Deck 4: Psychopharmacology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/191
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Psychopharmacology
1
This chemical is released from the adrenal gland and travels through the bloodstream.It fits into the receptors on almost every cell in the body.The chemical is a(n)
A) neurotransmitter.
B) neurohormone.
C) neuromodulator.
D) antagonist.
A) neurotransmitter.
B) neurohormone.
C) neuromodulator.
D) antagonist.
neurohormone.
2
Professor Murphy is studying neurons that release a particular small-molecule neurotransmitter.In these same neurons,the professor should expect to see
A) no other types of neurotransmitters.
B) a second type of small-molecule neurotransmitter.
C) at least one type of neuropeptide neurotransmitter.
D) at least one other type of small-molecule neurotransmitter and multiple types of neuropeptides neurotransmitters.
A) no other types of neurotransmitters.
B) a second type of small-molecule neurotransmitter.
C) at least one type of neuropeptide neurotransmitter.
D) at least one other type of small-molecule neurotransmitter and multiple types of neuropeptides neurotransmitters.
at least one type of neuropeptide neurotransmitter.
3
Acetylcholine (ACh)is synthesized from
A) acetyl coenzyme A,usually found in dietary fats,and choline,a substance formed by the actions of mitochondria within cells.
B) choline,usually found in dietary fats,and acetyl coenzyme A,a substance formed by the actions of mitochondria within cells.
C) the amino acid tyrosine,synthesized from the phenylalanine found in foods.
D) tryptophans,amino acids found in chocolate,milk,and poultry.
A) acetyl coenzyme A,usually found in dietary fats,and choline,a substance formed by the actions of mitochondria within cells.
B) choline,usually found in dietary fats,and acetyl coenzyme A,a substance formed by the actions of mitochondria within cells.
C) the amino acid tyrosine,synthesized from the phenylalanine found in foods.
D) tryptophans,amino acids found in chocolate,milk,and poultry.
choline,usually found in dietary fats,and acetyl coenzyme A,a substance formed by the actions of mitochondria within cells.
4
Chemical messengers that act on neurons in the immediate vicinity of their release are known as
A) neurotransmitters.
B) neuromodulators.
C) neurohormones.
D) neuroenzymes.
A) neurotransmitters.
B) neuromodulators.
C) neurohormones.
D) neuroenzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Acetylcholine (ACh)released into the synaptic gap is deactivated primarily by
A) diffusion away from the synapse.
B) absorption by astrocytes.
C) reuptake.
D) enzymes.
A) diffusion away from the synapse.
B) absorption by astrocytes.
C) reuptake.
D) enzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements regarding the synthesis of neurotransmitters is true?
A) Both small-molecule neurotransmitters and neuropeptides may be synthesized anywhere in the neuron.
B) Small-molecule neurotransmitters may be synthesized anywhere in the neuron,but neuropeptides must be synthesized in the cell body.
C) Neuropeptides may be synthesized anywhere in the neuron,but small-molecule neurotransmitters must be synthesized in the cell body.
D) Both small-molecule neurotransmitters and neuropeptides must be synthesized in the cell body.
A) Both small-molecule neurotransmitters and neuropeptides may be synthesized anywhere in the neuron.
B) Small-molecule neurotransmitters may be synthesized anywhere in the neuron,but neuropeptides must be synthesized in the cell body.
C) Neuropeptides may be synthesized anywhere in the neuron,but small-molecule neurotransmitters must be synthesized in the cell body.
D) Both small-molecule neurotransmitters and neuropeptides must be synthesized in the cell body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
This chemical is released from a neuron and diffuses away to influence neurons somewhat distant from the releasing neuron.The chemical is a(n)
A) neurotransmitter.
B) neuromodulator.
C) neurohormone.
D) enzyme.
A) neurotransmitter.
B) neuromodulator.
C) neurohormone.
D) enzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A chemical that is released from presynaptic axon terminals and fits in receptors on the post-synaptic neuron is acting as a(n)
A) neurotransmitter.
B) neurohormone.
C) neuromodulator.
D) agonist.
A) neurotransmitter.
B) neurohormone.
C) neuromodulator.
D) agonist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Given the characteristics of small-molecule transmitters and neuropeptides,we can conclude that small-molecule transmitters
A) are well-suited to roles as neurotransmitters,whereas neuropeptides are well-suited to roles as neuromodulators.
B) are well-suited to roles as neuromodulators,whereas neuropeptides are well-suited to roles as neurotransmitters.
C) and neuropeptides are equally well-suited to be either neurotransmitters or neuromodulators.
D) and neuropeptides frequently act as neuromodulators and neurohormones,but rarely function as neurotransmitters.
A) are well-suited to roles as neurotransmitters,whereas neuropeptides are well-suited to roles as neuromodulators.
B) are well-suited to roles as neuromodulators,whereas neuropeptides are well-suited to roles as neurotransmitters.
C) and neuropeptides are equally well-suited to be either neurotransmitters or neuromodulators.
D) and neuropeptides frequently act as neuromodulators and neurohormones,but rarely function as neurotransmitters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Neurons using which of the following neurotransmitters are especially likely to deteriorate in cases of Alzheimer's disease?
A) dopamine
B) GABA
C) acetylcholine (ACh)
D) serotonin
A) dopamine
B) GABA
C) acetylcholine (ACh)
D) serotonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The release of vesicles containing neuropeptides requires
A) higher levels of calcium than the release of small-molecule neurotransmitters.
B) lower levels of calcium than the release of small-molecule neurotransmitters.
C) approximately equal levels of calcium as the release of small-molecule neurotransmitters.
D) no calcium at all.
A) higher levels of calcium than the release of small-molecule neurotransmitters.
B) lower levels of calcium than the release of small-molecule neurotransmitters.
C) approximately equal levels of calcium as the release of small-molecule neurotransmitters.
D) no calcium at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following substances is found only in neurons that produce acetylcholine?
A) choline
B) acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA)
C) tryptophan
D) choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)
A) choline
B) acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl CoA)
C) tryptophan
D) choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
A) acts on the precursors of acetylcholine (ACh)to produce the final form of the neurotransmitter.
B) breaks down acetylcholine (ACh)in the synaptic gap.
C) acts on acetylcholine (ACh)to produce choline.
D) acts on choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)to produce acetylcholine (ACh).
A) acts on the precursors of acetylcholine (ACh)to produce the final form of the neurotransmitter.
B) breaks down acetylcholine (ACh)in the synaptic gap.
C) acts on acetylcholine (ACh)to produce choline.
D) acts on choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)to produce acetylcholine (ACh).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Henry Dale's assertion that neurons could contain only one type of neurotransmitter is
A) correct.
B) partially correct,in that neuropeptides and small-molecule transmitters are often found together,but the existence of two small-molecule transmitters in the same cell is controversial.
C) partially correct,in that neuropeptides are never found in the same neuron as amines or amino acids.
D) completely false.
A) correct.
B) partially correct,in that neuropeptides and small-molecule transmitters are often found together,but the existence of two small-molecule transmitters in the same cell is controversial.
C) partially correct,in that neuropeptides are never found in the same neuron as amines or amino acids.
D) completely false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Following release from the presynaptic cell,neuropeptides
A) are deactivated by enzymes,whereas small-molecule transmitters diffuse away or are deactivated by reuptake.
B) are deactivated by reuptake,whereas small-molecule transmitters diffuse away or are deactivated by enzymes.
C) diffuse away,whereas small-molecule transmitters are deactivated by enzymes or reuptake.
D) and small-molecule transmitters can be deactivated by diffusion,enzymes,or reuptake.
A) are deactivated by enzymes,whereas small-molecule transmitters diffuse away or are deactivated by reuptake.
B) are deactivated by reuptake,whereas small-molecule transmitters diffuse away or are deactivated by enzymes.
C) diffuse away,whereas small-molecule transmitters are deactivated by enzymes or reuptake.
D) and small-molecule transmitters can be deactivated by diffusion,enzymes,or reuptake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Chemical messengers that diffuse from their site of release to affect neurons at some distance away are known as
A) neurotransmitters.
B) neuromodulators.
C) neurohormones.
D) neuroenzymes.
A) neurotransmitters.
B) neuromodulators.
C) neurohormones.
D) neuroenzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Chemical messengers that often travel in the blood supply in order to affect target neurons that are quite distant are known as
A) neurotransmitters.
B) neuromodulators.
C) neurohormones.
D) neuroenzymes.
A) neurotransmitters.
B) neuromodulators.
C) neurohormones.
D) neuroenzymes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The primary neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction is
A) dopamine.
B) GABA.
C) acetylcholine (ACh).
D) serotonin.
A) dopamine.
B) GABA.
C) acetylcholine (ACh).
D) serotonin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In order to be considered a neurotransmitter,a chemical should
A) travel through the blood supply in order to reach its target.
B) be the only chemical messenger used by a particular cell.
C) be deactivated by enzymes in the synaptic gap.
D) be synthesized within a neuron.
A) travel through the blood supply in order to reach its target.
B) be the only chemical messenger used by a particular cell.
C) be deactivated by enzymes in the synaptic gap.
D) be synthesized within a neuron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Myasthenia gravis,a disease characterized by muscle weakness and fatigue,is often treated by medications that inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE).Which of the following statements best explains why this treatment would be effective?
A) Inhibiting AChE would delay the breakdown of acetylcholine (ACh)in the synaptic gap.This in turn would make smaller amounts of ACh more effective in stimulating muscles.
B) Inhibiting AChE would ensure that more acetylcholine (ACh)is transported back into the presynaptic neuron through the process of reuptake.
C) Inhibiting AChE would increase the rate of synthesis of acetylcholine (ACh)in motor neurons.
D) AChE has a general inhibitory effect in the brain,so blocking its action would be stimulating to many systems,including movement.
A) Inhibiting AChE would delay the breakdown of acetylcholine (ACh)in the synaptic gap.This in turn would make smaller amounts of ACh more effective in stimulating muscles.
B) Inhibiting AChE would ensure that more acetylcholine (ACh)is transported back into the presynaptic neuron through the process of reuptake.
C) Inhibiting AChE would increase the rate of synthesis of acetylcholine (ACh)in motor neurons.
D) AChE has a general inhibitory effect in the brain,so blocking its action would be stimulating to many systems,including movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Tyrosine serves as a substrate or building block for the synthesis of which of the following neurotransmitters?
A) acetylcholine (ACh)
B) all monoamines
C) all indoleamines,but not catecholamines
D) all catecholamines,but not indoleamines
A) acetylcholine (ACh)
B) all monoamines
C) all indoleamines,but not catecholamines
D) all catecholamines,but not indoleamines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following neurotransmitters is not a catecholamine?
A) serotonin
B) epinephrine
C) dopamine
D) norepinephrine
A) serotonin
B) epinephrine
C) dopamine
D) norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Nicotinic receptors respond to both nicotine and
A) muscarine.
B) norepinephrine.
C) serotonin.
D) ACh.
A) muscarine.
B) norepinephrine.
C) serotonin.
D) ACh.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Neurons releasing acetylcholine are found in the
A) preganglionic and postganglionic synapses of both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
B) preganglionic synapses of the sympathetic nervous system and both the preganglionic and postganglionic synapses of the parasympathetic nervous system.
C) preganglionic synapses of the parasympathetic nervous system and both the preganglionic and postganglionic synapses of the sympathetic nervous system.
D) postganglionic synapses of the sympathetic nervous system and the preganglionic synapses of the parasympathetic nervous system.
A) preganglionic and postganglionic synapses of both the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
B) preganglionic synapses of the sympathetic nervous system and both the preganglionic and postganglionic synapses of the parasympathetic nervous system.
C) preganglionic synapses of the parasympathetic nervous system and both the preganglionic and postganglionic synapses of the sympathetic nervous system.
D) postganglionic synapses of the sympathetic nervous system and the preganglionic synapses of the parasympathetic nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following neurotransmitters undergoes its final synthesis step within synaptic vesicles?
A) ACh
B) norepinephrine
C) epinephrine
D) dopamine
A) ACh
B) norepinephrine
C) epinephrine
D) dopamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Jessica is worried about the impact of her smoking habit on her health.After studying biological psychology,she knows that nicotine would have an effect on
A) her peripheral nervous system only.
B) her central nervous system only.
C) both her peripheral and central nervous systems.
D) neither her peripheral nor central nervous systems,because she only smokes a couple of cigarettes with friends during weekend parties.
A) her peripheral nervous system only.
B) her central nervous system only.
C) both her peripheral and central nervous systems.
D) neither her peripheral nor central nervous systems,because she only smokes a couple of cigarettes with friends during weekend parties.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Muscarinic receptors respond to
A) muscarine,a substance found in tobacco,and acetylcholine.
B) muscarine,a substance found in some mushrooms,and acetylcholine.
C) muscarine,nicotine,and acetylcholine.
D) acetylcholine only.
A) muscarine,a substance found in tobacco,and acetylcholine.
B) muscarine,a substance found in some mushrooms,and acetylcholine.
C) muscarine,nicotine,and acetylcholine.
D) acetylcholine only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The mesolimbic pathway uses the neurotransmitter
A) dopamine,and is important in movement.
B) dopamine,and is important in feelings of reward and addiction.
C) norepinephrine,and is important in vigilance.
D) serotonin,and is important in mood.
A) dopamine,and is important in movement.
B) dopamine,and is important in feelings of reward and addiction.
C) norepinephrine,and is important in vigilance.
D) serotonin,and is important in mood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Genes involved with the development of nicotinic receptors have been linked with increased risk of
A) smoking and lung cancer.
B) use of hallucinogenic mushrooms.
C) depression.
D) attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
A) smoking and lung cancer.
B) use of hallucinogenic mushrooms.
C) depression.
D) attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Cholinergic neurons in the brain are important to which of the following behaviors?
A) regulating mood and appetite
B) processing olfaction
C) learning and memory
D) maintaining homeostasis
A) regulating mood and appetite
B) processing olfaction
C) learning and memory
D) maintaining homeostasis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following neurotransmitters is not a monoamine?
A) serotonin
B) acetylcholine (ACh)
C) dopamine
D) norepinephrine
A) serotonin
B) acetylcholine (ACh)
C) dopamine
D) norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following statements about nicotinic and muscarinic receptors is true?
A) Nicotinic receptors are ionotropic,whereas muscarinic receptors are metabotropic.
B) Nicotinic receptors are metabotropic,whereas muscarinic receptors are ionotropic.
C) Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors are both ionotropic.
D) Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors are both metabotropic.
A) Nicotinic receptors are ionotropic,whereas muscarinic receptors are metabotropic.
B) Nicotinic receptors are metabotropic,whereas muscarinic receptors are ionotropic.
C) Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors are both ionotropic.
D) Nicotinic and muscarinic receptors are both metabotropic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Behaviors involving movement,reinforcement,and planning often involve brain systems that use the neurotransmitter
A) dopamine.
B) norepinephrine.
C) epinephrine.
D) serotonin.
A) dopamine.
B) norepinephrine.
C) epinephrine.
D) serotonin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following neurotransmitters is an indolamine?
A) epinephrine
B) norepinephrine
C) serotonin
D) dopamine
A) epinephrine
B) norepinephrine
C) serotonin
D) dopamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
L-dopa participates in the synthesis of
A) dopamine only.
B) dopamine and epinephrine.
C) dopamine and norepinephrine.
D) dopamine,epinephrine,and norepinephrine.
A) dopamine only.
B) dopamine and epinephrine.
C) dopamine and norepinephrine.
D) dopamine,epinephrine,and norepinephrine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Following release,monoamines are deactivated in the synaptic gap by
A) reuptake.
B) diffusion.
C) enzymes.
D) enzymes and reuptake.
A) reuptake.
B) diffusion.
C) enzymes.
D) enzymes and reuptake.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
During the synthesis of the neurotransmitter _________,a precursor is released from synaptic vesicles back into the intracellular fluid for conversion by the enzyme PNMT.
A) dopamine
B) norepinephrine
C) epinephrine
D) serotonin
A) dopamine
B) norepinephrine
C) epinephrine
D) serotonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Monoamine oxidase would break down all of the following neurotransmitters except
A) serotonin.
B) epinephrine.
C) norepinephrine.
D) acetylcholine (ACh).
A) serotonin.
B) epinephrine.
C) norepinephrine.
D) acetylcholine (ACh).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Rob and his friends were experimenting with the hallucinogenic Amanita mushrooms,and he experienced a sudden drop in blood pressure.Which of the following is the best explanation for Rob's symptoms?
A) The muscarine in the mushrooms interacted with dopaminergic receptors in Rob's peripheral nervous system.
B) The nicotine in the mushrooms interacted with cholinergic receptors in Rob's central nervous system.
C) The muscarine in the mushrooms interacted with cholinergic receptors in Rob's peripheral nervous system.
D) The muscarine in the mushrooms interacted with cholinergic receptors in Rob's central nervous system.
A) The muscarine in the mushrooms interacted with dopaminergic receptors in Rob's peripheral nervous system.
B) The nicotine in the mushrooms interacted with cholinergic receptors in Rob's central nervous system.
C) The muscarine in the mushrooms interacted with cholinergic receptors in Rob's peripheral nervous system.
D) The muscarine in the mushrooms interacted with cholinergic receptors in Rob's central nervous system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements accurately describes the locations of muscarinic and nicotinic receptors?
A) Muscarinic and nicotinic receptors are found in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
B) Muscarinic receptors are found in the central nervous system only,whereas nicotinic receptors are found in the peripheral nervous system only.
C) Nicotinic receptors are found in both the central and peripheral nervous systems,whereas muscarinic receptors are found in the central nervous system only.
D) Muscarinic receptors are found in both the central and peripheral nervous systems,whereas nicotinic receptors are found in the central nervous system only.
A) Muscarinic and nicotinic receptors are found in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
B) Muscarinic receptors are found in the central nervous system only,whereas nicotinic receptors are found in the peripheral nervous system only.
C) Nicotinic receptors are found in both the central and peripheral nervous systems,whereas muscarinic receptors are found in the central nervous system only.
D) Muscarinic receptors are found in both the central and peripheral nervous systems,whereas nicotinic receptors are found in the central nervous system only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The primary source of serotonin in the brain is the
A) substantia nigra.
B) raphe nucleus.
C) locus coeruleus.
D) nucleus accumbens.
A) substantia nigra.
B) raphe nucleus.
C) locus coeruleus.
D) nucleus accumbens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Excess amounts of which of the following neurotransmitters can be toxic to neurons?
A) glutamate
B) GABA
C) dopamine
D) serotonin
A) glutamate
B) GABA
C) dopamine
D) serotonin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The _________ receptor is both voltage-dependent and ligand-dependent?
A) NMDA
B) AMPA
C) kainate
D) muscarinic
A) NMDA
B) AMPA
C) kainate
D) muscarinic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD),people often feel hypervigilant,or unable to relax even when they're in a very safe situation.Which of the following neurotransmitters might be involved in this unusual state?
A) acetylcholine
B) serotonin
C) dopamine
D) norepinephrine
A) acetylcholine
B) serotonin
C) dopamine
D) norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Dopaminergic receptor subtypes are
A) always ionotropic.
B) always metabotropic.
C) metabotropic in systems involved with reward,but ionotropic in systems involved with movement.
D) metabotropic in systems involved with movement,but ionotropic in systems involved with reward.
A) always ionotropic.
B) always metabotropic.
C) metabotropic in systems involved with reward,but ionotropic in systems involved with movement.
D) metabotropic in systems involved with movement,but ionotropic in systems involved with reward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The regulation of sleep,mood,and appetite involve brain systems using the neurotransmitter
A) serotonin.
B) dopamine.
C) norepinephrine.
D) epinephrine.
A) serotonin.
B) dopamine.
C) norepinephrine.
D) epinephrine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Given the typical symptoms of attention deficit disorder (ADHD),including impulsivity,difficulty paying attention,and unusually high levels of motor behavior,which of the following neurotransmitters do you think would be involved?
A) serotonin
B) dopamine
C) norepinephrine
D) epinephrine
A) serotonin
B) dopamine
C) norepinephrine
D) epinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When at rest,the NMDA receptor is blocked by a molecule of
A) sodium.
B) magnesium.
C) potassium.
D) calcium.
A) sodium.
B) magnesium.
C) potassium.
D) calcium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The most frequently used excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system is
A) serotonin.
B) ACh.
C) GABA.
D) glutamate.
A) serotonin.
B) ACh.
C) GABA.
D) glutamate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Tryptophan serves as a precursor in the synthesis of
A) serotonin.
B) dopamine.
C) norepinephrine.
D) epinephrine.
A) serotonin.
B) dopamine.
C) norepinephrine.
D) epinephrine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following neurotransmitters are released by the autonomic nervous system?
A) epinephrine and norepinephrine
B) serotonin and dopamine
C) ACh and dopamine
D) ACh and norepinephrine
A) epinephrine and norepinephrine
B) serotonin and dopamine
C) ACh and dopamine
D) ACh and norepinephrine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The primary source of norepinephrine in the brain is the
A) substantia nigra.
B) raphe nucleus.
C) locus coeruleus.
D) nucleus accumbens.
A) substantia nigra.
B) raphe nucleus.
C) locus coeruleus.
D) nucleus accumbens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Jennifer enjoys Asian food,but carefully avoids the food additive MSG.If she eats it by mistake,she experiences a rapid pulse,chest pain,and nausea.Jennifer's symptoms result from interaction between MSG and which of the following neurotransmitters?
A) GABA
B) glutamate
C) serotonin
D) dopamine
A) GABA
B) glutamate
C) serotonin
D) dopamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The NMDA receptor,kainate receptor,and AMPA receptor all respond to
A) serotonin.
B) epinephrine.
C) glutamate.
D) GABA.
A) serotonin.
B) epinephrine.
C) glutamate.
D) GABA.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Parkinson's disease typically results from degeneration of brain systems using the neurotransmitter
A) dopamine.
B) norepinephrine.
C) epinephrine.
D) serotonin.
A) dopamine.
B) norepinephrine.
C) epinephrine.
D) serotonin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Adrenergic receptor subtypes are
A) always ionotropic.
B) always metabotropic.
C) ionotropic in synapses using norepinephrine and metabotropic in synapses using epinephrine.
D) ionotropic in synapses using epinephrine and metabotropic in synapses using norepinephrine.
A) always ionotropic.
B) always metabotropic.
C) ionotropic in synapses using norepinephrine and metabotropic in synapses using epinephrine.
D) ionotropic in synapses using epinephrine and metabotropic in synapses using norepinephrine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Relative to neurons using other neurotransmitters,serotonergic neurons
A) are quite numerous.
B) are surprisingly few in number.
C) project to very limited parts of the brain.
D) do not have different receptor subtypes.
A) are quite numerous.
B) are surprisingly few in number.
C) project to very limited parts of the brain.
D) do not have different receptor subtypes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
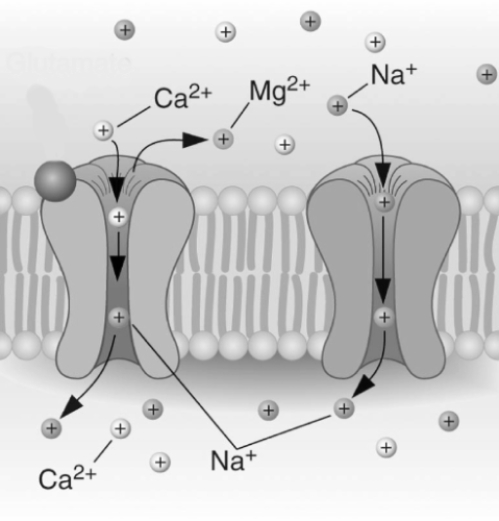 This image illustrates the activation of which of the following types of receptor?
This image illustrates the activation of which of the following types of receptor?A) an NMDA glutamate receptor
B) a kainate glutamate receptor
C) a nicotinic dopamine receptor
D) a GABAA receptor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Due to a very high level of stress and arousal,Kim is having difficulty getting to sleep at night.The activity of which of the following neurotransmitters might be participating in Kim's sleeping problem?
A) norepinephrine
B) acetylcholine
C) dopamine
D) GABA
A) norepinephrine
B) acetylcholine
C) dopamine
D) GABA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
In the human brain,about how many neurons use serotonin as their primary neurotransmitter?
A) 200,000
B) 1 million
C) 200 million
D) 1 billion
A) 200,000
B) 1 million
C) 200 million
D) 1 billion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Within the brain,nitric oxide (NO)
A) does not appear to play an important role in any system.
B) appears to play an important role in regulating breathing and blood pressure.
C) appears to play an important role in higher cognitive functions,such as attention.
D) appears to play an important role in regulating sensory input to the cortex.
A) does not appear to play an important role in any system.
B) appears to play an important role in regulating breathing and blood pressure.
C) appears to play an important role in higher cognitive functions,such as attention.
D) appears to play an important role in regulating sensory input to the cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following neurotransmitters is a byproduct of the energy molecule ATP?
A) glycine
B) GABA
C) glutamate
D) adenosine
A) glycine
B) GABA
C) glutamate
D) adenosine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When NMDA channels are opened,they allow the passage of _________ ions.
A) chloride
B) sodium and chloride
C) calcium
D) sodium and calcium
A) chloride
B) sodium and chloride
C) calcium
D) sodium and calcium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is the true statement about gaseous neurotransmitters?
A) They are contained in synaptic vesicles.
B) They may transfer information from a postsynaptic neuron to a presynaptic neuron.
C) They interact with receptors embedded in neural membranes.
D) They are deactivated by enzymes in the synaptic gap.
A) They are contained in synaptic vesicles.
B) They may transfer information from a postsynaptic neuron to a presynaptic neuron.
C) They interact with receptors embedded in neural membranes.
D) They are deactivated by enzymes in the synaptic gap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Neuropeptides serve as
A) neurotransmitters only.
B) neurotransmitters and neuromodulators,but not neurohormones.
C) neuromodulators and neurohormones,but not neurotransmitters.
D) neurotransmitters,neuromodulators,and neurohormones.
A) neurotransmitters only.
B) neurotransmitters and neuromodulators,but not neurohormones.
C) neuromodulators and neurohormones,but not neurotransmitters.
D) neurotransmitters,neuromodulators,and neurohormones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Adenosine is
A) often found in neurons that also release catecholamines.
B) often found in neurons that also release indoleamines.
C) often found in neurons that also release GABA.
D) never found in neurons that release another type of neurotransmitter.
A) often found in neurons that also release catecholamines.
B) often found in neurons that also release indoleamines.
C) often found in neurons that also release GABA.
D) never found in neurons that release another type of neurotransmitter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The formation of long-term memories may involve
A) dopamine autoreceptors.
B) muscarinic receptors.
C) nicotinic receptors.
D) NMDA receptors.
A) dopamine autoreceptors.
B) muscarinic receptors.
C) nicotinic receptors.
D) NMDA receptors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Viagra and other erectile dysfunction medications usually act by enhancing the activity of
A) substance P.
B) oxytocin.
C) nitric oxide (NO).
D) CCK.
A) substance P.
B) oxytocin.
C) nitric oxide (NO).
D) CCK.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A neuropeptide involved with the perception of pain is
A) substance P.
B) CCK.
C) oxytocin.
D) vasopressin.
A) substance P.
B) CCK.
C) oxytocin.
D) vasopressin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Brad very nearly died after consuming alcohol and barbiturates at a party.Which of the following statements is the best explanation for Brad's close call?
A) He must be allergic to one of these substances or perhaps to both.
B) He is an inexperienced user of barbiturates.
C) Both alcohol and barbiturates interact with the GABAA receptor,producing a dangerous level of central nervous system inhibition.
D) Both alcohol and barbiturates interact with the GABAA receptor,producing a dangerous level of central nervous system excitation.
A) He must be allergic to one of these substances or perhaps to both.
B) He is an inexperienced user of barbiturates.
C) Both alcohol and barbiturates interact with the GABAA receptor,producing a dangerous level of central nervous system inhibition.
D) Both alcohol and barbiturates interact with the GABAA receptor,producing a dangerous level of central nervous system excitation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Zoloft® is a drug that inhibits the reuptake of serotonin.This action makes this drug a(n)_________ for serotonin.
A) antagonist.
B) modulator
C) agonist
D) mimic
A) antagonist.
B) modulator
C) agonist
D) mimic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following neurotransmitters is involved most directly with the perception of pain?
A) GABA
B) glutamate
C) adenosine
D) cholecystokinin
A) GABA
B) glutamate
C) adenosine
D) cholecystokinin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Neurons in the brain that use nitric oxide (NO)are
A) very common,but are found only in the brainstem.
B) very common,and are widely distributed throughout the brain.
C) relatively uncommon,and are scattered throughout the brain.
D) relatively uncommon,and are restricted to the prefrontal cortex.
A) very common,but are found only in the brainstem.
B) very common,and are widely distributed throughout the brain.
C) relatively uncommon,and are scattered throughout the brain.
D) relatively uncommon,and are restricted to the prefrontal cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Adenosine often acts to _________ of other neurotransmitters.
A) stimulate the release
B) inhibit the release
C) inhibit the reuptake
D) enhance the reuptake
A) stimulate the release
B) inhibit the release
C) inhibit the reuptake
D) enhance the reuptake

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Glutamate can be toxic to neurons because
A) NMDA receptors allow calcium into a cell,and excess calcium can stimulate harmful levels of enzyme activity.
B) NMDA receptors block the movement of calcium into a cell,preventing the release of other neurotransmitters.
C) it blocks receptors for other types of neurotransmitters,preventing effective communication between cells.
D) its breakdown in the synaptic gap produces harmful free radicals.
A) NMDA receptors allow calcium into a cell,and excess calcium can stimulate harmful levels of enzyme activity.
B) NMDA receptors block the movement of calcium into a cell,preventing the release of other neurotransmitters.
C) it blocks receptors for other types of neurotransmitters,preventing effective communication between cells.
D) its breakdown in the synaptic gap produces harmful free radicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Your friend has a prescription for Valium that she takes for anxiety.She has taken Valium before the party you and she are attending.When she gets to the party,you see her heading for the bar.Based on what you have learned so far in this course,which of the following would you tell her?
A) You should probably not drink any alcohol because both alcohol and Valium act on the same system and their additive effects could be very dangerous.
B) You should limit yourself to six drinks because too much of the two drugs together could make you very ill.
C) Alcohol is not a drug,so there really isn't any reason to worry as long as you don't get drunk.
D) Don't worry,alcohol and valium act on very different neurotransmitters,so a drug interaction is very unlikely.
A) You should probably not drink any alcohol because both alcohol and Valium act on the same system and their additive effects could be very dangerous.
B) You should limit yourself to six drinks because too much of the two drugs together could make you very ill.
C) Alcohol is not a drug,so there really isn't any reason to worry as long as you don't get drunk.
D) Don't worry,alcohol and valium act on very different neurotransmitters,so a drug interaction is very unlikely.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Endogenous morphines (endorphins)are examples of
A) monoamines.
B) catecholamines.
C) indolamines.
D) neuropeptides.
A) monoamines.
B) catecholamines.
C) indolamines.
D) neuropeptides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If a drug blocks the action of acetylcholinesterase,it will serve as a(n)_________ for acetylcholine.
A) antagonist
B) modulator
C) agonist
D) mimic
A) antagonist
B) modulator
C) agonist
D) mimic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Which of the following substances is not a neuropeptide?
A) oxytocin
B) adenosine
C) vasopressin
D) insulin
A) oxytocin
B) adenosine
C) vasopressin
D) insulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The major inhibitory neurotransmitter of the central nervous system is
A) glutamate.
B) GABA.
C) serotonin.
D) acetylcholine (ACh).
A) glutamate.
B) GABA.
C) serotonin.
D) acetylcholine (ACh).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 191 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



