Deck 5: Consumer Choice
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/138
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Consumer Choice
1
If a product has a high marginal utility, then
A) Consumers will not purchase any more of the good.
B) The demand curve will be downward-sloping.
C) A consumer is willing to pay a high price for it.
D) Consumers will also have a low total utility.
A) Consumers will not purchase any more of the good.
B) The demand curve will be downward-sloping.
C) A consumer is willing to pay a high price for it.
D) Consumers will also have a low total utility.
A consumer is willing to pay a high price for it.
2
Total utility is
A) The additional utility from consuming one more unit of a good.
B) The sum of the marginal utilities from the consumption of good.
C) A function that always falls as a buyer enjoys more units of a good.
D) How much utility a seller gets from producing a good.
A) The additional utility from consuming one more unit of a good.
B) The sum of the marginal utilities from the consumption of good.
C) A function that always falls as a buyer enjoys more units of a good.
D) How much utility a seller gets from producing a good.
The sum of the marginal utilities from the consumption of good.
3
Sociopsychiatric explanations of consumer behavior include the
A) Desire for ego and status.
B) Level of income.
C) Level of wealth.
D) Prices of other goods.
A) Desire for ego and status.
B) Level of income.
C) Level of wealth.
D) Prices of other goods.
Desire for ego and status.
4
Marginal utility is
A) The sum of the total utility of consuming a certain amount of a good.
B) The additional utility a consumer enjoys from the consumption of one more unit of a good.
C) The diminishing nature of total utility.
D) Always negative or zero.
A) The sum of the total utility of consuming a certain amount of a good.
B) The additional utility a consumer enjoys from the consumption of one more unit of a good.
C) The diminishing nature of total utility.
D) Always negative or zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Utility refers to the
A) Satisfaction obtained from a good or service.
B) Additional satisfaction obtained from one more unit of a good or service.
C) Willingness to buy specific quantities of a good or service at a particular price.
D) Decrease in satisfaction as more of a good or service is consumed.
A) Satisfaction obtained from a good or service.
B) Additional satisfaction obtained from one more unit of a good or service.
C) Willingness to buy specific quantities of a good or service at a particular price.
D) Decrease in satisfaction as more of a good or service is consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If an individual demands a good, it means that he or she
A) Has a strong desire for the good.
B) Is willing and able to purchase the good at some price.
C) Must need the good.
D) Prefers the good to all other choices.
A) Has a strong desire for the good.
B) Is willing and able to purchase the good at some price.
C) Must need the good.
D) Prefers the good to all other choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is not a determinant of demand?
A) Desire for the good.
B) Income of the consumer.
C) The cost of the factor inputs.
D) The price of other goods.
A) Desire for the good.
B) Income of the consumer.
C) The cost of the factor inputs.
D) The price of other goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When economists refer to the determinants of demand, they are referring to factors that when changed,
A) Cause a movement down a demand curve.
B) Cause the demand curve to shift left or right.
C) Influence producer behavior.
D) Cause a movement up one demand curve.
A) Cause a movement down a demand curve.
B) Cause the demand curve to shift left or right.
C) Influence producer behavior.
D) Cause a movement up one demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Josh is eating pizza at his favorite Italian restaurant. Below is his utility from this consumption:
Table Refer to Table 19.1.What is Josh's total utility from consuming the third slice of pizza?
A) 20 utils.
B) 54 utils.
C) 5 utils.
D) 0 utils.
Table Refer to Table 19.1.What is Josh's total utility from consuming the third slice of pizza?
A) 20 utils.
B) 54 utils.
C) 5 utils.
D) 0 utils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The marginal utility for a good is computed as
A) Total utility divided by quantity.
B) Quantity divided by total utility.
C) The change in quantity divided by total utility.
D) The change in total utility divided by the change in quantity.
A) Total utility divided by quantity.
B) Quantity divided by total utility.
C) The change in quantity divided by total utility.
D) The change in total utility divided by the change in quantity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The additional pleasure or satisfaction from a good declines as more of it is consumed in a given period.This is the definition of the
A) Law of demand.
B) Law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) Law of diminishing total utility.
D) Total revenue rule.
A) Law of demand.
B) Law of diminishing marginal utility.
C) Law of diminishing total utility.
D) Total revenue rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Graphically, as a consumer buys more of a good, the marginal utility line will
A) Increase as more goods are consumed.
B) Increase steadily and then decline.
C) Continuously decline if diminishing returns are present.
D) Follow the same shape as the total utility line.
A) Increase as more goods are consumed.
B) Increase steadily and then decline.
C) Continuously decline if diminishing returns are present.
D) Follow the same shape as the total utility line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
As compared to sociologists and psychologists, economists accept consumer tastes as given and instead focus on
A) How price will affect actual consumer purchases.
B) How culture affects consumer preferences.
C) How advertising molds consumer desires.
D) What consumers desire.
A) How price will affect actual consumer purchases.
B) How culture affects consumer preferences.
C) How advertising molds consumer desires.
D) What consumers desire.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Josh is eating pizza at his favorite Italian restaurant. Below is his utility from this consumption:
Table Refer to Table 19.1.The marginal utility Josh enjoys from the fourth slice of pizza is
A) 20 utils.
B) 54 utils.
C) 5 utils.
D) 0 utils.
Table Refer to Table 19.1.The marginal utility Josh enjoys from the fourth slice of pizza is
A) 20 utils.
B) 54 utils.
C) 5 utils.
D) 0 utils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The law of diminishing marginal utility suggests that
A) People are willing to buy additional quantities of a good only if its price falls.
B) People will substitute lower-priced goods for more expensive goods, ceteris paribus.
C) Price and quantity demanded are directly related.
D) As marginal utility decreases, the willingness to pay increases.
A) People are willing to buy additional quantities of a good only if its price falls.
B) People will substitute lower-priced goods for more expensive goods, ceteris paribus.
C) Price and quantity demanded are directly related.
D) As marginal utility decreases, the willingness to pay increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Josh is eating pizza at his favorite Italian restaurant. Below is his utility from this consumption:
Table Refer to Table 19.1.For Josh, diminishing marginal utility begins
A) After the first slice of pizza.
B) After the third slice of pizza.
C) After the second slice of pizza.
D) To increase after the first slice of pizza.
Table Refer to Table 19.1.For Josh, diminishing marginal utility begins
A) After the first slice of pizza.
B) After the third slice of pizza.
C) After the second slice of pizza.
D) To increase after the first slice of pizza.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
As more satisfaction is achieved from consuming a good with diminishing marginal utility, then total utility
A) Increases at a decreasing rate.
B) Decreases as long as marginal utility is negative.
C) Decreases as long as marginal utility is positive.
D) Is negative as long as marginal utility is decreasing.
A) Increases at a decreasing rate.
B) Decreases as long as marginal utility is negative.
C) Decreases as long as marginal utility is positive.
D) Is negative as long as marginal utility is decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The law of diminishing marginal utility states that
A) The total utility of consuming the next unit of a good falls.
B) As a consumer enjoys successive units of a good, eventually marginal utility will fall.
C) Marginal utility always falls to zero after two or three units of a good consumed.
D) The total utility of a good rises at a fast rate as more units of a good are consumed.
A) The total utility of consuming the next unit of a good falls.
B) As a consumer enjoys successive units of a good, eventually marginal utility will fall.
C) Marginal utility always falls to zero after two or three units of a good consumed.
D) The total utility of a good rises at a fast rate as more units of a good are consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Jose goes to an all-you-can-eat buffet at a Chinese restaurant and consumes three plates of food.He does not go back for a fourth plate of food because
A) The price of the fourth plate is too high.
B) He has reached the point of increasing marginal utility.
C) The marginal utility of the fourth plate would be zero or even negative.
D) His total utility would increase with the fourth plate of food.
A) The price of the fourth plate is too high.
B) He has reached the point of increasing marginal utility.
C) The marginal utility of the fourth plate would be zero or even negative.
D) His total utility would increase with the fourth plate of food.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Economic explanations of consumer behavior take into consideration
A) Ego gratification.
B) Lack of self-confidence.
C) Social status.
D) Prices and income.
A) Ego gratification.
B) Lack of self-confidence.
C) Social status.
D) Prices and income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The market demand for a product is
A) The sum of all of the markets in the area.
B) The sum of all of the marginal utilities among consumers.
C) The total utility received for a good by all consumers in the market.
D) The sum of all of the individual demands for that product.
A) The sum of all of the markets in the area.
B) The sum of all of the marginal utilities among consumers.
C) The total utility received for a good by all consumers in the market.
D) The sum of all of the individual demands for that product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
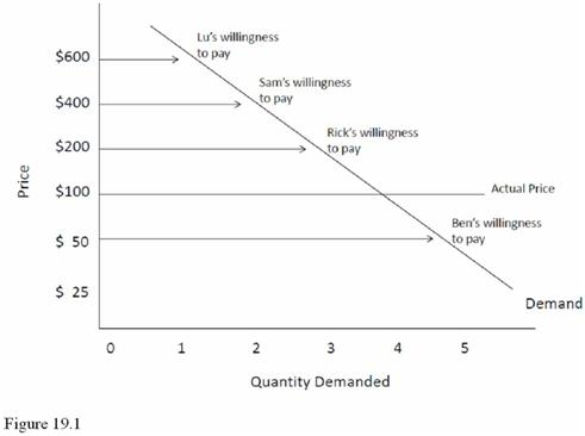 See Figure 19.1.Lu's consumer surplus is equal to
See Figure 19.1.Lu's consumer surplus is equal toA) $100.
B) $200.
C) $300.
D) $500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If a good had a zero price (i.e., the good was free), a rational person would consume
A) An infinite amount of the good.
B) The good until total utility was zero.
C) The good until the marginal utility was maximized.
D) The good until the marginal utility of the last unit was zero.
A) An infinite amount of the good.
B) The good until total utility was zero.
C) The good until the marginal utility was maximized.
D) The good until the marginal utility of the last unit was zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Consumer surplus measures
A) The difference between the maximum price a consumer is willing to pay and the price actually paid.
B) The difference between the minimum price a consumer is willing to pay and the price actually paid.
C) The difference between the amounts of a good a consumer is willing to pay, and how much of the good is available for sale.
D) The sum of all of the marginal utilities for that good
A) The difference between the maximum price a consumer is willing to pay and the price actually paid.
B) The difference between the minimum price a consumer is willing to pay and the price actually paid.
C) The difference between the amounts of a good a consumer is willing to pay, and how much of the good is available for sale.
D) The sum of all of the marginal utilities for that good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Most goods can yield
A) Only positive marginal utility.
B) Both positive and negative marginal utility.
C) Only negative marginal utility.
D) Only zero marginal utility.
A) Only positive marginal utility.
B) Both positive and negative marginal utility.
C) Only negative marginal utility.
D) Only zero marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The ___________ surplus will rise if the price of the good ________.
A) consumer; rises
B) consumer; falls
C) producer; falls
D) total; rises
A) consumer; rises
B) consumer; falls
C) producer; falls
D) total; rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The four determinants of demand that are held constant when we consider a movement along a demand curve include all of the following except
A) Price.
B) Income.
C) Tastes.
D) Availability and price of substitute goods.
A) Price.
B) Income.
C) Tastes.
D) Availability and price of substitute goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The benefit that consumers get when they buy goods at the equilibrium price but were willing to pay more is called
A) Marginal utility.
B) The law of demand.
C) Consumer surplus.
D) Maximum price.
A) Marginal utility.
B) The law of demand.
C) Consumer surplus.
D) Maximum price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Rosa is willing to pay $200 for the iPhone, but the actual price is $400.This means
A) Rosa will enjoy a consumer surplus of $200 if she buys the iPhone.
B) Rosa will not buy an iPhone.
C) Rosa will buy this product but will not receive any consumer surplus.
D) The iPhone is overpriced.
A) Rosa will enjoy a consumer surplus of $200 if she buys the iPhone.
B) Rosa will not buy an iPhone.
C) Rosa will buy this product but will not receive any consumer surplus.
D) The iPhone is overpriced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The law of diminishing marginal utility gives us a deeper understanding of the downward-sloping demand curve because
A) Consumers are willing to pay a higher price for a greater quantity.
B) Consumer tastes change due to advertising.
C) When marginal utility is high, we are willing to pay a higher price.
D) Consumers do not respond to a change in price.
A) Consumers are willing to pay a higher price for a greater quantity.
B) Consumer tastes change due to advertising.
C) When marginal utility is high, we are willing to pay a higher price.
D) Consumers do not respond to a change in price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Total utility is maximized when
A) Price is less than marginal utility.
B) Price is equal to marginal utility.
C) Marginal utility is zero.
D) Marginal utility is maximized.
A) Price is less than marginal utility.
B) Price is equal to marginal utility.
C) Marginal utility is zero.
D) Marginal utility is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If marginal utility is negative, then
A) Total utility will increase with additional consumption.
B) Total utility will decrease with additional consumption.
C) The good or service being consumed is an inferior good.
D) Total utility is at a minimum.
A) Total utility will increase with additional consumption.
B) Total utility will decrease with additional consumption.
C) The good or service being consumed is an inferior good.
D) Total utility is at a minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
According to the law of demand, ceteris paribus,
A) The quantity demanded increases at lower prices.
B) A consumer will purchase more of a good at higher prices than at lower prices.
C) Price and quantity supplied are directly related.
D) The responsiveness of consumer demand to a change in the price of a good is measured by the price elasticity of demand.
A) The quantity demanded increases at lower prices.
B) A consumer will purchase more of a good at higher prices than at lower prices.
C) Price and quantity supplied are directly related.
D) The responsiveness of consumer demand to a change in the price of a good is measured by the price elasticity of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The total consumer surplus is shown on a graph as
A) The area under the demand curve and below the actual price.
B) The area under the demand curve and above the actual price.
C) The area above the demand curve and above the actual price.
D) The area above the demand curve and below the actual price.
A) The area under the demand curve and below the actual price.
B) The area under the demand curve and above the actual price.
C) The area above the demand curve and above the actual price.
D) The area above the demand curve and below the actual price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is not held constant when considering a shift in the demand for pizza?
A) Consumer incomes.
B) The price of pizza.
C) The price of spaghetti (a substitute).
D) Expectations of higher prices for pizzas.
A) Consumer incomes.
B) The price of pizza.
C) The price of spaghetti (a substitute).
D) Expectations of higher prices for pizzas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The _________ of the demand curve corresponds to the idea that the marginal utility for the first few goods is _____________________.
A) top; lower
B) bottom; lower
C) top; higher
D) bottom; higher
A) top; lower
B) bottom; lower
C) top; higher
D) bottom; higher

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Evaluating a supply and a demand curve independently, if the equilibrium price rises,
A) The consumer surplus will fall.
B) The producer surplus will fall.
C) The consumer surplus will increase.
D) The producer surplus will increase.
A) The consumer surplus will fall.
B) The producer surplus will fall.
C) The consumer surplus will increase.
D) The producer surplus will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
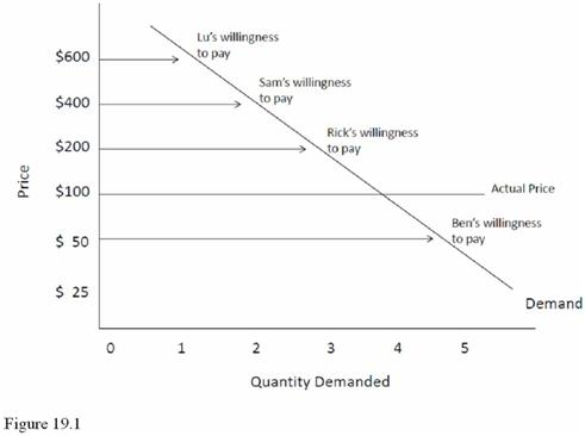 Refer to Figure 19.1.The total consumer surplus in this market is equal to
Refer to Figure 19.1.The total consumer surplus in this market is equal toA) $950.
B) $900.
C) $850.
D) $800.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
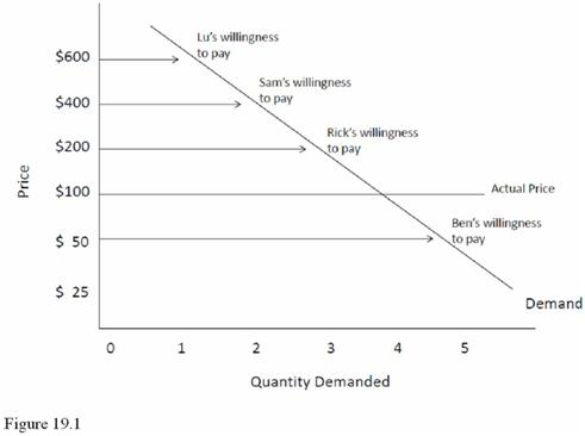 Refer to Figure 19.1.Ben's consumer surplus is equal to
Refer to Figure 19.1.Ben's consumer surplus is equal toA) $50.
B) $100.
C) $200.
D) $0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following statements best captures the concept of consumer surplus?
A) "I saw a sale for flowers, so I bought four bundles."
B) "I was willing to pay $30 for a dozen roses, but I bought them for $20."
C) "I was willing to pay $30 for roses, but they are selling for $35, so I did not buy."
D) "I paid $35 for roses last week and just saw them for sale now at $25."
A) "I saw a sale for flowers, so I bought four bundles."
B) "I was willing to pay $30 for a dozen roses, but I bought them for $20."
C) "I was willing to pay $30 for roses, but they are selling for $35, so I did not buy."
D) "I paid $35 for roses last week and just saw them for sale now at $25."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose Caesar allocates his entire budget to the purchase of soft drinks and chips.The marginal utility of the last bottle of soft drink purchased is 12 utils, and each bottle costs $1.20.The marginal utility of the last bag of chips purchased is 8 utils, and each bag costs $1.In order to maximize his utility, Caesar should
A) Buy more soft drinks and fewer chips since he gets more marginal utility per dollar from soft drinks.
B) Buy more chips and fewer soft drinks because of the lower price for chips.
C) Buy more soft drinks and fewer chips because the soft drink has fewer calories.
D) Not change anything because he has made the choice that gives him the most total utility.
A) Buy more soft drinks and fewer chips since he gets more marginal utility per dollar from soft drinks.
B) Buy more chips and fewer soft drinks because of the lower price for chips.
C) Buy more soft drinks and fewer chips because the soft drink has fewer calories.
D) Not change anything because he has made the choice that gives him the most total utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Complete Table 19.2 below:
Table
Utility Schedule In Table 19.2, diminishing marginal utility occurs
A) With the second and fourth units only.
B) With the first and third units only.
C) Only with the second unit.
D) With all units after the first.
Table
Utility Schedule In Table 19.2, diminishing marginal utility occurs
A) With the second and fourth units only.
B) With the first and third units only.
C) Only with the second unit.
D) With all units after the first.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Sellers can gain profits from price discrimination because
A) Charging different prices based on willingness to pay can increase revenues without increasing costs.
B) Total expenses are less with price discrimination.
C) Total revenues are maximized when all buyers pay the same price.
D) Different prices charged to different customers can lower total revenue.
A) Charging different prices based on willingness to pay can increase revenues without increasing costs.
B) Total expenses are less with price discrimination.
C) Total revenues are maximized when all buyers pay the same price.
D) Different prices charged to different customers can lower total revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Price discrimination occurs when
A) Minorities pay a higher price for a product than everyone else.
B) Sellers charge a higher price than is reasonable.
C) Sellers charge two separate prices for the same product to two different groups.
D) Sellers charge one price to all consumers but not wholesalers.
A) Minorities pay a higher price for a product than everyone else.
B) Sellers charge a higher price than is reasonable.
C) Sellers charge two separate prices for the same product to two different groups.
D) Sellers charge one price to all consumers but not wholesalers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Price discrimination
A) Is illegal.
B) Rarely occurs in the airline industry.
C) Is a way for sellers to exact the maximum willingness to pay from buyers.
D) Is a method used by sellers to pit one buyer against the other.
A) Is illegal.
B) Rarely occurs in the airline industry.
C) Is a way for sellers to exact the maximum willingness to pay from buyers.
D) Is a method used by sellers to pit one buyer against the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A consumer maximizes total utility from a given amount of income when the
A) Marginal utility obtained from the last dollar spent on each good is the same.
B) Marginal utility of the last unit of each good is the same.
C) Total utility obtained from each product is the same.
D) Amount spent for each product is the same.
A) Marginal utility obtained from the last dollar spent on each good is the same.
B) Marginal utility of the last unit of each good is the same.
C) Total utility obtained from each product is the same.
D) Amount spent for each product is the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Complete Table 19.2 below:
Table
Utility Schedule In Table 19.2, the total utility when two units are consumed is
A) 6.
B) 9.
C) 15.
D) 24.
Table
Utility Schedule In Table 19.2, the total utility when two units are consumed is
A) 6.
B) 9.
C) 15.
D) 24.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Price discrimination is ________ in the United States and ________ practiced.
A) legal; rarely
B) illegal; widely
C) legal; often
D) illegal; rarely
A) legal; rarely
B) illegal; widely
C) legal; often
D) illegal; rarely

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Complete Table 19.2 below:
Table
Utility Schedule In Table 19.2, the marginal utility of the third unit is
A) 3.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 30.
Table
Utility Schedule In Table 19.2, the marginal utility of the third unit is
A) 3.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 30.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which industry here is unlikely to exhibit price discrimination?
A) Airlines.
B) New cars.
C) Supermarkets.
D) Colleges.
A) Airlines.
B) New cars.
C) Supermarkets.
D) Colleges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of these examples is an example of price discrimination?
A) Goods are marked down on sale.
B) Wholesale prices differ from retail prices.
C) Seniors pay one price at the movie theater and adults pay more.
D) Cereal manufacturers put discount coupons inside their cereal boxes.
A) Goods are marked down on sale.
B) Wholesale prices differ from retail prices.
C) Seniors pay one price at the movie theater and adults pay more.
D) Cereal manufacturers put discount coupons inside their cereal boxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Maximum utility is achieved when
A) Total revenue is the greatest.
B) The price elasticity of demand is 1.0.
C) Marginal utility is zero.
D) Total utility equals marginal utility.
A) Total revenue is the greatest.
B) The price elasticity of demand is 1.0.
C) Marginal utility is zero.
D) Total utility equals marginal utility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Price discrimination works best when
A) Sellers cannot meet collectively.
B) Buyers do not have perfect information about the price.
C) Buyers have information about prices charged to different customers.
D) A product is purchased frequently by consumers.
A) Sellers cannot meet collectively.
B) Buyers do not have perfect information about the price.
C) Buyers have information about prices charged to different customers.
D) A product is purchased frequently by consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When sellers price discriminate,
A) They are attempting to charge a price that is the maximum price each individual is willing to pay.
B) They are trying to pit one group of buyers against another.
C) They are trying to find a minimum price the individual is willing to pay.
D) They are taking an illegal action.
A) They are attempting to charge a price that is the maximum price each individual is willing to pay.
B) They are trying to pit one group of buyers against another.
C) They are trying to find a minimum price the individual is willing to pay.
D) They are taking an illegal action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Complete Table 19.2 below:
Table
Utility Schedule In Table 19.2, the total utility when four units are consumed is
A) 33.
B) 30.
C) 6.
D) 3.
Table
Utility Schedule In Table 19.2, the total utility when four units are consumed is
A) 33.
B) 30.
C) 6.
D) 3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule In Table 19.3, what is the total utility of two units of cola?
A) 32.
B) 40.
C) 72.
D) 96.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule In Table 19.3, what is the total utility of two units of cola?
A) 32.
B) 40.
C) 72.
D) 96.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule In Table 19.3, what is the marginal utility of the fifth unit of cola?
A) 6.
B) 12.
C) 16.
D) 24.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule In Table 19.3, what is the marginal utility of the fifth unit of cola?
A) 6.
B) 12.
C) 16.
D) 24.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Car dealers can easily price discriminate because
A) Buyers do not know the car's price.
B) Sellers negotiate a separate price agreement with each individual buyer.
C) Each seller knows the price but the buyer does not.
D) Buyers get together to collectively negotiate a price.
A) Buyers do not know the car's price.
B) Sellers negotiate a separate price agreement with each individual buyer.
C) Each seller knows the price but the buyer does not.
D) Buyers get together to collectively negotiate a price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Assume Amanda always maximizes her total utility given her budget constraint.Every morning for breakfast she has two eggs and three sausages.If the marginal utility of the last egg is 10 utils and the price of eggs is $1 each, what can we say about the marginal utility of the last sausage if the price of each sausage is $2?
A) It must be equal to 20 utils.
B) It must be equal to 10 utils.
C) It must be equal to 5 utils.
D) It must be equal to 1 utils.
A) It must be equal to 20 utils.
B) It must be equal to 10 utils.
C) It must be equal to 5 utils.
D) It must be equal to 1 utils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Airline companies engage in price discrimination by
A) Charging unrestricted fares.
B) Giving a temporary price cut.
C) Charging business customers higher prices than vacation travelers.
D) Engaging in price-fixing.
A) Charging unrestricted fares.
B) Giving a temporary price cut.
C) Charging business customers higher prices than vacation travelers.
D) Engaging in price-fixing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule In Table 19.3 the marginal utility per dollar of the second cola is
A) 10.
B) 6.
C) 4.
D) 12.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule In Table 19.3 the marginal utility per dollar of the second cola is
A) 10.
B) 6.
C) 4.
D) 12.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule The marginal utility per dollar of the third pretzel is
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 12.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule The marginal utility per dollar of the third pretzel is
A) 4.
B) 5.
C) 6.
D) 12.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
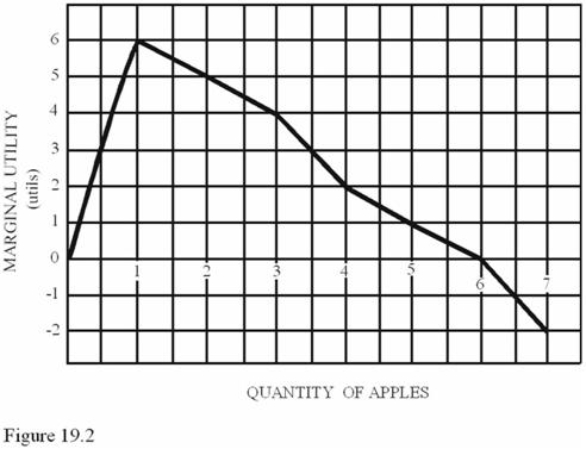 Refer to Figure 19.2.With no budget constraint, a rational consumer will consume _________ apple(s).
Refer to Figure 19.2.With no budget constraint, a rational consumer will consume _________ apple(s).A) zero
B) one
C) six
D) an infinite number of

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An indifference curve shows the
A) Maximum utility that can be achieved for a given consumer budget.
B) Maximum utility that can be achieved for different amounts of a good.
C) Combinations of goods giving equal utility to a consumer.
D) Optimal consumption combinations between two goods.
A) Maximum utility that can be achieved for a given consumer budget.
B) Maximum utility that can be achieved for different amounts of a good.
C) Combinations of goods giving equal utility to a consumer.
D) Optimal consumption combinations between two goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule Refer to Table 19.3.If Michael has $40 to spend on cola and pretzels, what is his maximum utility possible?
A) 40.
B) 174.
C) 190.
D) 208.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule Refer to Table 19.3.If Michael has $40 to spend on cola and pretzels, what is his maximum utility possible?
A) 40.
B) 174.
C) 190.
D) 208.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An indifference map shows
A) A set of indifference curves.
B) One indifference curve.
C) A set of indifference curves and a set of budget constraints.
D) A set of budget constraints and one indifference curve.
A) A set of indifference curves.
B) One indifference curve.
C) A set of indifference curves and a set of budget constraints.
D) A set of budget constraints and one indifference curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A successful advertising campaign will
A) Increase the demand for the advertised good.
B) Increase the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand for the advertised good.
C) Cause the quantity supplied of the advertised good to increase.
D) Reduce the perceived utility of the good.
A) Increase the demand for the advertised good.
B) Increase the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand for the advertised good.
C) Cause the quantity supplied of the advertised good to increase.
D) Reduce the perceived utility of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a successful advertising campaign increases brand loyalty, the
A) Supply of the advertised good will become less elastic.
B) Demand for the advertised good will become less elastic.
C) Supply of substitutes for the advertised good will increase.
D) Total level of consumption will decrease.
A) Supply of the advertised good will become less elastic.
B) Demand for the advertised good will become less elastic.
C) Supply of substitutes for the advertised good will increase.
D) Total level of consumption will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If advertising is successful,
A) The demand becomes more elastic.
B) The demand curve shifts to the left.
C) The demand curve shifts to the right and becomes steeper.
D) The demand curve shifts to the left, and demand becomes more price-elastic.
A) The demand becomes more elastic.
B) The demand curve shifts to the left.
C) The demand curve shifts to the right and becomes steeper.
D) The demand curve shifts to the left, and demand becomes more price-elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule Refer to Table 19.3.If Michael has $28 dollars to spend, why will three colas and four pretzels not be optimal?
A) This combination has less total utility.
B) This combination is affordable but does not maximize utility.
C) This combination is not affordable.
D) This combination has less marginal utility per dollar.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule Refer to Table 19.3.If Michael has $28 dollars to spend, why will three colas and four pretzels not be optimal?
A) This combination has less total utility.
B) This combination is affordable but does not maximize utility.
C) This combination is not affordable.
D) This combination has less marginal utility per dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The In the News article titled "Men vs.Women: How They Spend" differentiates the spending habits of women and men: "Men spend almost twice as much as women do on electronic equipment … young women spend twice as much money on clothing, personal care items, and their pets." Which determinant of demand is most likely involved?
A) Income.
B) Tastes.
C) Expectations.
D) Other goods (availability and prices).
A) Income.
B) Tastes.
C) Expectations.
D) Other goods (availability and prices).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule Refer to Table 19.3.Suppose Michael has $28 to spend on cola and pretzels.What combination should he purchase in order to maximize his utility?
A) Three colas and four pretzels.
B) One cola and five pretzels.
C) Three colas and one pretzel.
D) Two colas and three pretzels.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule Refer to Table 19.3.Suppose Michael has $28 to spend on cola and pretzels.What combination should he purchase in order to maximize his utility?
A) Three colas and four pretzels.
B) One cola and five pretzels.
C) Three colas and one pretzel.
D) Two colas and three pretzels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
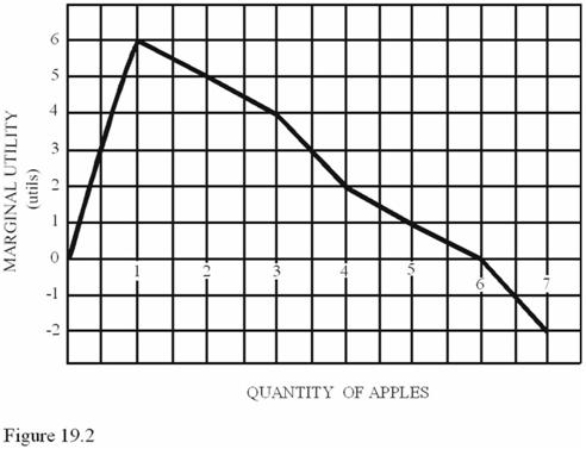 Refer to Figure 19.2.The total utility of five apples is
Refer to Figure 19.2.The total utility of five apples isA) 1 utils.
B) 17 utils.
C) 18 utils.
D) 20 utils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Complete Table 19.3 below.Assume the price of cola is $8 per unit and the price of pretzels is $4 per unit.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule Refer to Table 19.3.If Michael has $48 to spend on cola and pretzels, what combination should he purchase in order to maximize his utility?
A) Four colas and four pretzels.
B) Five colas and two pretzels.
C) Three colas and five pretzels.
D) Five colas and five pretzels.
Table 19.3
Michael's Utility Schedule Refer to Table 19.3.If Michael has $48 to spend on cola and pretzels, what combination should he purchase in order to maximize his utility?
A) Four colas and four pretzels.
B) Five colas and two pretzels.
C) Three colas and five pretzels.
D) Five colas and five pretzels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In the article "Men vs.Women: How They Spend,"
A) Both sexes spend more than they earn.
B) Both sexes make the same annual income.
C) Both sexes spend the same amount of money on clothing purchases.
D) Women earn more than men.
A) Both sexes spend more than they earn.
B) Both sexes make the same annual income.
C) Both sexes spend the same amount of money on clothing purchases.
D) Women earn more than men.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
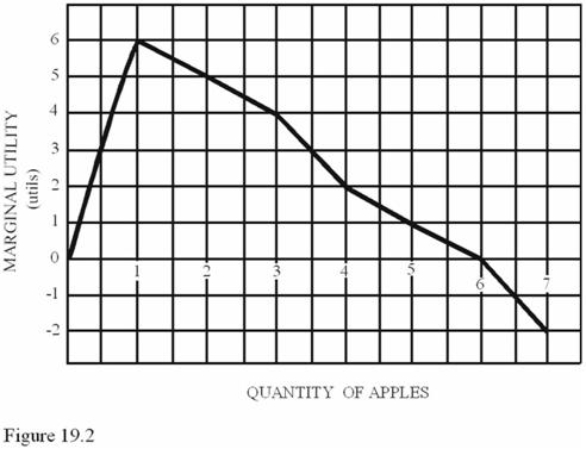 Refer to Figure 19.2.Total utility is maximized at
Refer to Figure 19.2.Total utility is maximized atA) 6 apples.
B) 7 apples.
C) 1 apple.
D) 3 apples.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When choosing among products, consumers look at
A) The marginal utility per dollar and their budget constraint.
B) The total utility that will be gained at the end of all consumption.
C) Only their budget.
D) The marginal utility of the good.
A) The marginal utility per dollar and their budget constraint.
B) The total utility that will be gained at the end of all consumption.
C) Only their budget.
D) The marginal utility of the good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
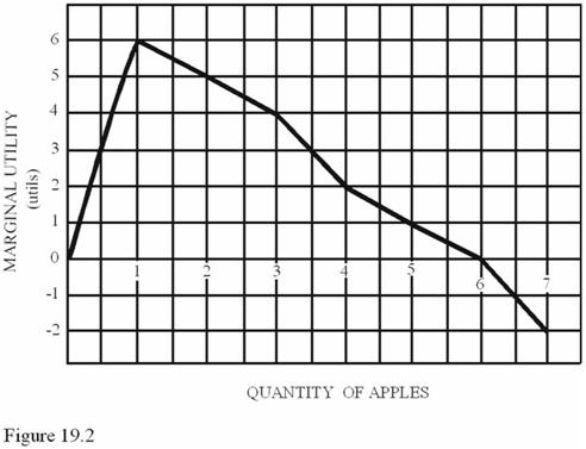 Refer to Figure 19.2.Diminishing marginal utility begins after
Refer to Figure 19.2.Diminishing marginal utility begins afterA) The fourth apple.
B) The fifth apple.
C) The third apple.
D) The first apple.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
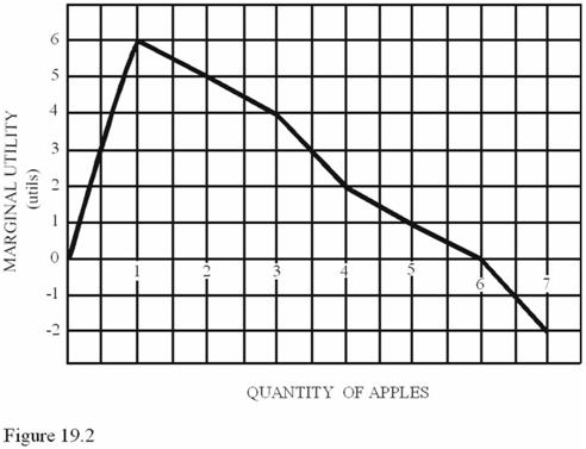 Refer to Figure 19.2.The total utility of two apples is
Refer to Figure 19.2.The total utility of two apples isA) 2 utils.
B) 5 utils.
C) 6 utils.
D) 11 utils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Marginal utility is the
A) Change in total utility obtained by spending one extra dollar on a good or service.
B) Change in total utility obtained by consuming one extra unit of a good or service.
C) Change in total utility obtained by selling one extra unit of a good or service.
D) Utility received from consuming the optimal combination of goods and services.
A) Change in total utility obtained by spending one extra dollar on a good or service.
B) Change in total utility obtained by consuming one extra unit of a good or service.
C) Change in total utility obtained by selling one extra unit of a good or service.
D) Utility received from consuming the optimal combination of goods and services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 138 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



