Deck 19: Fluid, electrolyte, and Acidbase Imbalances
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/22
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Fluid, electrolyte, and Acidbase Imbalances
1
What is the most reliable index of volume status when caring for a patient with a fluid imbalance?
A) Skin turgor
B) Presence of edema
C) Hourly urinary output
D) Daily weight patterns
A) Skin turgor
B) Presence of edema
C) Hourly urinary output
D) Daily weight patterns
Daily weight patterns
2
Following bowel surgery,a patient has been receiving normal saline intravenous (IV)fluids at 100 mL per hour;has a nasogastric tube attached to low,intermittent suction;and is on nothing by mouth (NPO)status.Which of the following assessment findings would alert the nurse to a major fluid and electrolyte problem?
A) Weight gain
B) Flushed,moist skin
C) A decreasing level of consciousness (LOC)
D) A serum sodium level of 138 mmol/L
A) Weight gain
B) Flushed,moist skin
C) A decreasing level of consciousness (LOC)
D) A serum sodium level of 138 mmol/L
A decreasing level of consciousness (LOC)
3
What is the normal approximate fluid balance in the adult?
A) 1000 mL
B) 1500 mL
C) 2000 mL
D) 2500 mL
A) 1000 mL
B) 1500 mL
C) 2000 mL
D) 2500 mL
2500 mL
4
A patient is receiving 3% NaCl solution for correction of hyponatremia.What is important for the nurse to monitor during administration of the solution?
A) Lung sounds
B) Peripheral pulses
C) Peripheral edema
D) Hourly urinary output
A) Lung sounds
B) Peripheral pulses
C) Peripheral edema
D) Hourly urinary output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A patient is in metabolic acidosis.Which of the following findings indicates to the nurse that the patient's body is attempting to compensate for the acidosis?
A) Rapid,deep respirations
B) An increase in urinary pH
C) Decreased plasma proteins
D) Increased urinary bicarbonate
A) Rapid,deep respirations
B) An increase in urinary pH
C) Decreased plasma proteins
D) Increased urinary bicarbonate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
For which of the following reasons would the nurse recognize that a patient's serum sodium level may not accurately reflect changes in total body sodium?
A) Total body sodium is not reflected in serum sodium levels.
B) Excess serum sodium is taken into the cells in exchange for potassium.
C) Increased serum sodium causes increased retention of water in the blood.
D) Serum sodium concentration is kept constant by the effect of ADH on the kidney.
A) Total body sodium is not reflected in serum sodium levels.
B) Excess serum sodium is taken into the cells in exchange for potassium.
C) Increased serum sodium causes increased retention of water in the blood.
D) Serum sodium concentration is kept constant by the effect of ADH on the kidney.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A patient who is receiving iso-osmolar continuous tube feedings develops restlessness,agitation,and weakness.Which serum laboratory finding would the nurse expect to find?
A) K+ 3.2 mmol/L
B) Ca2+ 1.95 mmol/L
C) Na+ 154 mmol/L
D) PO43- 1.55 mmol/L
A) K+ 3.2 mmol/L
B) Ca2+ 1.95 mmol/L
C) Na+ 154 mmol/L
D) PO43- 1.55 mmol/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A patient with renal insufficiency develops lethargy and somnolence with a blood pressure of 100/60 mm Hg,a pulse of 62 beats/min,and respirations of 10 breaths/min.The nurse notes that the patient has been taking an aluminum hydroxide-magnesium hydroxide suspension (Maalox)for indigestion.Which of the following drugs would the nurse expect to be used by IV administration in the management of this patient?
A) Calcium gluconate
B) Magnesium sulphate
C) Potassium chloride
D) 50% dextrose and regular insulin
A) Calcium gluconate
B) Magnesium sulphate
C) Potassium chloride
D) 50% dextrose and regular insulin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A patient has a small-cell carcinoma of the lung,which is causing the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH).Which of the following would the nurse expect the patient to manifest?
A) Weight loss
B) Increased urinary output
C) Decreased serum sodium level
D) Peripheral and pulmonary edema
A) Weight loss
B) Increased urinary output
C) Decreased serum sodium level
D) Peripheral and pulmonary edema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A postoperative patient with prolonged nasogastric suction is at risk for a specific acid-base imbalance.Which of the following symptoms noted by the nurse indicates that the patient is developing the acid-base imbalance?
A) Headache
B) Bradycardia
C) Hypotension
D) Hypoventilation
A) Headache
B) Bradycardia
C) Hypotension
D) Hypoventilation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the best area to assess for skin turgor in the older adult?
A) Forearm
B) Upper arm
C) Sternum
D) Thigh
A) Forearm
B) Upper arm
C) Sternum
D) Thigh

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Spironolactone (Aldactone),an aldosterone antagonist,is prescribed for a patient as a diuretic.What dietary modifications should the nurse teach the patient to prevent electrolyte imbalances?
A) Increasing foods high in sodium
B) Decreasing foods high in potassium
C) Restricting fluid intake to 1000 mL per day
D) Increasing intake of milk and milk products
A) Increasing foods high in sodium
B) Decreasing foods high in potassium
C) Restricting fluid intake to 1000 mL per day
D) Increasing intake of milk and milk products

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Water accounts for approximately which percentage of total adult body weight?
A) 30%
B) 40%
C) 50%
D) 60%
A) 30%
B) 40%
C) 50%
D) 60%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
When monitoring the fluid and electrolyte status of the older adult,what does the nurse recognize that impairment of the thirst mechanism may lead to?
A) Hyperosmolality
B) Cellular edema
C) Isotonic fluid deficit
D) Decreased production of ADH
A) Hyperosmolality
B) Cellular edema
C) Isotonic fluid deficit
D) Decreased production of ADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A patient in acid-base imbalance has altered potassium levels.What knowledge does the nurse use to recognize that the potassium levels are altered in acid-base imbalances?
A) Potassium is returned to extracellular fluid on correction of metabolic acidosis.
B) Hyperkalemia causes an alkalosis that results in potassium being shifted into the cell.
C) In acidosis,hydrogen ions in the blood are exchanged for potassium from the cell.
D) In alkalosis,potassium is shifted into extracellular fluid to bind excessive bicarbonate.
A) Potassium is returned to extracellular fluid on correction of metabolic acidosis.
B) Hyperkalemia causes an alkalosis that results in potassium being shifted into the cell.
C) In acidosis,hydrogen ions in the blood are exchanged for potassium from the cell.
D) In alkalosis,potassium is shifted into extracellular fluid to bind excessive bicarbonate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
IV potassium chloride is ordered for treatment of a patient with hypokalemia.What should the nurse be aware of when administering the potassium solution?
A) KCl should be administered as rapidly as necessary to correct hypokalemia.
B) To prevent hyperkalemia,the amount of KCl added to IV fluids should never exceed 80 mmol/L.
C) KCl should be given only through central lines to prevent venospasm and inflammation at the site of entry.
D) To prevent cardiac dysrhythmias and arrest,the maximum amount of KCl to be administered in 1 hour is 20 mEq.
A) KCl should be administered as rapidly as necessary to correct hypokalemia.
B) To prevent hyperkalemia,the amount of KCl added to IV fluids should never exceed 80 mmol/L.
C) KCl should be given only through central lines to prevent venospasm and inflammation at the site of entry.
D) To prevent cardiac dysrhythmias and arrest,the maximum amount of KCl to be administered in 1 hour is 20 mEq.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A patient is taking hydrochlorothiazide,a potassium-wasting diuretic,for treatment of hypertension.What symptoms should the nurse teach the patient to report?
A) Fatigue and muscle weakness
B) Anxiety and muscle twitching
C) Abdominal cramping and diarrhea
D) Confusion and personality changes
A) Fatigue and muscle weakness
B) Anxiety and muscle twitching
C) Abdominal cramping and diarrhea
D) Confusion and personality changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
To prevent laryngeal spasms and respiratory arrest in a patient who is at risk for hypocalcemia,the nurse should assess the patient for which early sign of hypocalcemia?
A) Tetany
B) Confusion
C) Constipation
D) Numbness and tingling around the lips or in the fingers
A) Tetany
B) Confusion
C) Constipation
D) Numbness and tingling around the lips or in the fingers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A patient who has required prolonged mechanical ventilation has the following arterial blood gas results: pH 7.48,PO2 85 mm Hg,PCO2 32 mm Hg,and HCO3- 25 mmol/L.How would the nurse interpret these results?
A) Metabolic acidosis
B) Metabolic alkalosis
C) Respiratory acidosis
D) Respiratory alkalosis
A) Metabolic acidosis
B) Metabolic alkalosis
C) Respiratory acidosis
D) Respiratory alkalosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is a clinical manifestation of hypokalemia?
A) Irritability
B) Soft,flabby muscles
C) Abdominal cramping
D) Oliguria
A) Irritability
B) Soft,flabby muscles
C) Abdominal cramping
D) Oliguria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which one of the following terms describes something that is capable of dissolving a substance that is a liquid or a gas?
A) Osmolarity
B) Osmolality
C) Solvent
D) Valence
A) Osmolarity
B) Osmolality
C) Solvent
D) Valence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A patient has the following arterial blood gas results: pH 7.32,PaO2 88 mm Hg,PaCO2 37 mm Hg,and HCO3¯ 16 mmol/L.The patient also has the following electrocardiogram (ECG)pattern: 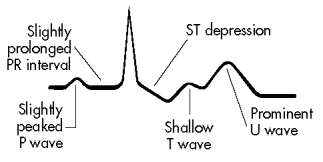
How should the nurse interpret these results?
A) Respiratory acidosis with hyperkalemia
B) Respiratory alkalosis with hyperkalemia
C) Metabolic acidosis with hypokalemia
D) Metabolic alkalosis with hypokalemia

How should the nurse interpret these results?
A) Respiratory acidosis with hyperkalemia
B) Respiratory alkalosis with hyperkalemia
C) Metabolic acidosis with hypokalemia
D) Metabolic alkalosis with hypokalemia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 22 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



