Deck 8: Growth,capital Accumulation
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/155
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 8: Growth,capital Accumulation
1
Catching-up growth is growth due to:
A) capital accumulation.
B) new ideas.
C) new human capital.
D) improving the organization of existing resources.
A) capital accumulation.
B) new ideas.
C) new human capital.
D) improving the organization of existing resources.
capital accumulation.
2
Countries on a "catching-up" growth path are growing primarily through:
A) capital accumulation.
B) new technological knowledge.
C) new ideas.
D) foreign aid.
A) capital accumulation.
B) new technological knowledge.
C) new ideas.
D) foreign aid.
capital accumulation.
3
In the Solow model production function,Y = F(A,K,eL),L stands for:
A) labor.
B) leisure.
C) liquidity.
D) long run.
A) labor.
B) leisure.
C) liquidity.
D) long run.
labor.
4
Imagine an economy with production function Y = F(K)= and 400 units of capital.If the fraction of output invested in new capital is = 0.2 and the depreciation rate is = .05,how much total capital will be available in the next period?
A) 380 units
B) 384 units
C) 400 units
D) 404 units
A) 380 units
B) 384 units
C) 400 units
D) 404 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In 2010,GDP per capita in the United States grew by 2.2%.In the same year,GDP per capita in China grew by almost:
A) 2%.
B) 5%.
C) 7%.
D) 10%.
A) 2%.
B) 5%.
C) 7%.
D) 10%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Countries on the "cutting edge" grow primarily by:
A) adopting ideas already used by other countries.
B) capital accumulation.
C) developing new ideas.
D) eliminating waste and inefficiency.
A) adopting ideas already used by other countries.
B) capital accumulation.
C) developing new ideas.
D) eliminating waste and inefficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In recent years,real GDP in China has grown:
A) at about the same rate as real GDP in the United States.
B) much faster than real GDP in the United States.
C) much slower than real GDP in the United States.
D) faster than real GDP in the United States in some years,slower than real GDP in the United States in other years.
A) at about the same rate as real GDP in the United States.
B) much faster than real GDP in the United States.
C) much slower than real GDP in the United States.
D) faster than real GDP in the United States in some years,slower than real GDP in the United States in other years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the Solow model production function,Y = F(A,K,eL),K stands for:
A) kurtosis.
B) consumption.
C) physical capital.
D) human capital.
A) kurtosis.
B) consumption.
C) physical capital.
D) human capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An economy with production function Y = F(K)= that has 400 units of capital will produce _____ units of output.
A) 1,600
B) 400
C) 40
D) 20
A) 1,600
B) 400
C) 40
D) 20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The "A" term in the production function Y = F(A,K,eL)represents which factor of production in the Solow growth model?
A) physical capital
B) human capital
C) technological knowledge
D) organization of resources
A) physical capital
B) human capital
C) technological knowledge
D) organization of resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The Solow growth model features _____ returns to physical capital.
A) decreasing
B) constant
C) increasing
D) no
A) decreasing
B) constant
C) increasing
D) no

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the Solow model production function,Y = F(A,K,eL),eL stands for:
A) efficiency.
B) liquidity.
C) elasticity.
D) human capital.
A) efficiency.
B) liquidity.
C) elasticity.
D) human capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Imagine an economy with production function Y = F(K)= and 400 units of capital.If the depreciation rate is = .05,how much capital will deteriorate in the next period?
A) 4 units
B) 8 units
C) 16 units
D) 20 units
A) 4 units
B) 8 units
C) 16 units
D) 20 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Imagine an economy with production function Y = F(K)= and 400 units of capital.If the fraction of output invested in new capital is = 0.2,how much new capital will be created in the next period?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In the Solow model production function,Y = F(A,K,eL),A stands for:
A) aggregate demand.
B) assets.
C) attitude.
D) ideas.
A) aggregate demand.
B) assets.
C) attitude.
D) ideas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The two types of economic growth are:
A) ultimate and immediate.
B) progressive and regressive.
C) fast and slow.
D) cutting-edge and catching-up.
A) ultimate and immediate.
B) progressive and regressive.
C) fast and slow.
D) cutting-edge and catching-up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which is NOT a key institution for economic growth?
A) property rights
B) honest government
C) political stability
D) income equality
A) property rights
B) honest government
C) political stability
D) income equality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Cutting-edge growth is growth due to:
A) capital accumulation.
B) new ideas.
C) new human capital.
D) improving the organization of existing resources.
A) capital accumulation.
B) new ideas.
C) new human capital.
D) improving the organization of existing resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The production function is a mathematical function that shows:
A) the most cost-efficient means of producing output.
B) the relationship between output and the factors of production.
C) how various inputs are produced.
D) the most efficient level of output produced in an economy.
A) the most cost-efficient means of producing output.
B) the relationship between output and the factors of production.
C) how various inputs are produced.
D) the most efficient level of output produced in an economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In 2010,China's GDP per capita grew by approximately:
A) 7%.
B) 8%.
C) 9%.
D) 10%.
A) 7%.
B) 8%.
C) 9%.
D) 10%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A small country's aggregate production function per hour of labor given by Y = K1/2.Its depreciation rate is 1% and its investment rate is 10%.What is its steady-state level of output?
A) 1
B) 10
C) 100
D) 1,000
A) 1
B) 10
C) 100
D) 1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A production function can be used to express the relationship between _____ and GDP.
A) GDP per capita
B) productivity
C) the factors of production
D) an economy's growth rate
A) GDP per capita
B) productivity
C) the factors of production
D) an economy's growth rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If investment is greater than depreciation,then the capital stock:
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) becomes negative.
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) becomes negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Imagine an economy with production function Y = F(K)= and 400 units of capital.If the fraction of output invested in new capital is = 0.2,the depreciation rate is = .05,and the economy starts with output of 20,what does the Solow model predict will happen to output in the long run?
A) It will remain at 20.
B) It will decline.
C) It will increase.
D) It will increase for a time and then return to 20.
A) It will remain at 20.
B) It will decline.
C) It will increase.
D) It will increase for a time and then return to 20.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
According to the Solow model,a higher investment rate leads to:
A) an increase in steady-state output.
B) a decrease in steady-state output.
C) no change in steady-state output.
D) volatility in steady-state output.
A) an increase in steady-state output.
B) a decrease in steady-state output.
C) no change in steady-state output.
D) volatility in steady-state output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Imagine an economy with production function Y = F(K)= and 400 units of capital.If the fraction of output invested in new capital increases from = 0.2 to = 0.5 and the depreciation rate is = .05,what is the new steady-state amount of capital?
A) 16 units
B) 64 units
C) 100 units
D) 256 units
A) 16 units
B) 64 units
C) 100 units
D) 256 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If we hold ideas,education,and labor constant in the Solow model,then output (GDP)is a function of:
A) human capital only.
B) physical capital only.
C) labor only.
D) technological knowledge only.
A) human capital only.
B) physical capital only.
C) labor only.
D) technological knowledge only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
_____ first developed the model that explains economic growth using a production function.
A) Milton Friedman
B) Robert Solow
C) John Maynard Keynes
D) Ben Bernanke
A) Milton Friedman
B) Robert Solow
C) John Maynard Keynes
D) Ben Bernanke

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A country in a steady state invests 50% of its output in new capital ( = 0.5)and depreciates 5% of its capital stock ( = .05).With a capital stock of 100 units,labor remains constant.Because of technological innovation,production improves from Y = to Y = 2
.What is the new steady-state level of output?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 40
D) 80
.What is the new steady-state level of output?
A) 10
B) 20
C) 40
D) 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Good institutions tend to:
A) decrease the rate of investment.
B) leave the rate of investment unchanged.
C) increase the rate of investment.
D) have an ambiguous effect on investment.
A) decrease the rate of investment.
B) leave the rate of investment unchanged.
C) increase the rate of investment.
D) have an ambiguous effect on investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In the Solow model,an increase in investment leads to:
A) an increase in growth rates in the short run but a return to zero growth in the long run as the economy converges to a new,higher steady state.
B) an increase in growth rates in both the short run and the long run,as new investment will lead to permanently higher levels of the capital stock.
C) a decrease in growth rates in both the short run and the long run,as fewer resources are available for production following the increase in investment.
D) no change in growth rates.
A) an increase in growth rates in the short run but a return to zero growth in the long run as the economy converges to a new,higher steady state.
B) an increase in growth rates in both the short run and the long run,as new investment will lead to permanently higher levels of the capital stock.
C) a decrease in growth rates in both the short run and the long run,as fewer resources are available for production following the increase in investment.
D) no change in growth rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
According to the Solow model,a higher investment rate leads to:
A) more capital and more output.
B) more capital and less output.
C) less capital and more output.
D) less capital and less output.
A) more capital and more output.
B) more capital and less output.
C) less capital and more output.
D) less capital and less output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An increase in the investment rate results in:
A) a lower steady-state capital stock and a lower steady-state output.
B) a lower steady-state capital stock but a higher steady-state output.
C) a higher steady-state capital stock and a higher steady-state output.
D) a higher steady-state capital stock but a lower steady-state output.
A) a lower steady-state capital stock and a lower steady-state output.
B) a lower steady-state capital stock but a higher steady-state output.
C) a higher steady-state capital stock and a higher steady-state output.
D) a higher steady-state capital stock but a lower steady-state output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A country in a steady state invests 50% of its output in new capital ( = 0.5)and depreciates 5% of its capital stock ( = .05).With a capital stock of 100 units,labor remains constant.Because of technological innovation,production improves from Y = to Y = 2
.What is the new steady-state level of K?
A) 100
B) 256
C) 400
D) 1,600
.What is the new steady-state level of K?
A) 100
B) 256
C) 400
D) 1,600

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the investment rate ( )increases in the Solow model,other things held constant,then capital growth:
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) becomes negative.
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) becomes negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The Solow model is based on:
A) a production function.
B) supply and demand curves.
C) the GDP accounts.
D) consumer preferences.
A) a production function.
B) supply and demand curves.
C) the GDP accounts.
D) consumer preferences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Imagine an economy with production function Y = F(K)= and 400 units of capital.If the fraction of output invested in new capital is = 0.2 and the depreciation rate is = .05,what is the steady-state amount of capital?
A) 16 units
B) 64 units
C) 100 units
D) 225 units
A) 16 units
B) 64 units
C) 100 units
D) 225 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If the investment rate ( )decreases in the Solow model,other things held constant,then capital growth:
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) changes indeterminately.
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) changes indeterminately.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If investment equals depreciation,then the capital stock:
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) equals zero.
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) equals zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If investment is less than depreciation,then the capital stock:
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) becomes negative.
A) decreases.
B) remains constant.
C) increases.
D) becomes negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Conditional convergence refers to the tendency for:
A) poorer countries to grow faster than richer countries,but only if they receive sufficient foreign investment.
B) richer countries to grow faster than poorer countries given similar steady-state capital stocks,so the poor countries never catch up with the rich countries.
C) poorer countries to grow faster than richer countries given similar steady-state capital stocks,but the poor countries will never catch up with the rich countries.
D) countries with similar steady-state levels of output to grow faster when they're poor than when they're rich until their per capita GDP levels converge.
A) poorer countries to grow faster than richer countries,but only if they receive sufficient foreign investment.
B) richer countries to grow faster than poorer countries given similar steady-state capital stocks,so the poor countries never catch up with the rich countries.
C) poorer countries to grow faster than richer countries given similar steady-state capital stocks,but the poor countries will never catch up with the rich countries.
D) countries with similar steady-state levels of output to grow faster when they're poor than when they're rich until their per capita GDP levels converge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements correctly differentiates catching-up growth from cutting-edge growth?
A) Cutting-edge growth leads to convergence while catching-up growth does not.
B) Cutting-edge growth comes primarily from capital accumulation while catching-up growth comes from technological development.
C) Poorer countries with low levels of capital stock will always display catching-up growth while rich countries will not.
D) Cutting-edge growth can go on indefinitely while catching-up growth cannot.
A) Cutting-edge growth leads to convergence while catching-up growth does not.
B) Cutting-edge growth comes primarily from capital accumulation while catching-up growth comes from technological development.
C) Poorer countries with low levels of capital stock will always display catching-up growth while rich countries will not.
D) Cutting-edge growth can go on indefinitely while catching-up growth cannot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
According to the Solow model,countries with higher savings rates have higher levels of:
A) investment.
B) output.
C) both investment and output.
D) neither investment nor output.
A) investment.
B) output.
C) both investment and output.
D) neither investment nor output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Consider an economy that is operating at its steady state.An increase in the investment rate in this economy will lead to:
A) an increase in the growth rate of output in both the short run and long run.
B) no change in the growth rates of either capital or output in either the short run or the long run,since the economy is already in the steady state.
C) an increase in the growth rate of output in the short run but lower overall growth in the long run as a result of increased depreciation.
D) an increase in the growth rate of output in the short run but zero growth in output in the long run.
A) an increase in the growth rate of output in both the short run and long run.
B) no change in the growth rates of either capital or output in either the short run or the long run,since the economy is already in the steady state.
C) an increase in the growth rate of output in the short run but lower overall growth in the long run as a result of increased depreciation.
D) an increase in the growth rate of output in the short run but zero growth in output in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Member nations of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)with a lower GDP per capita in 1960 experienced what sort of growth during the subsequent 40 years?
A) relatively lower growth than higher GDP per capita countries
B) relatively faster growth than higher GDP per capita countries
C) no growth at all
D) growth similar to countries with a high 1960 GDP per capita
A) relatively lower growth than higher GDP per capita countries
B) relatively faster growth than higher GDP per capita countries
C) no growth at all
D) growth similar to countries with a high 1960 GDP per capita

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
According to the Solow model,an increase in the fraction of output that is saved will increase _____ in the long run.
A) investment
B) output
C) both investment and output
D) neither investment nor output
A) investment
B) output
C) both investment and output
D) neither investment nor output

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Conditional convergence predicts that if two countries have the same steady-state level of output,the poorer country will:
A) grow but never be able to catch up with the richer country.
B) catch up with the richer country because the richer country will not be able to maintain its steady-state output level.
C) catch up with the richer country because it will grow faster than the rich country.
D) not grow at all and will fall further behind the rich country.
A) grow but never be able to catch up with the richer country.
B) catch up with the richer country because the richer country will not be able to maintain its steady-state output level.
C) catch up with the richer country because it will grow faster than the rich country.
D) not grow at all and will fall further behind the rich country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following statements correctly differentiates catching-up growth from cutting-edge growth?
A) Cutting-edge growth leads to convergence while catching-up growth does not.
B) Catching-up growth comes primarily from capital accumulation while cutting-edge growth comes from technological development.
C) Poorer countries with low levels of capital stock will always display catching-up growth while rich countries will not.
D) Catching-up growth can go on indefinitely while cutting-edge growth cannot.
A) Cutting-edge growth leads to convergence while catching-up growth does not.
B) Catching-up growth comes primarily from capital accumulation while cutting-edge growth comes from technological development.
C) Poorer countries with low levels of capital stock will always display catching-up growth while rich countries will not.
D) Catching-up growth can go on indefinitely while cutting-edge growth cannot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
According to the Solow model,a country will grow faster when its capital stock is:
A) at the steady-state value.
B) above the steady-state value.
C) just below the steady-state value.
D) far below the steady-state value.
A) at the steady-state value.
B) above the steady-state value.
C) just below the steady-state value.
D) far below the steady-state value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
If two countries have the same steady-state levels of output,the country that is _____ today will _____ in per capita output.
A) poorer;always lag behind
B) poorer;catch up
C) richer;eventually fall behind
D) richer;become even further ahead
A) poorer;always lag behind
B) poorer;catch up
C) richer;eventually fall behind
D) richer;become even further ahead

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Among countries with similar steady-state levels of output,the tendency for poorer countries to grow faster than richer countries is called:
A) Solow growth.
B) steady-state growth.
C) dynamic growth.
D) conditional convergence.
A) Solow growth.
B) steady-state growth.
C) dynamic growth.
D) conditional convergence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the name for the tendency-among countries with similar steady-state levels of output-for poorer countries to grow faster than richer countries until they reach the same income levels?
A) the diminishing rate of return
B) the marginal law of supply
C) conditional convergence
D) growth capitalization
A) the diminishing rate of return
B) the marginal law of supply
C) conditional convergence
D) growth capitalization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the Solow model,an increase in the investment rate will _____ the amount of capital needed to achieve a steady state.
A) increase
B) decrease
C) not affect
D) have an unpredictable effect on
A) increase
B) decrease
C) not affect
D) have an unpredictable effect on

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the long run,catching-up growth:
A) can continue indefinitely.
B) eventually stops when the economy reaches its steady state.
C) can explain an economy's growth in the very long run.
D) keeps the capital stock growing indefinitely,but not output.
A) can continue indefinitely.
B) eventually stops when the economy reaches its steady state.
C) can explain an economy's growth in the very long run.
D) keeps the capital stock growing indefinitely,but not output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Among countries with similar Solow steady states,poorer countries tend to grow _____ rich countries.
A) more slowly than
B) at the same rate as
C) faster than
D) sometimes faster and sometimes more slowly than
A) more slowly than
B) at the same rate as
C) faster than
D) sometimes faster and sometimes more slowly than

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Conditional convergence refers to the condition that among countries with similar steady states:
A) a country with a higher output level tends to grow more rapidly.
B) a country with a higher output level tends to grow more slowly.
C) all countries grow at the same rate regardless of their initial output levels.
D) whether one country's output converges to that of another country depends on their geographical proximity.
A) a country with a higher output level tends to grow more rapidly.
B) a country with a higher output level tends to grow more slowly.
C) all countries grow at the same rate regardless of their initial output levels.
D) whether one country's output converges to that of another country depends on their geographical proximity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Conditional convergence implies that there is _____ relationship between real GDP per capita and subsequent growth.
A) a positive
B) a negative
C) no
D) a vertical
A) a positive
B) a negative
C) no
D) a vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Provided they have the same steady state,the tendency for poorer countries to grow faster than richer countries and thus to converge in income is called:
A) standard convergence.
B) dynamic convergence.
C) income convergence.
D) conditional convergence.
A) standard convergence.
B) dynamic convergence.
C) income convergence.
D) conditional convergence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The Solow model predicts that a country will grow more rapidly the:
A) further its capital stock is above its steady-state value.
B) further its capital stock is below its steady-state value.
C) closer its capital stock is to its steady-state value from above.
D) closer its capital stock is to its steady-state value from below.
A) further its capital stock is above its steady-state value.
B) further its capital stock is below its steady-state value.
C) closer its capital stock is to its steady-state value from above.
D) closer its capital stock is to its steady-state value from below.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which statement is consistent with the predictions of the simple Solow model with no technological advancement?
A) In the long run,economic growth is zero.
B) In the long run,a higher capital stock raises economic growth.
C) In the long run,rich countries grow faster than poor countries.
D) In the long run,a higher saving rate reduces economic growth.
A) In the long run,economic growth is zero.
B) In the long run,a higher capital stock raises economic growth.
C) In the long run,rich countries grow faster than poor countries.
D) In the long run,a higher saving rate reduces economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Better ideas or technological knowledge causes:
A) the production function to shift upward.
B) the production function to shift downward.
C) the investment function to shift downward.
D) the depreciation function to shift downward.
A) the production function to shift upward.
B) the production function to shift downward.
C) the investment function to shift downward.
D) the depreciation function to shift downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The growth that results from better ideas or technological knowledge is:
A) catching-up growth.
B) cutting-edge growth.
C) capital growth.
D) short-run growth.
A) catching-up growth.
B) cutting-edge growth.
C) capital growth.
D) short-run growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
(Figure: The Solow Model)If the production function shifts from Y1 to Y2 in the accompanying graph of the Solow model,then:
A) no growth will occur.
B) catching-up growth will occur.
C) cutting-edge growth will occur.
D) both catching-up and cutting-edge growth will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Increases in productivity cause the:
A) depreciation function to shift downward.
B) production function to shift downward.
C) production function to shift upward.
D) investment curve to shift downward.
A) depreciation function to shift downward.
B) production function to shift downward.
C) production function to shift upward.
D) investment curve to shift downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Research by Solow indicated that about _____ of the increases in U.S.GDP per capita are due to better ideas.
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%
A) 25%
B) 50%
C) 75%
D) 100%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66

(Figure: The Solow Model)If the production function shifts from Y1 to Y2 in the accompanying graph of the Solow model,then:
A) the steady state will remain at K1.
B) a new steady state will occur at K2.
C) the steady state will move to K2 and then return to K1 in the long run.
D) a new steady state will occur somewhere between K1 and K2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The source of "cutting-edge" growth is:
A) investment in physical capital.
B) education and training to build human capital.
C) advances in technological knowledge.
D) foreign investment.
A) investment in physical capital.
B) education and training to build human capital.
C) advances in technological knowledge.
D) foreign investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Better ideas cause the:
A) depreciation function to shift downward.
B) production function to shift downward.
C) production function to shift upward.
D) investment curve to shift downward.
A) depreciation function to shift downward.
B) production function to shift downward.
C) production function to shift upward.
D) investment curve to shift downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the Solow production function,an increase in the term "A" refers to an increase in:
A) productivity.
B) the capital stock.
C) the rate of depreciation.
D) investment.
A) productivity.
B) the capital stock.
C) the rate of depreciation.
D) investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following can drive long-run economic growth in the Solow model?
A) human capital
B) physical capital
C) real capital
D) technological knowledge
A) human capital
B) physical capital
C) real capital
D) technological knowledge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The key to keeping the economy growing in the long run is:
A) investment in physical capital.
B) education and training to build human capital.
C) new ideas.
D) foreign investment.
A) investment in physical capital.
B) education and training to build human capital.
C) new ideas.
D) foreign investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Solow estimated that better ideas are responsible for about _____ of the U.S.standard of living.
A) one-fourth
B) one-half
C) three-fourths
D) all
A) one-fourth
B) one-half
C) three-fourths
D) all

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The key to escaping the "iron logic" of diminishing returns in the Solow model is:
A) investment in physical capital.
B) education and training to build human capital.
C) new ideas.
D) foreign investment.
A) investment in physical capital.
B) education and training to build human capital.
C) new ideas.
D) foreign investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74

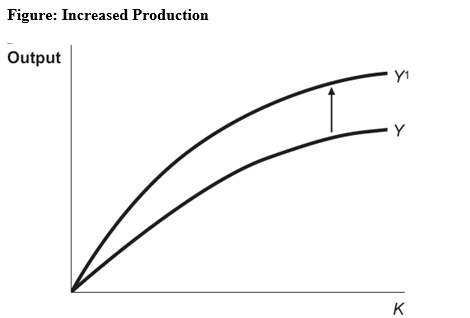
Figure: Increased Production In the accompanying graph,which of the following events could cause the upward shift of the production function?
A) foreign direct investment
B) technological advancement
C) an increase in the capital stock
D) an aging labor force

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75

(Figure: The Solow Model)In the accompanying graph of the Solow model,if the production function shifts from Y1 to Y2 while capital remains at K1,then the capital stock will:
A) decrease until it reaches the new steady-state level.
B) increase until it reaches the new steady-state level.
C) increase for a time and then return to K1.
D) remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The production function can shift upward because of:
A) higher depreciation.
B) an increase in investment.
C) better ideas.
D) an increase in capital stock.
A) higher depreciation.
B) an increase in investment.
C) better ideas.
D) an increase in capital stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77

(Figure: The Solow Model)Which of the following events would NOT shift the production function from Y1 to Y2 in the accompanying diagram of the Solow model?
A) increases in productivity
B) better ideas
C) physical capital accumulation
D) advances in technological knowledge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The key to keeping the economy growing in the long run is:
A) investment in physical capital.
B) education and training to build human capital.
C) advances in technological knowledge.
D) foreign investment.
A) investment in physical capital.
B) education and training to build human capital.
C) advances in technological knowledge.
D) foreign investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Better ideas or technological knowledge causes:
A) the production function to shift upward.
B) the investment function to shift upward.
C) both the production function and the investment function to shift upward.
D) neither the production function nor the investment function to shift upward.
A) the production function to shift upward.
B) the investment function to shift upward.
C) both the production function and the investment function to shift upward.
D) neither the production function nor the investment function to shift upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80

(Figure: The Solow Model)If the production function shifts from Y1 to Y2 in the accompanying graph of the Solow model,then:
A) no growth will occur.
B) growth will occur from capital accumulation only.
C) growth will occur from better ideas only.
D) growth from both capital accumulation and better ideas will occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 155 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



