Deck 11: Strategic Cost Management
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/121
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Strategic Cost Management
1
The industrial value-chain analysis
A) recognizes only complex linkages within the firm.
B) is not compatible with differentiation strategies.
C) determines a linked set of value-creating activities.
D) requires a firm to operate across the entire value chain.
A) recognizes only complex linkages within the firm.
B) is not compatible with differentiation strategies.
C) determines a linked set of value-creating activities.
D) requires a firm to operate across the entire value chain.
C
2
_______________ are those factors that drive the cost of day-to-day activities performed as a result of the structure and processes selected by the organization.
A) Organizational activities
B) Organizational cost drivers
C) Operational activities
D) Operational cost drivers
A) Organizational activities
B) Organizational cost drivers
C) Operational activities
D) Operational cost drivers
D
3
Building plants, management structuring, and grouping employees are examples of
A) executional activities.
B) structural activities.
C) operational activities.
D) both a and b.
A) executional activities.
B) structural activities.
C) operational activities.
D) both a and b.
B
4
When a computer company selects a mix of strategies in order to create sustainable competitive advantage, it is following a
A) focusing strategy.
B) low-cost strategy.
C) differentiation strategy.
D) strategic positioning strategy.
A) focusing strategy.
B) low-cost strategy.
C) differentiation strategy.
D) strategic positioning strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
When a computer company targets customers in the South, it is following a
A) focusing strategy.
B) low-cost strategy.
C) differentiation strategy.
D) strategic allocation strategy.
A) focusing strategy.
B) low-cost strategy.
C) differentiation strategy.
D) strategic allocation strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The total product is the complete range of _______________ that a customer receives from a purchased product.
A) tangible benefits
B) intangible benefits
C) activity
D) both a and b
A) tangible benefits
B) intangible benefits
C) activity
D) both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Structural and executional activities are types of
A) organizational activities.
B) operating activities.
C) JIT.
D) both a and b.
A) organizational activities.
B) operating activities.
C) JIT.
D) both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
_______________ is the use of cost data to develop and identify superior strategies that will produce a sustainable competitive advantage.
A) Strategic decision making
B) Strategic cost management
C) Competitive advantage
D) Customer value
A) Strategic decision making
B) Strategic cost management
C) Competitive advantage
D) Customer value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
______________ is creating better customer value for the same or lower cost than competitors or creating equivalent value for lower cost than offered by competitors.
A) Strategic decision making
B) Strategic cost management
C) Competitive advantage
D) Total product
A) Strategic decision making
B) Strategic cost management
C) Competitive advantage
D) Total product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
_______________ are structural and executional factors that determine the long-term cost structure of an organization.
A) Organizational activities
B) Organizational cost drivers
C) Operational activities
D) Operational cost drivers
A) Organizational activities
B) Organizational cost drivers
C) Operational activities
D) Operational cost drivers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
_______________ involves choosing among alternative strategies with the goal of selecting a strategy or strategies that provides a company with reasonable assurance of long-term growth and survival.
A) Strategic decision making
B) Strategic cost management
C) Competitive advantage
D) Customer value
A) Strategic decision making
B) Strategic cost management
C) Competitive advantage
D) Customer value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a computer company maintains the internal storage space for a lower price, it is following a
A) focusing strategy.
B) cost leadership strategy.
C) differentiation strategy.
D) strategic positioning strategy.
A) focusing strategy.
B) cost leadership strategy.
C) differentiation strategy.
D) strategic positioning strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A competitive advantage has been established when
A) customers see the variation as important and the value added to the customer exceeds the cost of providing differentiation.
B) a high-cost strategy increases customer value by minimizing customer sacrifices.
C) a low-profit item is dropped from the product line.
D) both a and b.
A) customers see the variation as important and the value added to the customer exceeds the cost of providing differentiation.
B) a high-cost strategy increases customer value by minimizing customer sacrifices.
C) a low-profit item is dropped from the product line.
D) both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
_______________ describe the relationships of a firm's value chain activities that are performed with its suppliers and customers.
A) External linkages
B) Internal linkages
C) Industrial value chain
D) Both a and b
A) External linkages
B) Internal linkages
C) Industrial value chain
D) Both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
_______________ is the difference between what a customer receives and what the customer gives up.
A) Strategic decision making
B) Strategic cost management
C) Competitive advantage
D) Customer value
A) Strategic decision making
B) Strategic cost management
C) Competitive advantage
D) Customer value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
When a computer company increases the internal storage space for the same price, it is following a
A) focusing strategy.
B) low-cost strategy.
C) differentiation strategy.
D) strategic positioning strategy.
A) focusing strategy.
B) low-cost strategy.
C) differentiation strategy.
D) strategic positioning strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Plant layout, quality management systems, and providing capacity are examples of
A) executional activities.
B) structural activities.
C) operational activities.
D) both a and b.
A) executional activities.
B) structural activities.
C) operational activities.
D) both a and b.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The operational activity of moving inventory is classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
_______________ are relationships among activities that are performed with a firm's portion of the value chain.
A) External linkages
B) Internal linkages
C) Industrial value chain
D) Both a and b
A) External linkages
B) Internal linkages
C) Industrial value chain
D) Both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
When a computer manufacturing company addresses supplier production problems, it is focusing on
A) external linkages.
B) internal linkages.
C) a differentiation strategy.
D) a cost leadership strategy.
A) external linkages.
B) internal linkages.
C) a differentiation strategy.
D) a cost leadership strategy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The industry value chain includes
A) shareholder value chain activities as well as firm activities.
B) buyer and supplier value chain activities as well as firm activities.
C) only firm activities.
D) only firm production activities.
A) shareholder value chain activities as well as firm activities.
B) buyer and supplier value chain activities as well as firm activities.
C) only firm activities.
D) only firm production activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The last link of the internal value chain is
A) design.
B) service.
C) market.
D) distribute.
A) design.
B) service.
C) market.
D) distribute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
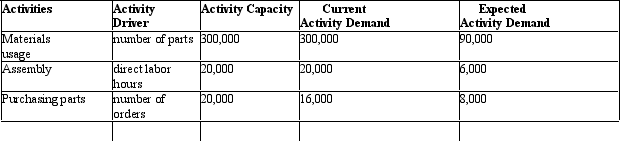
Figure 11-1 Clinton Corp.is a manufacturer of equipment used in manufacturing.It currently produces a product with 30 parts but through redesign has reduced the number of parts to 9.Then current activity capacity and demand for the 30 unit configuration and expected activity demand for the 9 part configuration are provided below:
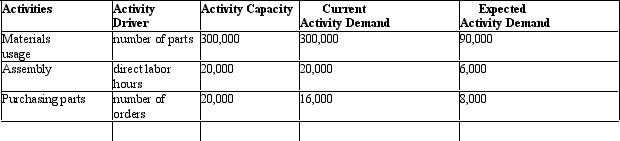 Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
-
Refer to Figure 11-1.What is the savings in materials usage cost with the new design changes?
A) $210,000
B) $1,050,000
C) $1,500,000
D) $400,000
 Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.-
Refer to Figure 11-1.What is the savings in materials usage cost with the new design changes?
A) $210,000
B) $1,050,000
C) $1,500,000
D) $400,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The operational activity of assembling parts is an example of a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In activity-based costing, supplier costs
A) must be narrower, including only the purchase price.
B) are allocated to products arbitrarily.
C) include costs of quality, reliability and timeliness and are assigned to products on a causal basis.
D) all of these statements are true.
A) must be narrower, including only the purchase price.
B) are allocated to products arbitrarily.
C) include costs of quality, reliability and timeliness and are assigned to products on a causal basis.
D) all of these statements are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The operational activity of redesigning products is classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Figure 11-2 Vibro Company sells a product used in many manufacturing processes.The sales activity involves three activity areas:
 The following customer information is given:
The following customer information is given:
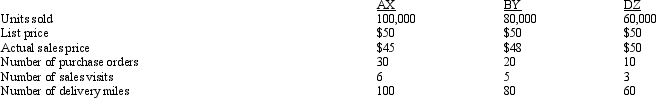
- Refer to Figure 11-2.Which customer has the least activity costs?
A) AX
B) BY
C) DZ
D) They are the same.
 The following customer information is given:
The following customer information is given: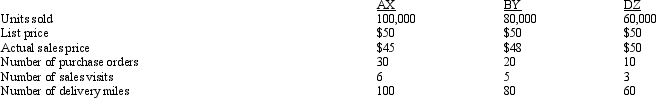
- Refer to Figure 11-2.Which customer has the least activity costs?
A) AX
B) BY
C) DZ
D) They are the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Figure 11-3 Vitella Company manufactures a product sold to retailers.It is considering suppliers for its process.The supplier quality involves four activity areas:
 The following supplier information is given:
The following supplier information is given:

- Refer to Figure 11-3.Which supplier is least costly?
A) X3
B) Y2
C) Z1
D) They are equally costly.
 The following supplier information is given:
The following supplier information is given:
- Refer to Figure 11-3.Which supplier is least costly?
A) X3
B) Y2
C) Z1
D) They are equally costly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Figure 11-1 Clinton Corp.is a manufacturer of equipment used in manufacturing.It currently produces a product with 30 parts but through redesign has reduced the number of parts to 9.Then current activity capacity and demand for the 30 unit configuration and expected activity demand for the 9 part configuration are provided below:
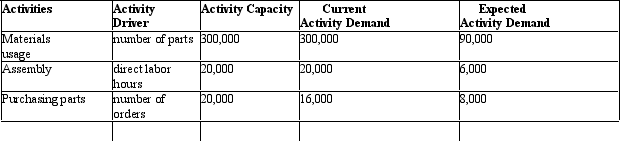 Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
-
Refer to Figure 11-1.If 10,000 units are being produced and the sales price is $500, what is the new sales price if the cost savings are passed on to the consumer?
A) $91.80
B) $280.20
C) $300.20
D) $199.80
 Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.-
Refer to Figure 11-1.If 10,000 units are being produced and the sales price is $500, what is the new sales price if the cost savings are passed on to the consumer?
A) $91.80
B) $280.20
C) $300.20
D) $199.80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The operational activity of setting up equipment is classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following are true about total quality control?
A) Total quality control is an approach to differentiate and reduce overall quality costs.
B) Total quality control demands production of defect-free products.
C) Total quality control links suppliers closely with the firm.
D) All of these statements are true about total quality control.
A) Total quality control is an approach to differentiate and reduce overall quality costs.
B) Total quality control demands production of defect-free products.
C) Total quality control links suppliers closely with the firm.
D) All of these statements are true about total quality control.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The operational activity of inspecting is classified as a
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.
A) unit-level activity.
B) batch-level activity.
C) product-level activity.
D) facility-level activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Figure 11-2 Vibro Company sells a product used in many manufacturing processes.The sales activity involves three activity areas:
 The following customer information is given:
The following customer information is given:
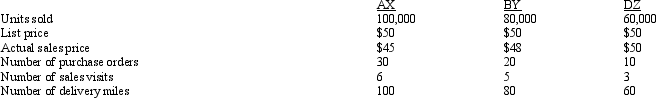
- Refer to Figure 11-2.What is the profitability of customer BY?
A) $4,000,000
B) $3,840,000
C) $3,837,670
D) $2,330,000
 The following customer information is given:
The following customer information is given: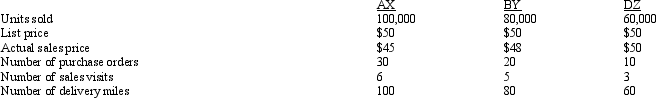
- Refer to Figure 11-2.What is the profitability of customer BY?
A) $4,000,000
B) $3,840,000
C) $3,837,670
D) $2,330,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Activities required to design, develop, produce, market, distribute, and service a product are known as
A) whole life activities.
B) value-chain activities.
C) target activities.
D) overhead.
A) whole life activities.
B) value-chain activities.
C) target activities.
D) overhead.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The first link of the internal value chain is
A) design.
B) develop.
C) market.
D) distribute.
A) design.
B) develop.
C) market.
D) distribute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Identifying profitable and unprofitable customers is an example of exploiting
A) supplier linkages.
B) the product life cycle.
C) consumable life.
D) customer linkages.
A) supplier linkages.
B) the product life cycle.
C) consumable life.
D) customer linkages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Figure 11-1 Clinton Corp.is a manufacturer of equipment used in manufacturing.It currently produces a product with 30 parts but through redesign has reduced the number of parts to 9.Then current activity capacity and demand for the 30 unit configuration and expected activity demand for the 9 part configuration are provided below:
 Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
-
Refer to Figure 11-1.What is the total cost reduction of the new design?
A) $1,998,000
B) $1,984,000
C) $1,414,000
D) $1,418,000
 Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.-
Refer to Figure 11-1.What is the total cost reduction of the new design?
A) $1,998,000
B) $1,984,000
C) $1,414,000
D) $1,418,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Analyzing how costs and other financial factors vary as different bundles of activities are considered to strengthen a firm's strategic position is the process of
A) exploiting linkages.
B) design.
C) cost driver analysis.
D) distribution.
A) exploiting linkages.
B) design.
C) cost driver analysis.
D) distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Figure 11-2 Vibro Company sells a product used in many manufacturing processes.The sales activity involves three activity areas:
 The following customer information is given:
The following customer information is given:
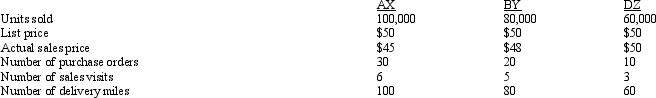
-Refer to Figure 11-2.Which customer is most profitable?
A) AX
B) BY
C) DZ
D) They are equally profitable.
 The following customer information is given:
The following customer information is given: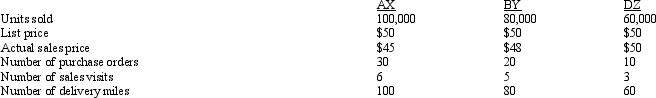
-Refer to Figure 11-2.Which customer is most profitable?
A) AX
B) BY
C) DZ
D) They are equally profitable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Figure 11-1 Clinton Corp.is a manufacturer of equipment used in manufacturing.It currently produces a product with 30 parts but through redesign has reduced the number of parts to 9.Then current activity capacity and demand for the 30 unit configuration and expected activity demand for the 9 part configuration are provided below:
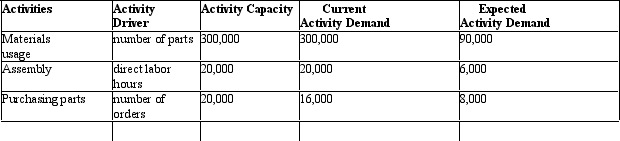 Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
-
Refer to Figure 11-1.What is the cost savings from purchasing parts?
A) $88,000
B) $80,000
C) $48,000
D) $40,000
 Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.
Materials usage has a rate of $5 per part and no fixed costs.Assembly has a rate of $20 per labor hour with no fixed component.Purchasing requires clerks that can process 5,000 purchase orders.Each clerk earns $40,000 per year.There is also a $1 per order processing cost.-
Refer to Figure 11-1.What is the cost savings from purchasing parts?
A) $88,000
B) $80,000
C) $48,000
D) $40,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Figure 11-3 Vitella Company manufactures a product sold to retailers.It is considering suppliers for its process.The supplier quality involves four activity areas:
 The following supplier information is given:
The following supplier information is given:

- Refer to Figure 11-3.Which supplier has the most defective units?
A) X3
B) Y2
C) Z1
D) They are equal.
 The following supplier information is given:
The following supplier information is given:
- Refer to Figure 11-3.Which supplier has the most defective units?
A) X3
B) Y2
C) Z1
D) They are equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Life-cycle cost management consists of
A) actions taken to enable a product to be designed, developed, produced, marketed, distributed, operated, maintained, serviced, and disposed of in order to maximize profits.
B) actions to extend the life of a product through design, development, production, and maintenance.
C) actions that focus on minimizing the cost of developing, designing, producing, distributing, operating, servicing, and disposal of a product.
D) actions taken to design, develop, test, market, distribute, maintain, service, and dispose of a product to maximize revenues.
A) actions taken to enable a product to be designed, developed, produced, marketed, distributed, operated, maintained, serviced, and disposed of in order to maximize profits.
B) actions to extend the life of a product through design, development, production, and maintenance.
C) actions that focus on minimizing the cost of developing, designing, producing, distributing, operating, servicing, and disposal of a product.
D) actions taken to design, develop, test, market, distribute, maintain, service, and dispose of a product to maximize revenues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which stage in the marketing viewpoint is characterized by preproduction and startup activities?
A) decline
B) introduction
C) growth
D) maturity
A) decline
B) introduction
C) growth
D) maturity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following is NOT a stage of the production life-cycle viewpoint?
A) design
B) introduction
C) research
D) testing
A) design
B) introduction
C) research
D) testing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
_______________ is the length of time that a product serves the needs of customers.
A) Product life cycle
B) Revenue producing life
C) Consumable life
D) Introduction stage
A) Product life cycle
B) Revenue producing life
C) Consumable life
D) Introduction stage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The _______________ is characterized by preproduction and startup activities.
A) introduction stage
B) growth stage
C) maturity stage
D) decline stage
A) introduction stage
B) growth stage
C) maturity stage
D) decline stage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the life-cycle viewpoints is the revenue-oriented viewpoint?
A) consumable life-cycle viewpoint
B) production viewpoint
C) marketing viewpoint
D) planning viewpoint
A) consumable life-cycle viewpoint
B) production viewpoint
C) marketing viewpoint
D) planning viewpoint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The _______________ is when the product loses market acceptance.
A) introduction stage
B) growth stage
C) maturity stage
D) decline stage
A) introduction stage
B) growth stage
C) maturity stage
D) decline stage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The _______________ is a period of time when sales increase at a decreasing rate.
A) introduction stage
B) growth stage
C) maturity stage
D) decline stage
A) introduction stage
B) growth stage
C) maturity stage
D) decline stage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the life-cycle viewpoints is the cost-oriented viewpoint?
A) product life-cycle
B) consumable life-cycle
C) production life-cycle
D) planning life-cycle
A) product life-cycle
B) consumable life-cycle
C) production life-cycle
D) planning life-cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
_______________ is the time a product exists-from conception to abandonment.
A) Product life cycle
B) Revenue producing life
C) Consumable life
D) Introduction stage
A) Product life cycle
B) Revenue producing life
C) Consumable life
D) Introduction stage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which stage of the marketing life-cycle has slow sales growth with peak sales?
A) introduction
B) growth
C) maturity
D) decline
A) introduction
B) growth
C) maturity
D) decline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
_______________ defines stages of the life cycle by changes in the type of activities performed.
A) Accounting viewpoint
B) Customer viewpoint
C) Production viewpoint
D) Marketing viewpoint
A) Accounting viewpoint
B) Customer viewpoint
C) Production viewpoint
D) Marketing viewpoint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is NOT a stage of the production life-cycle viewpoint?
A) planning
B) production
C) purchasing
D) logistics
A) planning
B) production
C) purchasing
D) logistics

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Figure 11-3 Vitella Company manufactures a product sold to retailers.It is considering suppliers for its process.The supplier quality involves four activity areas:
 The following supplier information is given:
The following supplier information is given:

-Refer to Figure 11-3.What is the cost of supplier Z1?
A) $503,358
B) $501,000
C) $498,642
D) $499,000
 The following supplier information is given:
The following supplier information is given:
-Refer to Figure 11-3.What is the cost of supplier Z1?
A) $503,358
B) $501,000
C) $498,642
D) $499,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following is NOT a stage of the marketing viewpoint of the product life cycle?
A) decline
B) growth
C) maturity
D) production
A) decline
B) growth
C) maturity
D) production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The _______________ is a period of time when sales increase at an increasing rate.
A) introduction stage
B) growth stage
C) maturity stage
D) decline stage
A) introduction stage
B) growth stage
C) maturity stage
D) decline stage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
_______________ describes the general sales pattern of a product as it passes through the introduction, growth, maturity, and decline stages.
A) Accounting viewpoint
B) Customer viewpoint
C) Production viewpoint
D) Marketing viewpoint
A) Accounting viewpoint
B) Customer viewpoint
C) Production viewpoint
D) Marketing viewpoint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which viewpoint of the product life-cycle is customer-value oriented?
A) production life-cycle
B) marketing life-cycle
C) consumable life-cycle
D) planning life-cycle
A) production life-cycle
B) marketing life-cycle
C) consumable life-cycle
D) planning life-cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is NOT a stage of the consumable life-cycle viewpoint?
A) disposal
B) maintaining
C) logistics
D) purchasing
A) disposal
B) maintaining
C) logistics
D) purchasing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
____________ manufacturing reduces inventory levels because production is geared to demand.
A) Traditional
B) Conventional
C) JIT
D) Both a and b
A) Traditional
B) Conventional
C) JIT
D) Both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
JIT manufacturing differs from traditional manufacturing in all of the following ways EXCEPT
A) the treatment of direct materials and direct labor for product costing.
B) the level of inventories.
C) the approach to quality control.
D) the physical layout of the manufacturing process.
A) the treatment of direct materials and direct labor for product costing.
B) the level of inventories.
C) the approach to quality control.
D) the physical layout of the manufacturing process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Chris Company sells a product for $225 per unit.Its market share is 20 percent.The marketing manager feels that the market share can be increased to 30 percent with a reduction in price to $195.The product is currently earning a profit of $36 per unit.
-The president of Chris Company feels that the $36 profit per unit must be maintained.What is the original cost per unit?
A) $225
B) $195
C) $189
D) $159
-The president of Chris Company feels that the $36 profit per unit must be maintained.What is the original cost per unit?
A) $225
B) $195
C) $189
D) $159

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
_______________ is the difference between the sales price needed to capture a predetermined market share and the desired profit per unit.
A) Gross profit
B) Target cost
C) Target price
D) Both a and b
A) Gross profit
B) Target cost
C) Target price
D) Both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of the following is a trait of a traditional manufacturing system?
A) push-through system
B) value-chain focus
C) total quality control
D) high employee involvement
A) push-through system
B) value-chain focus
C) total quality control
D) high employee involvement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Traditional manufacturing uses which of the following philosophies of quality control?
A) zero defects
B) total quality control
C) acceptable quality level
D) both a and b
A) zero defects
B) total quality control
C) acceptable quality level
D) both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Figure 11-4 Brad Company developed the following budgeted life-cycle income statement for two proposed products.Each product's life cycle is expected to be two years.
 A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
Relative to Product B, Product A requires more research and development costs but fewer resources to market the product.Sixty percent of the research and development costs are traceable to Product A, and 30 percent of the marketing costs are traceable to Product A.
-
If research and development costs and marketing costs are traced to each product, life-cycle income for Product B would be
A) $35,000.
B) $20,000.
C) $12,000.
D) $7,000.
 A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.Relative to Product B, Product A requires more research and development costs but fewer resources to market the product.Sixty percent of the research and development costs are traceable to Product A, and 30 percent of the marketing costs are traceable to Product A.
-
If research and development costs and marketing costs are traced to each product, life-cycle income for Product B would be
A) $35,000.
B) $20,000.
C) $12,000.
D) $7,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Chris Company sells a product for $225 per unit.Its market share is 20 percent.The marketing manager feels that the market share can be increased to 30 percent with a reduction in price to $195.The product is currently earning a profit of $36 per unit.
-The president of Chris Company feels that the $36 profit per unit must be maintained.What is the target cost per unit?
A) $225
B) $195
C) $189
D) $159
-The president of Chris Company feels that the $36 profit per unit must be maintained.What is the target cost per unit?
A) $225
B) $195
C) $189
D) $159

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Life-cycle cost management emphasizes
A) cost control.
B) cost reduction.
C) normal costing.
D) process costing.
A) cost control.
B) cost reduction.
C) normal costing.
D) process costing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Rudy Company sells a product for $450 per unit.Its market share is 25 percent.The marketing manager feels that the market share can be increased to 33 percent with a reduction in price to $390.The product is currently earning a profit of $72 per unit.The president of Rudy Company feels that the $72 profit per unit must be maintained.
-What is the original cost per unit?
A) $390
B) $450
C) $318
D) $378
-What is the original cost per unit?
A) $390
B) $450
C) $318
D) $378

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
According to the authors, 90 percent or more of a product's life-cycle costs are determined during
A) growth stage.
B) development stage.
C) decline stage.
D) maturity stage.
A) growth stage.
B) development stage.
C) decline stage.
D) maturity stage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Courteous Company developed the following budgeted life-cycle income statement for two proposed products.Each product's life cycle is expected to be two years.  A 12 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 12 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
A 12 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 12 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
Relative to Product BB, Product AA requires more research and development costs but fewer resources to market the product.Sixty-five percent of the research and development costs are traceable to Product AA, and 40 percent of the marketing costs are traceable to Product AA.
-
If research and development costs and marketing costs are traced to each product, life-cycle income for Product BB would be
A) $70,000.
B) $90,000.
C) $105,000.
D) $150,000.
 A 12 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 12 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
A 12 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 12 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.Relative to Product BB, Product AA requires more research and development costs but fewer resources to market the product.Sixty-five percent of the research and development costs are traceable to Product AA, and 40 percent of the marketing costs are traceable to Product AA.
-
If research and development costs and marketing costs are traced to each product, life-cycle income for Product BB would be
A) $70,000.
B) $90,000.
C) $105,000.
D) $150,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following is a trait of a JIT system?
A) push-through system
B) significant inventory
C) buyers' market
D) large supplier base
A) push-through system
B) significant inventory
C) buyers' market
D) large supplier base

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Courteous Company developed the following budgeted life-cycle income statement for two proposed products.Each product's life cycle is expected to be two years. 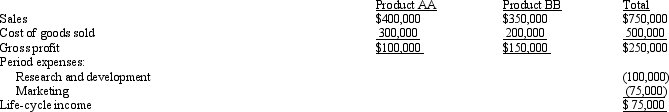 A 12 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 12 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
A 12 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 12 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
Relative to Product BB, Product AA requires more research and development costs but fewer resources to market the product.Sixty-five percent of the research and development costs are traceable to Product AA, and 40 percent of the marketing costs are traceable to Product AA.
-
If research and development costs and marketing costs are traced to each product, life-cycle income for Product AA would be
A) $3,000.
B) $5,000.
C) $35,000.
D) $100,000.
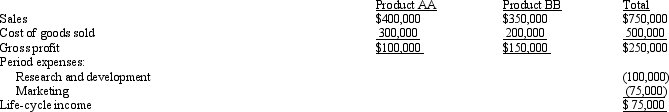 A 12 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 12 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
A 12 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 12 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.Relative to Product BB, Product AA requires more research and development costs but fewer resources to market the product.Sixty-five percent of the research and development costs are traceable to Product AA, and 40 percent of the marketing costs are traceable to Product AA.
-
If research and development costs and marketing costs are traced to each product, life-cycle income for Product AA would be
A) $3,000.
B) $5,000.
C) $35,000.
D) $100,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Chris Company sells a product for $225 per unit.Its market share is 20 percent.The marketing manager feels that the market share can be increased to 30 percent with a reduction in price to $195.The product is currently earning a profit of $36 per unit.
-The president of Chris Company feels that the $36 profit per unit must be maintained.What is the target price per unit?
A) $225
B) $195
C) $189
D) $159
-The president of Chris Company feels that the $36 profit per unit must be maintained.What is the target price per unit?
A) $225
B) $195
C) $189
D) $159

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
At which stage of the consumable life-cycle is price sensitivity low?
A) introduction
B) growth
C) maturity
D) decline
A) introduction
B) growth
C) maturity
D) decline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Rudy Company sells a product for $450 per unit.Its market share is 25 percent.The marketing manager feels that the market share can be increased to 33 percent with a reduction in price to $390.The product is currently earning a profit of $72 per unit.The president of Rudy Company feels that the $72 profit per unit must be maintained.
-What is the target price per unit?
A) $390
B) $450
C) $318
D) $378
-What is the target price per unit?
A) $390
B) $450
C) $318
D) $378

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Figure 11-4 Brad Company developed the following budgeted life-cycle income statement for two proposed products.Each product's life cycle is expected to be two years.
 A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
Relative to Product B, Product A requires more research and development costs but fewer resources to market the product.Sixty percent of the research and development costs are traceable to Product A, and 30 percent of the marketing costs are traceable to Product A.
-
Refer to Figure 11-4. Return on sales for Product A would be
A) 40.0%.
B) 25.0%.
C) 11.5%.
D) 2.5%.
 A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.Relative to Product B, Product A requires more research and development costs but fewer resources to market the product.Sixty percent of the research and development costs are traceable to Product A, and 30 percent of the marketing costs are traceable to Product A.
-
Refer to Figure 11-4. Return on sales for Product A would be
A) 40.0%.
B) 25.0%.
C) 11.5%.
D) 2.5%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Information for life-cycle cost management is supported by a(n)
A) functional-based costing system.
B) activity-based costing system.
C) normal costing system.
D) all of these.
A) functional-based costing system.
B) activity-based costing system.
C) normal costing system.
D) all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Figure 11-4 Brad Company developed the following budgeted life-cycle income statement for two proposed products.Each product's life cycle is expected to be two years.
 A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
Relative to Product B, Product A requires more research and development costs but fewer resources to market the product.Sixty percent of the research and development costs are traceable to Product A, and 30 percent of the marketing costs are traceable to Product A.
-
Refer to Figure 11-4. If research and development costs and marketing costs are traced to each product, life-cycle income for Product A would be
A) $38,000.
B) $27,000.
C) $23,000.
D) $15,000.
 A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.
A 10 percent return on sales is required for new products.Because the proposed products did not have a 10 percent return on sales, the products were going to be dropped.Relative to Product B, Product A requires more research and development costs but fewer resources to market the product.Sixty percent of the research and development costs are traceable to Product A, and 30 percent of the marketing costs are traceable to Product A.
-
Refer to Figure 11-4. If research and development costs and marketing costs are traced to each product, life-cycle income for Product A would be
A) $38,000.
B) $27,000.
C) $23,000.
D) $15,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 121 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



