Deck 10: Statistical Techniques
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/13
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Statistical Techniques
1
This technique associates a conditional probability value with each data instance.
A) linear regression
B) logistic regression
C) simple regression
D) multiple linear regression
A) linear regression
B) logistic regression
C) simple regression
D) multiple linear regression
B
2
Logistic regression is a ________ regression technique that is used to model data having a _____outcome.
A) linear, numeric
B) linear, binary
C) nonlinear, numeric
D) nonlinear, binary
A) linear, numeric
B) linear, binary
C) nonlinear, numeric
D) nonlinear, binary
D
3
The leaf nodes of a model tree are
A) averages of numeric output attribute values.
B) nonlinear regression equations.
C) linear regression equations.
D) sums of numeric output attribute values.
A) averages of numeric output attribute values.
B) nonlinear regression equations.
C) linear regression equations.
D) sums of numeric output attribute values.
C
4
The probability of a hypothesis before the presentation of evidence.
A) a priori
B) subjective
C) posterior
D) conditional
A) a priori
B) subjective
C) posterior
D) conditional

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
This clustering algorithm merges and splits nodes to help modify nonoptimal partitions.
A) agglomerative clustering
B) expectation maximization
C) conceptual clustering
D) K-Means clustering
A) agglomerative clustering
B) expectation maximization
C) conceptual clustering
D) K-Means clustering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
This supervised learning technique can process both numeric and categorical input attributes.
A) linear regression
B) Bayes classifier
C) logistic regression
D) backpropagation learning
A) linear regression
B) Bayes classifier
C) logistic regression
D) backpropagation learning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Simple regression assumes a __________ relationship between the input attribute and output attribute.
A) linear
B) quadratic
C) reciprocal
D) inverse
A) linear
B) quadratic
C) reciprocal
D) inverse

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Regression trees are often used to model _______ data.
A) linear
B) nonlinear
C) categorical
D) symmetrical
A) linear
B) nonlinear
C) categorical
D) symmetrical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Machine learning techniques differ from statistical techniques in that machine learning methods
A) typically assume an underlying distribution for the data.
B) are better able to deal with missing and noisy data.
C) are not able to explain their behavior.
D) have trouble with large-sized datasets.
A) typically assume an underlying distribution for the data.
B) are better able to deal with missing and noisy data.
C) are not able to explain their behavior.
D) have trouble with large-sized datasets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
This unsupervised clustering algorithm terminates when mean values computed for the current iteration of the algorithm are identical to the computed mean values for the previous iteration.
A) agglomerative clustering
B) conceptual clustering
C) K-Means clustering
D) expectation maximization
A) agglomerative clustering
B) conceptual clustering
C) K-Means clustering
D) expectation maximization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
This clustering algorithm initially assumes that each data instance represents a single cluster.
A) agglomerative clustering
B) conceptual clustering
C) K-Means clustering
D) expectation maximization
A) agglomerative clustering
B) conceptual clustering
C) K-Means clustering
D) expectation maximization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
With Bayes classifier, missing data items are
A) treated as equal compares.
B) treated as unequal compares.
C) replaced with a default value.
D) ignored.
A) treated as equal compares.
B) treated as unequal compares.
C) replaced with a default value.
D) ignored.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The table below contains counts and ratios for a set of data instances to be used for supervised Bayesian learning. The output attribute is sex with possible values male and female. Consider an individual who has said no to the life insurance promotion, yes to the magazine promotion, yes to the watch promotion and has credit card insurance. Use the values in the table together with Bayes classifier to determine which of a,b,c or d represents the probability that this individual is male. 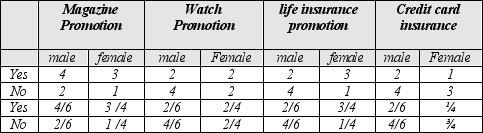
A) 4/6) 2/6) 2/6) 2/6) 6/10) / PE)
B) 4/6) 2/6) 3/4) 2/6) 3/4) / PE)
C) 4/6) 2/6) 4/6) 2/6) 6/10) / PE)
D) 2/6) 4/6) 4/6) 2/6) 4/10) / PE)

A) 4/6) 2/6) 2/6) 2/6) 6/10) / PE)
B) 4/6) 2/6) 3/4) 2/6) 3/4) / PE)
C) 4/6) 2/6) 4/6) 2/6) 6/10) / PE)
D) 2/6) 4/6) 4/6) 2/6) 4/10) / PE)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



