Deck 14: Valuation: Market-Based Approaches
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Valuation: Market-Based Approaches
1
Firms with low P/E ratios tend to have current residual income that is greater than
A) future actual income.
B) future residual income.
C) past actual income.
D) past residual income.
A) future actual income.
B) future residual income.
C) past actual income.
D) past residual income.
B
2
Which of the following normally does not introduce measurement error into the calculation of P/E ratios?
A) differences in firm specific growth rates
B) restructuring losses
C) transitory gains
D) deferred taxes
A) differences in firm specific growth rates
B) restructuring losses
C) transitory gains
D) deferred taxes
D
3
Strictly speaking, the price-earnings ratio assumes that firm value is
A) future value of a constant stream of expected future earnings, discounted at a constant expected future risk-free rate.
B) future value of a constant stream of expected future earnings, discounted at a constant expected future discount rate.
C) present value of a constant stream of expected future earnings, discounted at a constant expected future risk-free rate.
D) present value of a constant stream of expected future earnings, discounted at a constant expected future discount rate.
A) future value of a constant stream of expected future earnings, discounted at a constant expected future risk-free rate.
B) future value of a constant stream of expected future earnings, discounted at a constant expected future discount rate.
C) present value of a constant stream of expected future earnings, discounted at a constant expected future risk-free rate.
D) present value of a constant stream of expected future earnings, discounted at a constant expected future discount rate.
D
4
Wolverwine Company's current stock price is $45 per share and the company's trailing earnings per share were $2.12. Given that analysts are forecasting growth of 14% for Wolverwine what is the company's PEG ratio?
A) 21.2
B) 24.2
C) 2.97
D) 1.52
A) 21.2
B) 24.2
C) 2.97
D) 1.52

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Market multiples capture ____________________ valuation per dollar of book value or per dollar of earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Under the value-to-book model new projects will be abnormally profitable only when
A) ROCE equals ROA
B) ROCE equals RE
C) ROCE is greater than RE
D) ROCE is less than RE
A) ROCE equals ROA
B) ROCE equals RE
C) ROCE is greater than RE
D) ROCE is less than RE

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
One problem with the price-earnings ratios commonly reported is that
A) it divides share price, which reflects the present value of future earnings by historical earnings.
B) it divides share price, which reflects the present value of book value by historical earnings.
C) it does not take into consideration the present value of future earnings.
D) its based on analysts' expectations.
A) it divides share price, which reflects the present value of future earnings by historical earnings.
B) it divides share price, which reflects the present value of book value by historical earnings.
C) it does not take into consideration the present value of future earnings.
D) its based on analysts' expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The market price of a share of common equity reflects
A) the aggregated expectations of all of the market participants following that particular stock.
B) the present value of future residual income.
C) book value plus the present value of future residual income.
D) the correct value for the particular stock.
A) the aggregated expectations of all of the market participants following that particular stock.
B) the present value of future residual income.
C) book value plus the present value of future residual income.
D) the correct value for the particular stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Valuation using market multiples captures
A) absolute valuation per dollar of book value or per dollar of earnings.
B) dollar of book value or dollar of earnings per dollar of common equity.
C) relative valuation per dollar of book value or per dollar of earnings.
D) intrinsic valuation per dollar of book value or per dollar of earnings.
A) absolute valuation per dollar of book value or per dollar of earnings.
B) dollar of book value or dollar of earnings per dollar of common equity.
C) relative valuation per dollar of book value or per dollar of earnings.
D) intrinsic valuation per dollar of book value or per dollar of earnings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Under the value-to-book model a firm will be valued below book value when
A) the ROCE is greater than RE
B) the ROCE is equal to RE
C) the ROCE is less than RE
D) the firm's growth rate is above the industry average
A) the ROCE is greater than RE
B) the ROCE is equal to RE
C) the ROCE is less than RE
D) the firm's growth rate is above the industry average

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The market-to-book ratio is calculated by
A) dividing a firm's market value of total equity by the book value of total equity.
B) dividing a firm's market value of common equity by the book value of total equity.
C) dividing a firm's market value of common equity by the book value of common equity.
D) dividing a firm's market value of total equity by the book value of total debt.
A) dividing a firm's market value of total equity by the book value of total equity.
B) dividing a firm's market value of common equity by the book value of total equity.
C) dividing a firm's market value of common equity by the book value of common equity.
D) dividing a firm's market value of total equity by the book value of total debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is not a reason why price-earnings ratios would differ across firms?
A) Risk
B) Profitability
C) Growth
D) Operating leverage
A) Risk
B) Profitability
C) Growth
D) Operating leverage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Assuming that Ska's cost of equity capital is 14% and it expects to grow earnings at a rate of 8% per year, we would expect Ska's P/E ratio to be
A) 8
B) 16.7
C) 14
D) 4.5
A) 8
B) 16.7
C) 14
D) 4.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Under the value-to-book model a firm in steady state equilibrium earning ROCE = RE will
A) create additional shareholder wealth and be valued above book value.
B) maintain shareholder wealth and be valued at book value.
C) destroy shareholder wealth and be valued below book value.
D) be in a no growth state.
A) create additional shareholder wealth and be valued above book value.
B) maintain shareholder wealth and be valued at book value.
C) destroy shareholder wealth and be valued below book value.
D) be in a no growth state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A company with a PEG ratio of greater than one would be interpreted as having a stock price
A) that is consistent with the company's growth prospects
B) that is low relative to the company's growth prospects
C) that is high relative to the company's growth prospects
D) that is undervalued
A) that is consistent with the company's growth prospects
B) that is low relative to the company's growth prospects
C) that is high relative to the company's growth prospects
D) that is undervalued

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The price differential, or the amount by which the market has discounted share price for risk is calculated by
A) subtracting the book value from the residual income model book value calculated using the risk free rate.
B) subtracting the market price from the residual income model price calculated using the risk free rate.
C) multiplying the theoretical price-earnings ratio by the market price.
D) subtracting the residual income model price calculated using RE from the residual income model price calculated using the risk free rate.
A) subtracting the book value from the residual income model book value calculated using the risk free rate.
B) subtracting the market price from the residual income model price calculated using the risk free rate.
C) multiplying the theoretical price-earnings ratio by the market price.
D) subtracting the residual income model price calculated using RE from the residual income model price calculated using the risk free rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A company is expected to have a value of $142,857 at the start of next period and investors require a 14 percent return on equity capital. Using the assumptions of the price-earnings ratio what would be the company's earnings for the current year?
A) $20,000
B) $14,286
C) $2,800
D) $12,500
A) $20,000
B) $14,286
C) $2,800
D) $12,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A company is expected to generate $125,000 in earnings next period and requires a 16 percent return on equity capital. Using the assumptions of the price-earnings ratio what would be the company's value at the beginning of next period?
A) $781,250
B) $1,250,000
C) $2,000,000
D) $125,000
A) $781,250
B) $1,250,000
C) $2,000,000
D) $125,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The market price of a share of common equity reflects the _____________________________________________ of all of the market participants following that particular stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Companies value-to-book and market-to-book ratios may differ due to accounting reasons. An example of an accounting reason that would create a difference is
A) accelerated methods of depreciation.
B) successful research and development programs.
C) using LIFO versus FIFO for inventory.
D) high operating leverage.
A) accelerated methods of depreciation.
B) successful research and development programs.
C) using LIFO versus FIFO for inventory.
D) high operating leverage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A company with a PEG ratio of greater than one would be interpreted as having a stock price that is high relative to ______________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The theoretical PE model does not work when the growth rate in ____________________ exceeds the cost of equity capital

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The PE multiple assumes that firm value is the present value of a constant stream of _____________________________________________, discounted at a constant expected future discount rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
To estimate security's risk neutral value we can use the _____________________________________________ and risk-free rates of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The value-to-book model indicates that a firm in steady state equilibrium earnings ROCE=RE will be valued at _________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Sometimes a high market to book ratio is a result of having __________________________________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What methods have been developed to incorporate growth into price-earnings ratios? How do the methods incorporate growth? What are the advantages and/or disadvantages of these methods?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Industries with relatively high market-to-book ratios are more likely to have ___________________________________ assets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The ______________________________ represents the difference between the current stock price and risk-neutral value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Firms with low P/E ratios tend to have current residual income that is greater than _____________________________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The ______________________________ represents the value of the firm, based on book value of equity and forecasts of expected future earnings, in the absence of discounting for risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The differences in industry market-to-book ratios may be the result of differences in growth, ROCE relative to RE, as well as differences in _______________________________________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The value-to-book ratio reflects an analyst's expectation of the firm's ____________________ value to book value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The PEG ratio does not take into account differences in ____________________ and ________________________________________ across firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the value-to-book model growth adds value to shareholders only if the growth is ________________________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Analysts use the PEG ratio to assess share price relative to earnings and _________________________________________________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The process of ___________________________________ stock prices assumes that intrinsic value equals market price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Discuss how risk and profitability factors cause differences in price-earnings ratios across firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Economics teaches that, in equilibrium, firms will earn a return equal to the ______________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The risk of the firm increases the _____________________________________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In research examining market efficiency Bernard and Thomas examined quarterly earnings announcements. Discuss how Bernard and Thomas test the issue of market efficiency and the results of their research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Assume an analyst is evaluating a firm with $1,000 of book value of common equity and a cost of equity capital equal to 8 percent. Assume that the analyst forecasts that the firm will earn ROCE of 14 percent until year 2011, when the firm will start earning ROCE equal to 8 percent. The company pays no dividends and will not engage in any stock transactions. Use this information to complete the following table and calculate the firm's value-to-book ratio.
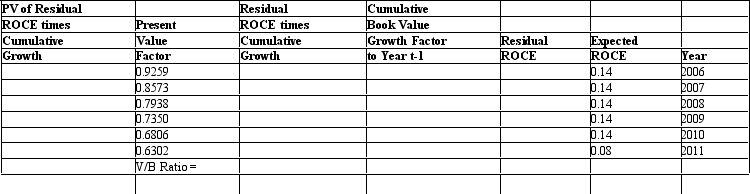


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Compute the price-earnings ratio under the following sets of assumptions:
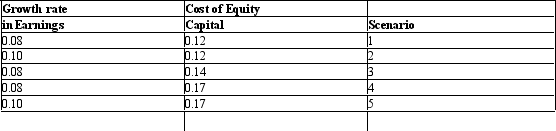


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the value of reverse engineering stock prices? How does the process work?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A firm's value-to-book and market-to-book ratios may differ from one for a number of reasons. Discuss how a successful internally funded research and development program would create a situation where the value-to-book and market-to-book ratios differ from one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is a price differential and how is it computed? What information does a price differential provide to an analyst?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The use of P/E ratios in valuation can result in measurement bias. What two items can result in measurement error and why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Assume an analyst is evaluating a firm with $1,000 of book value of common equity and a cost of equity capital equal to 12 percent. Assume that the analyst forecasts that the firm will earn ROCE of 18 percent until year 2010, when the firm will start earning ROCE equal to 12 percent. The company pays no dividends and will not engage in any stock transactions. Use this information to complete the following table and calculate the firm's value-to-book ratio.
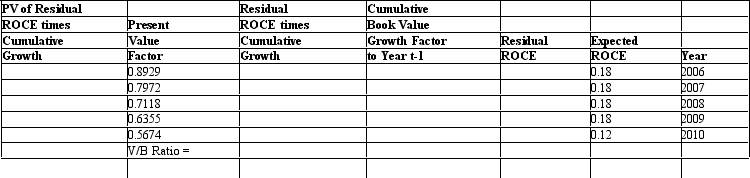


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What information can a PEG ratio provide about a company's stock price? What does a PEG ratio greater than mean? less than one?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Investors have invested $25,000 in common equity in a company. The investors expect that the company will reinvest all income back into projects. The company is forecasted to earn $6,000 the first year, $5,000 the second year, $5,500 the third year and $6,244 each year after the third year. The company's current stock price is $17 per share. Assuming that the company has 3,200 shares outstanding and the risk free rate of interest is 6% calculate the price differential for this company?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



