Deck 14: Transmission and Amplification Mechanisms
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/219
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Transmission and Amplification Mechanisms
1
If drought reduces farm output,farmers will probably:
A) work harder to try to make up for the lost output.
B) work less hard and devote less capital to their fields.
C) work the same amount as they normally do.
D) celebrate.
A) work harder to try to make up for the lost output.
B) work less hard and devote less capital to their fields.
C) work the same amount as they normally do.
D) celebrate.
work less hard and devote less capital to their fields.
2
Rapid changes in economic conditions that have large effects on the productivity of capital and labor are called:
A) business cycles.
B) recessions.
C) shocks.
D) transmission mechanisms.
A) business cycles.
B) recessions.
C) shocks.
D) transmission mechanisms.
shocks.
3
Historical data on India's rainfall amounts and real GDP growth show that:
A) economic fluctuations are negatively correlated with real shocks.
B) economic fluctuations are positively correlated with real shocks.
C) economic fluctuations have no correlation with any shocks.
D) real shocks affect only long-term economic growth,but not short-run economic fluctuations.
A) economic fluctuations are negatively correlated with real shocks.
B) economic fluctuations are positively correlated with real shocks.
C) economic fluctuations have no correlation with any shocks.
D) real shocks affect only long-term economic growth,but not short-run economic fluctuations.
economic fluctuations are positively correlated with real shocks.
4
Transmission mechanisms:
A) can amplify positive shocks.
B) can amplify negative shocks.
C) can amplify both positive and negative shocks.
D) amplify neither positive nor negative shocks.
A) can amplify positive shocks.
B) can amplify negative shocks.
C) can amplify both positive and negative shocks.
D) amplify neither positive nor negative shocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Intertemporal substitution refers to:
A) the tendency to work more when the returns to work are higher.
B) the decision on how to allocate time between work and leisure.
C) the preference for households to smooth their consumption over time.
D) the decision to substitute one television show for another during the same time slot.
A) the tendency to work more when the returns to work are higher.
B) the decision on how to allocate time between work and leisure.
C) the preference for households to smooth their consumption over time.
D) the decision to substitute one television show for another during the same time slot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is NOT an example of intertemporal substitution?
A) David decides to go to college after high school,since he has graduated in the middle of a big recession and jobs are hard to come by.
B) Luke is an accountant who works overtime during tax season.
C) Sandy works 10-hour days as a ski instructor during the winter months but takes a 3-week vacation during the summer.
D) Thomas studies economics 2 hours every night in order to get a good grade in the course.
A) David decides to go to college after high school,since he has graduated in the middle of a big recession and jobs are hard to come by.
B) Luke is an accountant who works overtime during tax season.
C) Sandy works 10-hour days as a ski instructor during the winter months but takes a 3-week vacation during the summer.
D) Thomas studies economics 2 hours every night in order to get a good grade in the course.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is NOT a transmission mechanism?
A) intertemporal substitution
B) irreversible investments
C) time bunching
D) shifts in LRAS
A) intertemporal substitution
B) irreversible investments
C) time bunching
D) shifts in LRAS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Intertemporal substitution is:
A) the cost of shifting workers from declining sectors of the economy to the growing sectors.
B) the tendency for economic activities to be coordinated at common points in time.
C) the allocation of consumption,work,and leisure across time to maximize well-being.
D) a reduction in the value of collateral.
A) the cost of shifting workers from declining sectors of the economy to the growing sectors.
B) the tendency for economic activities to be coordinated at common points in time.
C) the allocation of consumption,work,and leisure across time to maximize well-being.
D) a reduction in the value of collateral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is NOT a transmission mechanism of real shocks and aggregate demand shocks?
A) reversible investment
B) intertemporal substitutions
C) collateral damage
D) time bunching
A) reversible investment
B) intertemporal substitutions
C) collateral damage
D) time bunching

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Economic forces that can amplify shocks across time and sectors of the economy are called:
A) business cycles.
B) cyclical recessions.
C) shock magnifiers.
D) transmission mechanisms.
A) business cycles.
B) cyclical recessions.
C) shock magnifiers.
D) transmission mechanisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A transmission mechanism:
A) mitigates shocks by spreading them across time and through sectors of the economy.
B) amplifies shocks by spreading them across time and through sectors of the economy.
C) causes shocks to have an equal impact across time and sectors of the economy.
D) turns negative shocks into positive shocks over time.
A) mitigates shocks by spreading them across time and through sectors of the economy.
B) amplifies shocks by spreading them across time and through sectors of the economy.
C) causes shocks to have an equal impact across time and sectors of the economy.
D) turns negative shocks into positive shocks over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When a shock is amplified,a mild _____ shock is transformed into _____.
A) negative;a mild positive shock
B) negative;an economic boom
C) negative;a more serious reduction in output
D) positive;a mild negative shock
A) negative;a mild positive shock
B) negative;an economic boom
C) negative;a more serious reduction in output
D) positive;a mild negative shock

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is the best example of intertemporal substitution?
A) Timmy opens a lemonade stand on the weekends when he's not in school to earn money for a new bike.
B) Sam works overtime to earn extra money.
C) Mary studies an extra 3 hours the night before her economics final exam.
D) Sarah decides to stay home from work today because she is feeling ill.
A) Timmy opens a lemonade stand on the weekends when he's not in school to earn money for a new bike.
B) Sam works overtime to earn extra money.
C) Mary studies an extra 3 hours the night before her economics final exam.
D) Sarah decides to stay home from work today because she is feeling ill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Intertemporal substitution tends to amplify business cycles because:
A) assets are typically worth more in booms than in recessions.
B) the returns to work are higher in booms than in recessions,so people work more during booms and less during recessions.
C) the returns to investment are higher when others are investing as well,thus we see more investment during booms and less during recessions.
D) many people are hesitant to change jobs during recessions and thus resources are stuck in less productive uses.
A) assets are typically worth more in booms than in recessions.
B) the returns to work are higher in booms than in recessions,so people work more during booms and less during recessions.
C) the returns to investment are higher when others are investing as well,thus we see more investment during booms and less during recessions.
D) many people are hesitant to change jobs during recessions and thus resources are stuck in less productive uses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which is NOT an example of a transmission mechanism?
A) time bunching
B) intertemporal substitution
C) labor adjustment costs
D) irreversible employment
A) time bunching
B) intertemporal substitution
C) labor adjustment costs
D) irreversible employment

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The economic forces that amplify shocks by spreading them across time and sectors of the economy are called:
A) irreversible investments.
B) intertemporal substitutions.
C) transmission mechanisms.
D) aggregate demand conveyances.
A) irreversible investments.
B) intertemporal substitutions.
C) transmission mechanisms.
D) aggregate demand conveyances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is a transmission mechanism?
A) intertemporal substitution
B) irreversible employment
C) labor bunching
D) time substitution
A) intertemporal substitution
B) irreversible employment
C) labor bunching
D) time substitution

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following are people NOT more likely to do during a recession?
A) retire
B) shrink business operations
C) focus on homemaking
D) drop out of school
A) retire
B) shrink business operations
C) focus on homemaking
D) drop out of school

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following is NOT a transmission mechanism?
A) time bunching
B) intertemporal substitution
C) reversible investments
D) labor adjustment costs
A) time bunching
B) intertemporal substitution
C) reversible investments
D) labor adjustment costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is taking place when an economy experiences quick changes that have large effects on productivity?
A) economic shocks
B) geographic capital fluctuations
C) decreases in aggregate demand
D) time bunching
A) economic shocks
B) geographic capital fluctuations
C) decreases in aggregate demand
D) time bunching

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Figure: AS/AD Adjustment 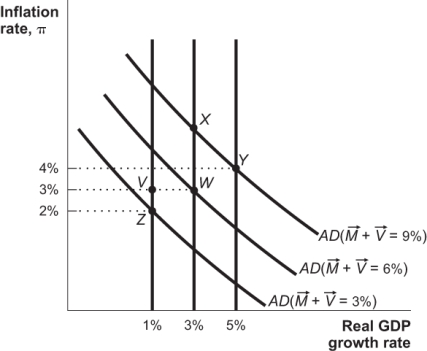 ` Beginning at Point W in the figure,suppose the government engages in a large increase in government expenditure.If workers react by displaying intertemporal substitution and enter the workforce,the economy should move to Point _____ in the short run.
` Beginning at Point W in the figure,suppose the government engages in a large increase in government expenditure.If workers react by displaying intertemporal substitution and enter the workforce,the economy should move to Point _____ in the short run.
A) V
B) X
C) Y
D) Z
 ` Beginning at Point W in the figure,suppose the government engages in a large increase in government expenditure.If workers react by displaying intertemporal substitution and enter the workforce,the economy should move to Point _____ in the short run.
` Beginning at Point W in the figure,suppose the government engages in a large increase in government expenditure.If workers react by displaying intertemporal substitution and enter the workforce,the economy should move to Point _____ in the short run.A) V
B) X
C) Y
D) Z

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If rainfall is below average,farmers may:
A) work harder and devote more capital to their fields.
B) work harder but devote less capital to their fields.
C) devote more capital to their fields but work less hard.
D) work less hard and devote less capital to their fields.
A) work harder and devote more capital to their fields.
B) work harder but devote less capital to their fields.
C) devote more capital to their fields but work less hard.
D) work less hard and devote less capital to their fields.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following individuals is practicing intertemporal substitution?
A) Sharona decides to stop being a stay-at-home mother and enters the workforce to get extra money for future college expenses.
B) Malika decides to stop being a stay-at-home mother and enters the workforce because the economy is booming.
C) Anneliese studies continuously throughout the semester for her final exams.
D) The United States enters a recession,and Tashika loses her job.
A) Sharona decides to stop being a stay-at-home mother and enters the workforce to get extra money for future college expenses.
B) Malika decides to stop being a stay-at-home mother and enters the workforce because the economy is booming.
C) Anneliese studies continuously throughout the semester for her final exams.
D) The United States enters a recession,and Tashika loses her job.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Tom works as an editor for a textbook company and devotes some of his time to his dream of writing a novel.Will he devote more time to writing the novel when the textbook company is busy and pays him overtime or when work is slow and no overtime pay is available?
A) when work is busy
B) when work is slow
C) equal amounts of time under both conditions
D) He will never actually write it as long as he works with the textbook publishing company.
A) when work is busy
B) when work is slow
C) equal amounts of time under both conditions
D) He will never actually write it as long as he works with the textbook publishing company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The allocation of consumption,work,and leisure across time to maximize well-being is called:
A) intertemporal substitution.
B) labor adjustment cost.
C) time bunching
D) collateral damage.
A) intertemporal substitution.
B) labor adjustment cost.
C) time bunching
D) collateral damage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Intertemporal substitution tends to magnify:
A) negative shocks only.
B) positive shocks only.
C) both negative and positive shocks.
D) neither negative nor positive shocks.
A) negative shocks only.
B) positive shocks only.
C) both negative and positive shocks.
D) neither negative nor positive shocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
People engage in intertemporal substitution because they:
A) are required to work longer hours when economies are expanding.
B) are rational.
C) are trying to achieve consumption smoothing.
D) prefer fluctuations in their incomes.
A) are required to work longer hours when economies are expanding.
B) are rational.
C) are trying to achieve consumption smoothing.
D) prefer fluctuations in their incomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The supply of labor:
A) increases during a boom and decreases during a recession.
B) decreases during a boom and increases during a recession.
C) increases during booms and recessions alike.
D) decreases during booms and recessions alike.
A) increases during a boom and decreases during a recession.
B) decreases during a boom and increases during a recession.
C) increases during booms and recessions alike.
D) decreases during booms and recessions alike.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Intertemporal substitution causes a positive productivity shock to:
A) make the LRAS curve less steep.
B) make the LRAS curve steeper.
C) shift the LRAS curve farther to the right.
D) shift the LRAS curve farther to the left.
A) make the LRAS curve less steep.
B) make the LRAS curve steeper.
C) shift the LRAS curve farther to the right.
D) shift the LRAS curve farther to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is NOT true?
A) There is a tendency for fewer people to enter college when wages are increasing.
B) People are more likely to retire or take early retirement during a boom.
C) Homemakers will likely choose to enter the workforce during boom periods.
D) There will be more people investing in their education when jobs are scarce.
A) There is a tendency for fewer people to enter college when wages are increasing.
B) People are more likely to retire or take early retirement during a boom.
C) Homemakers will likely choose to enter the workforce during boom periods.
D) There will be more people investing in their education when jobs are scarce.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
During an economic boom,people are more likely to:
A) retire early.
B) delay retirement.
C) leave retirement plans unchanged.
D) take a second job.
A) retire early.
B) delay retirement.
C) leave retirement plans unchanged.
D) take a second job.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Intertemporal substitution:
A) dampens economic shocks.
B) magnifies economic shocks.
C) does not affect economic shocks.
D) magnifies positive economic shocks and dampens negative economic shocks.
A) dampens economic shocks.
B) magnifies economic shocks.
C) does not affect economic shocks.
D) magnifies positive economic shocks and dampens negative economic shocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When GDP is growing faster than trend,the employment-to-population ratio tends to grow:
A) faster than trend.
B) more slowly than trend.
C) at its trend level.
D) unpredictably.
A) faster than trend.
B) more slowly than trend.
C) at its trend level.
D) unpredictably.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The allocation of consumption,work,and leisure across time to maximize well-being is called:
A) cross-sectional substitution.
B) cross-sectional complement.
C) intertemporal substitution.
D) intertemporal complement.
A) cross-sectional substitution.
B) cross-sectional complement.
C) intertemporal substitution.
D) intertemporal complement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
People engage in intertemporal substitution because they:
A) wish to reduce the overall number of hours they work.
B) seek to maximize their well-being.
C) are irrational.
D) always prefer leisure to work.
A) wish to reduce the overall number of hours they work.
B) seek to maximize their well-being.
C) are irrational.
D) always prefer leisure to work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
During an economic boom,the employment-to-population ratio rises because:
A) inflation tends to rise at that time.
B) the opportunity cost of leisure increases.
C) fewer people are available to work.
D) real wages tend to fall at that time.
A) inflation tends to rise at that time.
B) the opportunity cost of leisure increases.
C) fewer people are available to work.
D) real wages tend to fall at that time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Because of intertemporal substitution,the effect of a negative economic shock on real GDP will:
A) be larger than otherwise.
B) become a positive shock in the end.
C) disappear immediately.
D) occur only in the long run,but not during the short run.
A) be larger than otherwise.
B) become a positive shock in the end.
C) disappear immediately.
D) occur only in the long run,but not during the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The term "intertemporal substitution" refers to the allocation of time between:
A) making capital goods and making consumption goods.
B) consumption and saving.
C) friends and family.
D) leisure and work.
A) making capital goods and making consumption goods.
B) consumption and saving.
C) friends and family.
D) leisure and work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The idea that a person or business is most likely to work hard when doing so brings the greatest return is called:
A) intertemporal substitution.
B) irreversible investment.
C) labor adjustment cost.
D) time bunching.
A) intertemporal substitution.
B) irreversible investment.
C) labor adjustment cost.
D) time bunching.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following explains why intertemporal substitution magnifies a negative economic shock?
A) When things go bad,the return to work and investing fall,and often people work less and invest less.
B) When things go well,workers will tend to be less productive and invest less.
C) When things go bad,people often work more and harder to maintain their return to work.
D) When things go well,the return to work and investing rise,and often people work less and invest less.
A) When things go bad,the return to work and investing fall,and often people work less and invest less.
B) When things go well,workers will tend to be less productive and invest less.
C) When things go bad,people often work more and harder to maintain their return to work.
D) When things go well,the return to work and investing rise,and often people work less and invest less.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
If students decide to stay in college until a recession is over,they are practicing:
A) intertemporal substitution.
B) time bunching.
C) labor adjustment costs.
D) replacement wages.
A) intertemporal substitution.
B) time bunching.
C) labor adjustment costs.
D) replacement wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure: AS/AD 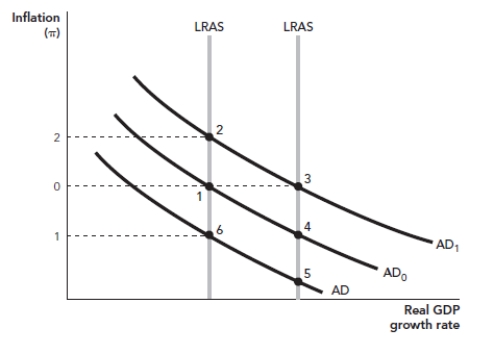 Assume that an economy begins initially at Point 1 in the figure.An increase in government spending accompanied by intertemporal substitution would move the economy to Point _____.
Assume that an economy begins initially at Point 1 in the figure.An increase in government spending accompanied by intertemporal substitution would move the economy to Point _____.
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6
 Assume that an economy begins initially at Point 1 in the figure.An increase in government spending accompanied by intertemporal substitution would move the economy to Point _____.
Assume that an economy begins initially at Point 1 in the figure.An increase in government spending accompanied by intertemporal substitution would move the economy to Point _____.A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Intertemporal substitution tends to:
A) reduce the impact of positive shocks and increase the impact of negative shocks.
B) reduce the impact of negative shocks and increase the impact of positive shocks.
C) reduce the impact of positive shocks and negative shocks.
D) increase the impact of positive and negative shocks.
A) reduce the impact of positive shocks and increase the impact of negative shocks.
B) reduce the impact of negative shocks and increase the impact of positive shocks.
C) reduce the impact of positive shocks and negative shocks.
D) increase the impact of positive and negative shocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
_____ have high value only under specific conditions.
A) Intertemporal reserves
B) Permanent assets
C) Irreversible investments
D) High-growth prices
A) Intertemporal reserves
B) Permanent assets
C) Irreversible investments
D) High-growth prices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When there is high uncertainty,investors are more likely to hold off on potential investment projects that:
A) are irreversible.
B) are reversible.
C) have many substitutes.
D) have low adjustment costs.
A) are irreversible.
B) are reversible.
C) have many substitutes.
D) have low adjustment costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Because of intertemporal substitution,a negative shock to aggregate demand could result in:
A) a shift of the LRAS curve to the right.
B) a shift of the LRAS curve to the left.
C) an upward movement along the LRAS curve.
D) a downward movement along the LRAS curve.
A) a shift of the LRAS curve to the right.
B) a shift of the LRAS curve to the left.
C) an upward movement along the LRAS curve.
D) a downward movement along the LRAS curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Because of intertemporal substitution,the supply of labor is likely to:
A) decrease when the economy grows more rapidly.
B) increase when the economy grows more rapidly.
C) remain constant regardless of how fast the economy grows.
D) become unpredictable when a shock occurs in an economy.
A) decrease when the economy grows more rapidly.
B) increase when the economy grows more rapidly.
C) remain constant regardless of how fast the economy grows.
D) become unpredictable when a shock occurs in an economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Waiting to open a factory in a country that has just had a government coup exaggerates that economic shock due to:
A) uncertainty.
B) labor adjustment costs.
C) time bunching.
D) flexible investing.
A) uncertainty.
B) labor adjustment costs.
C) time bunching.
D) flexible investing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For a given increase in government spending growth,intertemporal substitution is more widespread when the impact of AD growth on:
A) both inflation and real GDP growth is stronger.
B) both inflation and real GDP growth is weaker.
C) inflation is stronger and the impact of the AD growth on real GDP growth is weaker.
D) inflation is weaker and the impact of AD growth on real GDP growth is stronger.
A) both inflation and real GDP growth is stronger.
B) both inflation and real GDP growth is weaker.
C) inflation is stronger and the impact of the AD growth on real GDP growth is weaker.
D) inflation is weaker and the impact of AD growth on real GDP growth is stronger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Spending on capital goods that cannot be easily moved,adjusted,or reversed is called:
A) irreversible investment.
B) fixed investment.
C) bunched investment.
D) intertemporal investment.
A) irreversible investment.
B) fixed investment.
C) bunched investment.
D) intertemporal investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
When a drought (negative rainfall shock)occurs,farmers tend to put in less effort than they did before to till their farms because:
A) agricultural output falls and even though farmers put in the same level of effort,the effort per hour falls.
B) extra hours of labor and capital usage do not yield much extra output.
C) people work hardest when their hard work yields lower returns.
D) they switch to crops that use less water.
A) agricultural output falls and even though farmers put in the same level of effort,the effort per hour falls.
B) extra hours of labor and capital usage do not yield much extra output.
C) people work hardest when their hard work yields lower returns.
D) they switch to crops that use less water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Labor supply tends to:
A) remain constant during recessions.
B) remain constant during booms.
C) increase during recessions.
D) increase during booms.
A) remain constant during recessions.
B) remain constant during booms.
C) increase during recessions.
D) increase during booms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Jamie has a fixed amount of savings and is planning to invest in one of two different projects with the same expected return on investment.Other things being equal,Jamie will most likely invest in:
A) the project that is more easily reversed.
B) the project that is less easily reversed.
C) either of the two projects regardless of how reversible they are.
D) neither of the two projects because there is always uncertainty in their returns.
A) the project that is more easily reversed.
B) the project that is less easily reversed.
C) either of the two projects regardless of how reversible they are.
D) neither of the two projects because there is always uncertainty in their returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following scenarios explains why uncertainty can lead to increased volatility in economic fluctuations from investment?
A) You are not sure whether your fiancé will retain his job in the uncertain economic environment,so you decide not to purchase a home with him.
B) Your firm starts laying off workers and you are not sure whether you will keep your job,so you reduce your spending by half.
C) Your friend warns you that your bank is about to collapse,so you withdraw your savings from that bank.
D) You anticipate a recession may be coming,so you reduce the number of hours you work.
A) You are not sure whether your fiancé will retain his job in the uncertain economic environment,so you decide not to purchase a home with him.
B) Your firm starts laying off workers and you are not sure whether you will keep your job,so you reduce your spending by half.
C) Your friend warns you that your bank is about to collapse,so you withdraw your savings from that bank.
D) You anticipate a recession may be coming,so you reduce the number of hours you work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What economic effect has people allocating consumption across time to bring the greatest return?
A) sticky wage benefits
B) irreversible investment
C) intertemporal substitution
D) labor adjustment cost
A) sticky wage benefits
B) irreversible investment
C) intertemporal substitution
D) labor adjustment cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Because of intertemporal substitution,real GDP growth tends to be:
A) positively related to the employment-population ratio.
B) negatively related to the employment-population ratio.
C) unrelated to the employment-population ratio.
D) positively or negatively related to the employment-population ratio,depending on the stage of the business cycle.
A) positively related to the employment-population ratio.
B) negatively related to the employment-population ratio.
C) unrelated to the employment-population ratio.
D) positively or negatively related to the employment-population ratio,depending on the stage of the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An economy with a long-run potential growth rate of 1% experiences a positive real economic shock that increases the growth rate to 2%.If intertemporal substitution subsequently takes place,what could the eventual new GDP growth rate be?
A) 0%
B) 1%
C) 2%
D) 3%
A) 0%
B) 1%
C) 2%
D) 3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Because of intertemporal substitution,an increase in government spending growth results in:
A) a leftward shift of both the LRAS curve and the AD curve.
B) a leftward shift of the LRAS curve but a rightward shift of the AD curve.
C) a rightward shift of both the LRAS curve and the AD curve.
D) a rightward shift of the LRAS curve but a leftward shift of the AD curve.
A) a leftward shift of both the LRAS curve and the AD curve.
B) a leftward shift of the LRAS curve but a rightward shift of the AD curve.
C) a rightward shift of both the LRAS curve and the AD curve.
D) a rightward shift of the LRAS curve but a leftward shift of the AD curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
After 9/11,why were many investors unwilling to engage in new construction in New York City?
A) Construction companies were unwilling to work in New York City.
B) Uncertainty regarding future terrorist attacks left investors unsure about the demand for new offices.
C) The cost of steel had skyrocketed and building new construction became very expensive.
D) The Mayor of New York abolished new construction for a period of 6 months.
A) Construction companies were unwilling to work in New York City.
B) Uncertainty regarding future terrorist attacks left investors unsure about the demand for new offices.
C) The cost of steel had skyrocketed and building new construction became very expensive.
D) The Mayor of New York abolished new construction for a period of 6 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Uncertainty magnifies negative shocks by:
A) keeping resources in unproductive areas.
B) slowing the speed of transmission of the negative shocks.
C) providing clear investment signals.
D) increasing the number of irreversible investments.
A) keeping resources in unproductive areas.
B) slowing the speed of transmission of the negative shocks.
C) providing clear investment signals.
D) increasing the number of irreversible investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Suppose that Kristi is unsure about what to do with her life.Should she go to graduate school now or wait until she decides what she wants to do?
A) She should go now.
B) She should wait until she decides.
C) It doesn't matter.
D) Each choice is equally valid.
A) She should go now.
B) She should wait until she decides.
C) It doesn't matter.
D) Each choice is equally valid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Negative shocks tend to:
A) increase uncertainty.
B) decrease uncertainty.
C) have no impact on uncertainty.
D) first decrease and then increase uncertainty.
A) increase uncertainty.
B) decrease uncertainty.
C) have no impact on uncertainty.
D) first decrease and then increase uncertainty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
For a given economic shock,more irreversible investments in an economy will:
A) moderate the effect of the shock on the economy.
B) amplify the effect of the shock on the economy.
C) make the transmission mechanism for the shock longer.
D) make the transmission mechanism for the shock shorter.
A) moderate the effect of the shock on the economy.
B) amplify the effect of the shock on the economy.
C) make the transmission mechanism for the shock longer.
D) make the transmission mechanism for the shock shorter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Irreversible investments:
A) are the costs of shifting workers from declining sectors of the economy to the growing sectors.
B) are valuable assets that are pledged to a lender to secure a loan.
C) are the tendency for economic activities to be coordinated at common points in time.
D) have high value only under specific conditions-they cannot be easily moved,adjusted,or reversed if conditions change.
A) are the costs of shifting workers from declining sectors of the economy to the growing sectors.
B) are valuable assets that are pledged to a lender to secure a loan.
C) are the tendency for economic activities to be coordinated at common points in time.
D) have high value only under specific conditions-they cannot be easily moved,adjusted,or reversed if conditions change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Uncertainty tends to amplify business cycles because:
A) many investments are irreversible with large sunk costs;thus investors decrease investment during bad times and wait until they are more certain about the future direction of the economy.
B) fewer people tend to go to college during recessions because of the uncertainty in the job market and thus lower education leads to lower productivity.
C) investment tends to correlate with prices and therefore both prices and investment tend to rise during booms and decrease during recessions.
D) resource providers have less demand for their materials during recessions and thus less certain sales expectations.
A) many investments are irreversible with large sunk costs;thus investors decrease investment during bad times and wait until they are more certain about the future direction of the economy.
B) fewer people tend to go to college during recessions because of the uncertainty in the job market and thus lower education leads to lower productivity.
C) investment tends to correlate with prices and therefore both prices and investment tend to rise during booms and decrease during recessions.
D) resource providers have less demand for their materials during recessions and thus less certain sales expectations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If investors are less certain about the economic outlook,they will:
A) reduce capital investments that are less irreversible.
B) reduce capital investments that are more irreversible.
C) raise capital investments that are less irreversible.
D) raise capital investments that are more irreversible.
A) reduce capital investments that are less irreversible.
B) reduce capital investments that are more irreversible.
C) raise capital investments that are less irreversible.
D) raise capital investments that are more irreversible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The more uncertain the world appears:
A) the harder it is for investors to receive definite signals about where to invest their resources.
B) the easier it is for investors to receive definite signals about where to invest their resources.
C) the lower the expected return necessary to justify an investment.
D) the lower the payoff to waiting.
A) the harder it is for investors to receive definite signals about where to invest their resources.
B) the easier it is for investors to receive definite signals about where to invest their resources.
C) the lower the expected return necessary to justify an investment.
D) the lower the payoff to waiting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When an investment has a high value under a specific condition but can't be shut down when conditions change,it is said to be:
A) irreversible.
B) diversified.
C) profitable.
D) uncertain.
A) irreversible.
B) diversified.
C) profitable.
D) uncertain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A negative shock reduces capital investments because:
A) capital investments involve sunk costs.
B) investments are always very speculative.
C) capital investments are easily reversible.
D) investors react only to capital investments that bring high returns.
A) capital investments involve sunk costs.
B) investments are always very speculative.
C) capital investments are easily reversible.
D) investors react only to capital investments that bring high returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
After the 9/11 attacks:
A) people rushed to invest in New York City.
B) the economy's long-run potential growth rate increased.
C) people held off on business investment until it became clear that the attacks would not become regular occurrences.
D) the need for information about the future went out the window.
A) people rushed to invest in New York City.
B) the economy's long-run potential growth rate increased.
C) people held off on business investment until it became clear that the attacks would not become regular occurrences.
D) the need for information about the future went out the window.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The idea that some investments cannot be easily moved,adjusted,or reversed if conditions change is called:
A) intertemporal substitution.
B) irreversible investment.
C) time bunching
D) collateral damage.
A) intertemporal substitution.
B) irreversible investment.
C) time bunching
D) collateral damage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which is widely considered to be the most irreversible decision for a typical person?
A) getting engaged with a loved one
B) buying a house
C) having a baby
D) buying a car
A) getting engaged with a loved one
B) buying a house
C) having a baby
D) buying a car

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which investment project is most irreversible?
A) the construction of an open office space that can be used for different businesses
B) the construction of a bank branch location that can be later converted into an insurance company office
C) the purchase of a Japanese restaurant that can be easily converted into a bistro
D) the construction of a chemical plant that manufactures only a specific type of paint
A) the construction of an open office space that can be used for different businesses
B) the construction of a bank branch location that can be later converted into an insurance company office
C) the purchase of a Japanese restaurant that can be easily converted into a bistro
D) the construction of a chemical plant that manufactures only a specific type of paint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is NOT true of irreversible investments?
A) When investors wait to see what happens,that means resources are sitting idle rather than being productive.
B) Uncertainty usually slows investment and keeps resources in less productive uses.
C) Once an investment opportunity is identified,the execution should follow immediately.
D) If new information casts suspicion on a potential investment,the truth is typically sought out before proceeding.
A) When investors wait to see what happens,that means resources are sitting idle rather than being productive.
B) Uncertainty usually slows investment and keeps resources in less productive uses.
C) Once an investment opportunity is identified,the execution should follow immediately.
D) If new information casts suspicion on a potential investment,the truth is typically sought out before proceeding.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A capital investment is more irreversible if it involves a high:
A) sunk cost.
B) labor cost.
C) maintenance cost.
D) depreciation rate.
A) sunk cost.
B) labor cost.
C) maintenance cost.
D) depreciation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is the best example of an irreversible investment?
A) the decision to work an extra 2 hours per week
B) starting a new automobile line
C) a first date
D) hiring a new employee
A) the decision to work an extra 2 hours per week
B) starting a new automobile line
C) a first date
D) hiring a new employee

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Uncertainty tends to keep resources:
A) in more productive uses.
B) in less productive uses.
C) fully employed.
D) moving from country to country.
A) in more productive uses.
B) in less productive uses.
C) fully employed.
D) moving from country to country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Irreversible investments can be costly because they:
A) are expensive.
B) involve a large number of workers.
C) involve sunk costs.
D) are intertemporal.
A) are expensive.
B) involve a large number of workers.
C) involve sunk costs.
D) are intertemporal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Many investments are irreversible because they involve:
A) labor costs.
B) international costs.
C) construction costs.
D) sunk costs.
A) labor costs.
B) international costs.
C) construction costs.
D) sunk costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Many investments involve _____,which are a characteristic of irreversible investments.
A) fixed costs
B) opportunity costs
C) operating costs
D) sunk costs
A) fixed costs
B) opportunity costs
C) operating costs
D) sunk costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 219 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



