Deck 14: GlM 3: Factorial Designs
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/30
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: GlM 3: Factorial Designs
1
An experiment was done to look at whether there is an effect of the number of hours spent practising a musical instrument and gender on the level of musical ability. A sample of 30 (15 men and 15 women) participants who had never learnt to play a musical instrument before were recruited. Participants were randomly allocated to one of three groups that varied in the number of hours they would spend practising every day for 1 year (0 hours, 1 hours, 2 hours). Men and women were divided equally across groups. All participants had a one-hour lesson each week over the course of the year, after which their level of musical skill was measured on a 10-point scale ranging from 0 (you can't play for toffee) to 10 ('Are you Mozart reincarnated?').
- An ANOVA was conducted on the data from the experiment. What can we say about the effect of practice on musical skill?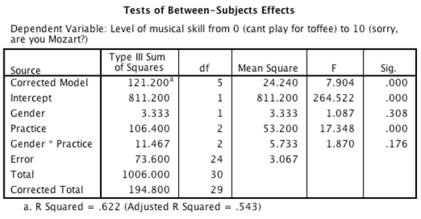
A)There was a significant effect of practice on skill level, which is likely to reflect the increase in musical skill when some weekly practice is engaged in compared to no hours practice.
B)There was a non-significant effect of practice on skill level, which implies that skill levels were similar regardless of how much practice per week was engaged in.
C)There was a significant effect of practice on skill level, which is likely to reflect a significant improvement when engaging in 1 hour per week practice compared to none, and when practising for 2 hours per week compared to 1.
D)There was a significant effect of practice on skill level, but this effect is superseded by the interaction between practice and gender.
- An ANOVA was conducted on the data from the experiment. What can we say about the effect of practice on musical skill?


A)There was a significant effect of practice on skill level, which is likely to reflect the increase in musical skill when some weekly practice is engaged in compared to no hours practice.
B)There was a non-significant effect of practice on skill level, which implies that skill levels were similar regardless of how much practice per week was engaged in.
C)There was a significant effect of practice on skill level, which is likely to reflect a significant improvement when engaging in 1 hour per week practice compared to none, and when practising for 2 hours per week compared to 1.
D)There was a significant effect of practice on skill level, but this effect is superseded by the interaction between practice and gender.
There was a significant effect of practice on skill level, which is likely to reflect the increase in musical skill when some weekly practice is engaged in compared to no hours practice.
2
If we were to run a four-way between-groups ANOVA, how many sources of variance would there be?
A)16
B)4
C)8
D)15
A)16
B)4
C)8
D)15
A
3
A study was conducted to look at whether caffeine improves productivity at work in different conditions. There were two independent variables. The first independent variable was email, which had two levels: 'email access' and 'no email access'. The second independent variable was caffeine, which also had two levels: 'caffeinated drink' and 'decaffeinated drink'. Different participants took part in each condition. Productivity was recorded at the end of the day on a scale of 0 (I may as well have stayed in bed) to 20 (wow! I got enough work done today to last all year).
- Looking at the group means in the table below, which of the following statements best describes the data?
A)There is likely to be a significant main effect of caffeine.
B)A significant interaction effect is likely to be present between caffeine consumption and email access.
C)The effect of email is relatively unaffected by whether the drink was caffeinated.
D)The effect of caffeine is about the same regardless of whether the person had email access.
- Looking at the group means in the table below, which of the following statements best describes the data?
A)There is likely to be a significant main effect of caffeine.
B)A significant interaction effect is likely to be present between caffeine consumption and email access.
C)The effect of email is relatively unaffected by whether the drink was caffeinated.
D)The effect of caffeine is about the same regardless of whether the person had email access.
A significant interaction effect is likely to be present between caffeine consumption and email access.
4
What type of ANOVA is used when there are two independent variables each with more than two levels, and with different participants taking part in each condition?
A)Mixed
B)One-way between subjects
C)Factorial
D)One-way independent
A)Mixed
B)One-way between subjects
C)Factorial
D)One-way independent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A study found that 50 pedestrians gave more money to a street beggar if the beggar had a cute and hungry-looking dog with them compared to if they were alone. The gender of the pedestrians was also noted. Which of the following sentences describes a simple effects analysis on these data?
A)The difference in donations when the beggar had a dog compared to not
B)The effect of having a dog compared to not on donations calculated separately for male and female pedestrians
C)The relative difference between male donations and female donations when the beggar had a dog compared to not
D)Using a graph to do a simple inspection of the mean donations from male and female pedestrians when the beggar had a dog or was alone
A)The difference in donations when the beggar had a dog compared to not
B)The effect of having a dog compared to not on donations calculated separately for male and female pedestrians
C)The relative difference between male donations and female donations when the beggar had a dog compared to not
D)Using a graph to do a simple inspection of the mean donations from male and female pedestrians when the beggar had a dog or was alone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Simple effects analysis looks at:
A)The effect of one independent variable at individual levels of the dependent variable
B)The main effects of the independent variables, controlling for interaction effects
C)The effect of one independent variable at individual levels of the other independent variable
D)The difference between the main effects of two independent variables controlling for error
A)The effect of one independent variable at individual levels of the dependent variable
B)The main effects of the independent variables, controlling for interaction effects
C)The effect of one independent variable at individual levels of the other independent variable
D)The difference between the main effects of two independent variables controlling for error

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
An experiment was done to look at whether there is an effect of the number of hours spent practising a musical instrument and gender on the level of musical ability. A sample of 30 (15 men and 15 women) participants who had never learnt to play a musical instrument before were recruited. Participants were randomly allocated to one of three groups that varied in the number of hours they would spend practising every day for 1 year (0 hours, 1 hours, 2 hours). Men and women were divided equally across groups. All participants had a one-hour lesson each week over the course of the year, after which their level of musical skill was measured on a 10-point scale ranging from 0 (you can't play for toffee) to 10 ('Are you Mozart reincarnated?').
-An ANOVA was conducted on these data, and the results revealed significant main effects of gender and the number of hours spent practising. Which of the following contrasts could we use to break down the effect of gender?
A)Repeated contrast
B)Helmert contrast
C)None
D)Simple contrast
-An ANOVA was conducted on these data, and the results revealed significant main effects of gender and the number of hours spent practising. Which of the following contrasts could we use to break down the effect of gender?
A)Repeated contrast
B)Helmert contrast
C)None
D)Simple contrast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When interpreting F(3, 26) = 12.66, p < .01, how many groups were tested?
A)4
B)26
C)25
D)3
A)4
B)26
C)25
D)3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is the Interaction effect in an Independent Factorial Design?
A)The combined effect of two or more predictor variables on an outcome variable.
B)The effect of one predictor variable on an outcome variable.
C)The combined effect of two or more predictor variables on more than one outcome variable.
D)The combined effect of the errors of two or more predictor variables on an outcome variable
A)The combined effect of two or more predictor variables on an outcome variable.
B)The effect of one predictor variable on an outcome variable.
C)The combined effect of two or more predictor variables on more than one outcome variable.
D)The combined effect of the errors of two or more predictor variables on an outcome variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is Independent Factorial Design?
A)An experiment, which compares the means of one categorical predictor, which is measured using different entities.
B)Main effects are effects of higher order than interaction effects.
C)An experiment, which compares the means of one categorical predictor, which is measured using the same conditions.
D)An experiment, which compares the means of two or more categorical predictors, each of which is measured using different entities.
A)An experiment, which compares the means of one categorical predictor, which is measured using different entities.
B)Main effects are effects of higher order than interaction effects.
C)An experiment, which compares the means of one categorical predictor, which is measured using the same conditions.
D)An experiment, which compares the means of two or more categorical predictors, each of which is measured using different entities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
An experiment was done to look at whether there is an effect of the number of hours spent practising a musical instrument and gender on the level of musical ability. A sample of 30 (15 men and 15 women) participants who had never learnt to play a musical instrument before were recruited. Participants were randomly allocated to one of three groups that varied in the number of hours they would spend practising every day for 1 year (0 hours, 1 hours, 2 hours). Men and women were divided equally across groups. All participants had a one-hour lesson each week over the course of the year, after which their level of musical skill was measured on a 10-point scale ranging from 0 (you can't play for toffee) to 10 ('Are you Mozart reincarnated?').
-An ANOVA was conducted on these data, and the results revealed significant main effects of gender and the number of hours spent practising. You predicted that some practice would be better than none, and that 2 hours would be better than 1. Which of SPSS's built-in contrasts should you use to test these hypotheses?
A)Repeated contrast
B)Helmert contrast
C)Simple contrast
D)Difference contrast
-An ANOVA was conducted on these data, and the results revealed significant main effects of gender and the number of hours spent practising. You predicted that some practice would be better than none, and that 2 hours would be better than 1. Which of SPSS's built-in contrasts should you use to test these hypotheses?
A)Repeated contrast
B)Helmert contrast
C)Simple contrast
D)Difference contrast

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An experiment was done to look at whether there is an effect of the number of hours spent practising a musical instrument and gender on the level of musical ability. A sample of 30 (15 men and 15 women) participants who had never learnt to play a musical instrument before were recruited. Participants were randomly allocated to one of three groups that varied in the number of hours they would spend practising every day for 1 year (0 hours, 1 hours, 2 hours). Men and women were divided equally across groups. All participants had a one-hour lesson each week over the course of the year, after which their level of musical skill was measured on a 10-point scale ranging from 0 (you can't play for toffee) to 10 ('Are you Mozart reincarnated?').
-An ANOVA was conducted on the data from the experiment. Looking at the output below, which of the following sentences is correct?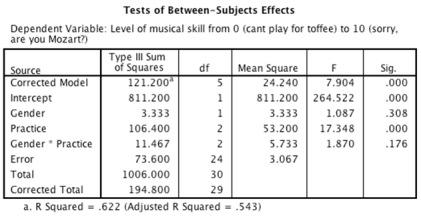
A)There was no significant main effect of gender.This means that overall, when we ignore the number of hours spent practising, the gender of the participant did not have a significant effect on the level of musical skill.
B)There was no significant practice ? gender interaction effect, indicating that if we ignore the gender of the participant, the number of hours spent practising did not significantly affect the level of musical skill.
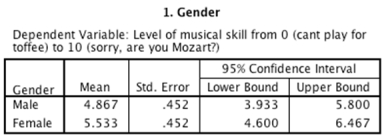
C)There was a significant main effect of gender.Looking at the group means, we can see that women achieved a significantly higher level of musical skill (M = 5.53) than males (M = 4.87).
D)There was a significant main effect of practice.This means that men and women significantly differed in the amount of practice that they did.
-An ANOVA was conducted on the data from the experiment. Looking at the output below, which of the following sentences is correct?


A)There was no significant main effect of gender.This means that overall, when we ignore the number of hours spent practising, the gender of the participant did not have a significant effect on the level of musical skill.
B)There was no significant practice ? gender interaction effect, indicating that if we ignore the gender of the participant, the number of hours spent practising did not significantly affect the level of musical skill.
C)There was a significant main effect of gender.Looking at the group means, we can see that women achieved a significantly higher level of musical skill (M = 5.53) than males (M = 4.87).
D)There was a significant main effect of practice.This means that men and women significantly differed in the amount of practice that they did.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An experiment was done to look at whether there is an effect of the number of hours spent practising a musical instrument and gender on the level of musical ability. A sample of 30 (15 men and 15 women) participants who had never learnt to play a musical instrument before were recruited. Participants were randomly allocated to one of three groups that varied in the number of hours they would spend practising every day for 1 year (0 hours, 1 hours, 2 hours). Men and women were divided equally across groups. All participants had a one-hour lesson each week over the course of the year, after which their level of musical skill was measured on a 10-point scale ranging from 0 (you can't play for toffee) to 10 ('Are you Mozart reincarnated?').
-Which of the following sentences regarding the ANOVA output below is correct?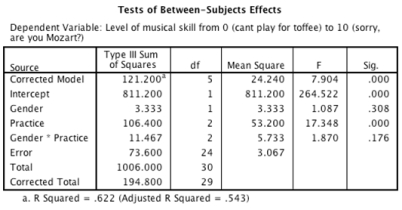
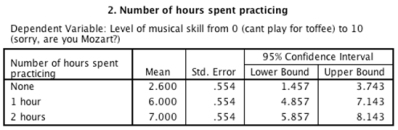
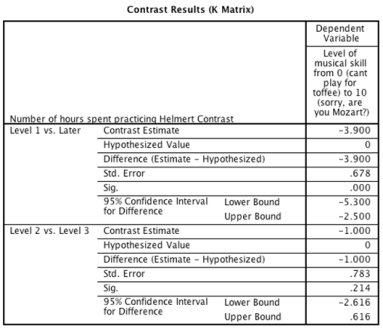
A)Practicing for 2 hours per day significantly increased skill level compared to when only 1 hour was spent practising per day.
B)Any amount of time spent practising significantly decreased skill level compared to when no time was spent practising.
C)Any amount of time spent practising significantly increased skill level compared to when no time was spent practising.
D)Practicing for 2 hours a day significantly decreased skill level compared to when only 1 hour was spent practising a day.
-Which of the following sentences regarding the ANOVA output below is correct?



A)Practicing for 2 hours per day significantly increased skill level compared to when only 1 hour was spent practising per day.
B)Any amount of time spent practising significantly decreased skill level compared to when no time was spent practising.
C)Any amount of time spent practising significantly increased skill level compared to when no time was spent practising.
D)Practicing for 2 hours a day significantly decreased skill level compared to when only 1 hour was spent practising a day.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Two-way ANOVA is basically the same as one-way ANOVA, except that:
A)We calculate the model sum of squares by looking at the difference between each group mean and the overall mean.
B)The model sum of squares is partitioned into three parts.
C)The model sum of squares is partitioned into two parts.
D)The residual sum of squares represents individual differences in performance.
A)We calculate the model sum of squares by looking at the difference between each group mean and the overall mean.
B)The model sum of squares is partitioned into three parts.
C)The model sum of squares is partitioned into two parts.
D)The residual sum of squares represents individual differences in performance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
study was conducted to look at whether caffeine improves productivity at work in different conditions. There were two independent variables. The first independent variable was email, which had two levels: 'email access' and 'no email access'. The second independent variable was caffeine, which also had two levels: 'caffeinated drink' and 'decaffeinated drink'. Different participants took part in each condition. Productivity was recorded at the end of the day on a scale of 0 (I may as well have stayed in bed) to 20 (wow! I got enough work done today to last all year).
- Which of the following tests could we use to analyse these data?
A)Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA
B)Three-way ANOVA
C)t-test
D)Two-way independent ANOVA
- Which of the following tests could we use to analyse these data?
A)Two-way repeated-measures ANOVA
B)Three-way ANOVA
C)t-test
D)Two-way independent ANOVA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
study was conducted to look at whether caffeine improves productivity at work in different conditions. There were two independent variables. The first independent variable was email, which had two levels: 'email access' and 'no email access'. The second independent variable was caffeine, which also had two levels: 'caffeinated drink' and 'decaffeinated drink'. Different participants took part in each condition. Productivity was recorded at the end of the day on a scale of 0 (I may as well have stayed in bed) to 20 (wow! I got enough work done today to last all year).
-Looking at the group means in the table below, which of the interpretations below is correct?
A)A simple effects analysis is likely to show an effect of email on productivity for decaffeinated drinks but not caffeinated ones.
B)A simple effects analysis is likely to show an effect of caffeine on productivity only for 'no email'.
C)A simple effects analysis is likely to show an effect of caffeine on productivity at both levels of email.
D)A simple effects analysis is likely to show an effect of email on productivity at both levels of caffeine.
-Looking at the group means in the table below, which of the interpretations below is correct?
A)A simple effects analysis is likely to show an effect of email on productivity for decaffeinated drinks but not caffeinated ones.
B)A simple effects analysis is likely to show an effect of caffeine on productivity only for 'no email'.
C)A simple effects analysis is likely to show an effect of caffeine on productivity at both levels of email.
D)A simple effects analysis is likely to show an effect of email on productivity at both levels of caffeine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is calculated or presented in the same way for both repeated-measures and between-subjects designs?
A)The simple effects
B)The model error
C)The degrees of freedom
D)Partial eta squared
A)The simple effects
B)The model error
C)The degrees of freedom
D)Partial eta squared

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An experiment was done to look at the positive arousing effects of imagery on different people. A sample of statistics lecturers was compared against a group of students. Both groups received presentations of positive images (e.g., cats and bunnies), neutral images (e.g., duvets and light bulbs), and negative images (e.g., corpses and vivisection photographs). Positive arousal was measured physiologically (high values indicate positive arousal) both before and after each batch of images. The order in which participants saw the batches of positive, neutral and negative images was randomized to avoid order effects. It was hypothesized that positive images would increase positive arousal, negative images would reduce positive arousal and that neutral images would have no effect. Differences between the subject groups (lecturers and students) were not expected. What technique should be used to analyse these data?
A)Three-way mixed ANOVA
B)Two-way mixed ANOVA
C)Three-way repeated-measures ANOVA
D)Two-way mixed analysis of covariance
A)Three-way mixed ANOVA
B)Two-way mixed ANOVA
C)Three-way repeated-measures ANOVA
D)Two-way mixed analysis of covariance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following sentences is correct?
A)Main effects should still be investigated and interpreted even when there is a significant interaction involving that main effect.
B)Main effects are effects of higher order than interaction effects.
C)Non-parallel lines on an interaction graph always reflect significant interaction effects.
D)You don't need to interpret main effects if an interaction effect involving that variable is significant.
A)Main effects should still be investigated and interpreted even when there is a significant interaction involving that main effect.
B)Main effects are effects of higher order than interaction effects.
C)Non-parallel lines on an interaction graph always reflect significant interaction effects.
D)You don't need to interpret main effects if an interaction effect involving that variable is significant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
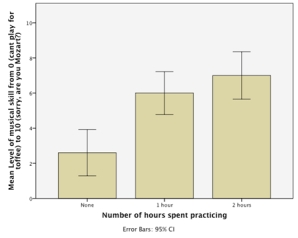
An experiment was done to look at whether there is an effect of the number of hours spent practising a musical instrument and gender on the level of musical ability. A sample of 30 (15 men and 15 women) participants who had never learnt to play a musical instrument before were recruited. Participants were randomly allocated to one of three groups that varied in the number of hours they would spend practising every day for 1 year (0 hours, 1 hours, 2 hours). Men and women were divided equally across groups. All participants had a one-hour lesson each week over the course of the year, after which their level of musical skill was measured on a 10-point scale ranging from 0 (you can't play for toffee) to 10 ('Are you Mozart reincarnated?').
-An ANOVA was conducted on the data from the experiment. Which of the following sentences best describes the pattern of results shown in the graph?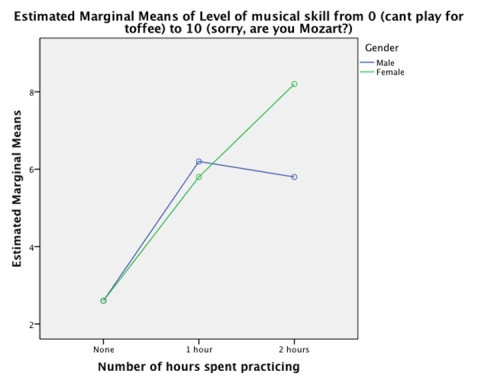
A)The graph indicates that men and women were most musically skilled when they practised for 2 hours per day.
B)Women were more musically skilled than men.
C)The graph shows that the relationship between musical skill and time spent practising was different for men and women.
D)The graph shows that the relationship between musical skill and time spent practising was the same for men and women.
-An ANOVA was conducted on the data from the experiment. Which of the following sentences best describes the pattern of results shown in the graph?

A)The graph indicates that men and women were most musically skilled when they practised for 2 hours per day.
B)Women were more musically skilled than men.
C)The graph shows that the relationship between musical skill and time spent practising was different for men and women.
D)The graph shows that the relationship between musical skill and time spent practising was the same for men and women.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
How can you resolve the problem identified in the previous question?
A)By manually creating dummy variables in SPSS.
B)By automatically creating dummy variables in SPSS.
C)By manually calculating Bayes factors.
D)By manually bootstrapping variables in SPSS.
A)By manually creating dummy variables in SPSS.
B)By automatically creating dummy variables in SPSS.
C)By manually calculating Bayes factors.
D)By manually bootstrapping variables in SPSS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An educational researcher wanted to test and compare the impact of three different learning environments on children's confidence with maths. She randomly selected 24 students and then randomly divided this group into three subgroups: a 'Placebo' group who did a maths test in their usual classroom environment; an 'Outdoor' group who did a maths test in an outdoor setting within the school grounds; and a 'Chill out' group who did a maths test in a 'chill out' space within the school, that had dimmed lighting, music and casual seating. The children spent one hour within their settings and their maths scores were recorded at the end of the test. What sort of research design is this?
A)Repeated-measures factorial design.
B)Independent factorial design.
C)ANOVA.
D)Multiple linear regression.
A)Repeated-measures factorial design.
B)Independent factorial design.
C)ANOVA.
D)Multiple linear regression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A sports researcher wanted to test and compare the impact of three different energy drinks as a means to examine to what extent energy drinks consumed during a workout increases workout rates. He randomly selected 36 gym goers and then randomly divided this group into three subgroups: a 'Placebo' group who drank water; a 'Caffeine' group who took a caffeine-rich energy drink; and a 'Sugar' group who took a sugar-rich energy drink. The study involved the groups drinking their energy drink prior to a thirty-minute workout. At the end or their workouts, their workout rates were recorded. What sort of research design is this?
A)Repeated-measures factorial design.
B)Independent factorial design.
C)ANOVA.
D)Multiple linear regression.
A)Repeated-measures factorial design.
B)Independent factorial design.
C)ANOVA.
D)Multiple linear regression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A medical researcher wanted to test and compare the impact of three different dietary supplements as a means to examine to what extent dietary supplements can speed up wound healing times. She randomly selected 36 patients and then randomly divided this group into three subgroups: a 'Placebo' group who ingested sugar-pills; a 'Vitamin X' group who took vitamin pills; and a 'Kale' group who took Kale pills. The study involved the groups taking their pill-based supplements three times a day for one week and at the end, their wound healing times were recorded What sort of research design is this?
A)Repeated-measures factorial design.
B)Independent factorial design.
C)ANOVA.
D)Multiple linear regression.
A)Repeated-measures factorial design.
B)Independent factorial design.
C)ANOVA.
D)Multiple linear regression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What do non-parallel lines on an interaction graph indicate?
A)Some degree of interaction between the variables and a definitive interaction effect.
B)No interaction between the variables and a therefore no interaction effect.
C)Some degree of interaction between the variables and a possible interaction effect.
D)No interaction between the variables but a possible interaction effect.
A)Some degree of interaction between the variables and a definitive interaction effect.
B)No interaction between the variables and a therefore no interaction effect.
C)Some degree of interaction between the variables and a possible interaction effect.
D)No interaction between the variables but a possible interaction effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What would be the point of bootstrapping post hoc tests in a factorial design?
A)To make the post hoc tests more robust particularly against potential bias caused by heteroscedasticity.
B)To make the post hoc tests more robust particularly against potential bias caused by homoscedasticity.
C)To make the post hoc tests less robust particularly against potential bias caused by heteroscedasticity.
D)To make the post hoc tests less powerful particularly against potential bias caused by homoscedasticity.
A)To make the post hoc tests more robust particularly against potential bias caused by heteroscedasticity.
B)To make the post hoc tests more robust particularly against potential bias caused by homoscedasticity.
C)To make the post hoc tests less robust particularly against potential bias caused by heteroscedasticity.
D)To make the post hoc tests less powerful particularly against potential bias caused by homoscedasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A new product tester (working for 'Fizzy Sugary Delight') wanted to test and compare the consumer rating of two new fizzy drinks; his own company's drink and a rival's drink. He randomly selected 12 participants and then randomly divided this group into three subgroups: a 'Placebo' group who drank fizzy sugary water; a 'new Improved Formula' group who drank the new Fizzy Sugary Delight drink; and a 'Rival fizz' group who drank the new fizzy drink belonging to a rival company. Each group consumed one glass each of their designated drink and then rated its taste. What sort of research design is this?
A)Independent factorial design.
B)Repeated-measures factorial design.
C)ANOVA.
D)Multiple linear regression.
A)Independent factorial design.
B)Repeated-measures factorial design.
C)ANOVA.
D)Multiple linear regression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How can you counter the problem of heteroscedasticity in factorial designs?
A)It is impossible to counter this problem.
B)Run robust models using parameter estimates with robust standard errors.
C)Run post hoc tests.
D)Run tests for significance.
A)It is impossible to counter this problem.
B)Run robust models using parameter estimates with robust standard errors.
C)Run post hoc tests.
D)Run tests for significance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Why might it be useful to use a stricter criterion than 0.05 for accepting an F statistic as significant in a factorial design?
A)Because the F statistics are independent and thus do control the Type I error rate.
B)Because the F statistics are independent and thus do not control the Type I error rate.
C)Because the F statistics are not independent and thus do not control the Type I error rate.
D)Because the F statistics are not independent and thus do control the Type I error rate.
A)Because the F statistics are independent and thus do control the Type I error rate.
B)Because the F statistics are independent and thus do not control the Type I error rate.
C)Because the F statistics are not independent and thus do not control the Type I error rate.
D)Because the F statistics are not independent and thus do control the Type I error rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What problem is faced when trying to compute Bayes factors for factorial designs using SPSS?
A)The model does not automatically compute interaction effects or the main effects.
B)The model automatically computes interaction effects, but not the main effects.
C)It is impossible to compute Bayes factors for factorial designs using SPSS.
D)The model does not automatically compute interaction effects, only the main effects.
A)The model does not automatically compute interaction effects or the main effects.
B)The model automatically computes interaction effects, but not the main effects.
C)It is impossible to compute Bayes factors for factorial designs using SPSS.
D)The model does not automatically compute interaction effects, only the main effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 30 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



