Deck 9: Long-Run Economic Growth
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/298
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Long-Run Economic Growth
1
Suppose that a panel of economists predicts that a nation's real GDP per capita will have an average annual growth rate of 2%.According to the rule of 70,how many years will it take for this nation's real GDP per capita to double?
A) 35
B) 70
C) 140
D) 20
A) 35
B) 70
C) 140
D) 20
35
2
Economists use real GDP per capita to measure economic growth:
A) because it ignores the effect of price changes.
B) because poor nations have a large population and the population of richer nations is declining.
C) because it is the inflation-adjusted value of a country's production of goods and services corrected for the change in a country's population.
D) even though nominal GNP per capita is a far superior measure of economic growth.
A) because it ignores the effect of price changes.
B) because poor nations have a large population and the population of richer nations is declining.
C) because it is the inflation-adjusted value of a country's production of goods and services corrected for the change in a country's population.
D) even though nominal GNP per capita is a far superior measure of economic growth.
because it is the inflation-adjusted value of a country's production of goods and services corrected for the change in a country's population.
3
Output per capita in Canada in 2015 was about _____ as high as it was in 1900.
A) twice
B) 3 times
C) 9 times
D) 10 times
A) twice
B) 3 times
C) 9 times
D) 10 times
9 times
4
The standard of living in a country can be BEST measured by:
A) nominal GDP per capita.
B) real GDP per capita.
C) the productivity growth rate.
D) the business cycles.
A) nominal GDP per capita.
B) real GDP per capita.
C) the productivity growth rate.
D) the business cycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Real GDP per capita in Canada increased almost _____ times between 1900 and 2016.
A) 2
B) 3
C) 8
D) 10
A) 2
B) 3
C) 8
D) 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
China has much higher rate of growth than Canada,but the average Chinese household is _____ a typical Canadian household.China's real GDP per capita is _____ that of Canada.
A) as well off as;catching up with
B) richer than;much higher than
C) still a bit poorer than;catching up with
D) still far poorer than;much lower than
A) as well off as;catching up with
B) richer than;much higher than
C) still a bit poorer than;catching up with
D) still far poorer than;much lower than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The rule of 70 indicates that a 6% annual increase in the level of real GDP would lead to the output doubling in approximately _____ years.
A) 6
B) 12
C) 24
D) 30
A) 6
B) 12
C) 24
D) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which factor is the MOST widely accepted measure of economic growth over time?
A) inflation
B) increases in real per capita GDP
C) decline in real interest rates
D) increases in the available labour supply
A) inflation
B) increases in real per capita GDP
C) decline in real interest rates
D) increases in the available labour supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the following to answer questions: 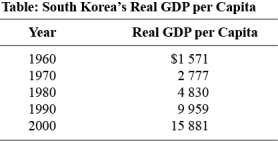
(Table: South Korea's Real GDP per Capita)Use Table: South Korea's Real GDP per Capita.As a percentage of real GDP per capita in 2000,approximately how much did South Korea produce in 1960?
A) 10%
B) 15%
C) 151%
D) 1 011%

(Table: South Korea's Real GDP per Capita)Use Table: South Korea's Real GDP per Capita.As a percentage of real GDP per capita in 2000,approximately how much did South Korea produce in 1960?
A) 10%
B) 15%
C) 151%
D) 1 011%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The BEST available measure of the standard of living in a country is:
A) nominal GDP per capita.
B) real GDP per capita.
C) the unemployment rate.
D) the growth rate of productivity.
A) nominal GDP per capita.
B) real GDP per capita.
C) the unemployment rate.
D) the growth rate of productivity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Canadian real GDP per capita in 2015 was _____% as much per person as it was in 1900.
A) 16
B) 189
C) 46
D) 905
A) 16
B) 189
C) 46
D) 905

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The rule of 70 states that a variable's approximate doubling time equals:
A) 70 times the growth rate.
B) the growth rate divided by 70.
C) 70 divided by the doubling time.
D) 70 divided by the growth rate.
A) 70 times the growth rate.
B) the growth rate divided by 70.
C) 70 divided by the doubling time.
D) 70 divided by the growth rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a country has a population of 1 000 people,an area of 100 square miles,and a GDP of $5 million,then its GDP per capita is:
A) $500.
B) $5 000.
C) $50 000.
D) $5 million.
A) $500.
B) $5 000.
C) $50 000.
D) $5 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A key input for measuring economic growth is:
A) the size of the government's budget.
B) real GDP per capita.
C) life expectancy.
D) the S&P/TSX Composite Index.
A) the size of the government's budget.
B) real GDP per capita.
C) life expectancy.
D) the S&P/TSX Composite Index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Today,more than _____ of the world's population lives in countries poorer than Canada was a century ago.
A) one-fifth
B) one-third
C) one-quarter
D) two-fifths
A) one-fifth
B) one-third
C) one-quarter
D) two-fifths

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The key measure used to track economic growth is:
A) real GDP per capita.
B) nominal GDP.
C) real GDP.
D) nominal GDP per capita.
A) real GDP per capita.
B) nominal GDP.
C) real GDP.
D) nominal GDP per capita.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In an economy whose aggregate real output is growing faster than the total population:
A) real GDP per capita is rising.
B) standard of living is declining.
C) national income is falling.
D) nominal GDP per capita is decreasing.
A) real GDP per capita is rising.
B) standard of living is declining.
C) national income is falling.
D) nominal GDP per capita is decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A typical family in Canada in 1900 had a purchasing power equal to _____% of the real Canadian GDP per capita in 2015.
A) 1
B) 11
C) 70
D) 136
A) 1
B) 11
C) 70
D) 136

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Suppose that a panel of economists predicts that a nation's real GDP per capita will double in approximately 20 years.According to the rule of 70,what must be the predicted annual growth rate of real GDP per capita?
A) 140%
B) 3.5%
C) 2.85%
D) 14%
A) 140%
B) 3.5%
C) 2.85%
D) 14%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Table: South Korea's Real GDP per Capita)Use Table: South Korea's Real GDP per Capita.As a percentage of real GDP per capita in 1960,approximately how much did South Korea produce in 2000?
A) 10%
B) 15%
C) 151%
D) 1 011%

(Table: South Korea's Real GDP per Capita)Use Table: South Korea's Real GDP per Capita.As a percentage of real GDP per capita in 1960,approximately how much did South Korea produce in 2000?
A) 10%
B) 15%
C) 151%
D) 1 011%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The formula for the rule of 70,where n is number of years and r is growth rate,is expressed as:
A) n * 70 = r.
B) n / r = 70.
C) r / n = 70.
D) n * r = 70.
A) n * 70 = r.
B) n / r = 70.
C) r / n = 70.
D) n * r = 70.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If real GDP grows at an annual rate of 1%,it will double in approximately _____ years.
A) 11
B) 23
C) 35
D) 70
A) 11
B) 23
C) 35
D) 70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose that real GDP per capita of Canada is $32 000 and its growth rate is 2% per year and that real GDP per capita of China is $4 000,and its annual growth rate is 7%.How many years will it take for China's real GDP per capita to be larger than real GDP per capita in Canada?
A) 70-75 years
B) 40-45 years
C) 15-20 years
D) 5-10 years
A) 70-75 years
B) 40-45 years
C) 15-20 years
D) 5-10 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
India is growing at a rate of 9% per year,and its real GDP per capita is about $3 500,while Canada is growing at a rate of 3% per year,and its real GDP per capita is about $47 000.How long will it take India to double its real GDP per capita?
A) 7.8 years
B) 10.2 years
C) 14.6 years
D) 90 years
A) 7.8 years
B) 10.2 years
C) 14.6 years
D) 90 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
There are two countries on a peninsula.The first has a per capita annual growth rate of 2%,and its neighbour to the south has an annual growth rate of 5%.How much sooner will the country in the south double its GDP per capita than will its neighbour in the north?
A) 5 years
B) 10 years
C) 15 years
D) 21 years
A) 5 years
B) 10 years
C) 15 years
D) 21 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Suppose that real GDP per capita of Canada is $32 000 and its growth rate is 2% per year and that real GDP per capita of China is $4 000,and its annual growth rate is 7%.According to the rule of 70,how large will China's real GDP per capita be in 20 years?
A) $5 600
B) $8 000
C) $16 000
D) $28 000
A) $5 600
B) $8 000
C) $16 000
D) $28 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
India is growing at a rate of 9% per year,and its real GDP per capita is about $3 500,while Canada is growing at a rate of 3% per year,and its real GDP per capita is about $47 000.About how much will India's real GDP per capita be in 20 years?
A) approximately $20 000
B) approximately $56 000
C) approximately $14 000
D) approximately $30 000
A) approximately $20 000
B) approximately $56 000
C) approximately $14 000
D) approximately $30 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose that real GDP per capita of Canada is $32 000 and its growth rate is 2% per year and that real GDP per capita of China is $4 000,and its annual growth rate is 7%.How long will it take real GDP per capita of Canada to double?
A) 35 years
B) 50 years
C) 2.25 years
D) 14 years
A) 35 years
B) 50 years
C) 2.25 years
D) 14 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
India is growing at a rate of 9% per year,and its real GDP per capita is about $3 500,while Canada is growing at a rate of 3% per year,and its real GDP per capita is about $47 000.How long will it take Canada to double its real GDP per capita?
A) 10.5 years
B) 23.3 years
C) 30 years
D) 50 years
A) 10.5 years
B) 23.3 years
C) 30 years
D) 50 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
India is growing at a rate of 9% per year,and its real GDP per capita is about $3 500,while Canada is growing at a rate of 3% per year,and its real GDP per capita is about $47 000.About how much will Canadian real GDP per capita be in 14 years?
A) $71 000
B) $28 000
C) $112 000
D) $224 000
A) $71 000
B) $28 000
C) $112 000
D) $224 000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose that real GDP per capita of Canada is $32 000 and its growth rate is 2% per year and that real GDP per capita of China is $4 000,and its annual growth rate is 7%.How long will it take China's real GDP per capita to double?
A) 14 years
B) 10 years
C) 35 years
D) 50 years
A) 14 years
B) 10 years
C) 35 years
D) 50 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If real GDP doubles in 35 years,its average annual growth rate is approximately:
A) 1%.
B) 2%.
C) 3%.
D) 4%.
A) 1%.
B) 2%.
C) 3%.
D) 4%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If real GDP per capita grows at 5% per year consistently over time,how many years will it take for it to double?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 14
D) 70
A) 5
B) 10
C) 14
D) 70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
According to the rule of 70,if a country doubles its real GDP per capita every 20 years,that country must be growing at an annual rate of:
A) 2%.
B) 3.5%.
C) 35%.
D) 70%.
A) 2%.
B) 3.5%.
C) 35%.
D) 70%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The rule of 70 states that:
A) the average score on standardized tests is normally distributed with a mean of 70 and a standard deviation of 10.
B) everyone should retire by age 70.
C) the number of years for a variable to double equals 70 divided by its annual growth rate.
D) Pension benefits should increase when people reach 70.
A) the average score on standardized tests is normally distributed with a mean of 70 and a standard deviation of 10.
B) everyone should retire by age 70.
C) the number of years for a variable to double equals 70 divided by its annual growth rate.
D) Pension benefits should increase when people reach 70.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If real GDP grows at an average rate of 3% per year,it will double in _____ years.
A) less than 10
B) approximately 17
C) approximately 23
D) approximately 36
A) less than 10
B) approximately 17
C) approximately 23
D) approximately 36

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Real GDP per capita,growing at a constant rate over a 35-year period,has doubled at the end of that period.What must the annual growth rate of real GDP per capita be for this economy?
A) 1%
B) 2%
C) 4%
D) 15%
A) 1%
B) 2%
C) 4%
D) 15%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If output is growing at 5% annually,how many years will it take for output to quadruple?
A) 14 years
B) 10 years
C) 20 years
D) 28 years
A) 14 years
B) 10 years
C) 20 years
D) 28 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The rule of 70 is MOST useful in:
A) identifying the causes of economic growth.
B) identifying the sources of economic growth.
C) estimating the productivity of labour.
D) estimating the doubling time of real GDP for a given growth rate.
A) identifying the causes of economic growth.
B) identifying the sources of economic growth.
C) estimating the productivity of labour.
D) estimating the doubling time of real GDP for a given growth rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If real GDP doubles in 12 years,its average annual growth rate is approximately:
A) 6%.
B) 5%.
C) 4%.
D) 3%.
A) 6%.
B) 5%.
C) 4%.
D) 3%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010)Use Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010.Aggregate output per capita at the beginning of 2010 was:
A) $5 000.
B) $10 000.
C) $775.
D) $7 750.

(Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010)Use Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010.Aggregate output per capita at the beginning of 2010 was:
A) $5 000.
B) $10 000.
C) $775.
D) $7 750.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010)Use Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010.Aggregate output at the end of 2010,assuming no changes in the price level,was about:
A) $326 billion.
B) $32.612 billion.
C) $3 635 billion.
D) $6 500 billion.

(Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010)Use Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010.Aggregate output at the end of 2010,assuming no changes in the price level,was about:
A) $326 billion.
B) $32.612 billion.
C) $3 635 billion.
D) $6 500 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The Rule of 70 applies:
A) only to GDP.
B) only to GDP per capita.
C) to any growth rate.
D) only to developed countries.
A) only to GDP.
B) only to GDP per capita.
C) to any growth rate.
D) only to developed countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
To find the approximate number of years it takes the economy to double:
A) divide its growth rate by 70.
B) divide 70 by its growth rate.
C) divide its growth rate by 100.
D) multiply its growth rate by 20.
A) divide its growth rate by 70.
B) divide 70 by its growth rate.
C) divide its growth rate by 100.
D) multiply its growth rate by 20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
According to the rule of 70,if real GDP per capita is growing at 2% a year,in 100 years it will have increased by:
A) about 4 times.
B) about 7 times.
C) almost 30 times.
D) almost 60 times.
A) about 4 times.
B) about 7 times.
C) almost 30 times.
D) almost 60 times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Over the course of the twentieth century,real GDP per capita in Canada rose MOSTLY as a result of:
A) rising population.
B) rising employment.
C) rising productivity.
D) reduced vacation time.
A) rising population.
B) rising employment.
C) rising productivity.
D) reduced vacation time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
From 2010 to 2011,nation A's real GDP increased from $100 billion to $106 billion and its population grew from 50 million to 51 million.Its annual growth rate in real GDP per capita was approximately _____%.
A) 1
B) -3
C) 4
D) 6
A) 1
B) -3
C) 4
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
According to the rule of 70,if a country's real GDP per capita grows at an annual rate of 2% instead of 3%,it will take _____ additional years for that country to double its level of real GDP per capita.
A) 35
B) 11.67
C) 23.3
D) 30
A) 35
B) 11.67
C) 23.3
D) 30

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010)Use Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010.The population at the end of 2010 was about:
A) 400 million.
B) 41 million.
C) 14 million.
D) 401 million.

(Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010)Use Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010.The population at the end of 2010 was about:
A) 400 million.
B) 41 million.
C) 14 million.
D) 401 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Productivity is declining when:
A) the number of hours worked exceeds the number of workers.
B) population growth exceeds real GDP growth.
C) the ratio of adult civilians employed outside the home rises.
D) real GDP growth exceeds the population growth.
A) the number of hours worked exceeds the number of workers.
B) population growth exceeds real GDP growth.
C) the ratio of adult civilians employed outside the home rises.
D) real GDP growth exceeds the population growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Economists say that long-run economic growth is almost entirely due to:
A) rising productivity.
B) population growth.
C) a democratically elected government.
D) a balanced budget.
A) rising productivity.
B) population growth.
C) a democratically elected government.
D) a balanced budget.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Long-run economic growth depends almost entirely on:
A) labour productivity growth.
B) population growth.
C) agricultural production growth.
D) the number of hours worked.
A) labour productivity growth.
B) population growth.
C) agricultural production growth.
D) the number of hours worked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which country had the LOWEST growth rate of real GDP per capita between 1980 and 2015?
A) Ireland
B) France
C) Argentina
D) Zimbabwe
A) Ireland
B) France
C) Argentina
D) Zimbabwe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
From 2010 to 2011,nation A's real GDP increased from $100 billion to $106 billion and its population grew from 50 million to 51 million.As a result,real GDP per capita _____ because real GDP rose _____ than the population.
A) increased;more slowly
B) increased;faster
C) decreased;more slowly
D) decreased;faster
A) increased;more slowly
B) increased;faster
C) decreased;more slowly
D) decreased;faster

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Productivity is equal to:
A) real GDP divided by the number of workers.
B) real GDP divided by the population.
C) the number of workers per machine.
D) the total output produced.
A) real GDP divided by the number of workers.
B) real GDP divided by the population.
C) the number of workers per machine.
D) the total output produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which change would contribute to a nation's rapid long-run economic growth?
A) faster technological progress
B) faster population growth
C) less physical capital per worker
D) lower levels of average human capital
A) faster technological progress
B) faster population growth
C) less physical capital per worker
D) lower levels of average human capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Labour productivity growth can be attributed to:
A) improvement in technology.
B) a decline in university attendance.
C) an increase in population growth.
D) a decline in the physical capital per worker.
A) improvement in technology.
B) a decline in university attendance.
C) an increase in population growth.
D) a decline in the physical capital per worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010)Use Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010.Aggregate output per capita at the end of 2010,assuming no changes in the price level,was:
A) $7 000.
B) $7 005.
C) $795.
D) $7 490.

(Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010)Use Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010.Aggregate output per capita at the end of 2010,assuming no changes in the price level,was:
A) $7 000.
B) $7 005.
C) $795.
D) $7 490.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010)Use Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010.During 2010,assuming no changes in the price level,aggregate output per capita in Kenya grew at a rate of:
A) 0.6%.
B) 2.6%.
C) 5.2%.
D) 7.8%.

(Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010)Use Table: Kenya's Economy in 2010.During 2010,assuming no changes in the price level,aggregate output per capita in Kenya grew at a rate of:
A) 0.6%.
B) 2.6%.
C) 5.2%.
D) 7.8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which country had the FASTEST growth rate of real GDP per capita between 1980 and 2015?
A) Canada
B) Ireland
C) China
D) France
A) Canada
B) Ireland
C) China
D) France

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Human capital refers to:
A) output per worker.
B) the education and knowledge embodied in the workforce.
C) society's investment in capital goods.
D) people working with capital goods.
A) output per worker.
B) the education and knowledge embodied in the workforce.
C) society's investment in capital goods.
D) people working with capital goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The MOST important driver for economic growth appears to be:
A) increase in physical capital.
B) increase in human capital.
C) technological progress.
D) foreign investment.
A) increase in physical capital.
B) increase in human capital.
C) technological progress.
D) foreign investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
For developed countries,which factor is considered the MOST important driver in productivity growth?
A) the level of educational attainment
B) the amount of physical capital
C) technological progress
D) the abundance of natural resources
A) the level of educational attainment
B) the amount of physical capital
C) technological progress
D) the abundance of natural resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which factor will NOT increase labour's productivity?
A) education
B) technology
C) new capital
D) growth in the population
A) education
B) technology
C) new capital
D) growth in the population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A reason that does NOT explain why average workers in Canada today produce more than their counterparts did a century ago is that the modern worker:
A) is better educated.
B) has more physical capital to work with.
C) has better technology to work with.
D) works longer hours.
A) is better educated.
B) has more physical capital to work with.
C) has better technology to work with.
D) works longer hours.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An example of human capital is a person's:
A) money.
B) job skills.
C) capital goods or machines.
D) stocks and bonds.
A) money.
B) job skills.
C) capital goods or machines.
D) stocks and bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Workers today are more productive than workers were in the past because:
A) they now are physically stronger on average.
B) they now have more physical capital embodying better technology.
C) more of them use the same number of machines as in the past.
D) they are paid more.
A) they now are physically stronger on average.
B) they now have more physical capital embodying better technology.
C) more of them use the same number of machines as in the past.
D) they are paid more.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The skills,training,and education possessed by workers that contribute to economic growth are known as:
A) saving.
B) human capital.
C) natural resources.
D) output of labour.
A) saving.
B) human capital.
C) natural resources.
D) output of labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Human capital is:
A) the improvement in labour made possible by education and knowledge that is embodied in the workforce.
B) the machinery and tools that each worker owns.
C) robots that can perform tasks that only humans could do in the past.
D) not as important as physical capital.
A) the improvement in labour made possible by education and knowledge that is embodied in the workforce.
B) the machinery and tools that each worker owns.
C) robots that can perform tasks that only humans could do in the past.
D) not as important as physical capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which change will NOT increase the productivity of labour?
A) technological improvements
B) an increase in the capital stock
C) improvements in education
D) an increase in the size of the labour force
A) technological improvements
B) an increase in the capital stock
C) improvements in education
D) an increase in the size of the labour force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Rising high school graduation rates are an example of an increase in:
A) technological progress.
B) human capital.
C) population stock.
D) fertility rates.
A) technological progress.
B) human capital.
C) population stock.
D) fertility rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Physical capital includes:
A) a worker's education or knowledge.
B) machine tools.
C) money.
D) shares of stock.
A) a worker's education or knowledge.
B) machine tools.
C) money.
D) shares of stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If technology advances:
A) more output can be obtained from the same inputs.
B) more inputs are needed to produce the same output.
C) less output can be obtained from the same inputs.
D) less output can be produced even with more inputs.
A) more output can be obtained from the same inputs.
B) more inputs are needed to produce the same output.
C) less output can be obtained from the same inputs.
D) less output can be produced even with more inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
To acquire human capital a person would:
A) save to buy a printing press.
B) purchase a printing press rather than a very large television.
C) learn to use a printing press.
D) sell the books that the printing press produces.
A) save to buy a printing press.
B) purchase a printing press rather than a very large television.
C) learn to use a printing press.
D) sell the books that the printing press produces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
An example of physical capital is a:
A) truck that a company purchases for deliveries.
B) worker who physically learns to work on a truck his company buys.
C) truck that a worker buys for personal use.
D) a truck a company purchases for work,a worker who physically learns to work on a truck his company buys,or a truck a worker buys for personal use.
A) truck that a company purchases for deliveries.
B) worker who physically learns to work on a truck his company buys.
C) truck that a worker buys for personal use.
D) a truck a company purchases for work,a worker who physically learns to work on a truck his company buys,or a truck a worker buys for personal use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The improvement in labour made possible by education and knowledge that is embodied in the work force is known as _____ capital.
A) physical
B) human
C) financial
D) real
A) physical
B) human
C) financial
D) real

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If technology advances:
A) GDP per capita declines.
B) physical capital is less productive.
C) workers can produce more with fixed amounts of physical and human capital.
D) human capital is less useful.
A) GDP per capita declines.
B) physical capital is less productive.
C) workers can produce more with fixed amounts of physical and human capital.
D) human capital is less useful.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A factor that does NOT drive productivity growth is:
A) growth convergence.
B) physical capital.
C) technological progress.
D) human capital.
A) growth convergence.
B) physical capital.
C) technological progress.
D) human capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Technological progress allows workers to produce more:
A) because it increases the amount of physical capital available.
B) because it increases the amount of human capital available.
C) even when the amount of physical capital and human capital do not change.
D) only if the amount of physical capital grows at the same rate.
A) because it increases the amount of physical capital available.
B) because it increases the amount of human capital available.
C) even when the amount of physical capital and human capital do not change.
D) only if the amount of physical capital grows at the same rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The term human capital describes improvement:
A) made possible by better machines and equipment.
B) in the technology available to the work force.
C) in a worker's skills made possible by education,training,and knowledge.
D) in the robotics technology that can substitute for a human worker.
A) made possible by better machines and equipment.
B) in the technology available to the work force.
C) in a worker's skills made possible by education,training,and knowledge.
D) in the robotics technology that can substitute for a human worker.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 298 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



