Deck 7: International Trade
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: International Trade
1
Which of the following would be expected by Heckscher-Ohlin trade theory?
A)A country with abundant fertile land exporting agricultural products
B)A country with abundant capital importing manufactured goods
C)A country with abundant fertile land importing agricultural goods
D)A country with abundant labor exporting agricultural products
A)A country with abundant fertile land exporting agricultural products
B)A country with abundant capital importing manufactured goods
C)A country with abundant fertile land importing agricultural goods
D)A country with abundant labor exporting agricultural products
A
2
What is protectionism?
A)The creation of alliances to ward off threats to a country
B)Excessive worry about attacks from other countries
C)The use of conscious measures to shield domestic producers from imports
D)The use of free trade to improve the efficiency of domestic producers
A)The creation of alliances to ward off threats to a country
B)Excessive worry about attacks from other countries
C)The use of conscious measures to shield domestic producers from imports
D)The use of free trade to improve the efficiency of domestic producers
C
3
What is trade liberalization?
A)Being tolerant of exporting to other countries
B)Strengthening government oversight of imports
C)Reducing barriers to trade between countries
D)Imposing controls on the free flow of goods
A)Being tolerant of exporting to other countries
B)Strengthening government oversight of imports
C)Reducing barriers to trade between countries
D)Imposing controls on the free flow of goods
C
4
Which of the following statements about trade policy is true?
A)No country in the world currently maintains trade barriers.
B)Few countries in the world maintain trade barriers.
C)A bare majority of countries in the world maintain some trade barriers.
D)Every country in the world maintains some trade barriers.
A)No country in the world currently maintains trade barriers.
B)Few countries in the world maintain trade barriers.
C)A bare majority of countries in the world maintain some trade barriers.
D)Every country in the world maintains some trade barriers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is most likely a developed country?
A)A country with no quotas on manufactured goods
B)A country that imposes a tax on technology exports
C)A country that has trade restrictions on agricultural imports
D)A country that has high tariffs on manufactured goods
A)A country with no quotas on manufactured goods
B)A country that imposes a tax on technology exports
C)A country that has trade restrictions on agricultural imports
D)A country that has high tariffs on manufactured goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Developing countries have been surprisingly receptive to free trade since the 1980s.According to scholars,this is likely because of which other development?
A)More developing countries became democratic rather than authoritarian.
B)The United Nations mandated free trade among developing countries.
C)Developing nations began doing more trade with each other.
D)Offshoring of jobs from developed nations encouraged developing countries to embrace free trade.
A)More developing countries became democratic rather than authoritarian.
B)The United Nations mandated free trade among developing countries.
C)Developing nations began doing more trade with each other.
D)Offshoring of jobs from developed nations encouraged developing countries to embrace free trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why do countries often restrict trade?
A)Some influential interest groups may benefit from tariffs.
B)Trade restrictions are usually the best way to improve a country's overall economy.
C)Free trade hurts industries that make use of the most abundant resource in a country.
D)Trade restrictions are more important to consumers than to producers of products.
A)Some influential interest groups may benefit from tariffs.
B)Trade restrictions are usually the best way to improve a country's overall economy.
C)Free trade hurts industries that make use of the most abundant resource in a country.
D)Trade restrictions are more important to consumers than to producers of products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is a factor of production?
A)Export industries
B)Military power
C)Unskilled labor
D)Multinational firms
A)Export industries
B)Military power
C)Unskilled labor
D)Multinational firms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following describes comparative advantage?
A)A country specializing in what they do most well or least poorly
B)A country producing everything better than other countries
C)The advantage that countries that export many products have over more specialized economies
D)The ability of workers in industrialized economies to work more efficiently than those in developing countries
A)A country specializing in what they do most well or least poorly
B)A country producing everything better than other countries
C)The advantage that countries that export many products have over more specialized economies
D)The ability of workers in industrialized economies to work more efficiently than those in developing countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a quota?
A)A toll on land and sea traffic entering a country
B)A ban on imports from another country
C)A limit to the amount of a foreign good that can be sold in a country
D)A tax on imports levied at the border,paid by the importer
A)A toll on land and sea traffic entering a country
B)A ban on imports from another country
C)A limit to the amount of a foreign good that can be sold in a country
D)A tax on imports levied at the border,paid by the importer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of these is most likely a poor,developing country?
A)A country that exports aircraft
B)A country that exports copper
C)A country that exports computer chips
D)A country that exports automobiles and trucks
A)A country that exports aircraft
B)A country that exports copper
C)A country that exports computer chips
D)A country that exports automobiles and trucks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The trade protection that the United States steel industry receives has which of the following effects?
A)It raises the cost of steel for American consumers.
B)It lowers the profits of American steel companies.
C)It lowers the prices of products made with steel,such as cars and appliances.
D)It increases the sales of foreign steel products in the United States.
A)It raises the cost of steel for American consumers.
B)It lowers the profits of American steel companies.
C)It lowers the prices of products made with steel,such as cars and appliances.
D)It increases the sales of foreign steel products in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a nontariff barrier to trade?
A)A subsidy on domestic production
B)A tax on imports
C)A quota on imports
D)Consumer preference for domestic goods
A)A subsidy on domestic production
B)A tax on imports
C)A quota on imports
D)Consumer preference for domestic goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Why is "intra-industry" trade difficult for the Heckscher-Ohlin trade theory to explain?
A)Most of it is conducted between developing countries,which the theory predicts little of.
B)Since the products are within the same industry and made with the same factors,differences in factor endowment cannot explain it.
C)Countries with abundant labor are not expected to also import labor-intensive products.
D)Industries are expected to compete with each and not trade with each when factors are immobile.
A)Most of it is conducted between developing countries,which the theory predicts little of.
B)Since the products are within the same industry and made with the same factors,differences in factor endowment cannot explain it.
C)Countries with abundant labor are not expected to also import labor-intensive products.
D)Industries are expected to compete with each and not trade with each when factors are immobile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a tariff?
A)A toll on land and sea traffic entering a country
B)A ban on imports from another country
C)A limit to the amount of a foreign good that can be sold in a country
D)A tax on imports levied at the border,paid by the importer
A)A toll on land and sea traffic entering a country
B)A ban on imports from another country
C)A limit to the amount of a foreign good that can be sold in a country
D)A tax on imports levied at the border,paid by the importer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is an example of absolute advantage?
A)Since Turkey controls the Bosporus Strait,the countries on the Black Sea are completely dependent on it for access to the Mediterranean.
B)Portugal is better at producing wine than producing cloth.
C)The United States makes software more efficiently than any other country.
D)Labor can more easily move between industries than can capital.
A)Since Turkey controls the Bosporus Strait,the countries on the Black Sea are completely dependent on it for access to the Mediterranean.
B)Portugal is better at producing wine than producing cloth.
C)The United States makes software more efficiently than any other country.
D)Labor can more easily move between industries than can capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an example of specialization and division of labor?
A)A farm family building its own tractor
B)A worker in a Toyota plant welding a rear axle on a Corolla all day,every day
C)A popular motorcycle manufacturer beginning to produce small automobiles
D)Workers in a bottling plant rotating positions on the assembly line in order to master the entire process
A)A farm family building its own tractor
B)A worker in a Toyota plant welding a rear axle on a Corolla all day,every day
C)A popular motorcycle manufacturer beginning to produce small automobiles
D)Workers in a bottling plant rotating positions on the assembly line in order to master the entire process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Given the following exports,which of these is most likely a rich,developed country?
A)A country that exports shoes
B)A country that exports computer chips
C)A country that exports copper
D)A country that exports oil
A)A country that exports shoes
B)A country that exports computer chips
C)A country that exports copper
D)A country that exports oil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why does division of labor make international trade profitable?
A)Every country can produce all the products it needs.
B)The countries that are most efficient at producing particular products produce them.
C)Countries can learn to create products that they are inefficient at producing.
D)Workers always benefit when their labor is divided.
A)Every country can produce all the products it needs.
B)The countries that are most efficient at producing particular products produce them.
C)Countries can learn to create products that they are inefficient at producing.
D)Workers always benefit when their labor is divided.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of these periods was most characterized by trade liberalization?
A)The early 1800s
B)The late 1800s until World War I
C)During World War I
D)Between World War I and World War II
A)The early 1800s
B)The late 1800s until World War I
C)During World War I
D)Between World War I and World War II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why does protectionism cause a "deadweight loss" in trade?
A)Protectionism is likely to cause trade partners to raise trade barriers,thus costing exporters sales.
B)Developing countries have to go into debt to subsidize consumers so they can buy the higher priced imports.
C)It causes countries to switch production to industries where lack of comparative advantage makes production less efficient.
D)It creates a loss of sales tax revenue from decreased consumption.
A)Protectionism is likely to cause trade partners to raise trade barriers,thus costing exporters sales.
B)Developing countries have to go into debt to subsidize consumers so they can buy the higher priced imports.
C)It causes countries to switch production to industries where lack of comparative advantage makes production less efficient.
D)It creates a loss of sales tax revenue from decreased consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The creation of the European Common Market and the subsequent growth of the customs union in Europe is best an example of the importance of ________ in international trade.
A)interests
B)institutions
C)ideas
D)interactions
A)interests
B)institutions
C)ideas
D)interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following explains why the 2016 American presidential election was particularly anti-trade?
A)In the year prior to the election,Congress had delegated more trade power to the president,increasing the salience of the issue in the election.
B)After the 2008 economic crisis,U.S.exports had decreased so dramatically that hardly any jobs depended on trade anymore.
C)The recent surge in imports from China had led to more polarization about trade in some parts of the United States than previously.
D)Increased competition from the European Union created a desire in both parties to limit trade.
A)In the year prior to the election,Congress had delegated more trade power to the president,increasing the salience of the issue in the election.
B)After the 2008 economic crisis,U.S.exports had decreased so dramatically that hardly any jobs depended on trade anymore.
C)The recent surge in imports from China had led to more polarization about trade in some parts of the United States than previously.
D)Increased competition from the European Union created a desire in both parties to limit trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is "dumping"?
A)Subsidizing domestic production of goods
B)Destroying imports that exceed a country's quota
C)Outsourcing low-skilled jobs to a cheaper location
D)Selling goods below their cost of production
A)Subsidizing domestic production of goods
B)Destroying imports that exceed a country's quota
C)Outsourcing low-skilled jobs to a cheaper location
D)Selling goods below their cost of production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A major effect of trade barriers such as tariffs,quotas,and nontariff barriers is that:
A)aggregate social welfare is increased by keeping wealth within the country.
B)consumers lose from higher prices,while import-competing producers benefit.
C)export-oriented producers are supported,while there is no effect on consumers.
D)states are no longer allowed to be members of the World Trade Organization.
A)aggregate social welfare is increased by keeping wealth within the country.
B)consumers lose from higher prices,while import-competing producers benefit.
C)export-oriented producers are supported,while there is no effect on consumers.
D)states are no longer allowed to be members of the World Trade Organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is explained well by the Stolper-Samuelson theorem?
A)Farmers in land-poor France tend to favor liberal trade policies.
B)Farmers in land-rich Argentina tend to favor liberal trade policies.
C)Workers in the scarce-labor United States tend to oppose protectionist trade policies.
D)Workers in labor-rich Bangladesh tend to favor protectionist trade policies.
A)Farmers in land-poor France tend to favor liberal trade policies.
B)Farmers in land-rich Argentina tend to favor liberal trade policies.
C)Workers in the scarce-labor United States tend to oppose protectionist trade policies.
D)Workers in labor-rich Bangladesh tend to favor protectionist trade policies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Why can trade negotiations between two countries be viewed as a Prisoner's Dilemma?
A)While mutual free trade is better than mutual protection for both countries,each country may have an incentive to unilaterally impose protection if they care more about producers than consumers.
B)Trade negotiations often hold other elements of diplomacy "hostage" while they are ongoing.
C)If all sides in the negotiations reveal all of the information about their industrial capabilities and production plans,specialization can more easily occur,but both sides also have an incentive to keep quiet and use their industrial secrets to exploit the other side.
D)As long as one side implements free trade,it is always better for the other side to do so as well; so the key to getting mutual free trade is to assure the other side of your intentions.
A)While mutual free trade is better than mutual protection for both countries,each country may have an incentive to unilaterally impose protection if they care more about producers than consumers.
B)Trade negotiations often hold other elements of diplomacy "hostage" while they are ongoing.
C)If all sides in the negotiations reveal all of the information about their industrial capabilities and production plans,specialization can more easily occur,but both sides also have an incentive to keep quiet and use their industrial secrets to exploit the other side.
D)As long as one side implements free trade,it is always better for the other side to do so as well; so the key to getting mutual free trade is to assure the other side of your intentions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following is explained well by the specific-factor approach (Ricardo-Viner model)?
A)Steel workers and steel factory owners both lobby for tariffs on imported steel.
B)Steel workers and agricultural workers join together to oppose tariffs.
C)Owners of factories in a country with abundant fertile land promote free trade.
D)Workers in an automobile factory promote free trade while the factory owners lobby for tariffs on imported cars.
A)Steel workers and steel factory owners both lobby for tariffs on imported steel.
B)Steel workers and agricultural workers join together to oppose tariffs.
C)Owners of factories in a country with abundant fertile land promote free trade.
D)Workers in an automobile factory promote free trade while the factory owners lobby for tariffs on imported cars.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following countries is most likely to follow a liberal trade policy?
A)A country led by a dictator who suppresses national political parties
B)A country led by a dictator who allows limited elections to take place
C)A country led by a small group of military officers
D)A democratic country with strong national political parties and a powerful executive
A)A country led by a dictator who suppresses national political parties
B)A country led by a dictator who allows limited elections to take place
C)A country led by a small group of military officers
D)A democratic country with strong national political parties and a powerful executive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which type of actor does the newer alternative to the Stolper-Samuelson and Ricardo-Viner theorems focus on?
A)Large firms
B)Family farms
C)Skilled labor
D)Export industries
A)Large firms
B)Family farms
C)Skilled labor
D)Export industries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is the effect of trade barriers?
A)Imports become less expensive for domestic producers.
B)A glut of imported products develops.
C)Domestic producers of a protected good can sell their product at a higher price.
D)Domestic producers of a protected good have to lower the wages paid to their workers.
A)Imports become less expensive for domestic producers.
B)A glut of imported products develops.
C)Domestic producers of a protected good can sell their product at a higher price.
D)Domestic producers of a protected good have to lower the wages paid to their workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The key assumption distinguishing the Ricardo-Viner (RV)model from the Stolper-Samuelson (SS)model is that:
A)RV assumes that factor mobility is high; SS assumes that factor mobility is low.
B)RV assumes that factor mobility is low; SS assumes that factor mobility is high.
C)RV assumes that free trade benefits consumers; SS assumes that free trade hurts consumers.
D)RV assumes that free trade hurts consumers; SS assumes that free trade benefits consumers.
A)RV assumes that factor mobility is high; SS assumes that factor mobility is low.
B)RV assumes that factor mobility is low; SS assumes that factor mobility is high.
C)RV assumes that free trade benefits consumers; SS assumes that free trade hurts consumers.
D)RV assumes that free trade hurts consumers; SS assumes that free trade benefits consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is an implication of the Ricardo-Viner explanation for trade-policy preferences?
A)A country's government will usually prefer to protect owners of capital.
B)The interests of groups in society toward trade are determined by the factor of production of which they are part.
C)The interests of factors of production are often determined by the industry sector,rather than by the factor of production.
D)A country will import goods that make intensive use of the resources a country has in abundance.
A)A country's government will usually prefer to protect owners of capital.
B)The interests of groups in society toward trade are determined by the factor of production of which they are part.
C)The interests of factors of production are often determined by the industry sector,rather than by the factor of production.
D)A country will import goods that make intensive use of the resources a country has in abundance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What was the common interest that the future members of the European Union shared in the wake of World War II that led them to start the process of creating a single market?
A)A desire to overtake the United States economically
B)The need to decolonize cooperatively
C)A desire to rebuild after the devastation of the war
D)An interest in appeasing the Soviet Union to prevent a third World War
A)A desire to overtake the United States economically
B)The need to decolonize cooperatively
C)A desire to rebuild after the devastation of the war
D)An interest in appeasing the Soviet Union to prevent a third World War

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When the United States established steel tariffs in 2002,who benefited?
A)Steel exporters in other countries
B)Consumers in the United States
C)Producers in the United States that used steel as an input
D)Producers of steel in the United States
A)Steel exporters in other countries
B)Consumers in the United States
C)Producers in the United States that used steel as an input
D)Producers of steel in the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following trade policy results would be most expected given the logic of collective action?
A)Factory workers successfully lobbying for lower tariffs on imported automobiles
B)Consumers successfully lobbying for higher tariffs on imported corn
C)Consumers successfully lobbying for lower tariffs on imported televisions
D)Automobile manufacturers successfully lobbying for higher tariffs on imported automobiles
A)Factory workers successfully lobbying for lower tariffs on imported automobiles
B)Consumers successfully lobbying for higher tariffs on imported corn
C)Consumers successfully lobbying for lower tariffs on imported televisions
D)Automobile manufacturers successfully lobbying for higher tariffs on imported automobiles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the Stolper-Samuelson theorem?
A)The theory that protection hurts the scarce sector
B)The theory that protection hurts the scarce factor of production
C)The theory that protection benefits the abundant factor of production
D)The theory that protection benefits the scarce factor of production
A)The theory that protection hurts the scarce sector
B)The theory that protection hurts the scarce factor of production
C)The theory that protection benefits the abundant factor of production
D)The theory that protection benefits the scarce factor of production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Why can one often ignore the effect of trade on consumers when analyzing the politics of trade?
A)Trade has no effect on consumers.
B)The number of consumers hurt by trade is exactly offset by the number of consumers helped by trade.
C)Consumers are a large group and the effect of trade on them is dispersed,so they are more likely to suffer collective action problems.
D)Consumers are allied with labor in developing countries and with capital in developed countries,so we only need to focus on the effect of trade on these factors rather than consumers themselves.
A)Trade has no effect on consumers.
B)The number of consumers hurt by trade is exactly offset by the number of consumers helped by trade.
C)Consumers are a large group and the effect of trade on them is dispersed,so they are more likely to suffer collective action problems.
D)Consumers are allied with labor in developing countries and with capital in developed countries,so we only need to focus on the effect of trade on these factors rather than consumers themselves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is most likely to benefit from protectionism?
A)Consumers of all goods,because they are protected from inferior products
B)Consumers of imported products
C)Domestic producers of goods that are also imported from foreign countries
D)Domestic producers of goods that are exported to other countries
A)Consumers of all goods,because they are protected from inferior products
B)Consumers of imported products
C)Domestic producers of goods that are also imported from foreign countries
D)Domestic producers of goods that are exported to other countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Why does compensating those harmed by trade represent a "Pareto improvement"?
A)Trade benefits the country as a whole sufficiently that the country can provide compensation,thus improving the outcome for those hurt by trade,while still coming out ahead overall.
B)Tying compensation to trade makes trade so costly that it will only occur when it is extremely beneficial to the country.
C)Generous compensation will draw additional workers from abroad,thus increasing the output of the protected industry.
D)Compensation improves the efficiency of workers,which can counteract the comparative disadvantage labor has in a developed economy.
A)Trade benefits the country as a whole sufficiently that the country can provide compensation,thus improving the outcome for those hurt by trade,while still coming out ahead overall.
B)Tying compensation to trade makes trade so costly that it will only occur when it is extremely beneficial to the country.
C)Generous compensation will draw additional workers from abroad,thus increasing the output of the protected industry.
D)Compensation improves the efficiency of workers,which can counteract the comparative disadvantage labor has in a developed economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Mercosur is a regional trade agreement on what continent?
A)Africa
B)Asia
C)Europe
D)South America
A)Africa
B)Asia
C)Europe
D)South America

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
In the figure,at what level will domestic firms produce under liberalization?
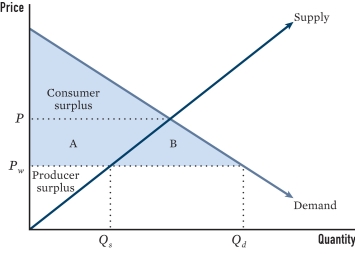
A)Q??
B)Qd
C)A
D)P

A)Q??
B)Qd
C)A
D)P

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT)was replaced by which of the following organizations?
A)The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
B)The World Bank (WB)
C)The Bank for International Settlements (BIS)
D)The World Trade Organization (WTO)
A)The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
B)The World Bank (WB)
C)The Bank for International Settlements (BIS)
D)The World Trade Organization (WTO)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is an example of "reciprocity" in international trade?
A)Most of the countries in the European Union have adopted the same currency.
B)France reduced tariffs on wheat imports after Great Britain reduced tariffs on wheat imports.
C)A majority of the world's countries have joined the World Trade Organization.
D)Oil-producing states cooperate on how much oil they will export.
A)Most of the countries in the European Union have adopted the same currency.
B)France reduced tariffs on wheat imports after Great Britain reduced tariffs on wheat imports.
C)A majority of the world's countries have joined the World Trade Organization.
D)Oil-producing states cooperate on how much oil they will export.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which country has a comparative advantage in cloth in the table?
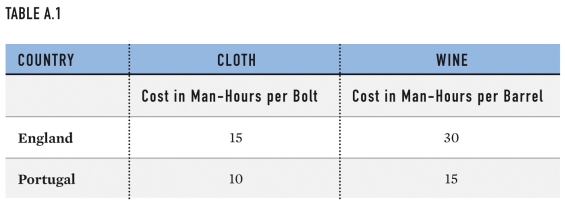
A)Portugal
B)England
C)Neither country
D)Both countries

A)Portugal
B)England
C)Neither country
D)Both countries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to Ricardo's theory on trade,in the example described by the table,Portugal should:
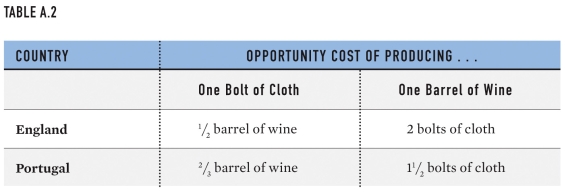
A)produce wine exclusively.
B)produce cloth exclusively.
C)produce everything itself.
D)produce half the wine and half the cloth needed by both parties.

A)produce wine exclusively.
B)produce cloth exclusively.
C)produce everything itself.
D)produce half the wine and half the cloth needed by both parties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Antiglobalization critics criticize the WTO because they think it:
A)favors domestic workers over other actors.
B)disregards environmental and safety issues.
C)is overly concerned about workers' health and safety.
D)is not doing enough to reduce government subsidies for domestic producers in developing countries.
A)favors domestic workers over other actors.
B)disregards environmental and safety issues.
C)is overly concerned about workers' health and safety.
D)is not doing enough to reduce government subsidies for domestic producers in developing countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is most-favored-nation trading status?
A)When countries give each other the same trade concessions they give to all other countries
B)When a country gives special trade privileges to a close ally
C)When a country spares no expense to increase trade with another country
D)When a country promotes trade with military allies
A)When countries give each other the same trade concessions they give to all other countries
B)When a country gives special trade privileges to a close ally
C)When a country spares no expense to increase trade with another country
D)When a country promotes trade with military allies

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Line Qₛ to Qd in the figure represents what occurring under liberalization?
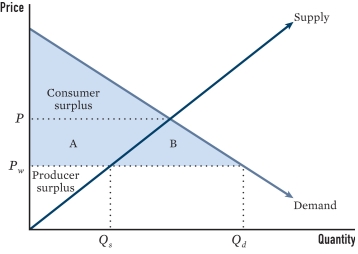
A)The new price of the good within the state
B)How much of the good consumers will demand
C)How much of the good will be imported by the state
D)How much domestic firms will produce for domestic consumption

A)The new price of the good within the state
B)How much of the good consumers will demand
C)How much of the good will be imported by the state
D)How much domestic firms will produce for domestic consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is true of a state that adopts a tariff in the scenario depicted in the figure?
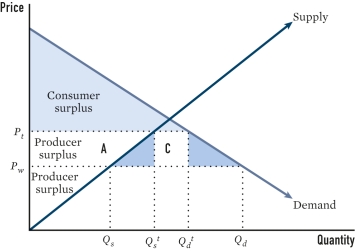
A)It will increase domestic consumption of the goods.
B)It will have no effect on domestic consumption of the goods.
C)It will decrease domestic production of the goods.
D)It will increase domestic production of the goods.

A)It will increase domestic consumption of the goods.
B)It will have no effect on domestic consumption of the goods.
C)It will decrease domestic production of the goods.
D)It will increase domestic production of the goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Line Qd ᵗ to Qd represents what occurring under the tariff in the figure?
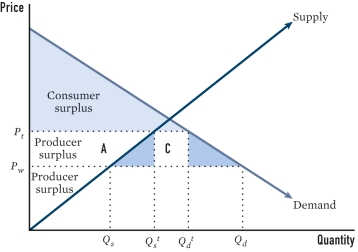
A)Increased revenue for the state
B)The new price of the good within the state
C)How much of the good that will be imported by the state
D)How much less the consumers would demand when compared to the world price

A)Increased revenue for the state
B)The new price of the good within the state
C)How much of the good that will be imported by the state
D)How much less the consumers would demand when compared to the world price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Why are those who favor free trade concerned about regional trade agreements?
A)They think there are too few regional trade agreements.
B)They think regional trade agreements are biased toward workers' rights.
C)They think regional trade agreements will be stepping stones toward a more integrated world economy.
D)They think regional trade agreements may result in the members trading only among themselves.
A)They think there are too few regional trade agreements.
B)They think regional trade agreements are biased toward workers' rights.
C)They think regional trade agreements will be stepping stones toward a more integrated world economy.
D)They think regional trade agreements may result in the members trading only among themselves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is the theory of hegemonic stability?
A)The spread of free trade throughout the world will lead to a stable single trading system.
B)The longer countries keep their free-trade policies,the more likely they are to remain pro-free trade.
C)Having one single hegemonic source of information can improve the chances of stability in international trade.
D)One large state that is willing and powerful enough can solve the collective action problems of international trade.
A)The spread of free trade throughout the world will lead to a stable single trading system.
B)The longer countries keep their free-trade policies,the more likely they are to remain pro-free trade.
C)Having one single hegemonic source of information can improve the chances of stability in international trade.
D)One large state that is willing and powerful enough can solve the collective action problems of international trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The table is an example of:
A)negative externality.
B)comparative advantage.
C)the Prisoner's Dilemma.
D)the Stag Hunt.

A)negative externality.
B)comparative advantage.
C)the Prisoner's Dilemma.
D)the Stag Hunt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the figure,at what level will domestic firms produce under the tariff?
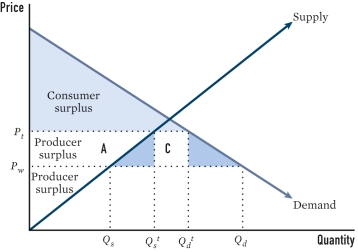
A)Q??
B)Qdt
C)A
D)pw

A)Q??
B)Qdt
C)A
D)pw

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which is true of Portugal in the table?
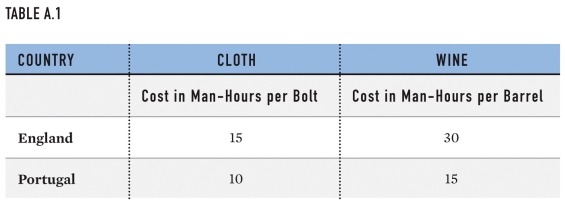
A)Portugal has an absolute advantage over England in both cloth and wine.
B)England's opportunity cost for producing wine is lower than Portugal's.
C)Portugal can produce more wine than England.
D)Neither country has a comparative advantage in the production of cloth.

A)Portugal has an absolute advantage over England in both cloth and wine.
B)England's opportunity cost for producing wine is lower than Portugal's.
C)Portugal can produce more wine than England.
D)Neither country has a comparative advantage in the production of cloth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following is an example of absolute advantage?
A)Germany makes cars more efficiently than the United States but less efficiently than Japan
B)The United States is likely to win in a trade war against either Germany or Japan.
C)Japan makes cars more efficiently than any other country.
D)All countries are equally efficient at making software.
A)Germany makes cars more efficiently than the United States but less efficiently than Japan
B)The United States is likely to win in a trade war against either Germany or Japan.
C)Japan makes cars more efficiently than any other country.
D)All countries are equally efficient at making software.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is most likely to help countries overcome trade problems with each other?
A)When a large number of countries participate in trade negotiations so they can gain broader consensus
B)When countries have limited interactions over time,and therefore little chance for disputes
C)When countries are able to restrict the information that other countries have about their products
D)When countries can negotiate concessions in different industries to achieve an agreement
A)When a large number of countries participate in trade negotiations so they can gain broader consensus
B)When countries have limited interactions over time,and therefore little chance for disputes
C)When countries are able to restrict the information that other countries have about their products
D)When countries can negotiate concessions in different industries to achieve an agreement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Why would transparency affect trade cooperation?
A)A country would be more reluctant to enter into a free-trade agreement if it has little information about another country's subsidies to domestic producers.
B)Two countries with too much information about each other's tax policies would find it difficult to negotiate a free-trade agreement.
C)Countries that negotiate simpler trade agreements are more likely to suspect the other side of cheating.
D)Countries try to conceal information about their domestic policies to improve the likelihood of negotiating an effective free-trade agreement.
A)A country would be more reluctant to enter into a free-trade agreement if it has little information about another country's subsidies to domestic producers.
B)Two countries with too much information about each other's tax policies would find it difficult to negotiate a free-trade agreement.
C)Countries that negotiate simpler trade agreements are more likely to suspect the other side of cheating.
D)Countries try to conceal information about their domestic policies to improve the likelihood of negotiating an effective free-trade agreement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In which of the following scenarios does the United States have a comparative advantage in iron production?
A)A U.S.worker can produce 10 tons of iron or 5 bushels of wheat,while a British worker can produce 1 ton of iron or 1 bushel of wheat.
B)A U.S.worker can produce 10 tons of iron or 5 bushels of wheat,while a British worker can produce 20 tons of iron or 10 bushels of wheat.
C)A U.S.worker can produce 10 tons of iron or 5 bushels of wheat,while a British worker can produce 5 tons of iron or 1 bushel of wheat.
D)A U.S.worker can produce 10 tons of iron or 5 bushels of wheat,while a British worker can produce 2 tons of iron or 1 bushel of wheat.
A)A U.S.worker can produce 10 tons of iron or 5 bushels of wheat,while a British worker can produce 1 ton of iron or 1 bushel of wheat.
B)A U.S.worker can produce 10 tons of iron or 5 bushels of wheat,while a British worker can produce 20 tons of iron or 10 bushels of wheat.
C)A U.S.worker can produce 10 tons of iron or 5 bushels of wheat,while a British worker can produce 5 tons of iron or 1 bushel of wheat.
D)A U.S.worker can produce 10 tons of iron or 5 bushels of wheat,while a British worker can produce 2 tons of iron or 1 bushel of wheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain how trade bargaining problems can resemble a Prisoner's Dilemma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Explain how domestic political interests,institutions,and interactions affect the likelihood of trade liberalization or trade restriction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
How do strategic interactions create problems in international trade policy,and how might these problems be resolved?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Why do economists believe that free trade would be beneficial for the world economy? Why do nations still erect barriers in the face of those arguments?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Explain how interests,institutions,and interactions led to increasing amounts of free trade in developing countries starting in the 1980s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What factors explain why countries trade what they do and who they trade with?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
How do the Stolper-Samuelson theorem and Ricardo-Viner model differ in their predictions of who will support protection and who will support free trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Explain hegemonic stability theory and how one or a few powerful countries can affect the international trading system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Imagine that you are the economic adviser to the executive of a state.What factors would you tell him or her to consider before announcing a new policy on trade? Which groups in society would you expect to be in favor of protectionism? Which groups would you expect to be in favor of free trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How do international institutions affect whether the world trading system is more or less open?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
How do domestic political institutions affect whether a country will adopt trade liberalization or protectionism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
How do compensation programs create a Pareto improvement in trade policy? Why might they create more support for trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Why have the United States and other developed countries become less supportive of trade recently? What effect has this decreased support had (or will it likely have in the future)?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What factors make it more likely that countries will have trade agreements? How do strategic interactions make it more or less likely that a country will sign these agreements?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Demonstrate mathematically how comparative advantage suggests that two countries should specialize and trade.Despite the math,why would countries refuse to partake in trade?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



