Deck 2: Data Mining: a Closer Look
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/16
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Data Mining: a Closer Look
1
Use the three-class confusion matrix below to answer questions 1 through 3.
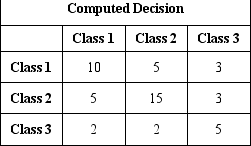
How many class 2 instances are in the dataset?

How many class 2 instances are in the dataset?
23
2
The average positive difference between computed and desired outcome values.
A) root mean squared error
B) mean squared error
C) mean absolute error
D) mean positive error
A) root mean squared error
B) mean squared error
C) mean absolute error
D) mean positive error
C
3
Another name for an output attribute.
A) predictive variable
B) independent variable
C) estimated variable
D) dependent variable
A) predictive variable
B) independent variable
C) estimated variable
D) dependent variable
D
4
Classification problems are distinguished from estimation problems in that
A) classification problems require the output attribute to be numeric.
B) classification problems require the output attribute to be categorical.
C) classification problems do not allow an output attribute.
D) classification problems are designed to predict future outcome.
A) classification problems require the output attribute to be numeric.
B) classification problems require the output attribute to be categorical.
C) classification problems do not allow an output attribute.
D) classification problems are designed to predict future outcome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which statement about outliers is true?
A) Outliers should be identified and removed from a dataset.
B) Outliers should be part of the training dataset but should not be present in the test data.
C) Outliers should be part of the test dataset but should not be present in the training data.
D) The nature of the problem determines how outliers are used.
E) More than one of a,b,c or d is true.
A) Outliers should be identified and removed from a dataset.
B) Outliers should be part of the training dataset but should not be present in the test data.
C) Outliers should be part of the test dataset but should not be present in the training data.
D) The nature of the problem determines how outliers are used.
E) More than one of a,b,c or d is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Use the confusion matrix for Model X and confusion matrix for Model Y to answer questions 4 through 6.
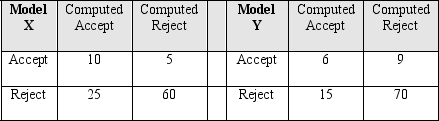
Compute the lift for Model Y.

Compute the lift for Model Y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the confusion matrix for Model X and confusion matrix for Model Y to answer questions 4 through 6.

You will notice that the lift for both models is the same. Assume that the cost of a false reject is significantly higher than the cost of a false accept. Which model is the better choice?
Answers to Chapter 2 Questions
Multiple Choice Questions

You will notice that the lift for both models is the same. Assume that the cost of a false reject is significantly higher than the cost of a false accept. Which model is the better choice?
Answers to Chapter 2 Questions
Multiple Choice Questions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Assume that we have a dataset containing information about 200 individuals. One hundred of these individuals have purchased life insurance. A supervised data mining session has discovered the following rule: IF age < 30 & credit card insurance = yes
THEN life insurance = yes
Rule Accuracy: 70%
Rule Coverage: 63%
How many individuals in the class life insurance= no have credit card insurance and are less than 30 years old?
A) 63
B) 70
C) 30
D) 27
THEN life insurance = yes
Rule Accuracy: 70%
Rule Coverage: 63%
How many individuals in the class life insurance= no have credit card insurance and are less than 30 years old?
A) 63
B) 70
C) 30
D) 27

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Use the three-class confusion matrix below to answer questions 1 through 3.

What percent of the instances were correctly classified?

What percent of the instances were correctly classified?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which statement is true about neural network and linear regression models?
A) Both models require input attributes to be numeric.
B) Both models require numeric attributes to range between 0 and 1.
C) The output of both models is a categorical attribute value.
D) Both techniques build models whose output is determined by a linear sum of weighted input attribute values.
E) More than one of a,b,c or d is true.
A) Both models require input attributes to be numeric.
B) Both models require numeric attributes to range between 0 and 1.
C) The output of both models is a categorical attribute value.
D) Both techniques build models whose output is determined by a linear sum of weighted input attribute values.
E) More than one of a,b,c or d is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Unlike traditional production rules, association rules
A) allow the same variable to be an input attribute in one rule and an output attribute in another rule.
B) allow more than one input attribute in a single rule.
C) require input attributes to take on numeric values.
D) require each rule to have exactly one categorical output attribute.
A) allow the same variable to be an input attribute in one rule and an output attribute in another rule.
B) allow more than one input attribute in a single rule.
C) require input attributes to take on numeric values.
D) require each rule to have exactly one categorical output attribute.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which statement is true about prediction problems?
A) The output attribute must be categorical.
B) The output attribute must be numeric.
C) The resultant model is designed to determine future outcomes.
D) The resultant model is designed to classify current behavior.
A) The output attribute must be categorical.
B) The output attribute must be numeric.
C) The resultant model is designed to determine future outcomes.
D) The resultant model is designed to classify current behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the confusion matrix for Model X and confusion matrix for Model Y to answer questions 4 through 6.

How many instances were classified as an accept by Model X?

How many instances were classified as an accept by Model X?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Use the three-class confusion matrix below to answer questions 1 through 3.

How many instances were incorrectly classified with class 3?

How many instances were incorrectly classified with class 3?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is a common use of unsupervised clustering?
A) detect outliers
B) determine a best set of input attributes for supervised learning
C) evaluate the likely performance of a supervised learner model
D) determine if meaningful relationships can be found in a dataset
E) All of a,b,c, and d are common uses of unsupervised clustering.
A) detect outliers
B) determine a best set of input attributes for supervised learning
C) evaluate the likely performance of a supervised learner model
D) determine if meaningful relationships can be found in a dataset
E) All of a,b,c, and d are common uses of unsupervised clustering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Given desired class C and population P, lift is defined as
A) the probability of class C given population P divided by the probability of C given a sample taken from the population.
B) the probability of population P given a sample taken from P.
C) the probability of class C given a sample taken from population P.
D) the probability of class C given a sample taken from population P divided by the probability of C within the entire population P.
A) the probability of class C given population P divided by the probability of C given a sample taken from the population.
B) the probability of population P given a sample taken from P.
C) the probability of class C given a sample taken from population P.
D) the probability of class C given a sample taken from population P divided by the probability of C within the entire population P.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 16 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



