of banks and the laws regulating banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In Canada,chartered bank reserves consist of:
A) currency and the deposits of bank customers.
B) vault cash and deposits at the Bank of Canada.
C) gold deposits at the Bank of Canada.
D) the money supply.
A) currency and the deposits of bank customers.
B) vault cash and deposits at the Bank of Canada.
C) gold deposits at the Bank of Canada.
D) the money supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In a fractional-reserve banking system,banks create money because:
A) each dollar of reserves generates many dollars of deposits.
B) banks have the legal authority to issue new currency.
C) funds are transferred from households wishing to save to firms wishing to borrow.
D) the wealth of the economy expands when borrowers undertake new debt obligations.
A) each dollar of reserves generates many dollars of deposits.
B) banks have the legal authority to issue new currency.
C) funds are transferred from households wishing to save to firms wishing to borrow.
D) the wealth of the economy expands when borrowers undertake new debt obligations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When the Bank of Canada conducts an open-market purchase,it buys bonds from the:
A) public.
B) Finance Canada.
C) Revenue Canada.
D) International Monetary Fund.
A) public.
B) Finance Canada.
C) Revenue Canada.
D) International Monetary Fund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the monetary base equals $400 billion and the money multiplier equals 2,then the money supply equals:
A) $200 billion.
B) $400 billion.
C) $800 billion.
D) $1,000 billion.
A) $200 billion.
B) $400 billion.
C) $800 billion.
D) $1,000 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the currency-deposit ratio equals 0.5 and the reserve-deposit ratio equals 0.1,then the money multiplier equals:
A) 0.6.
B) 1.67.
C) 2.0.
D) 2.5.
A) 0.6.
B) 1.67.
C) 2.0.
D) 2.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If currency held by the public equals $100 billion,reserves held by banks equal $50 billion,and bank deposits equal $500 billion,then the money supply equals:
A) $100 billion.
B) $150 billion.
C) $600 billion.
D) $650 billion.
A) $100 billion.
B) $150 billion.
C) $600 billion.
D) $650 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The ratio of the money supply to the monetary base is called the:
A) currency-deposit ratio.
B) reserve-deposit ratio.
C) high-powered money.
D) money multiplier.
A) currency-deposit ratio.
B) reserve-deposit ratio.
C) high-powered money.
D) money multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the ratio of reserves to deposits (rr)increases,while the ratio of currency to deposits (cr)is constant and the monetary base (B)is constant,then:
A) it cannot be determined whether the money supply increases or decreases.
B) the money supply increases.
C) the money supply decreases.
D) the money supply does not change.
A) it cannot be determined whether the money supply increases or decreases.
B) the money supply increases.
C) the money supply decreases.
D) the money supply does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
When the Bank of Canada makes an open-market sale of government bonds,it:
A) increases the money multiplier (m).
B) increases the currency-deposit ratio (cr).
C) increases the monetary base (B).
D) decreases the monetary base (B).
A) increases the money multiplier (m).
B) increases the currency-deposit ratio (cr).
C) increases the monetary base (B).
D) decreases the monetary base (B).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If you hear in the news that the Bank of Canada conducted open-market purchases of government bonds,then you should expect ______ to increase.
A) reserve requirements
B) the overnight lending rate
C) the money supply
D) the reserve-deposit ratio
A) reserve requirements
B) the overnight lending rate
C) the money supply
D) the reserve-deposit ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The money supply will decrease if the:
A) monetary base increases.
B) currency-deposit ratio increases.
C) discount rate decreases.
D) reserve-deposit ratio decreases.
A) monetary base increases.
B) currency-deposit ratio increases.
C) discount rate decreases.
D) reserve-deposit ratio decreases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
To increase the money supply,the Bank of Canada can:
A) conduct open-market sales.
B) switch government deposits away from the Bank of Canada.
C) raise the required reserve ratio.
D) lower the required reserve ratio.
A) conduct open-market sales.
B) switch government deposits away from the Bank of Canada.
C) raise the required reserve ratio.
D) lower the required reserve ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the monetary base is denoted by B,rr is the ratio of reserves to deposits,and cr is the ratio of currency to deposits,then the money supply is equal to ______ divided by ______ multiplied by B.
A) (rr + 1); (rr + cr)
B) (cr + 1); (cr + rr)
C) (rr + cr); (rr + 1)
D) (rr + cr); (cr + 1)
A) (rr + 1); (rr + cr)
B) (cr + 1); (cr + rr)
C) (rr + cr); (rr + 1)
D) (rr + cr); (cr + 1)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
To increase the monetary base,the Bank of Canada can:
A) conduct open-market purchases.
B) conduct open-market sales.
C) raise the required reserve ratio.
D) lower the required reserve ratio.
A) conduct open-market purchases.
B) conduct open-market sales.
C) raise the required reserve ratio.
D) lower the required reserve ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the reserve-deposit ratio is less than one,and the monetary base increases by $1 million,then the money supply will:
A) increase by $1 million.
B) decrease by $1 million.
C) increase by more than $1 million.
D) decrease by more than $1 million.
A) increase by $1 million.
B) decrease by $1 million.
C) increase by more than $1 million.
D) decrease by more than $1 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The most frequently used tool of monetary policy is:
A) open-market operations.
B) changes in the overnight lending rate.
C) changes in reserve requirements.
D) changes in the money multiplier.
A) open-market operations.
B) changes in the overnight lending rate.
C) changes in reserve requirements.
D) changes in the money multiplier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The reserve-deposit ratio is determined by:
A) the Bank of Canada.
B) business policies of chartered banks and the laws regulating banks.
C) preferences of households about the form of money they wish to hold.
D) the Canadian Deposit Insurance Corporation (CDIC).
A) the Bank of Canada.
B) business policies of chartered banks and the laws regulating banks.
C) preferences of households about the form of money they wish to hold.
D) the Canadian Deposit Insurance Corporation (CDIC).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
High-powered money is another name for:
A) currency.
B) demand deposits.
C) the monetary base.
D) M3.
A) currency.
B) demand deposits.
C) the monetary base.
D) M3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The currency-deposit ratio is determined by:
A) the Bank of Canada.
B) business policies of chartered banks and the laws regulating banks.
C) preferences of households about the form of money they wish to hold.
D) the Canadian Deposit Insurance Corporation (CDIC).
A) the Bank of Canada.
B) business policies of chartered banks and the laws regulating banks.
C) preferences of households about the form of money they wish to hold.
D) the Canadian Deposit Insurance Corporation (CDIC).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The money supply will increase if the:
A) currency-deposit ratio increases.
B) reserve-deposit ratio increases.
C) monetary base increases.
D) discount rate increases.
A) currency-deposit ratio increases.
B) reserve-deposit ratio increases.
C) monetary base increases.
D) discount rate increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The preferences of households determine the:
A) reserve-deposit ratio.
B) currency-deposit ratio.
C) size of the monetary base.
D) loan-deposit ratio.
A) reserve-deposit ratio.
B) currency-deposit ratio.
C) size of the monetary base.
D) loan-deposit ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If the ratio of currency to deposits (cr)increases,while the ratio of reserves to deposits (rr)is constant and the monetary base (B)is constant,then:
A) it cannot be determined whether the money supply increases or decreases.
B) the money supply increases.
C) the money supply decreases.
D) the money supply does not change.
A) it cannot be determined whether the money supply increases or decreases.
B) the money supply increases.
C) the money supply decreases.
D) the money supply does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The minimum amount of owner's equity in a bank mandated by regulators is called a ______ requirement.
A) reserve
B) margin
C) liquidity
D) capital
A) reserve
B) margin
C) liquidity
D) capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
If the Bank of Canada wishes to increase the money supply,it should:
A) switch government deposits to chartered banks.
B) raise the Bank rate.
C) sell government bonds.
D) decrease the monetary base.
A) switch government deposits to chartered banks.
B) raise the Bank rate.
C) sell government bonds.
D) decrease the monetary base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If many banks fail,this is likely to:
A) cause surviving banks to lower their ratios of reserves to deposits.
B) cause surviving banks to raise their ratios of reserves to deposits.
C) have no effect on the ratio of reserves to deposits in surviving banks.
D) cause surviving banks to hold less currency.
A) cause surviving banks to lower their ratios of reserves to deposits.
B) cause surviving banks to raise their ratios of reserves to deposits.
C) have no effect on the ratio of reserves to deposits in surviving banks.
D) cause surviving banks to hold less currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A bank balance sheet consists of only the following items: Deposits

What is the value of bank capital?
A) - $1,000
B) + $500
C) + $1,000
D) + $1,500

What is the value of bank capital?
A) - $1,000
B) + $500
C) + $1,000
D) + $1,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Switching government deposits from the Bank of Canada to chartered banks I: increases the money supply.II: increases the federal budget deficit.
A) I is true; II is not.
B) II is true; I is not.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Neither I nor II is true.
A) I is true; II is not.
B) II is true; I is not.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Neither I nor II is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The use of borrowed funds to supplement existing funds for purposes of investment is called:
A) arbitrage.
B) leverage.
C) convergence.
D) intermediation.
A) arbitrage.
B) leverage.
C) convergence.
D) intermediation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If many banks fail,this is likely to:
A) increase the ratio of currency to deposits.
B) decrease the ratio of currency to deposits.
C) have no effect on the ratio of currency to deposits.
D) decrease the amount of currency in circulation,if the Bank of Canada takes no action.
A) increase the ratio of currency to deposits.
B) decrease the ratio of currency to deposits.
C) have no effect on the ratio of currency to deposits.
D) decrease the amount of currency in circulation,if the Bank of Canada takes no action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the following to answer question :
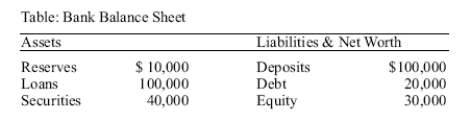
(Table: Bank Balance Sheet)Based on the table,what is the leverage ratio at the bank?
A) 3
B) 4.67
C) 5
D) 10

(Table: Bank Balance Sheet)Based on the table,what is the leverage ratio at the bank?
A) 3
B) 4.67
C) 5
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Between August 1929 and March 1933,the money supply in the United States fell 28 percent.At that time the monetary base ______ and the currency-deposit and reserve-deposit ratios both ______.
A) fell; fell
B) fell; rose
C) rose; fell
D) rose; rose
A) fell; fell
B) fell; rose
C) rose; fell
D) rose; rose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The value of banks owners' equity is called bank:
A) deposits.
B) reserves.
C) capital.
D) liquidity.
A) deposits.
B) reserves.
C) capital.
D) liquidity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following to answer questions :
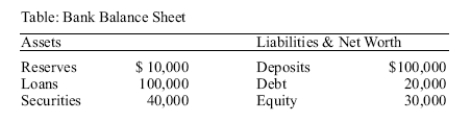
(Table: Bank Balance Sheet)Based on the table,what is the reserve ratio at the bank?
A) 3 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 10 percent
D) 15 percent

(Table: Bank Balance Sheet)Based on the table,what is the reserve ratio at the bank?
A) 3 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 10 percent
D) 15 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Deposit insurance in Canada I: insures all deposits in chartered banks up to a maximum of $100,000.II: would generate incentives for more desirable outcomes if it involved a small deductible that is not covered.
A) I is true; II is not.
B) II is true; I is not.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Neither I nor II is true.
A) I is true; II is not.
B) II is true; I is not.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Neither I nor II is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In 2008 and 2009,the U.S.Treasury put public funds in some banks in an attempt to restore bank lending to more normal levels.This infusion of funds initially increased what item on the banks' balance sheets?
A) capital
B) loans
C) securities
D) deposits
A) capital
B) loans
C) securities
D) deposits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A shortage of bank capital in 2008 and 2009 led to:
A) decreased money demand.
B) decreased bank lending.
C) increased interest rates.
D) increased reserve requirements.
A) decreased money demand.
B) decreased bank lending.
C) increased interest rates.
D) increased reserve requirements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the following to answer questions :

(Table: Bank Balance Sheet)Based on the table,owners' equity will fall to zero if loan defaults reduce the value of total assets by ______ percent.
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 40

(Table: Bank Balance Sheet)Based on the table,owners' equity will fall to zero if loan defaults reduce the value of total assets by ______ percent.
A) 10
B) 20
C) 30
D) 40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Deposit insurance I: makes any failures of financial intermediaries that occur less costly.II: makes failures of financial intermediaries more likely.
A) I is true; II is not.
B) II is true; I is not.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Neither I nor II is true.
A) I is true; II is not.
B) II is true; I is not.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Neither I nor II is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An open-market purchase of government bonds I: affects the money supply in the same direction as does following a fixed-exchange rate policy when the domestic currency is held at a value below its equilibrium value;
II: affects the money supply in the same direction as does a switch in government deposits to the central bank.
A) I is true; II is not.
B) II is true; I is not.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Neither I nor II is true.
II: affects the money supply in the same direction as does a switch in government deposits to the central bank.
A) I is true; II is not.
B) II is true; I is not.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Neither I nor II is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The Monetary Conditions Index I: is a weighted average of the overnight lending rate and the exchange rate.II: is an index that indicates contractionary monetary policy when it increases.
A) I is true; II is not.
B) II is true; I is not.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Neither I nor II is true.
A) I is true; II is not.
B) II is true; I is not.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Neither I nor II is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The amount of capital that banks are required to hold depends on the:
A) amount of deposits held at a bank.
B) riskiness of the bank's assets.
C) reserve requirements set by the Bank of Canada.
D) level of deposit insurance coverage.
A) amount of deposits held at a bank.
B) riskiness of the bank's assets.
C) reserve requirements set by the Bank of Canada.
D) level of deposit insurance coverage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The interest rate charged on loans by the Bank of Canada to chartered banks is called the:
A) Federal Funds rate.
B) Prime rate.
C) Bank rate.
D) Treasury Bill rate.
A) Federal Funds rate.
B) Prime rate.
C) Bank rate.
D) Treasury Bill rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the Baumol-Tobin model of the transactions demand for money,the number of trips to the bank will:
A) increase as the interest rate decreases.
B) increase as the interest rate increases.
C) decrease as expenditure increases.
D) increase as wealth increases.
A) increase as the interest rate decreases.
B) increase as the interest rate increases.
C) decrease as expenditure increases.
D) increase as wealth increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Portfolio theories of the demand for money are based on money's function as a ________,while transaction theories of the demand for money are based on money's function as a ______.
A) medium of exchange; store of value
B) medium of exchange; unit of account
C) store of value; medium of exchange
D) store of value; unit of account
A) medium of exchange; store of value
B) medium of exchange; unit of account
C) store of value; medium of exchange
D) store of value; unit of account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Portfolio theories of money demand emphasize the role of money as a:
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) standard for making deferred payments.
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) standard for making deferred payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
According to the Baumol-Tobin model,the demand for money will increase if:
A) automatic teller machines become more readily available.
B) Internet banking becomes widely available.
C) bank service charges increase.
D) real wages decrease.
A) automatic teller machines become more readily available.
B) Internet banking becomes widely available.
C) bank service charges increase.
D) real wages decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The demand for money as a medium of exchange is best explained by ______ theories of money demand,while the demand for money as a store of value is best explained by ______ theories of money demand.
A) rational expectations; quantity
B) quantity; rational expectations
C) portfolio; transaction
D) transaction; portfolio
A) rational expectations; quantity
B) quantity; rational expectations
C) portfolio; transaction
D) transaction; portfolio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
According to the Baumol-Tobin model,an increase in the fixed costs of going to the bank will ______ the demand for money.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) not change
D) possibly increase or decrease
A) increase
B) decrease
C) not change
D) possibly increase or decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In the portfolio theory of money demand,all of the following economic factors play a direct role except:
A) the expected real return on stock.
B) the expected inflation rate.
C) the unemployment rate.
D) wealth.
A) the expected real return on stock.
B) the expected inflation rate.
C) the unemployment rate.
D) wealth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
According to portfolio theories of money demand,increases in wealth ______ the demand for money,and increases in the expected inflation rate ______ the demand for money.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Most empirical studies of money demand find that:
A) the income elasticity of money demand is greater than one-half,and the interest elasticity of money demand is less than one-half.
B) the income elasticity of money demand is less than one-half,and the interest elasticity of money demand is greater than one-half.
C) both the income elasticity of money demand and the interest elasticity of money demand are less than one-half.
D) both the income elasticity of money demand and the interest elasticity of money demand are greater than one-half.
A) the income elasticity of money demand is greater than one-half,and the interest elasticity of money demand is less than one-half.
B) the income elasticity of money demand is less than one-half,and the interest elasticity of money demand is greater than one-half.
C) both the income elasticity of money demand and the interest elasticity of money demand are less than one-half.
D) both the income elasticity of money demand and the interest elasticity of money demand are greater than one-half.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
According to the Baumol-Tobin model,an increase in the interest rate ______ the demand for money,and an increase in expenditures ______ the demand for money.
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases
A) increases; increases
B) increases; decreases
C) decreases; increases
D) decreases; decreases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In the Baumol-Tobin model,the benefit of holding money is:
A) the interest forgone.
B) convenience.
C) the lower risk and higher return compared to other assets.
D) the interest elasticity of money demand.
A) the interest forgone.
B) convenience.
C) the lower risk and higher return compared to other assets.
D) the interest elasticity of money demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In the Baumol-Tobin model of the transactions demand for money,the average money holding will:
A) increase as the interest rate increases.
B) increase as wealth increases.
C) decrease as transaction costs per trip to the bank increase.
D) increase as expenditure increases.
A) increase as the interest rate increases.
B) increase as wealth increases.
C) decrease as transaction costs per trip to the bank increase.
D) increase as expenditure increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In the Baumol-Tobin model,if the nominal interest rate is 0.05,the cost of trips to the bank is $12,and expenditures equals $48,000,then average money holdings equal:
A) $980.
B) $2,400.
C) $3,394.
D) $4,000.
A) $980.
B) $2,400.
C) $3,394.
D) $4,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The quantity theory of money assumes that the demand for real money balances:
A) depends on both the interest rate and income.
B) depends only on the interest rate.
C) is proportional to income.
D) is proportional to the interest rate.
A) depends on both the interest rate and income.
B) depends only on the interest rate.
C) is proportional to income.
D) is proportional to the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Portfolio theories of money demand emphasize the ______ of money compared to other assets.
A) combination of risk and return
B) liquidity
C) optimal quantity
D) demand and supply
A) combination of risk and return
B) liquidity
C) optimal quantity
D) demand and supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Transaction theories of money demand emphasize the role of money as a:
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) standard for making deferred payments.
A) medium of exchange.
B) store of value.
C) unit of account.
D) standard for making deferred payments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The only tax that those in the underground economy probably cannot evade is the:
A) personal income tax.
B) sales tax.
C) inflation tax.
D) corporate profit tax.
A) personal income tax.
B) sales tax.
C) inflation tax.
D) corporate profit tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The notion of a "dominated asset" implies that the portfolio theory of money demand should not be used to explain the demand for:
A) M1.
B) M2.
C) either M1 or M2.
D) M3.
A) M1.
B) M2.
C) either M1 or M2.
D) M3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In the Baumol-Tobin model,the optimal number of trips to the bank is determined by minimizing the total costs of holding money that are the:
A) forgone interest.
B) costs of trips to the bank.
C) forgone interest plus the costs of trips to the bank.
D) costs of trips to the bank minus the forgone interest.
A) forgone interest.
B) costs of trips to the bank.
C) forgone interest plus the costs of trips to the bank.
D) costs of trips to the bank minus the forgone interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
According to portfolio theories of money demand,increases in the expected return on stock ______ the demand for money,and increases in the expected return on bonds ______ the demand for money.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 102 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



